Patents
Literature
74 results about "Microvia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microvias are used as the interconnects between layers in high density interconnect (HDI) substrates and printed circuit boards (PCBs) to accommodate the high input/output (I/O) density of advanced packages. Driven by portability and wireless communications, the electronics industry strives to produce affordable, light, and reliable products with increased functionality. At the electronic component level, this translates to components with increased I/Os with smaller footprint areas (e.g. flip-chip packages, chip-scale packages, and direct chip attachments), and on the printed circuit board and package substrate level, to the use of high density interconnects (HDIs) (e.g. finer lines and spaces, and smaller vias).
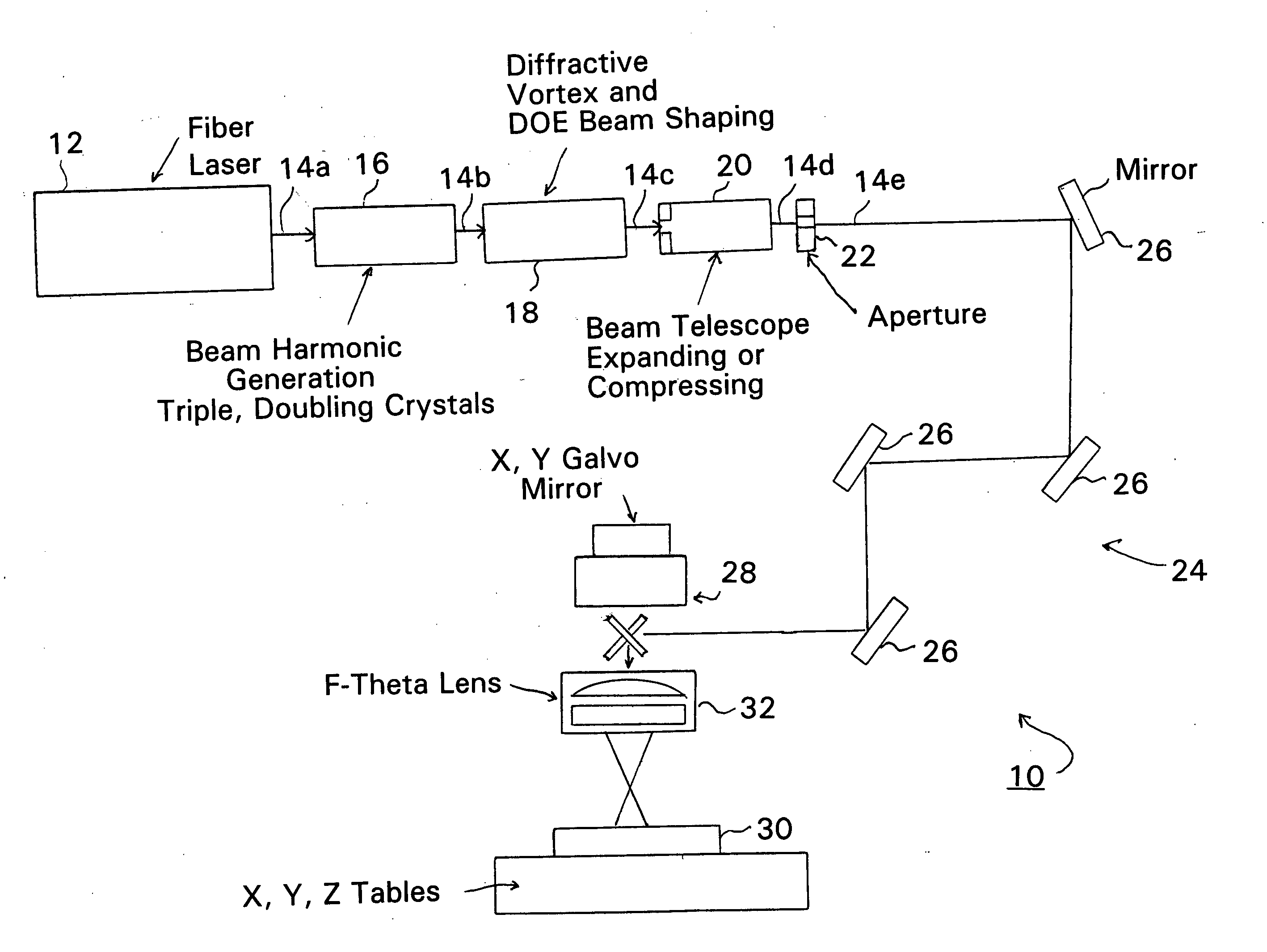
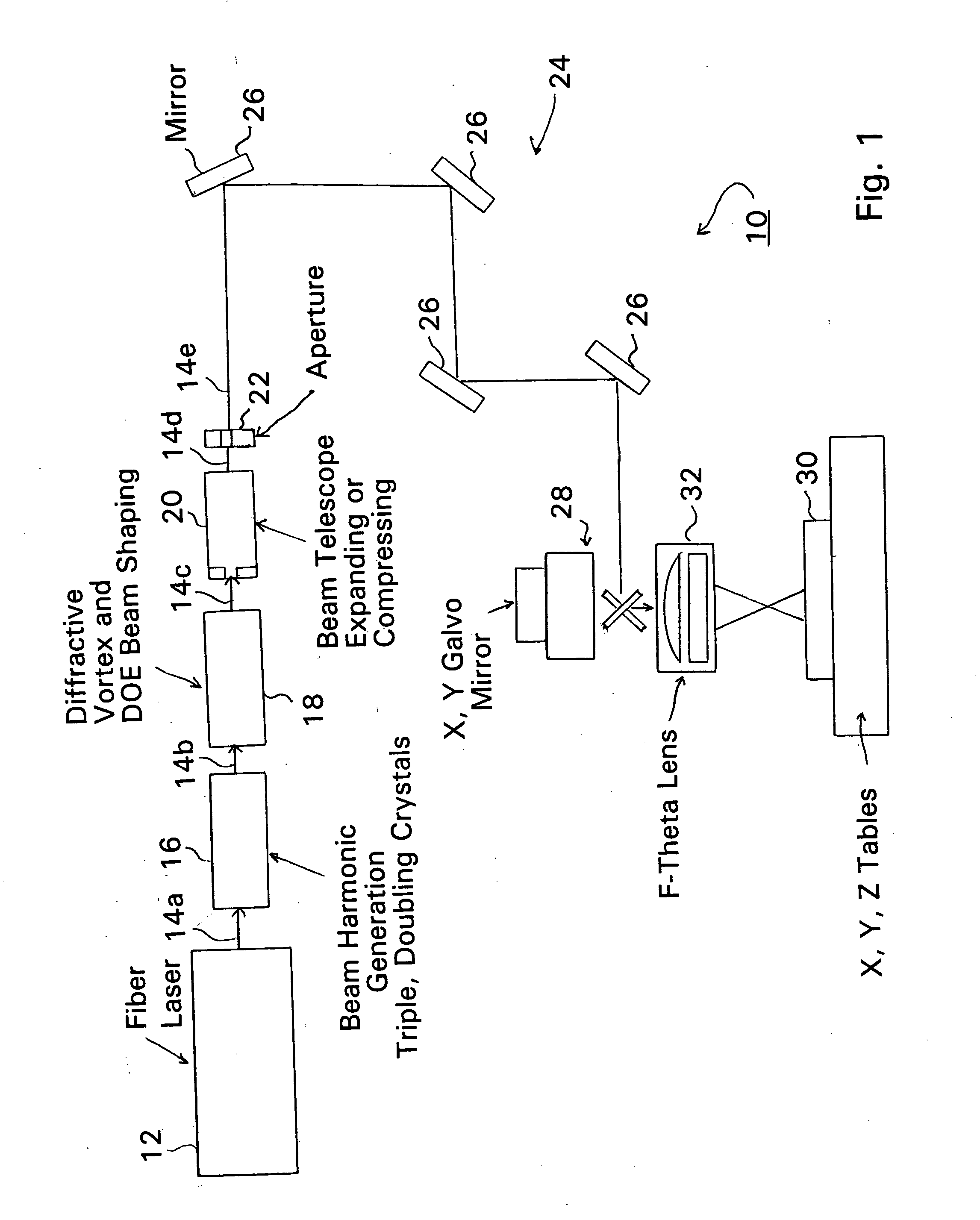
