Wiring board construction and methods of making same
a wiring board and wire technology, applied in the field of wiring board construction, can solve the problems of time-consuming and expensive, forming through holes by drilling through the pads individually, and reducing so as to increase the wiring capacity of the board, little or no loss in valuable spa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
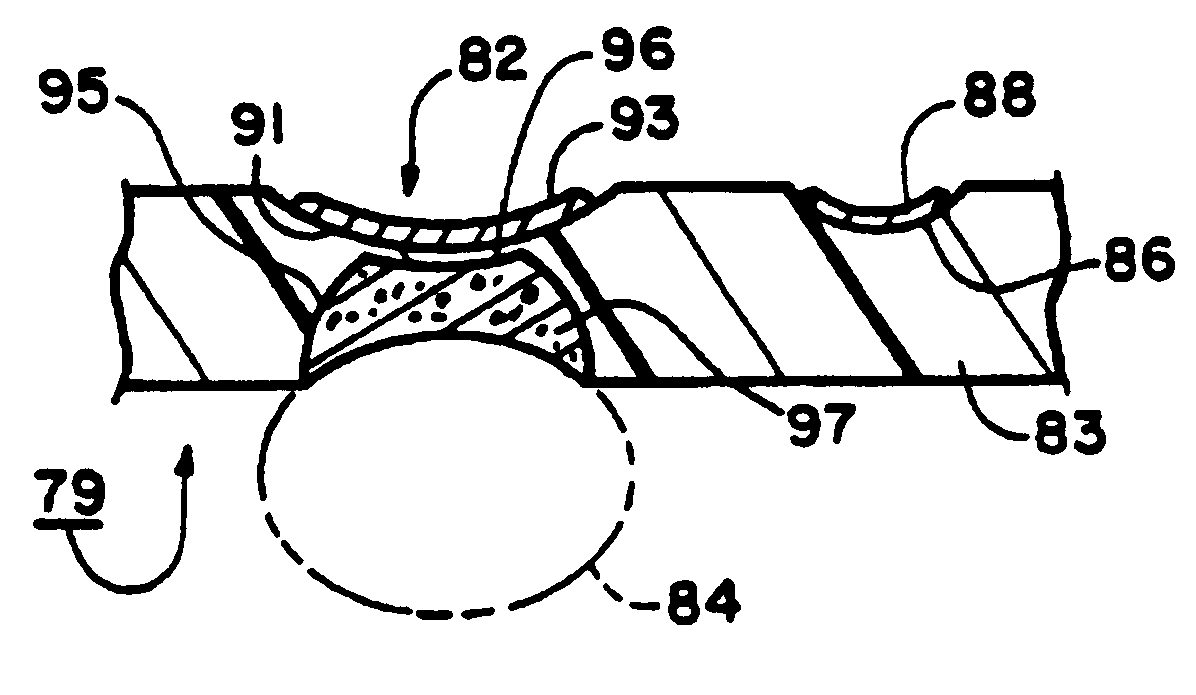
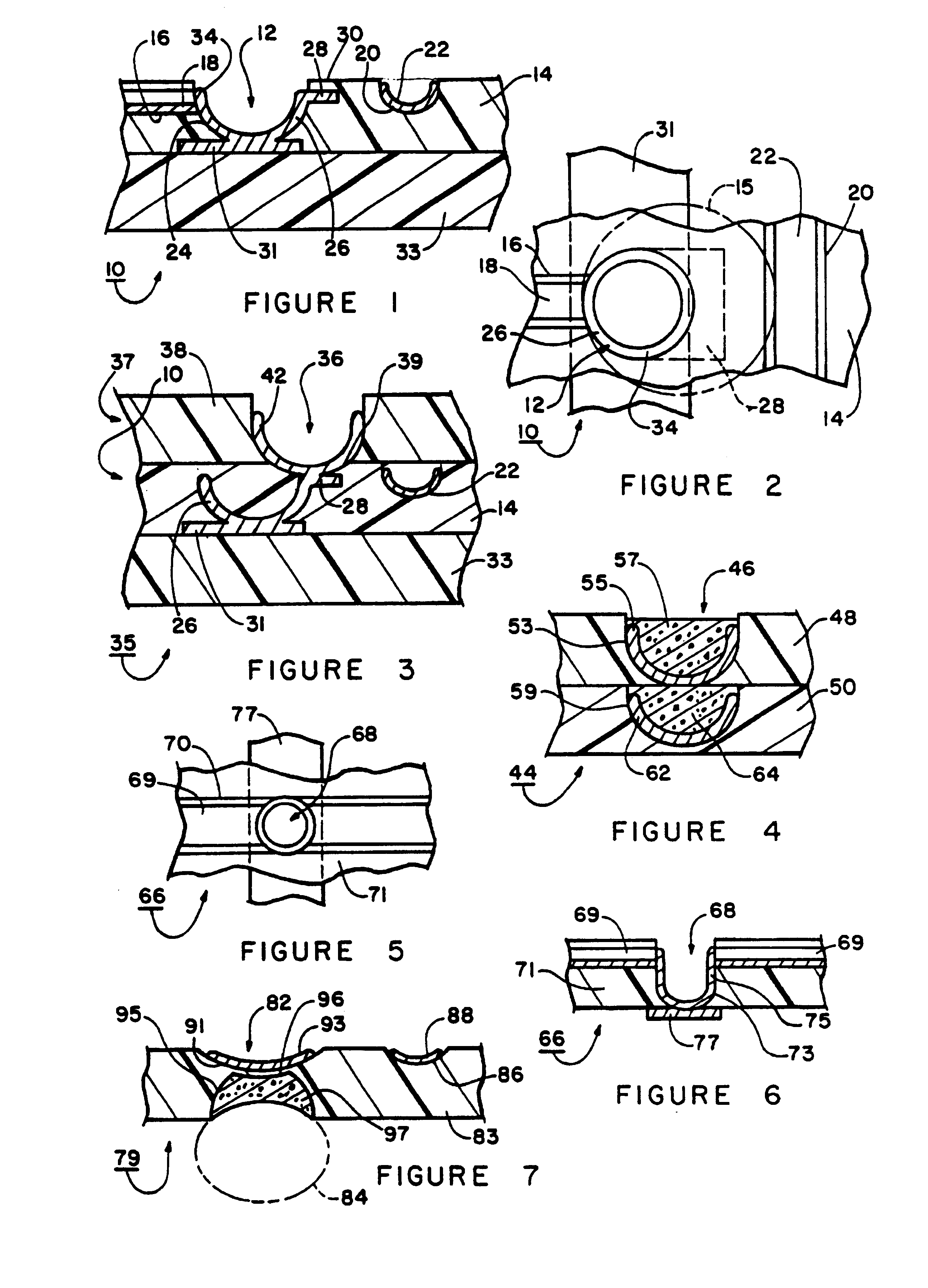
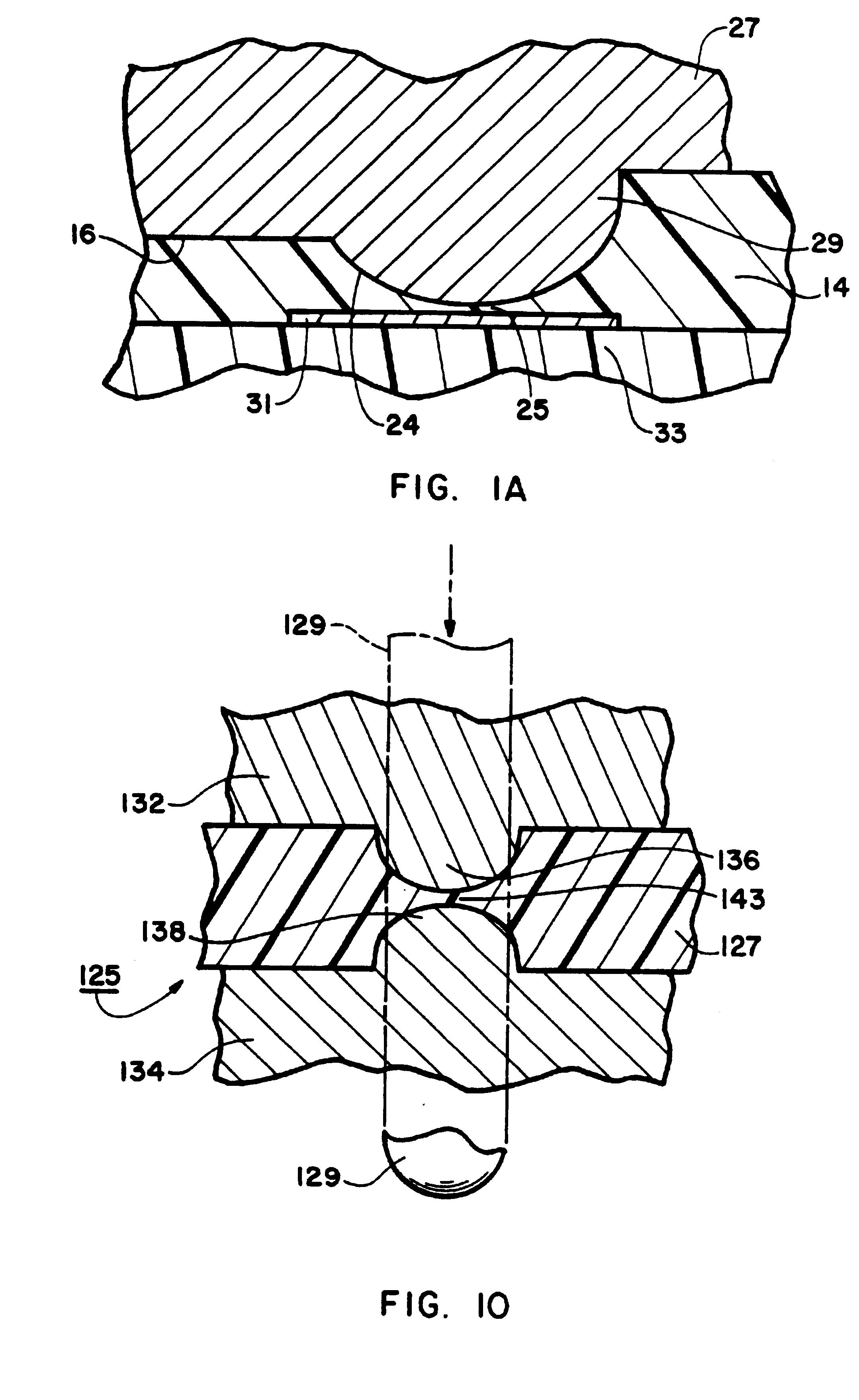
Referring now to the drawings, and more particularly to FIGS. 1, 1A and 2 thereof, there is shown a wiring board construction 10, which is constructed in accordance with the present invention. The terms "wiring board" as used herein are intended to refer to and to include the terms "printed circuit board."
The wiring board construction 10 includes a microvia 12 formed in the wiring board construction 10 in accordance with the present invention. As seen in FIG. 2, the size of the microvia 12 is substantially smaller than the size of a conventional pad as indicated at 15 which would surround a conventional microvia (not shown), thereby greatly improving wiring density for the wiring board construction 10 as compared with conventional wiring densities.
A conductor shallow groove 16 has a conductor pad 18 or trace electrically connected to the microvia 12. The curved conductor trace 18 is formed in the top substrate 14 in accordance with fabrication methods disclosed in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrically conductive | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressible | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com