Method for imaging the earth's subsurface using passive seismic sensing
a technology of seismic sensing and earth's subsurface, which is applied in the field of seismic imaging of the earth's subsurface, can solve the problems of unsafe or impracticable use of seismic sources, ambiguous pstt, and inability to use conventional controlled source seismic techniques
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
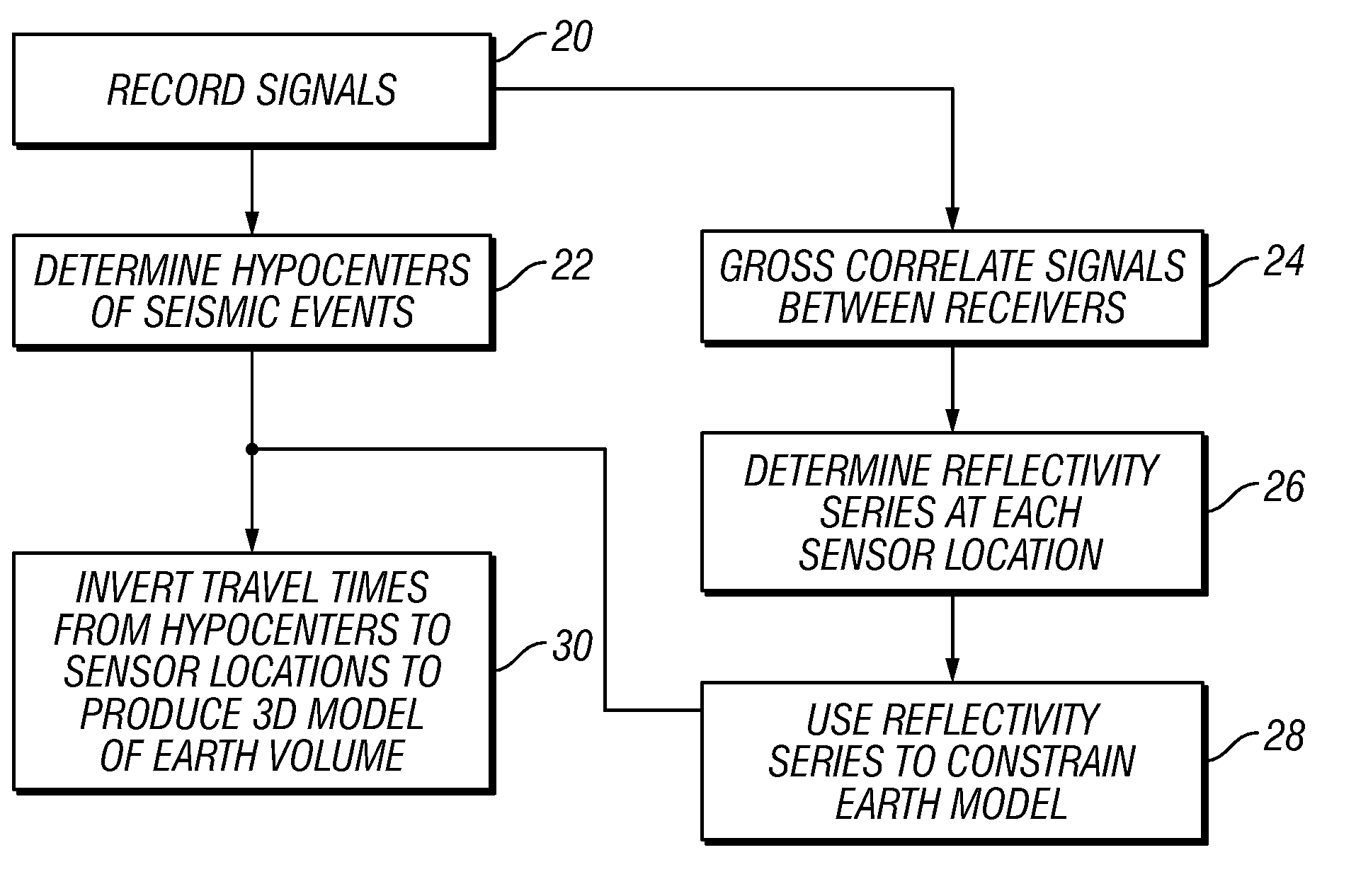
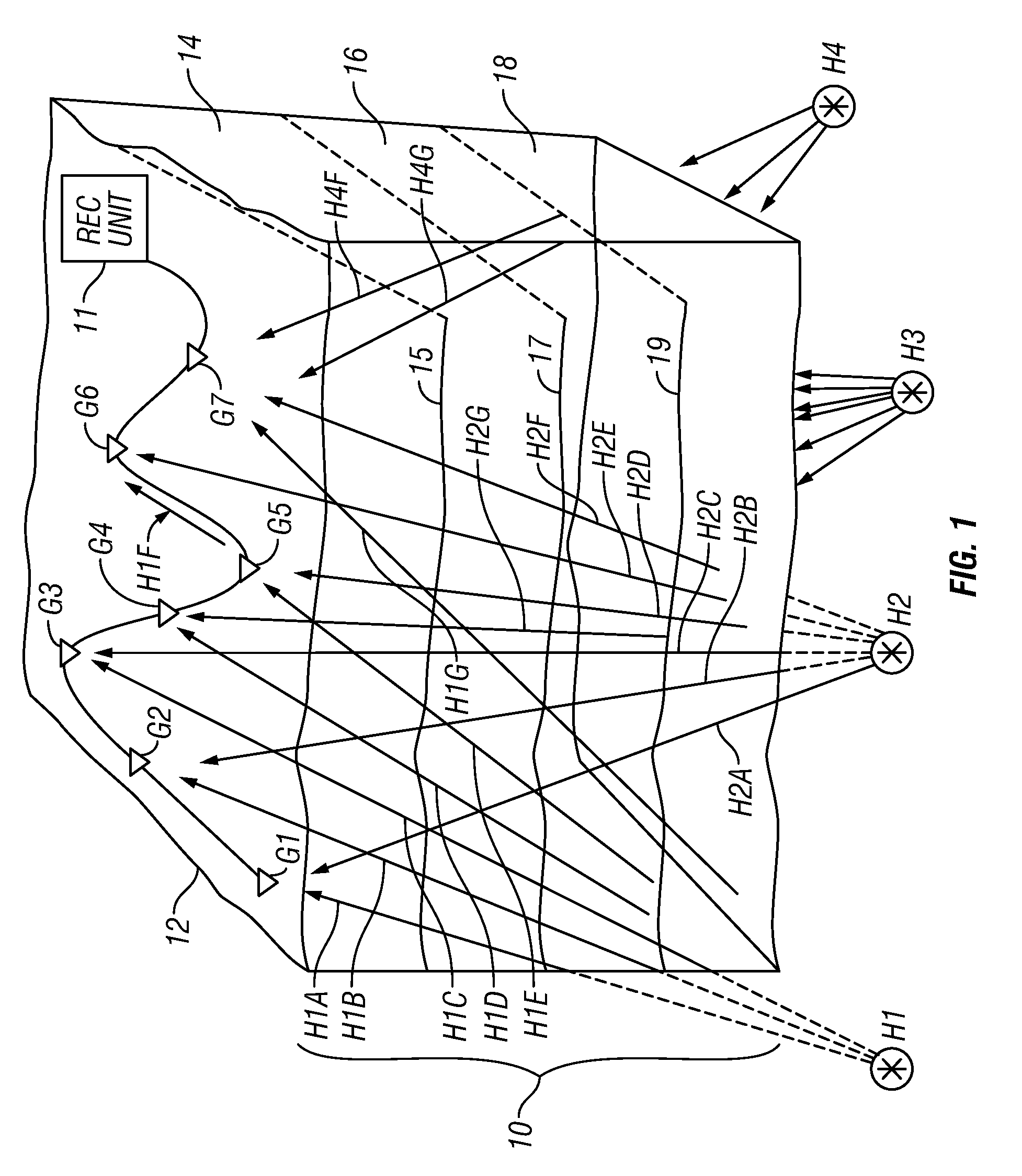
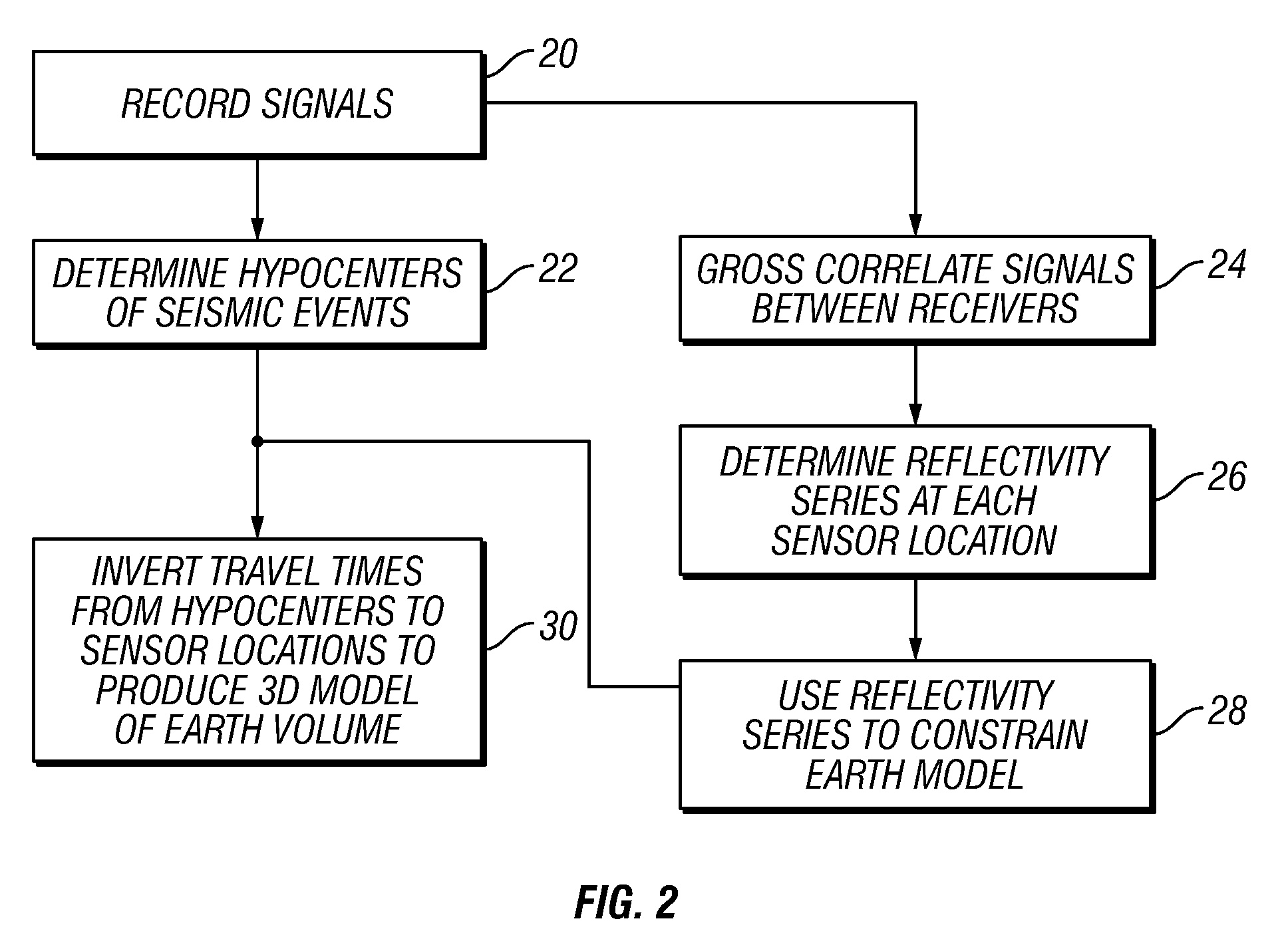
[0014]FIG. 1 shows an array of seismic sensors, individually identified as G1 through G7, disposed at selected positions near or on the surface 12 of the Earth above a volume 10 of the Earth's subsurface to be imaged using passive seismic signals. The subsurface volume 10 may include a plurality of different formations, examples of which are shown at 14, 16 and 18, each having distinct seismic properties (e.g., acoustic impedance). A boundary 15, 17, and 19 may represent the surface that separates two adjacent formations 14, 16 and 18, respectively. The seismic sensors G1 through G7 may be one- or three-component particle motion sensors, such as geophones, accelerometers or any similar
[0015]During recording of the signals produced by each of the seismic sensors G1-G7, various microearthquakes or other seismic events, shown at their possible points or origin (“hypocenters”) H1, H2, H3 and H4, may occur in the subsurface in or below the volume 10. The seismic events each produce seism...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com