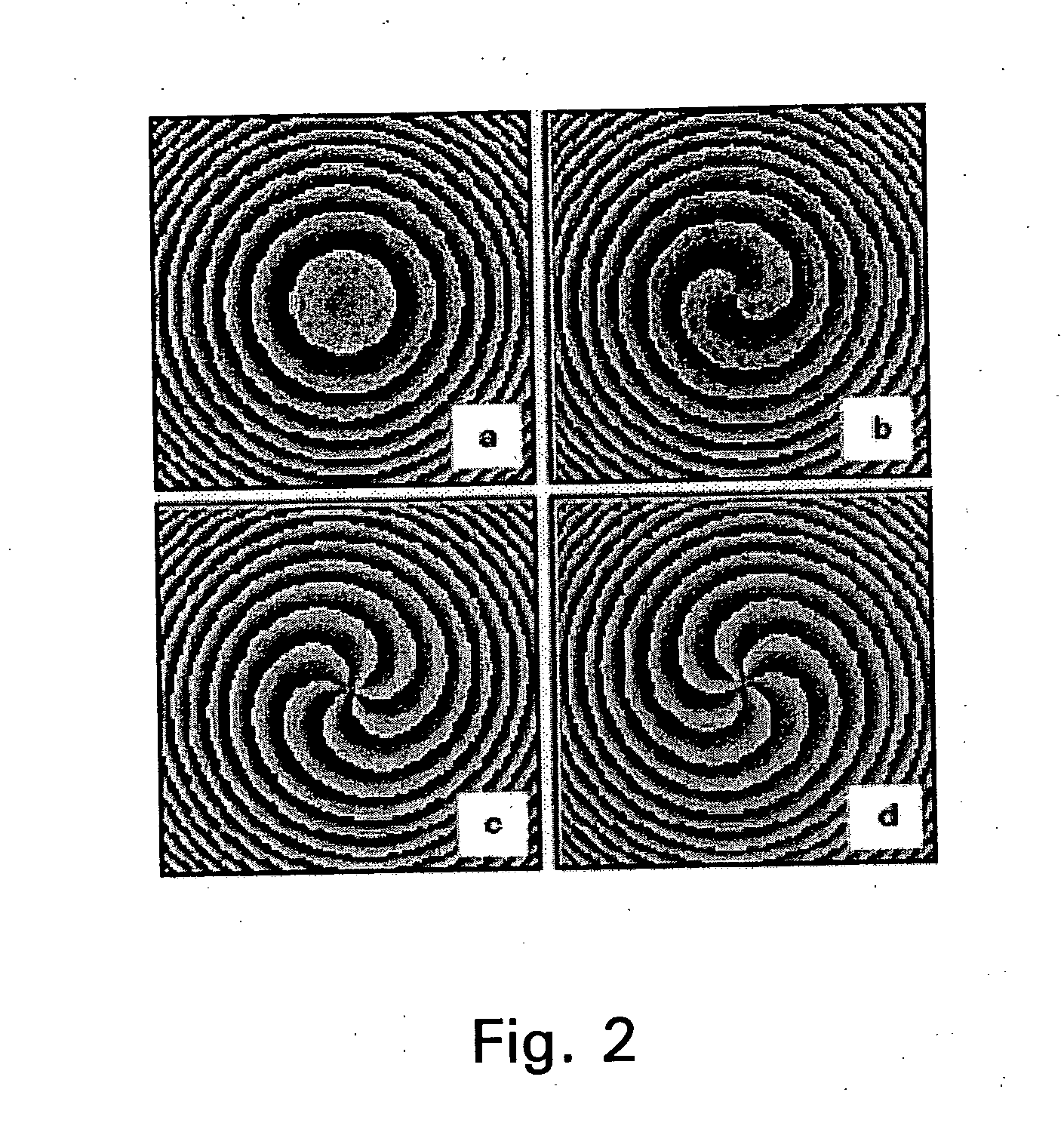
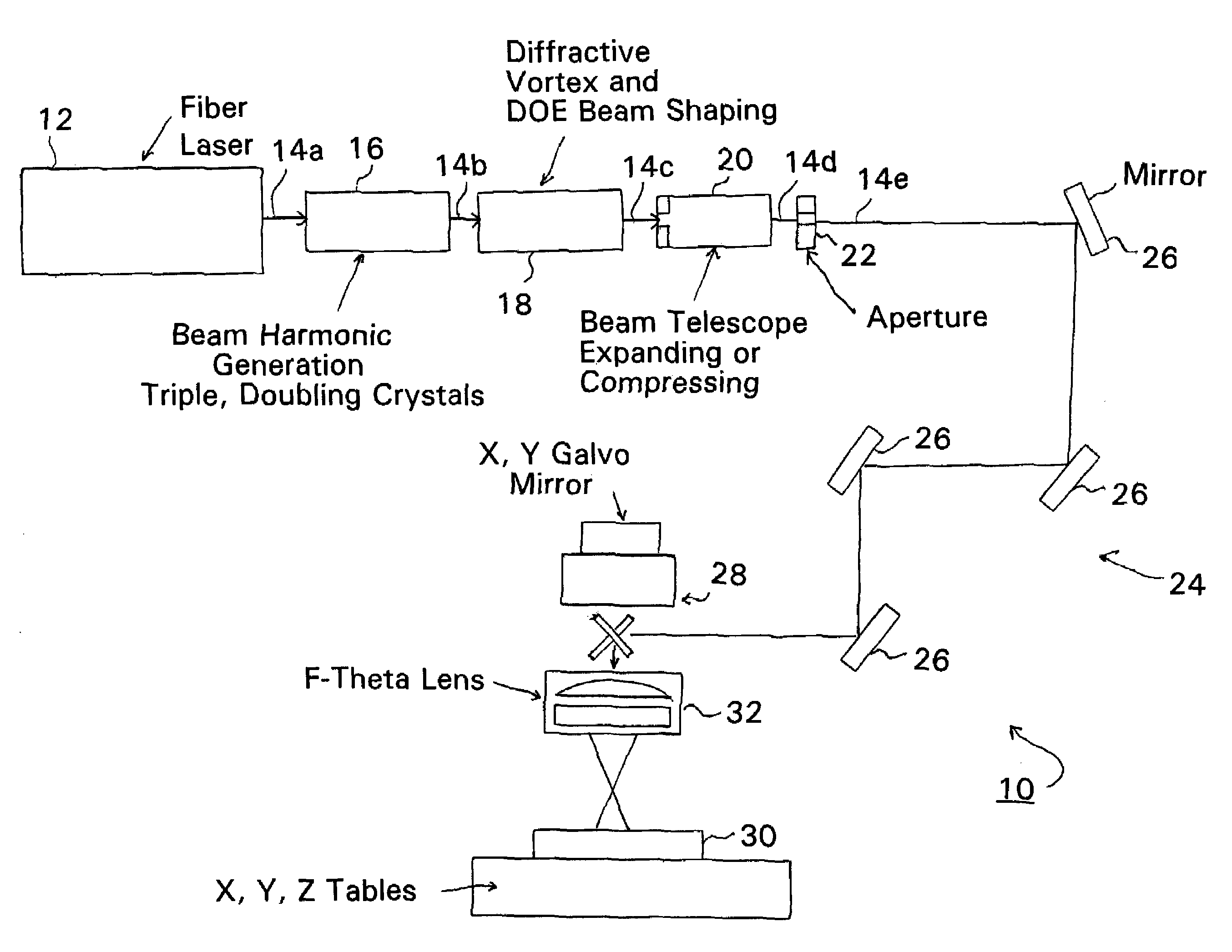
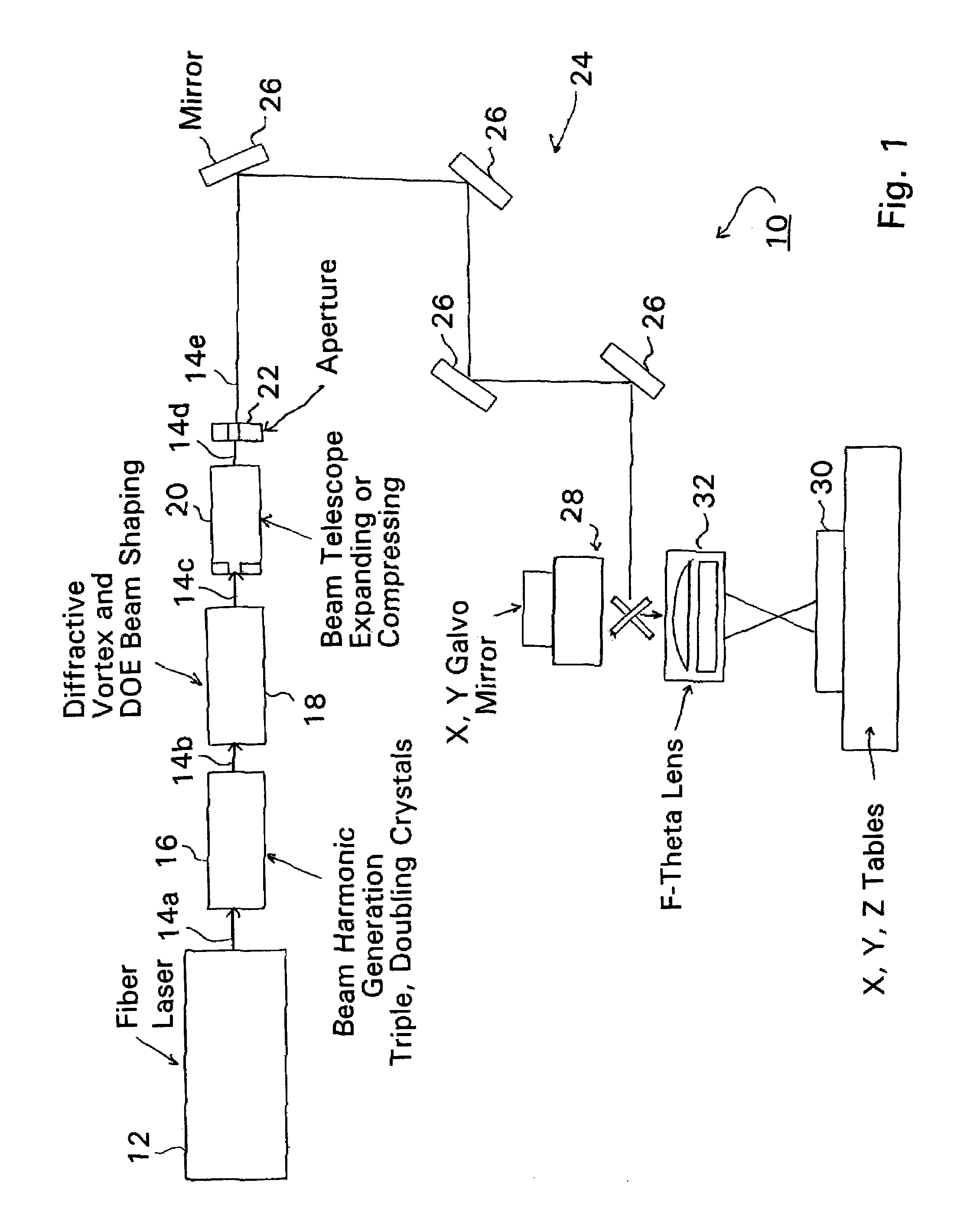
Fiber laser based production of laser drilled microvias for multi-layer drilling, dicing, trimming or milling applications
InactiveUS20060065640A1Additive manufacturing apparatusLaser using scattering effectsNano machiningOptoelectronics
Fiber lasers and methods for constructing and using fiber lasers for micro- / nano-machining with output beams including stacked pulses and combinations of continuous wave, pseudo-continuous wave and pulse sequence components.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
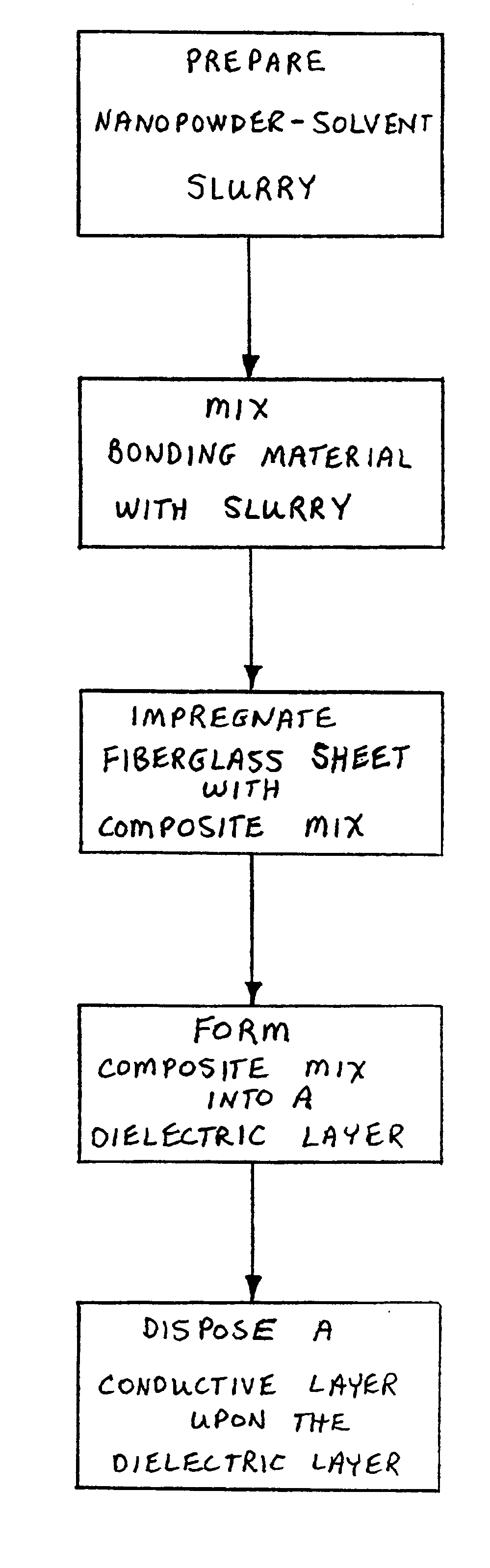
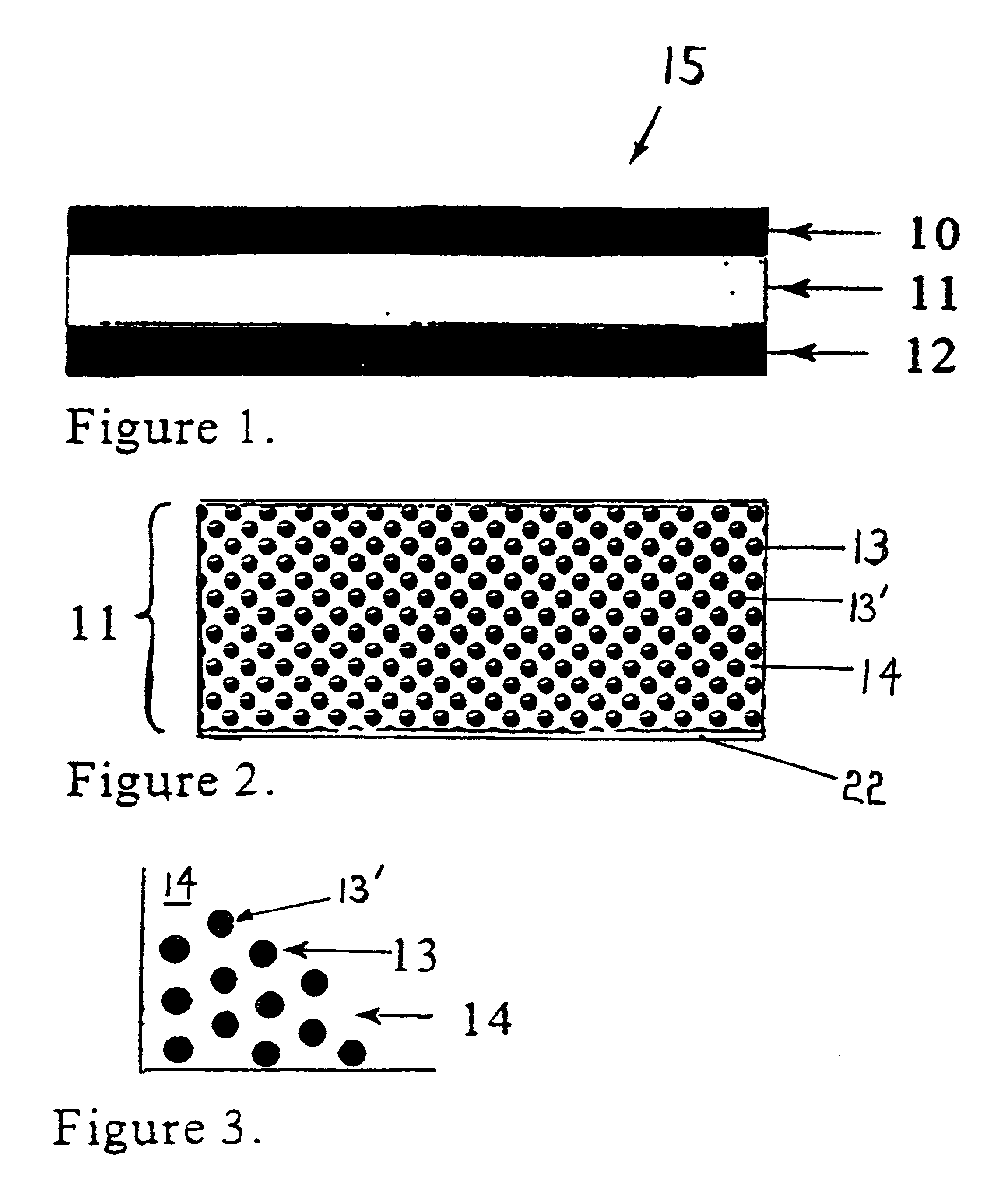
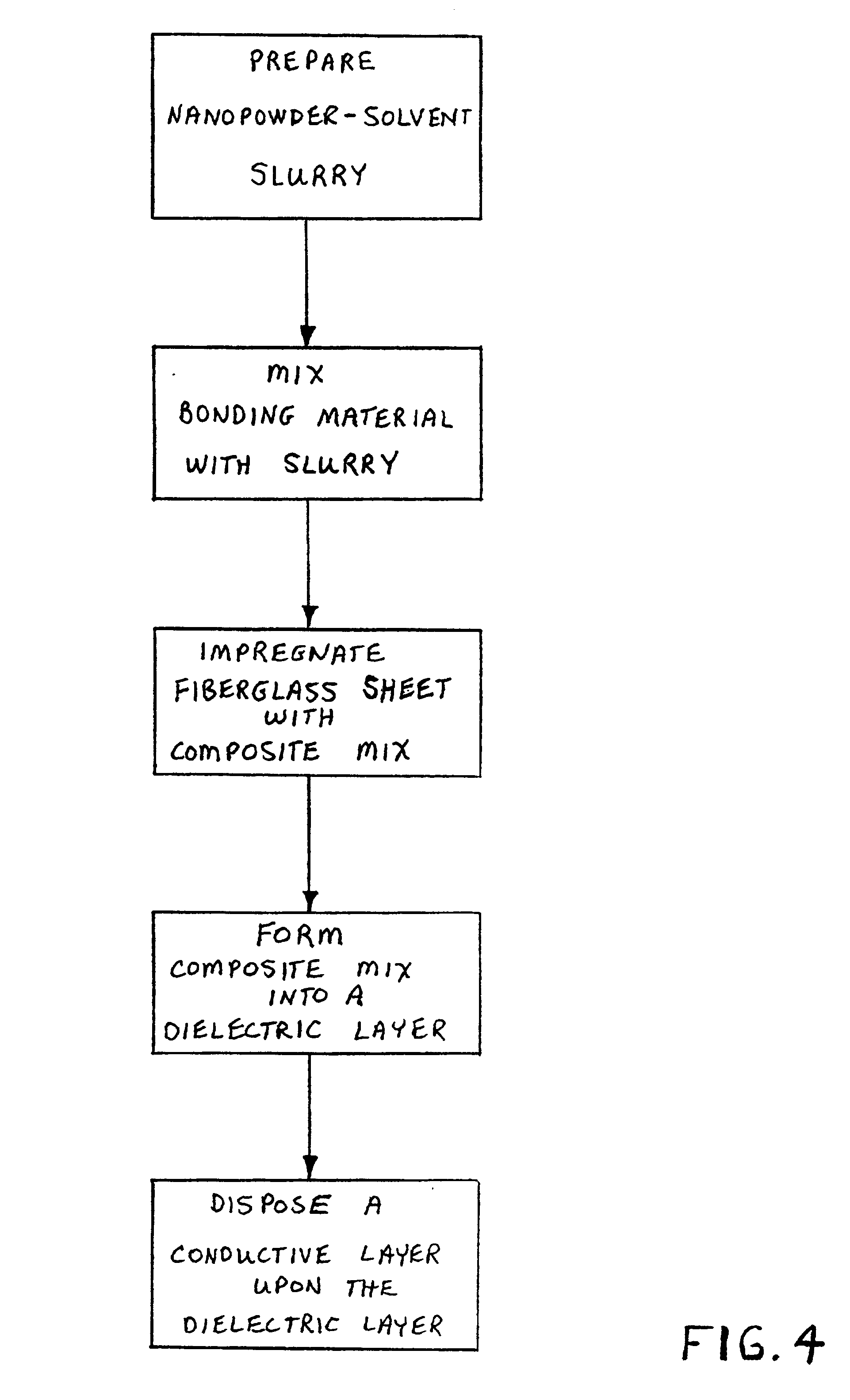
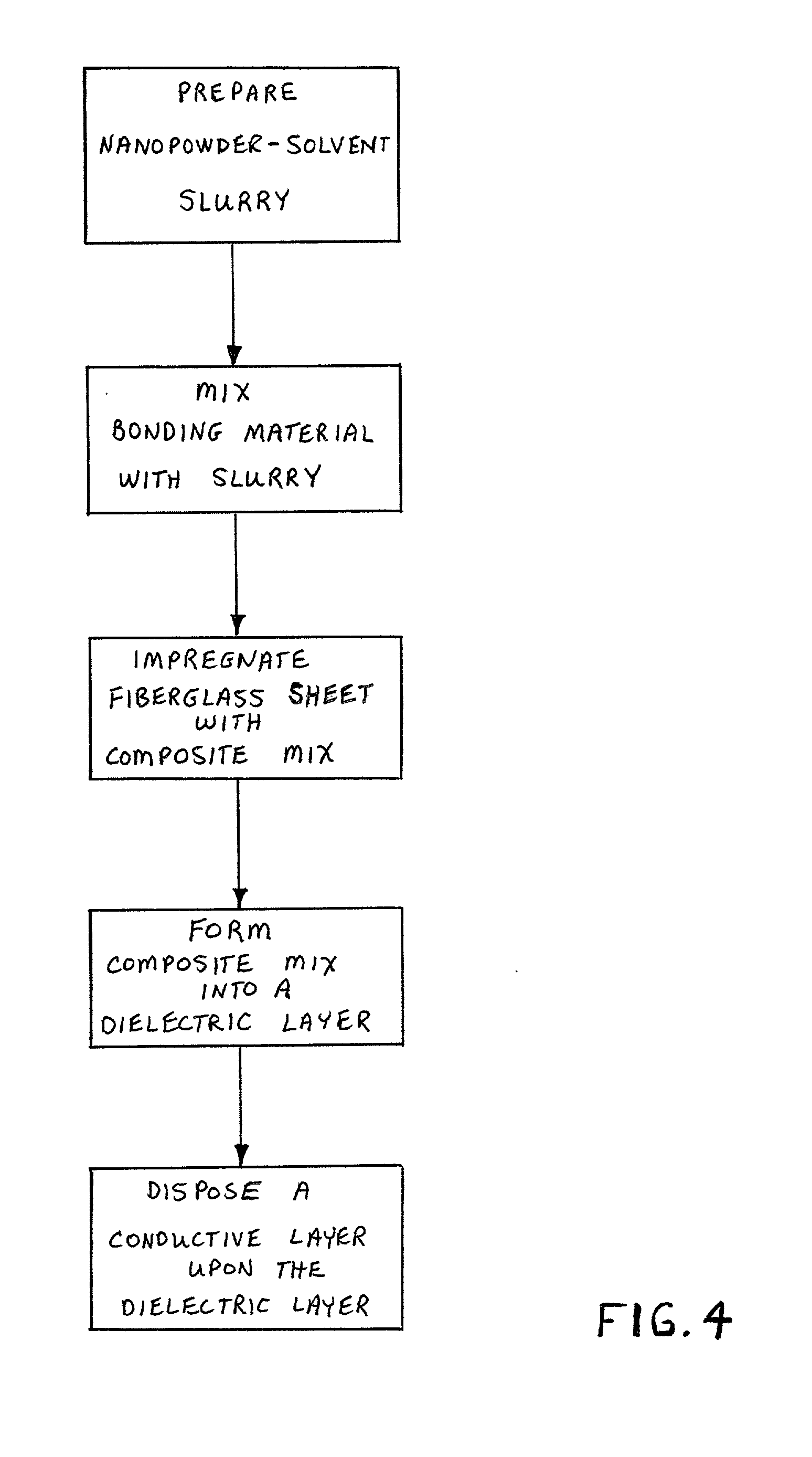
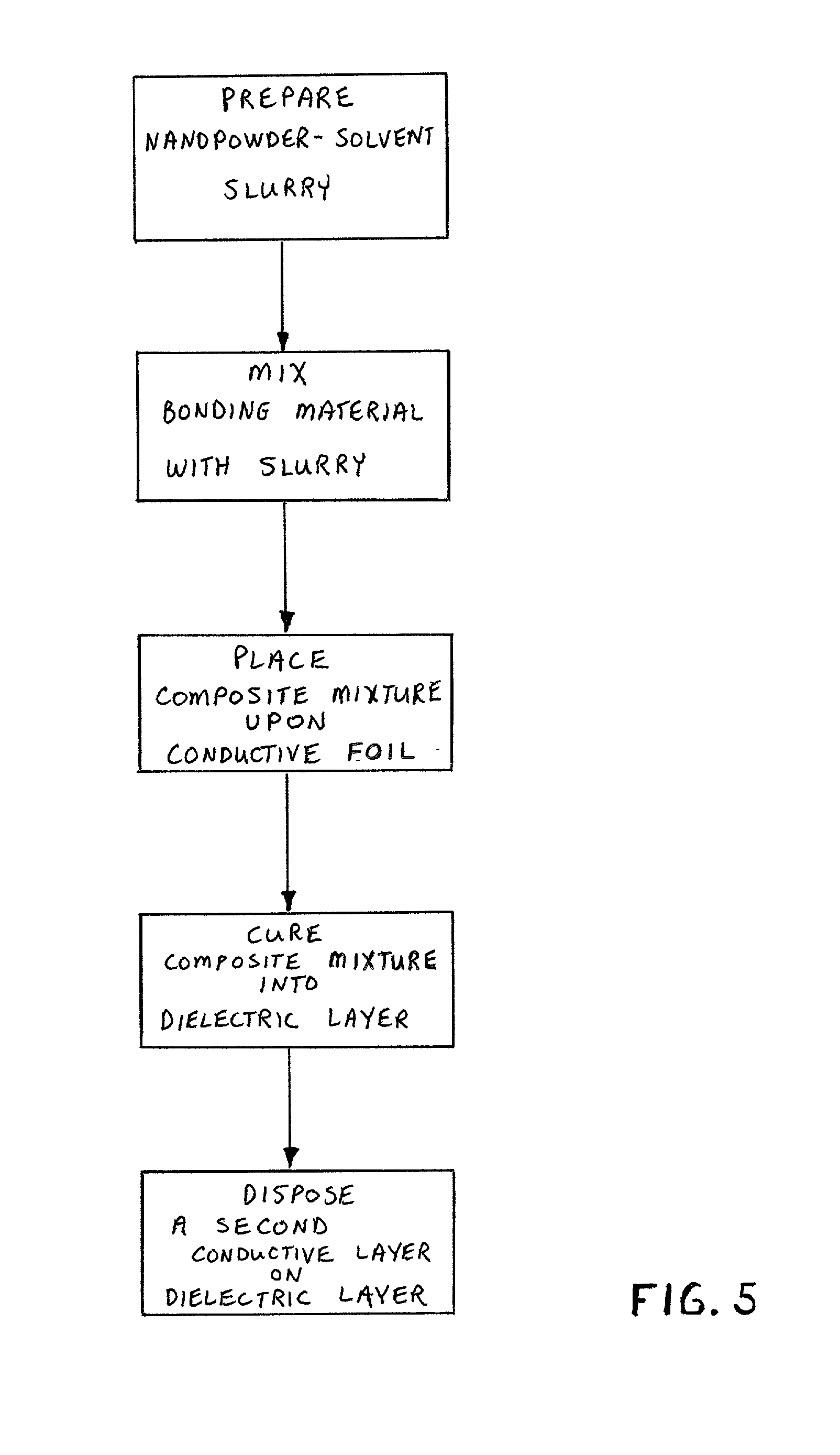
Integral capacitance for printed circuit board using dielectric nanopowders
InactiveUS6616794B2Adhesive processes with surface pretreatmentPrinted circuit aspectsCapacitanceSputtering
A method for producing integral capacitance components for inclusion within printed circuit boards. Hydrothermally prepared nanopowders permit the fabrication of a very thin dielectric layers that offer increased dielectric constants and are readily penetrated by microvias. Disclosed is a method of preparing a slurry or suspension of a hydrothermally prepared nanopowder and solvent. A suitable bonding material, such as a polymer is mixed with the nanopowder slurry, to generate a composite mixture which is formed into a dielectric layer. The dielectric layer may be placed upon a conductive layer prior to curing, or conductive layers may be applied upon a cured dielectric layer, either by lamination or by metallization processes, such as vapor deposition or sputtering.
