Data cable for high-speed data transmissions
a data cable and high-speed technology, applied in the direction of cables/conductor manufacture, cable/conductor manufacturing, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of low processing speed high attenuation peak at high frequencies, etc., and achieve good transmission properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
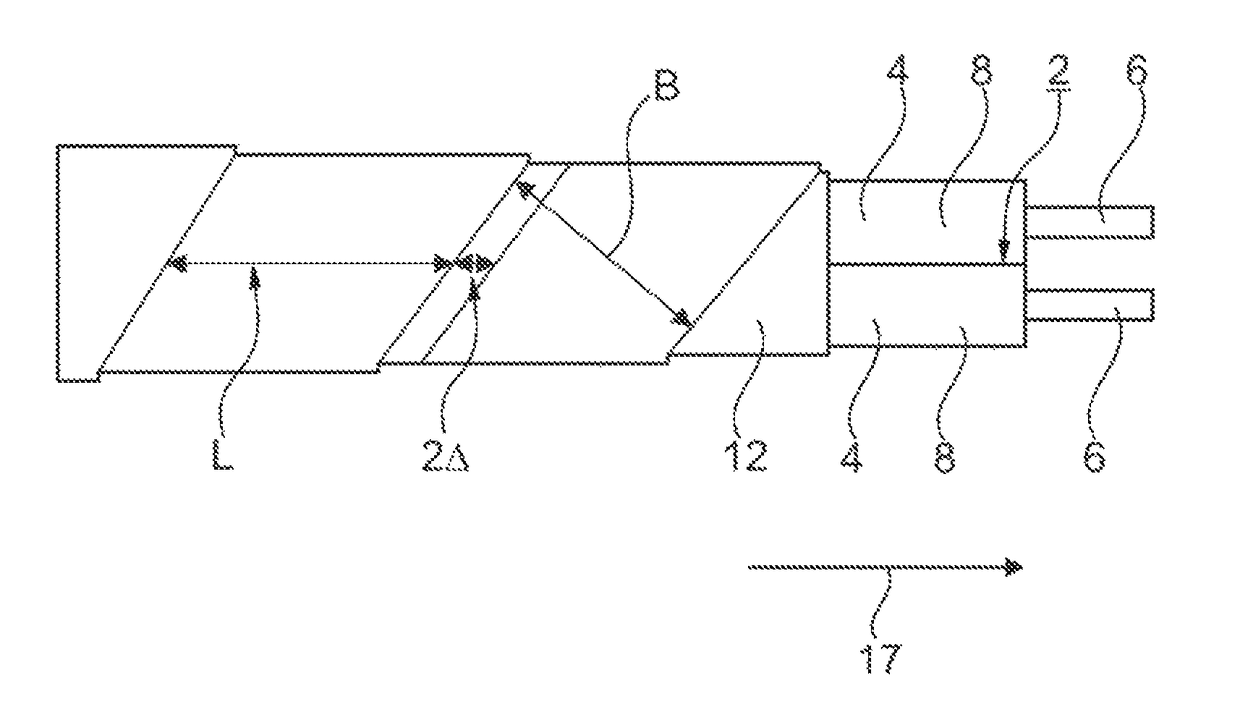
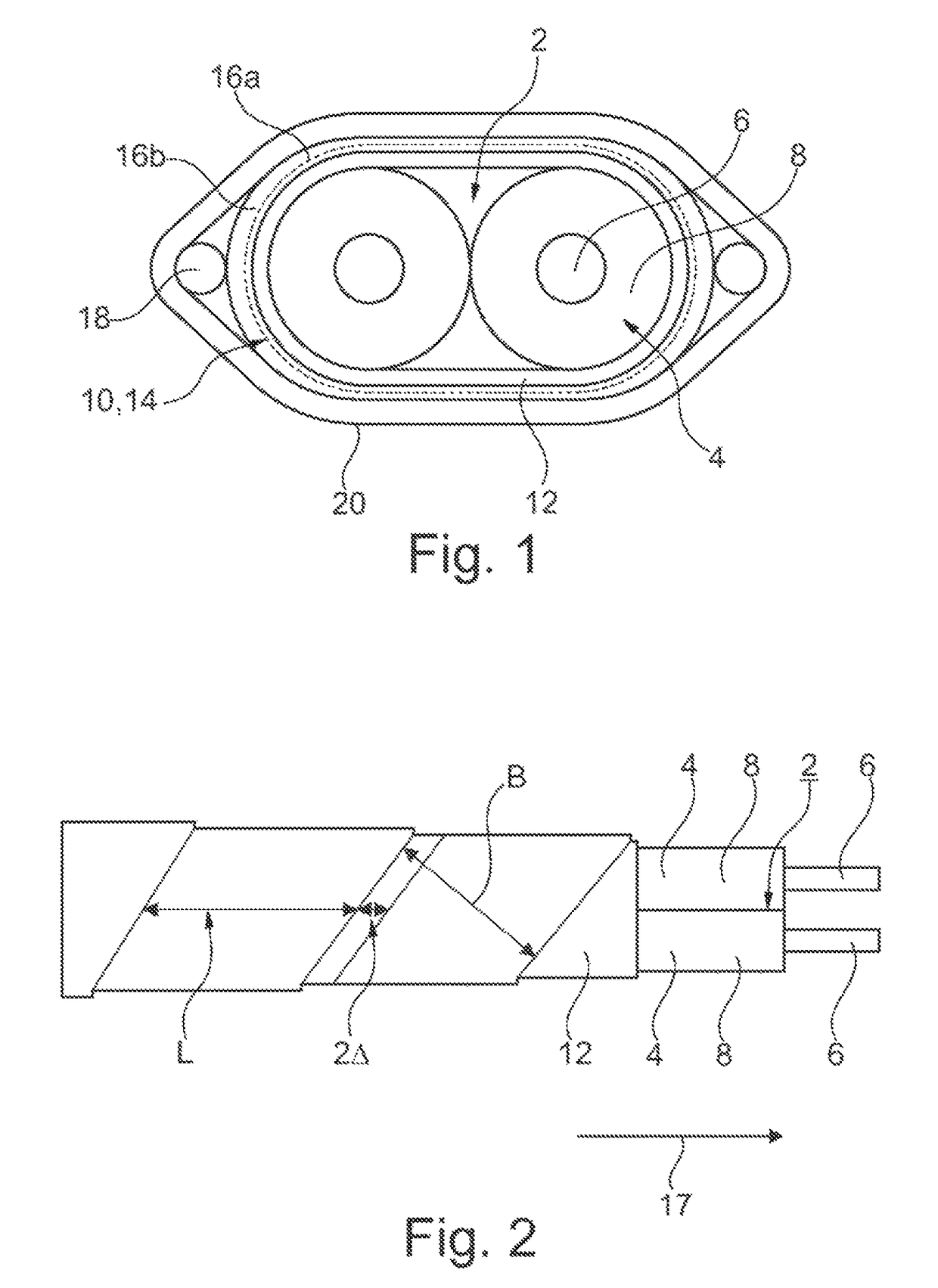
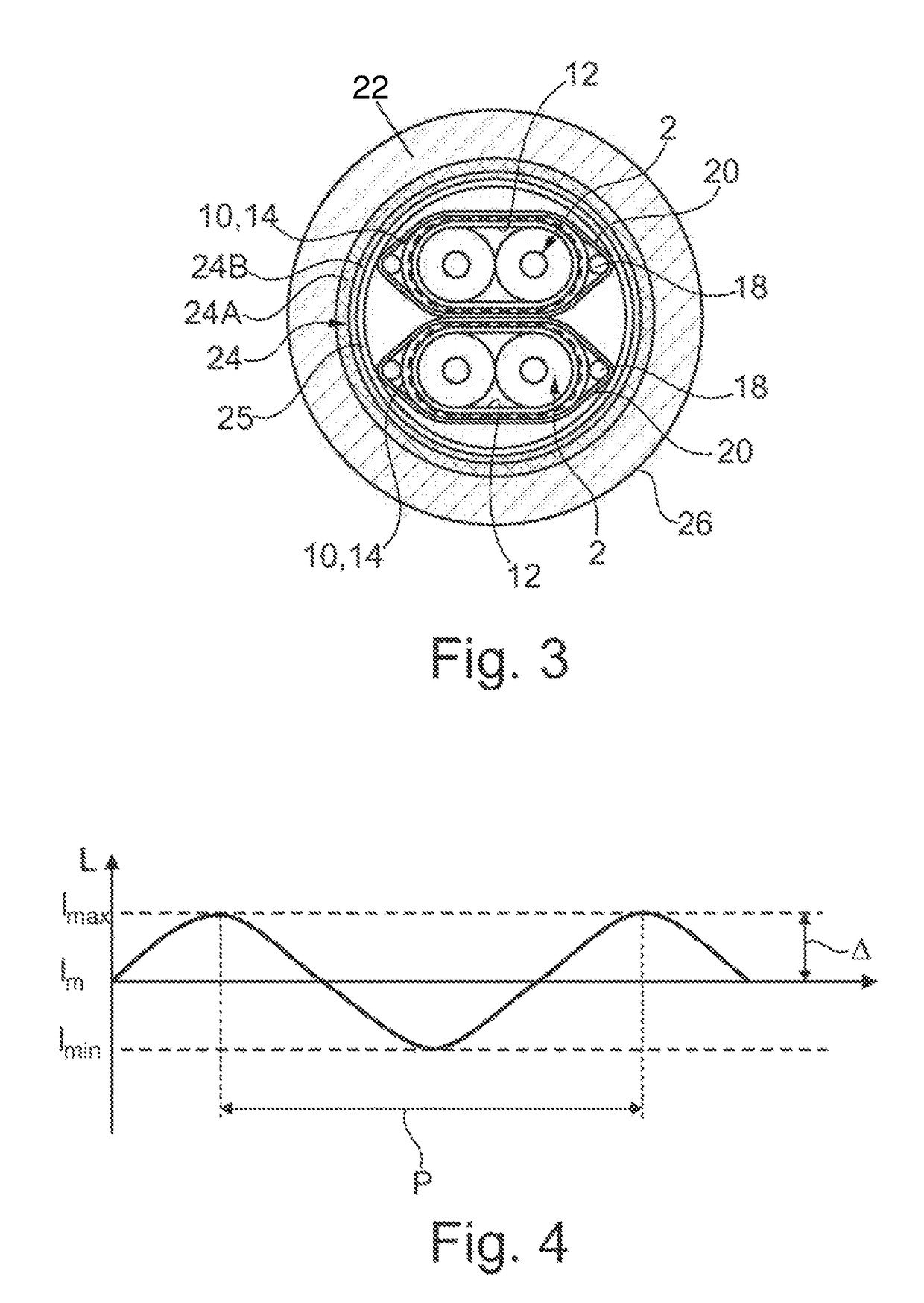
[0040]Referring now to the figures of the drawings in detail and first, particularly, to FIGS. 1-3 thereof, there is seen at least one wire pair 2, formed of two wires 4, in which each wire 4 in turn exhibits a central conductor 6 which is surrounded by a wire insulation 8. The wire pair 2 is surrounded in each instance by a pair shielding 10 which surrounds the wire pair 2, with the insertion or interposition of an intermediate film 12.
[0041]In the embodiment variant according to FIG. 1, the pair shielding 10 has been formed by a single multilayered shielding foil 14 which is formed of a backing layer 16a taking the form of a PET backing film and also an aluminum coating, attached thereto, by way of a conductive layer 16b. The conductive layer 16b is oriented outward. In the case of the shielding foil 14, a longitudinally folded shielding foil 14 is used having longitudinal edges which therefore run parallel to the wires 4 in a longitudinal direction 17. The wires 4 run in the long...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mean length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com