N-Path Interleaving Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) with Offset gain and Timing Mismatch Calibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
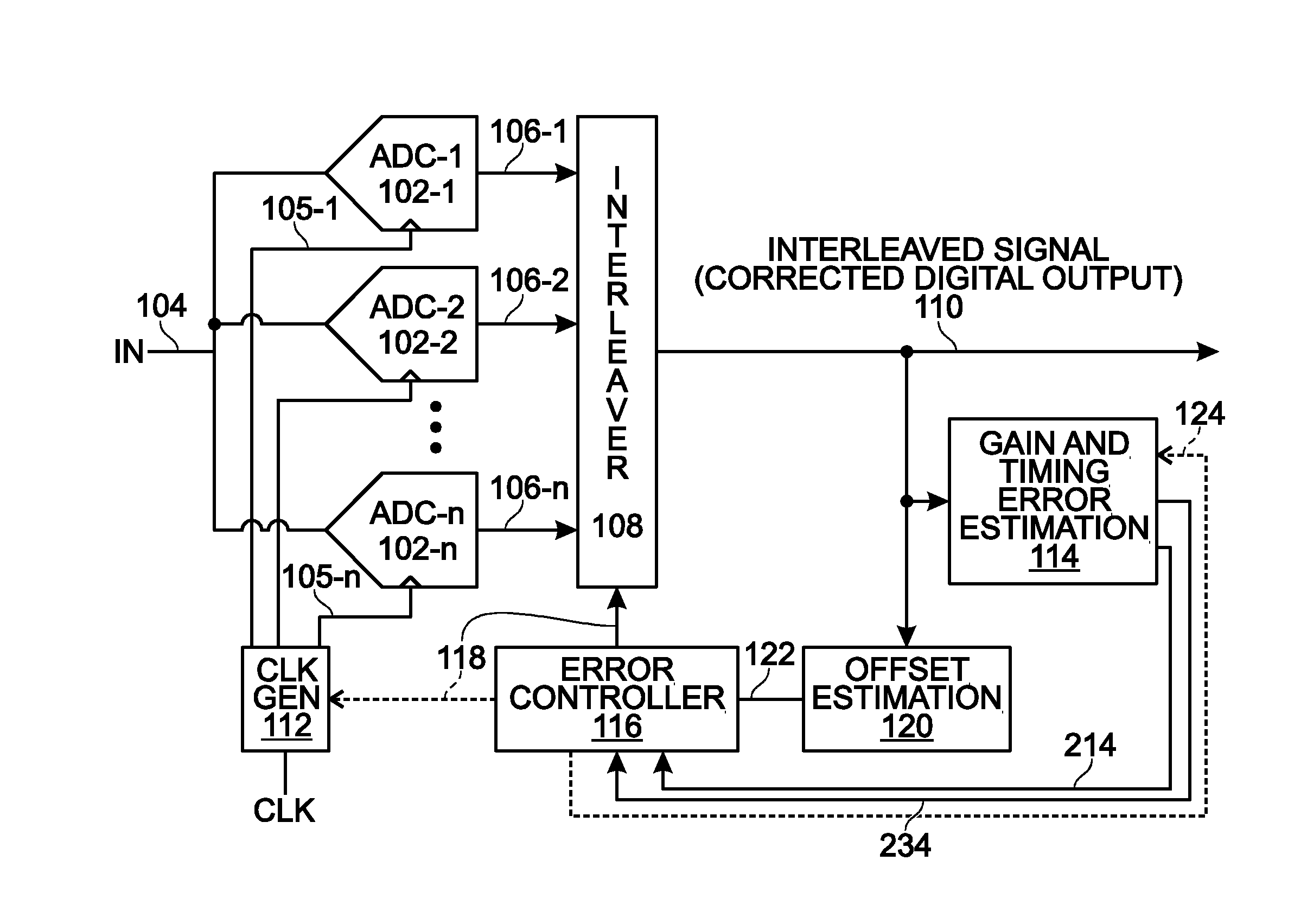
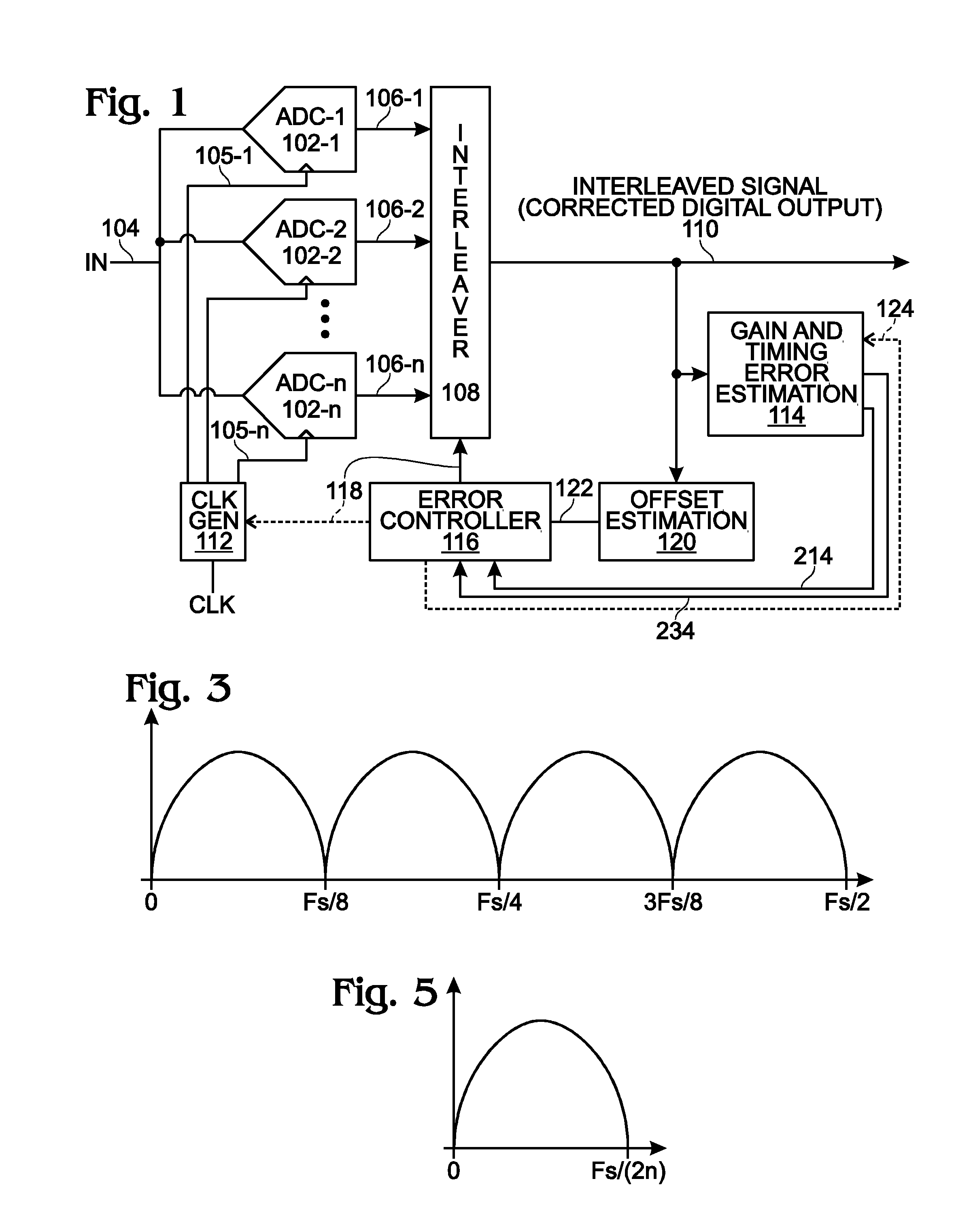
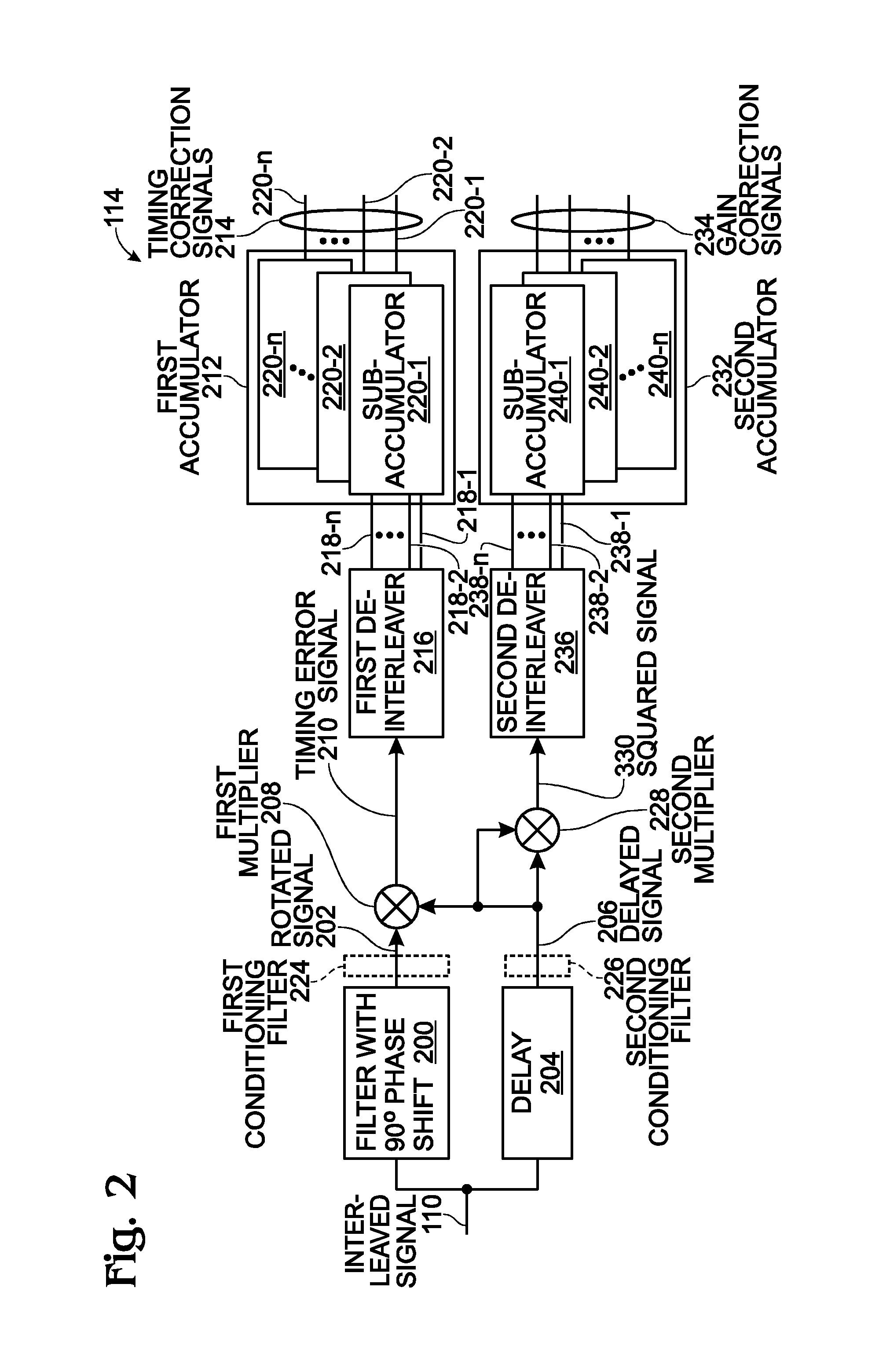
[0032]FIG. 1 is a schematic block diagram of an n-path time interleaved analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with a system for calibrating timing mismatch. The ADC 100 comprises at least n ADCs 102-1 through 102-n. Each ADC has an input on line 104 to accept the analog input, and input on lines 105-1 through 105-n to accept clock signals, and an output path, respectively 106-1 through 106-n, to supply a. digital sample signal, where n is an integer greater than 1. An interleaver 108 has inputs to accept the digital sample signals on lines 106-1 through 106-n, and an output on line 110 to supply a digital n-path interleaved ADC signal. Since this path occurs after error correction, it may also be known as a corrected digital output. A clock 112 is also shown to provide n number of different phases of the sampling clock fs to the ADCs 102-1 through 102-n. The ADC 100 further comprises a gain and timing error estimation block 114. Offset estimation block 120 accepts the interleaved ADC si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com