Owner:TPL INC
Circuit board having plated thru-holes and ground columns
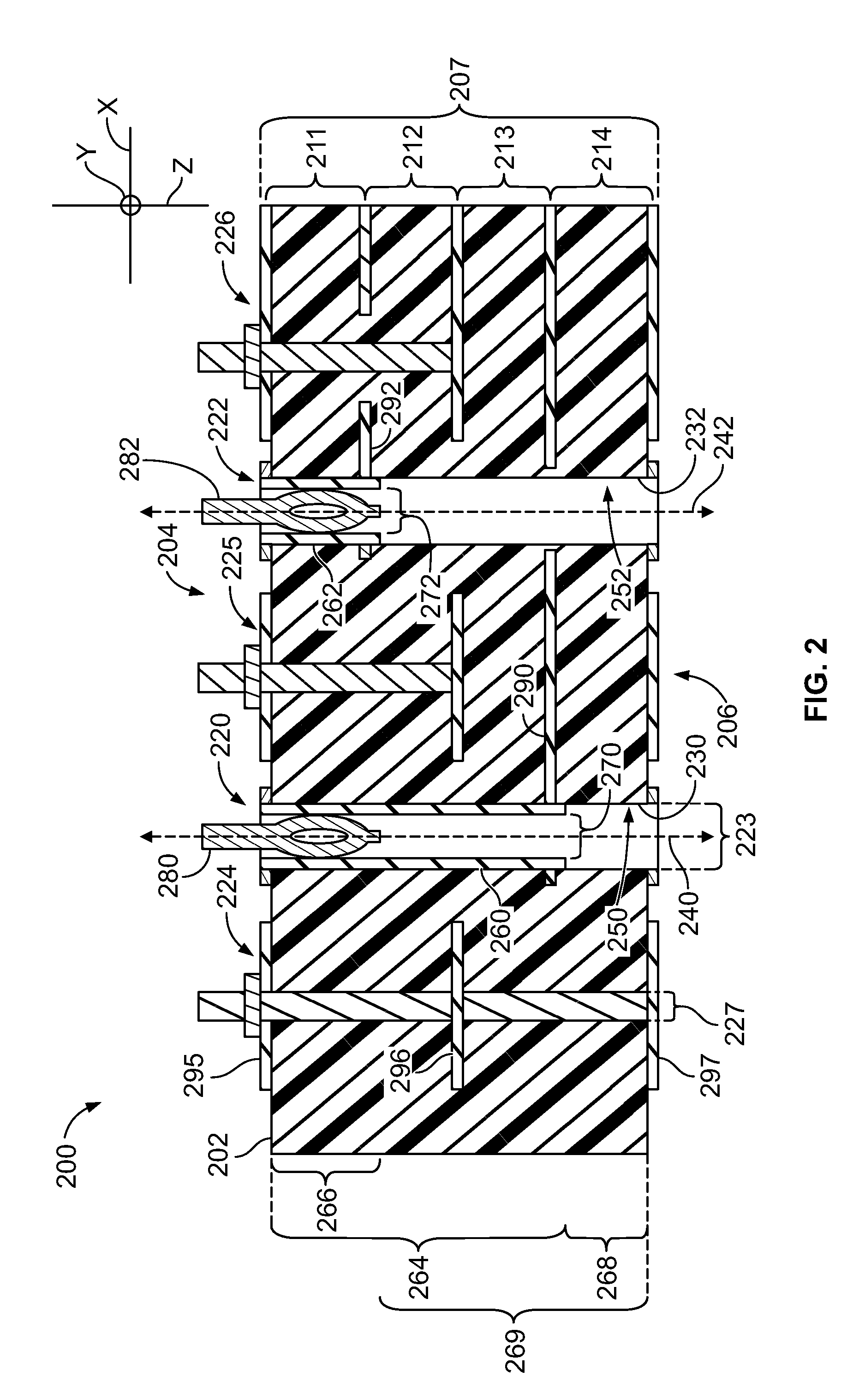
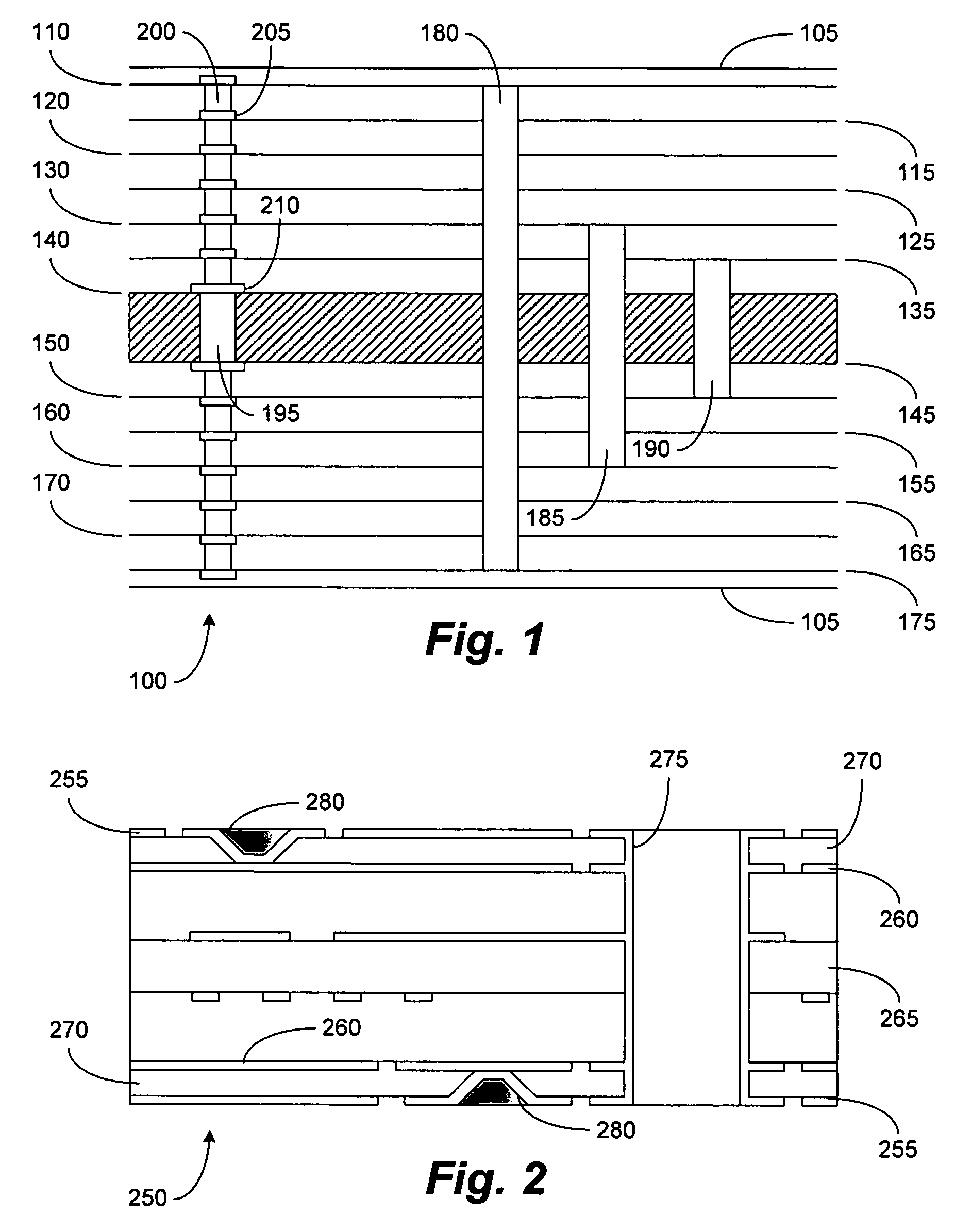
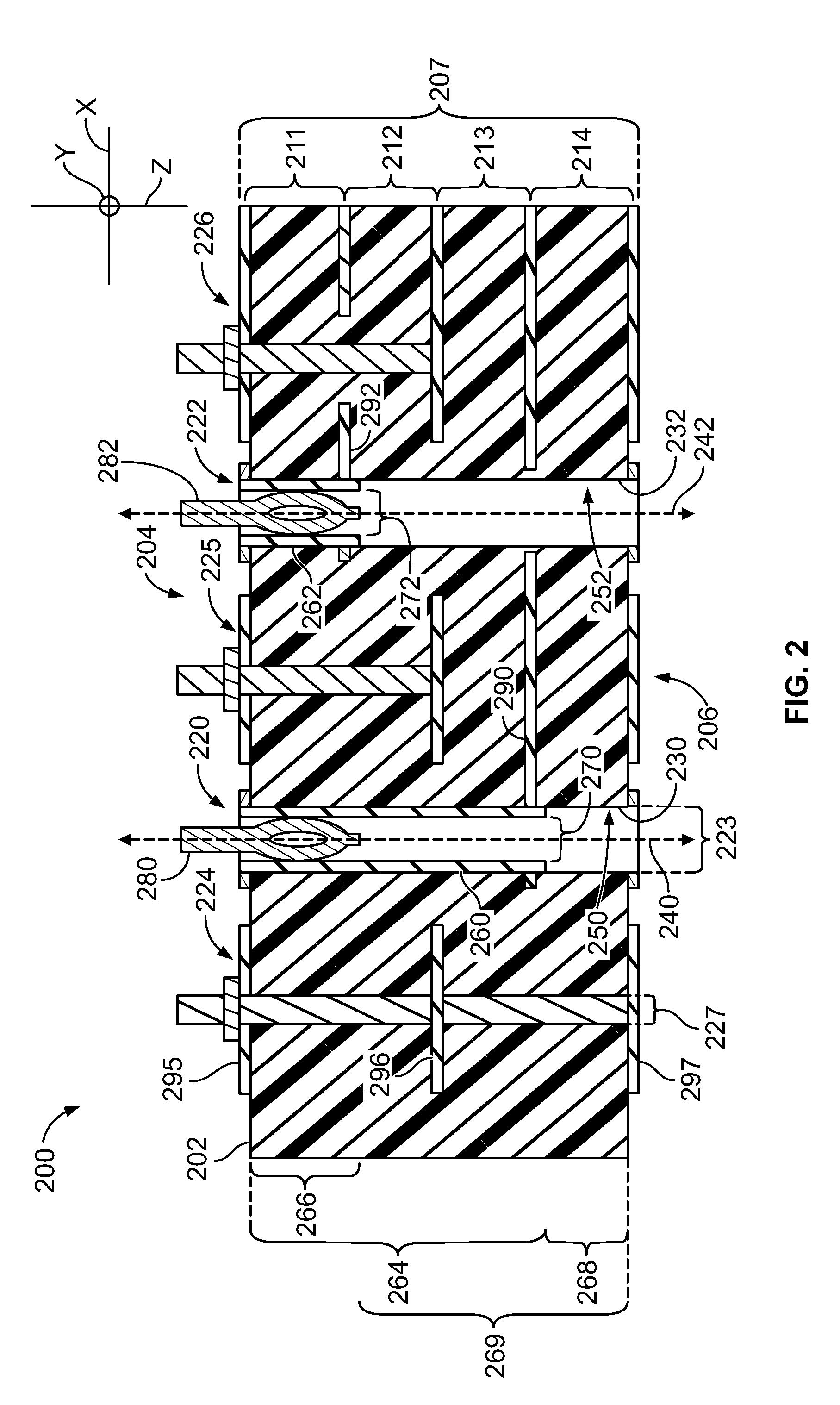
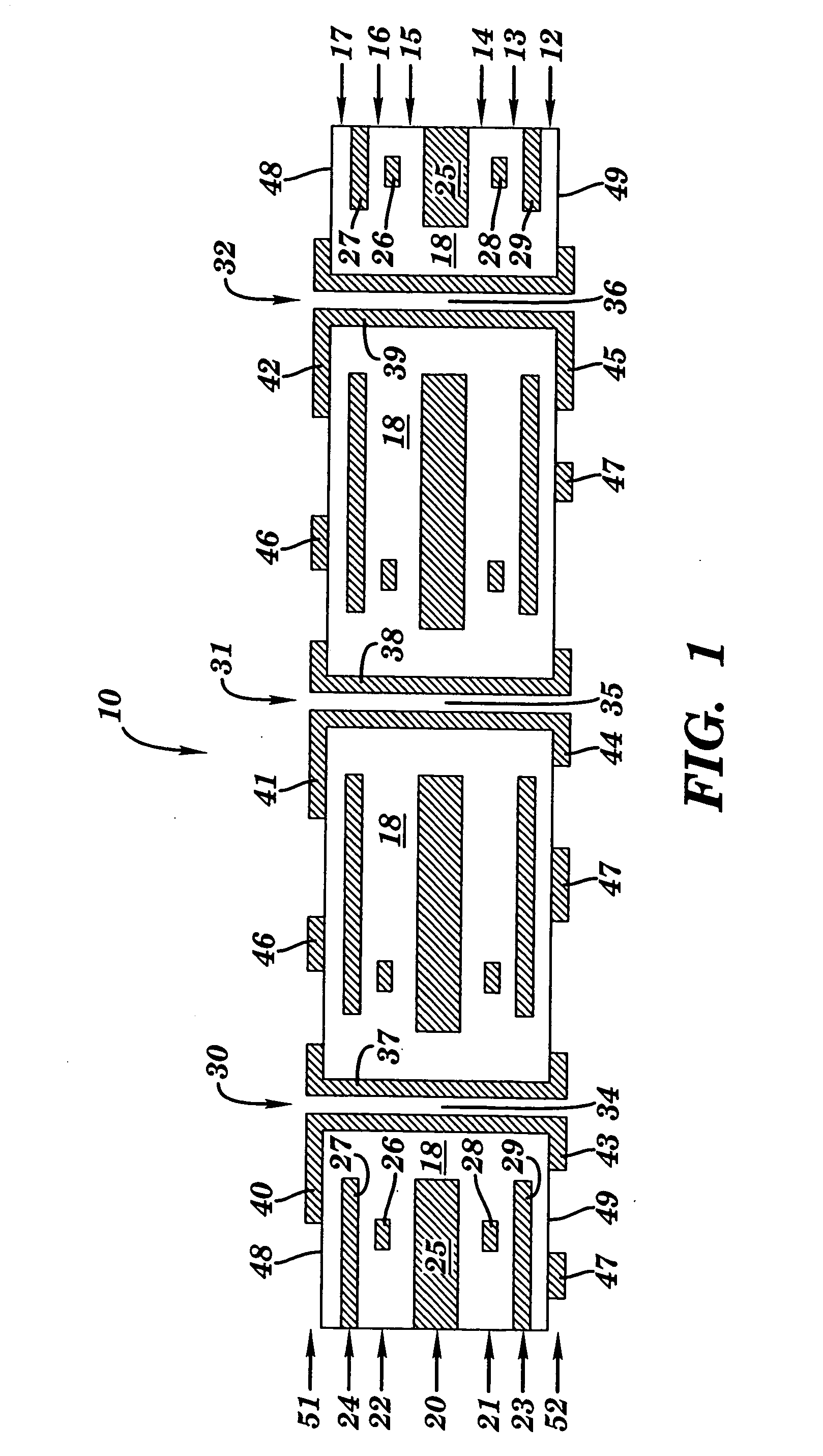
A circuit board including a board substrate having opposite first and second sides. The board substrate has a thickness measured along a z-axis that is perpendicular to the first and second sides. The circuit board also includes plated thru-hole (PTH) vias extending along the z-axis from the first side into the board substrate. The PTH vias are arranged to form multiple signal pairs. The circuit board also includes signal traces that are directly coupled to the PTH vias and extend perpendicular to the z-axis in the board substrate. The signal traces and the PTH vias are configured to transmit differential signals. The circuit board also includes ground columns that extend along the z-axis in the board substrate. The ground columns are distributed relative to the signal pairs to form shield arrays. Each of the shield arrays surrounds one of the signal pairs, wherein the ground columns comprise microvias.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Selective passivation of exposed silicon
InactiveUS20050164500A1Thickness is easy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAtmospheric airAtmospheric temperature
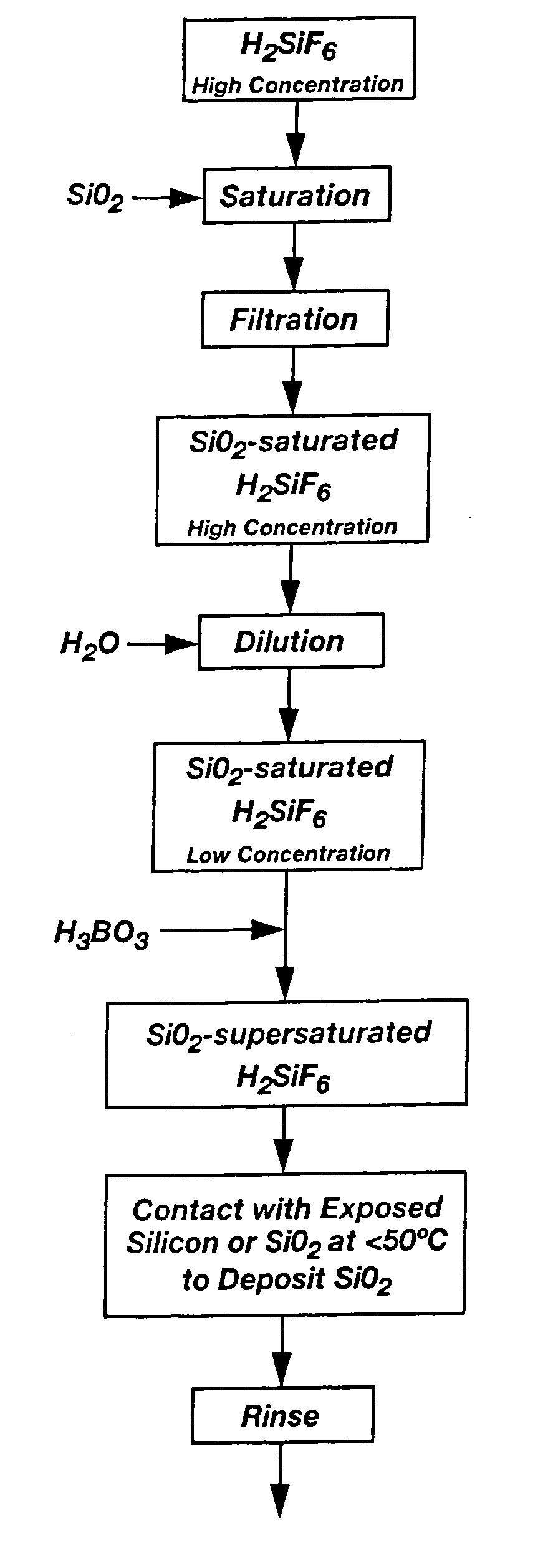
A method for applying a passivation layer selectively on an exposed silicon surface from a liquid phase solution supersaturated in silicon dioxide. The immersion is conducted at substantially atmospheric temperature and pressure and achieves an effective passivation layer in an abbreviated immersion time, and without subsequent heat treatment. In one embodiment, rapid coating of a wafer back side with silicon dioxide permits the use of a high-speed electroless process for plating the bond pad with a solder-enhancing material. In another embodiment, the walls of via holes and microvia holes in a silicon body may be passivated by immersion in the supersaturated solution prior to plugging the holes with conductive material.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Conductive dome probes for measuring system level multi-ghz signals
ActiveUS20080250377A1Final product manufactureCross-talk/noise/interference reductionHigh densityReflection loss
Methods and apparatus for accessing a high speed signal routed on a conductive trace on an internal layer of a printed circuit board (PCB) using high density interconnect (HDI technology) are provided. The conductive trace may be coupled to a microvia (μVia) having a conductive dome disposed above the outer layer pad of the μVia. In-circuit test (ICT) fixtures or high speed test probes may interface with the conductive dome to test the high speed signal with decreased reflection loss and other parasitic effects when compared to conventional test points utilizing plated through-hole (PTH) technology.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
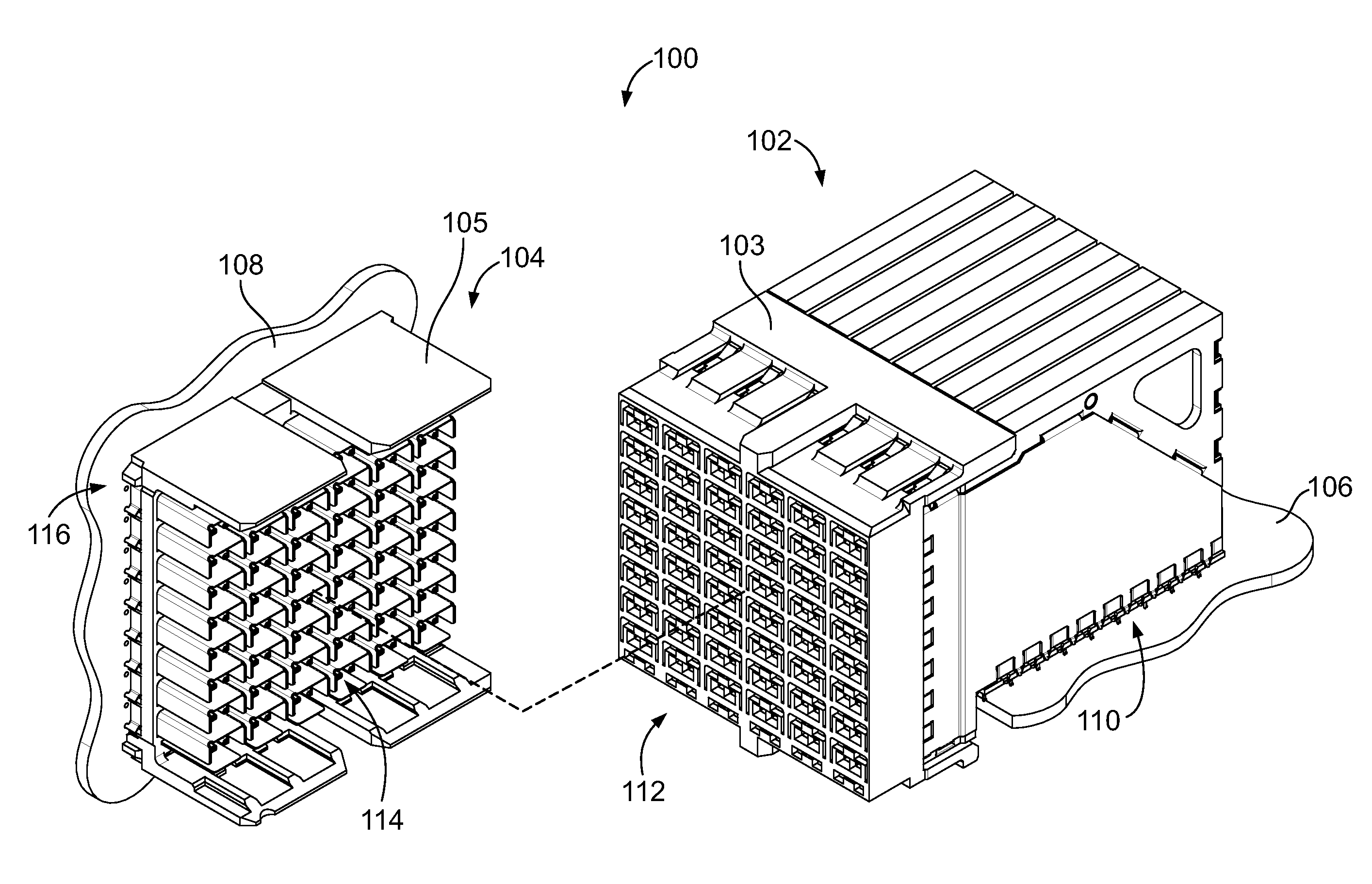
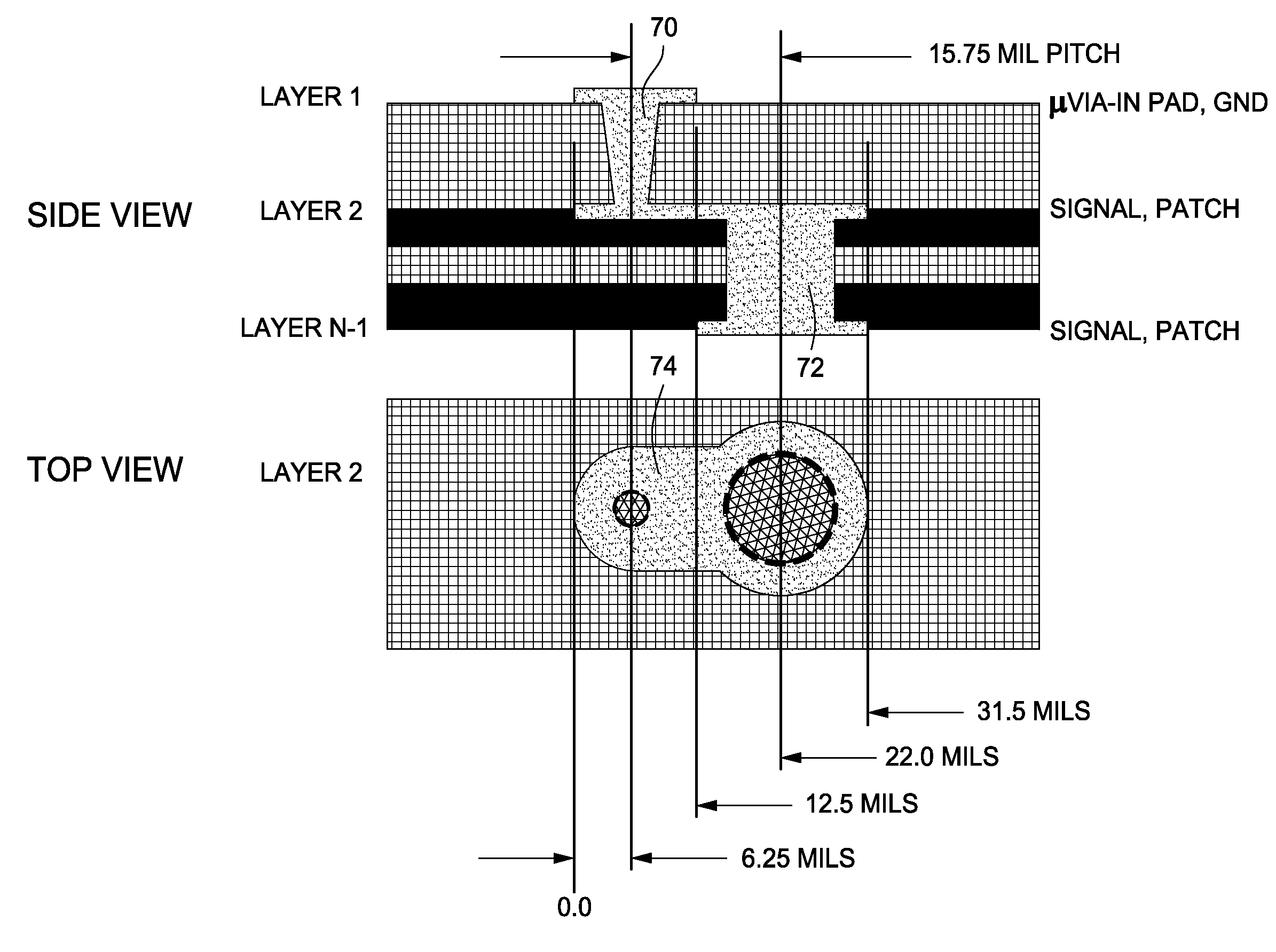
Stacked microvias and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20060289202A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringMicrovia
Owner:INTEL CORP
Circuit board having plated thru-holes and ground columns
A circuit board including a board substrate having opposite first and second sides. The board substrate has a thickness measured along a z-axis that is perpendicular to the first and second sides. The circuit board also includes plated thru-hole (PTH) vias extending along the z-axis from the first side into the board substrate. The PTH vias are arranged to form multiple signal pairs. The circuit board also includes signal traces that are directly coupled to the PTH vias and extend perpendicular to the z-axis in the board substrate. The signal traces and the PTH vias are configured to transmit differential signals. The circuit board also includes ground columns that extend along the z-axis in the board substrate. The ground columns are distributed relative to the signal pairs to form shield arrays. Each of the shield arrays surrounds one of the signal pairs, wherein the ground columns comprise microvias.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Hyperbga buildup laminate
InactiveUS6879492B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic structureDielectric layer
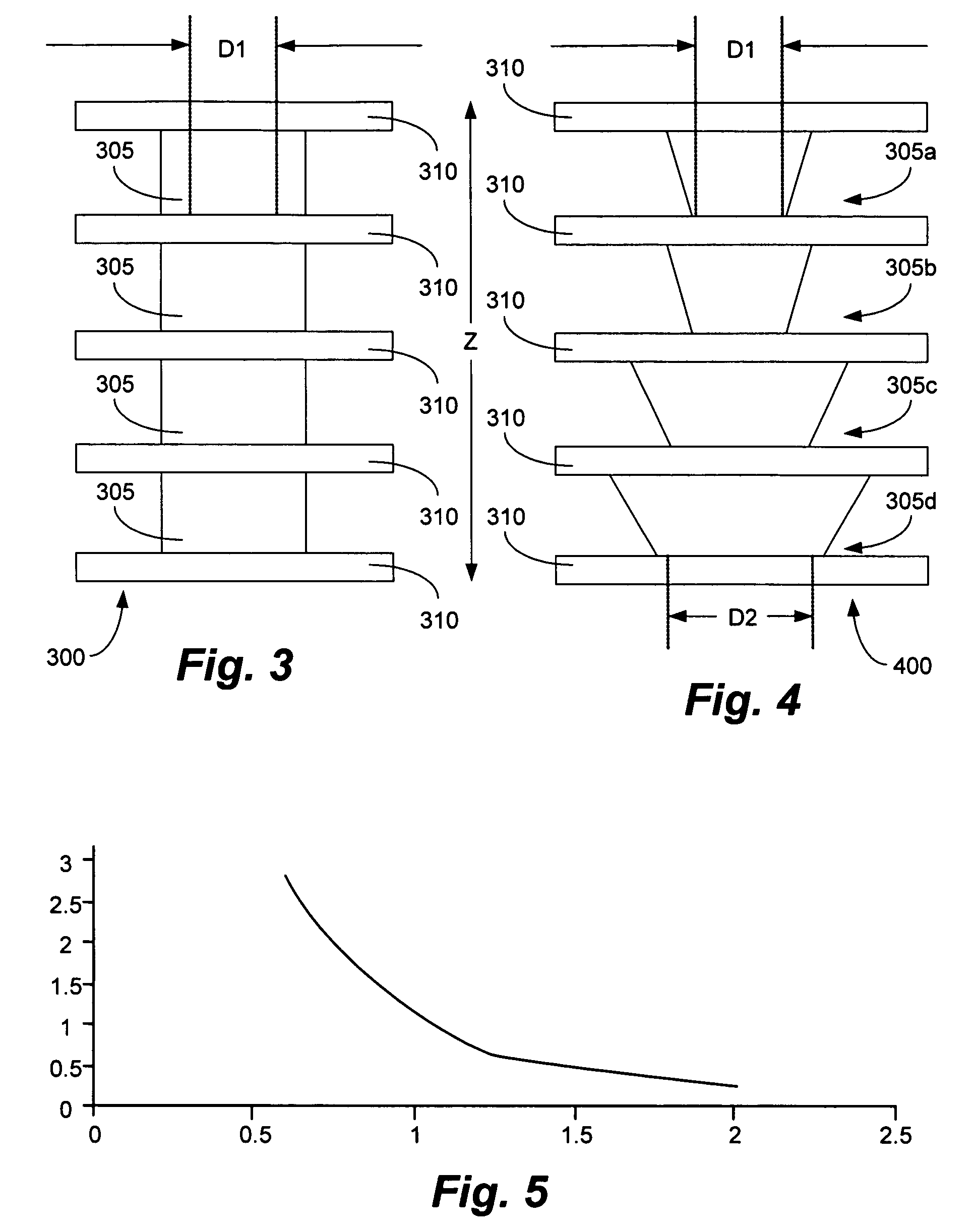
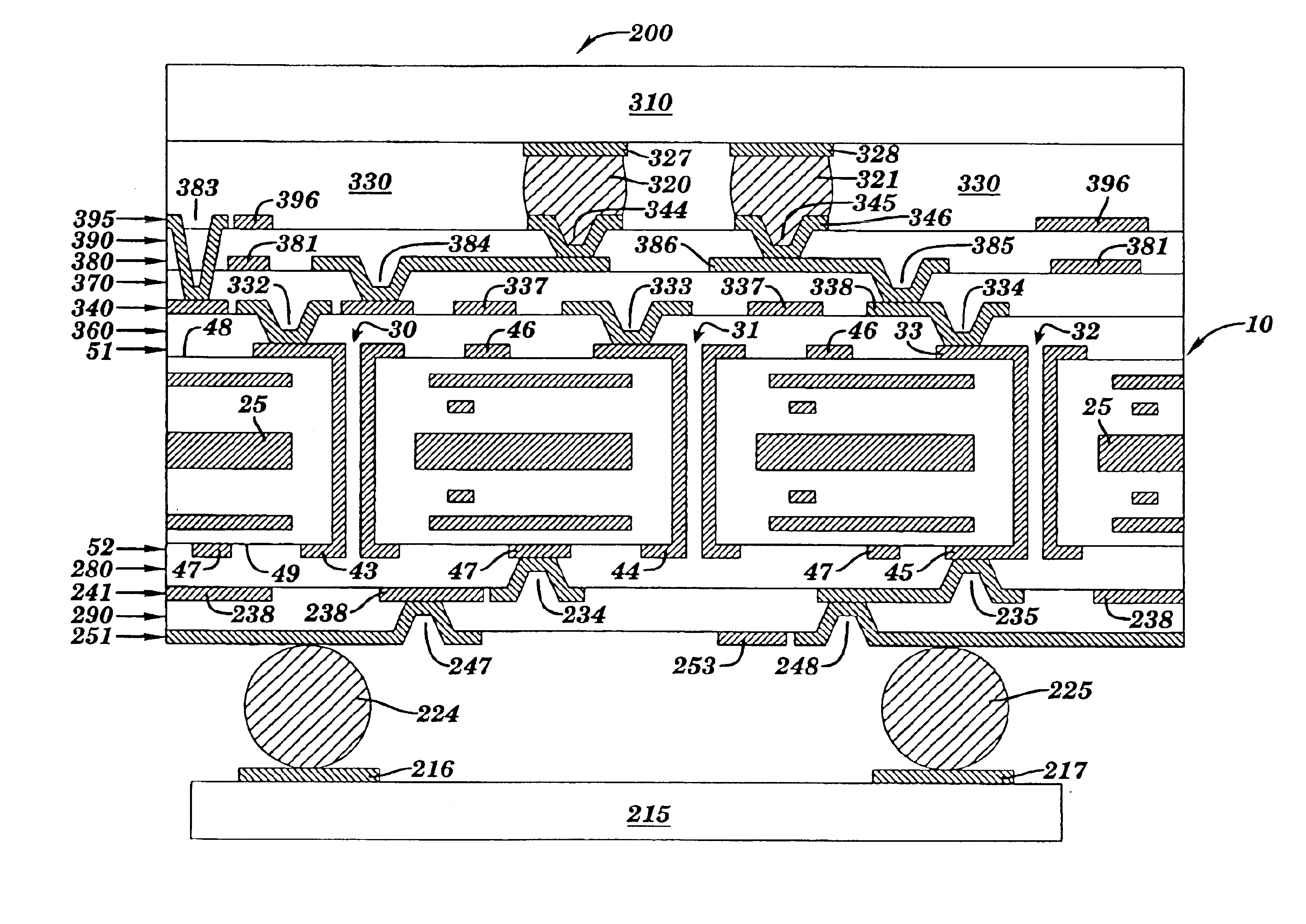
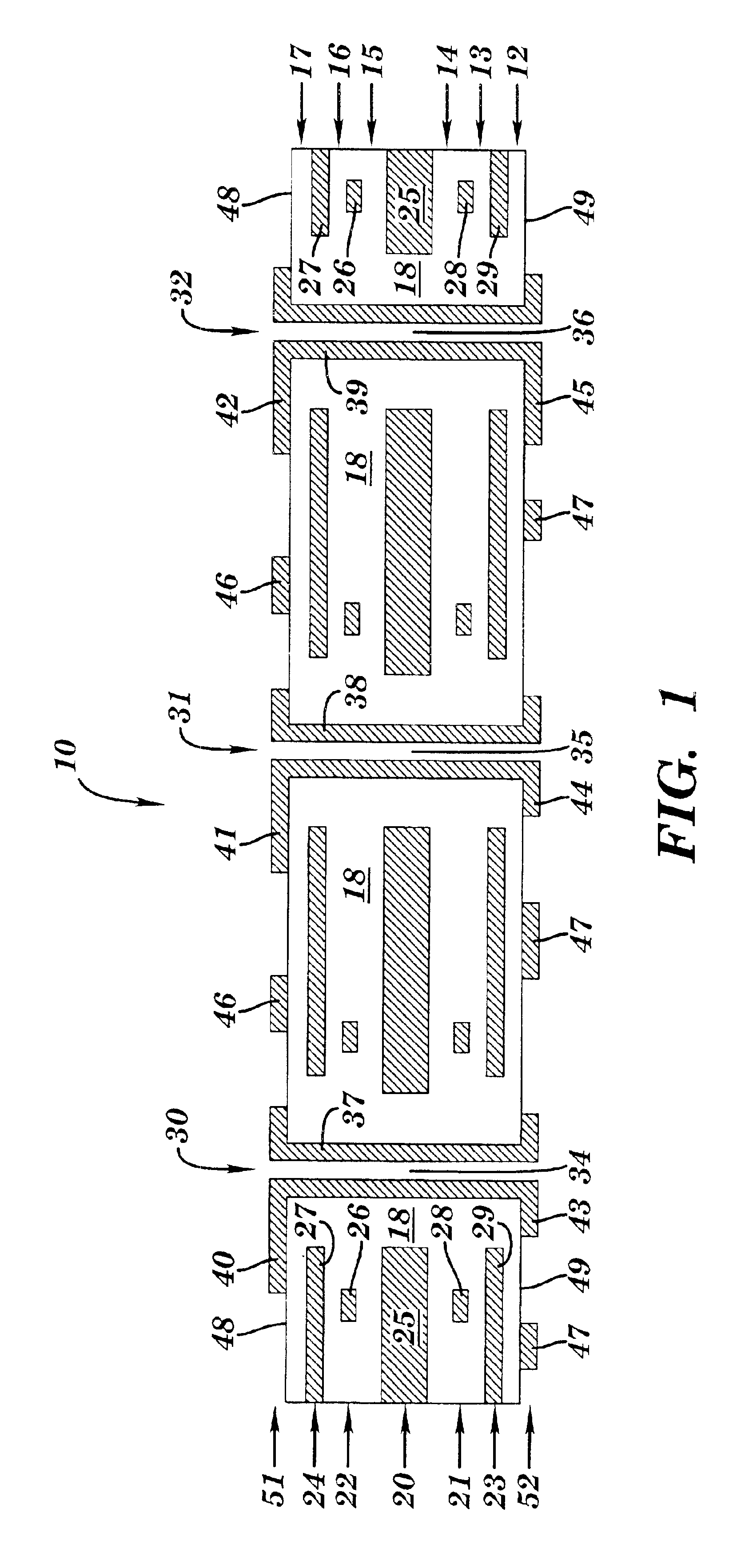
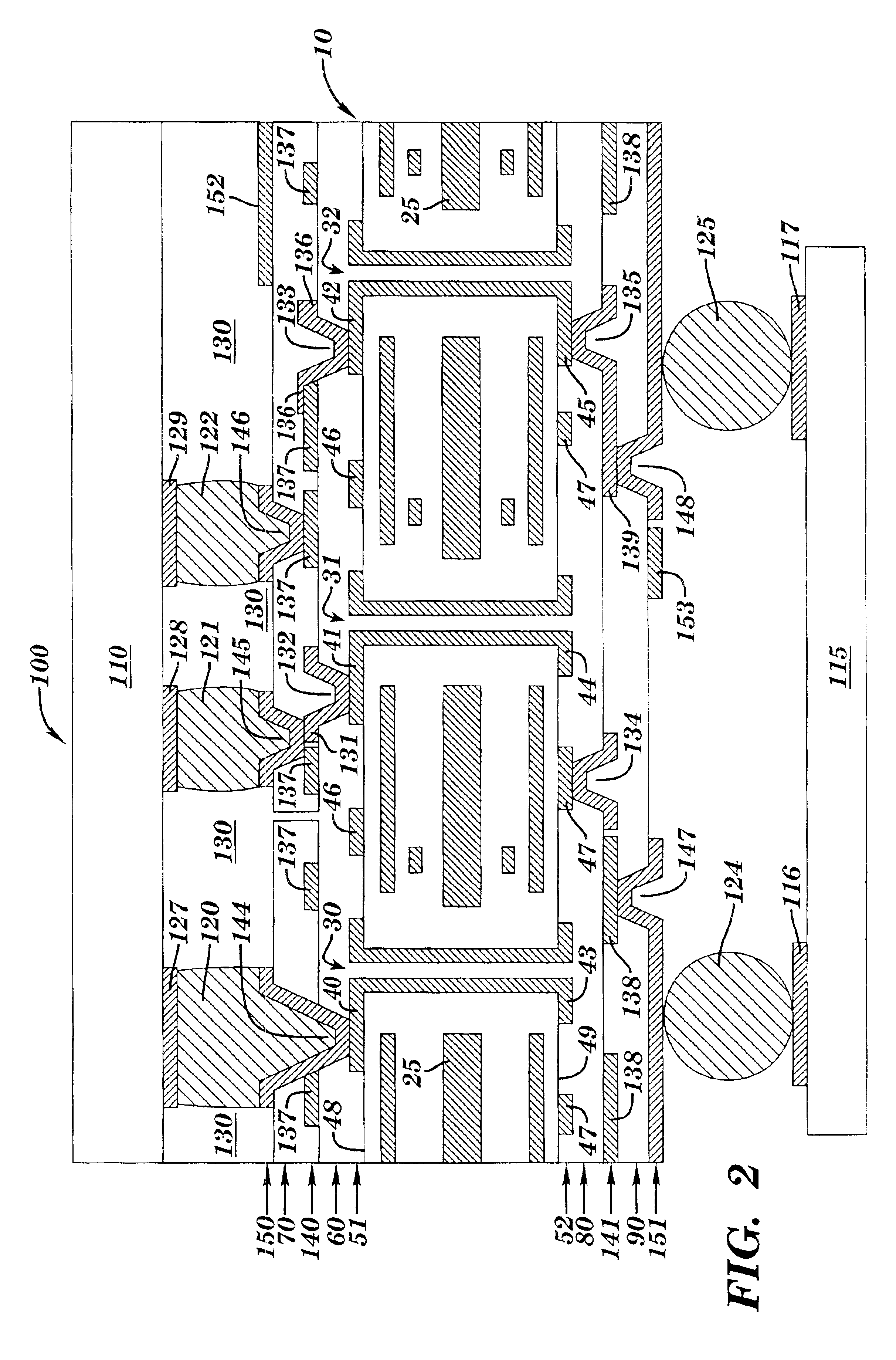
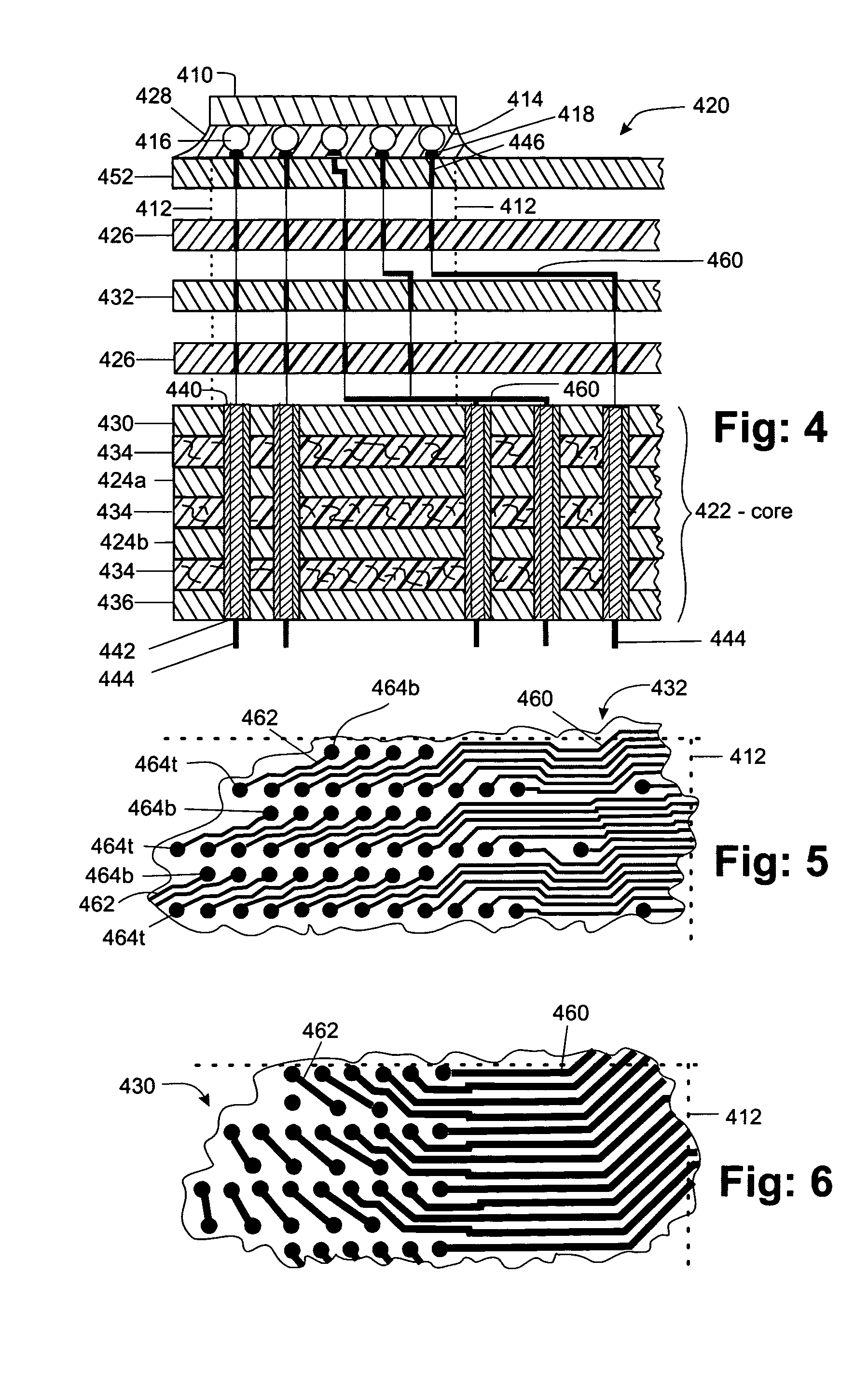
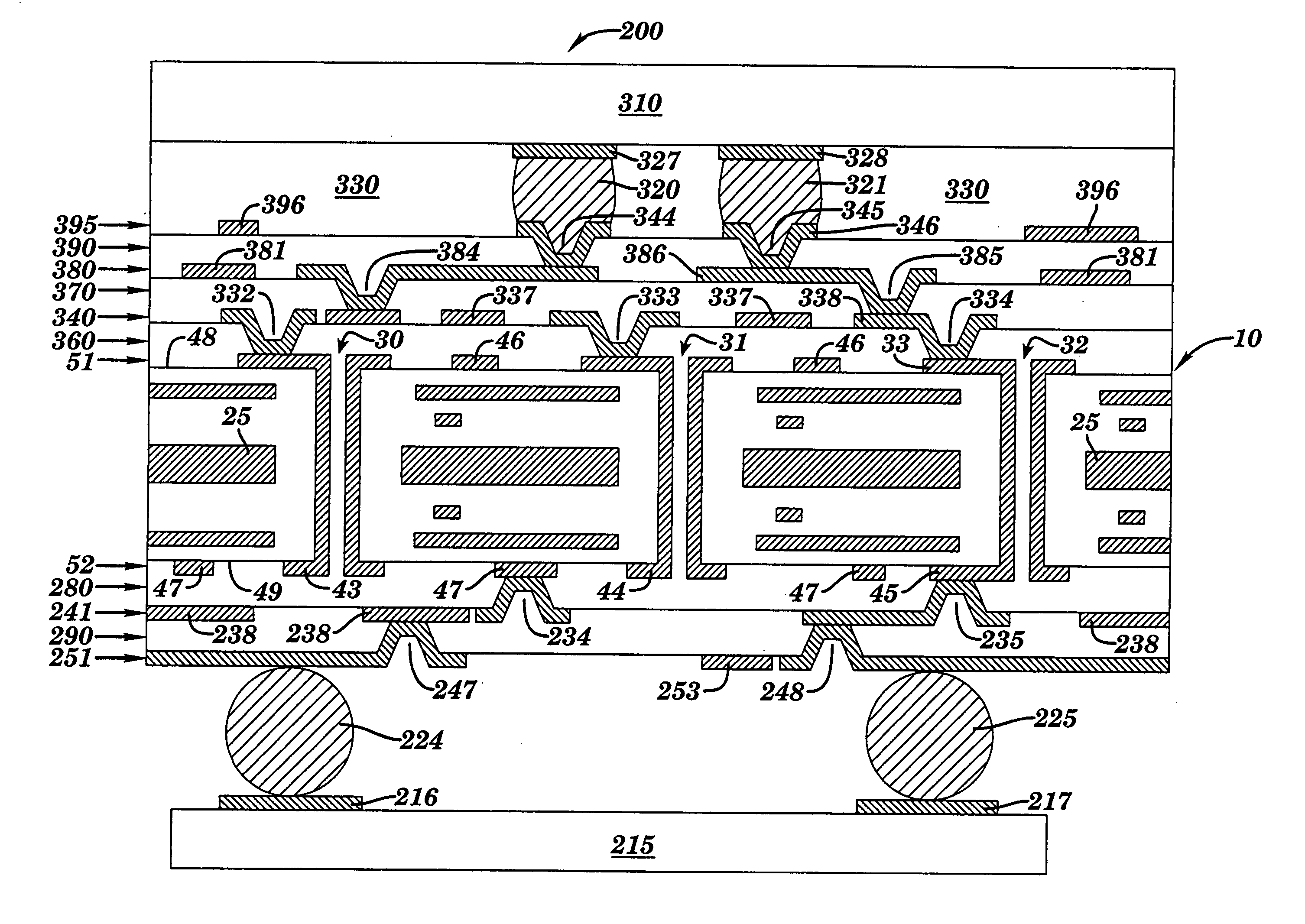
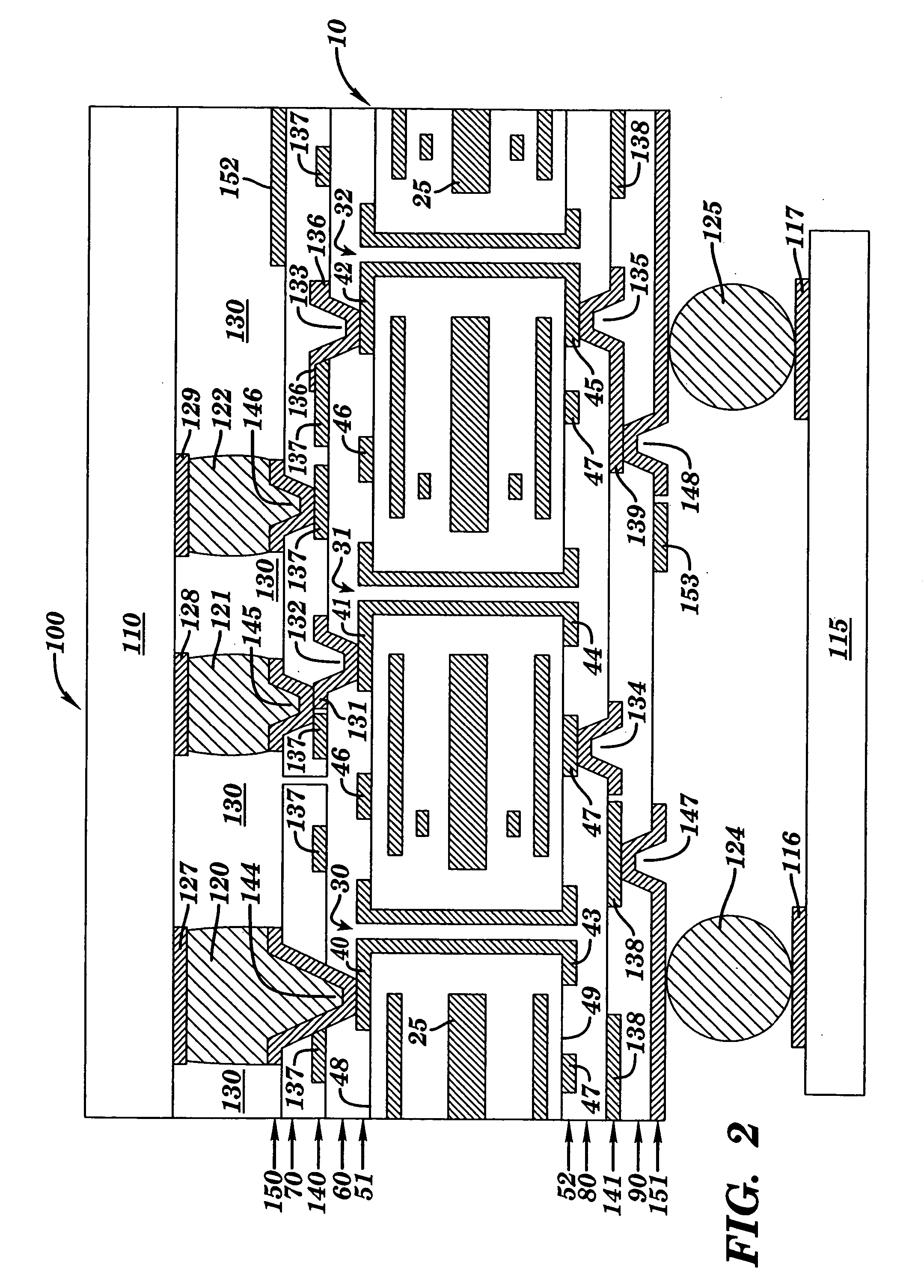
A method and structure for forming an electronic structure that comprises a redistribution structure on a circuitized substrate. The redistribution structure includes N dielectric layers (N ≧2) and N metal planes formed in the following sequence: dielectric layer 1 on a metallic plane that exists on a surface of the substrate, metal plane 1 on dielectric layer 1, dielectric layer 2 on dielectric layer 1 and metal plane 1, metal plane 2 on the dielectric layer 2, . . . , dielectric layer N on dielectric layer N-1 and metal plane N-1, and metal plane N on the dielectric layer N. Metal planes or metallic planes may include signal planes, power planes, ground planes, etc. A microvia structure, which is formed through the N dielectric layers and electrically couples metal plane N to the metallic plane, includes a microvia or a portion of a microvia through each dielectric layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
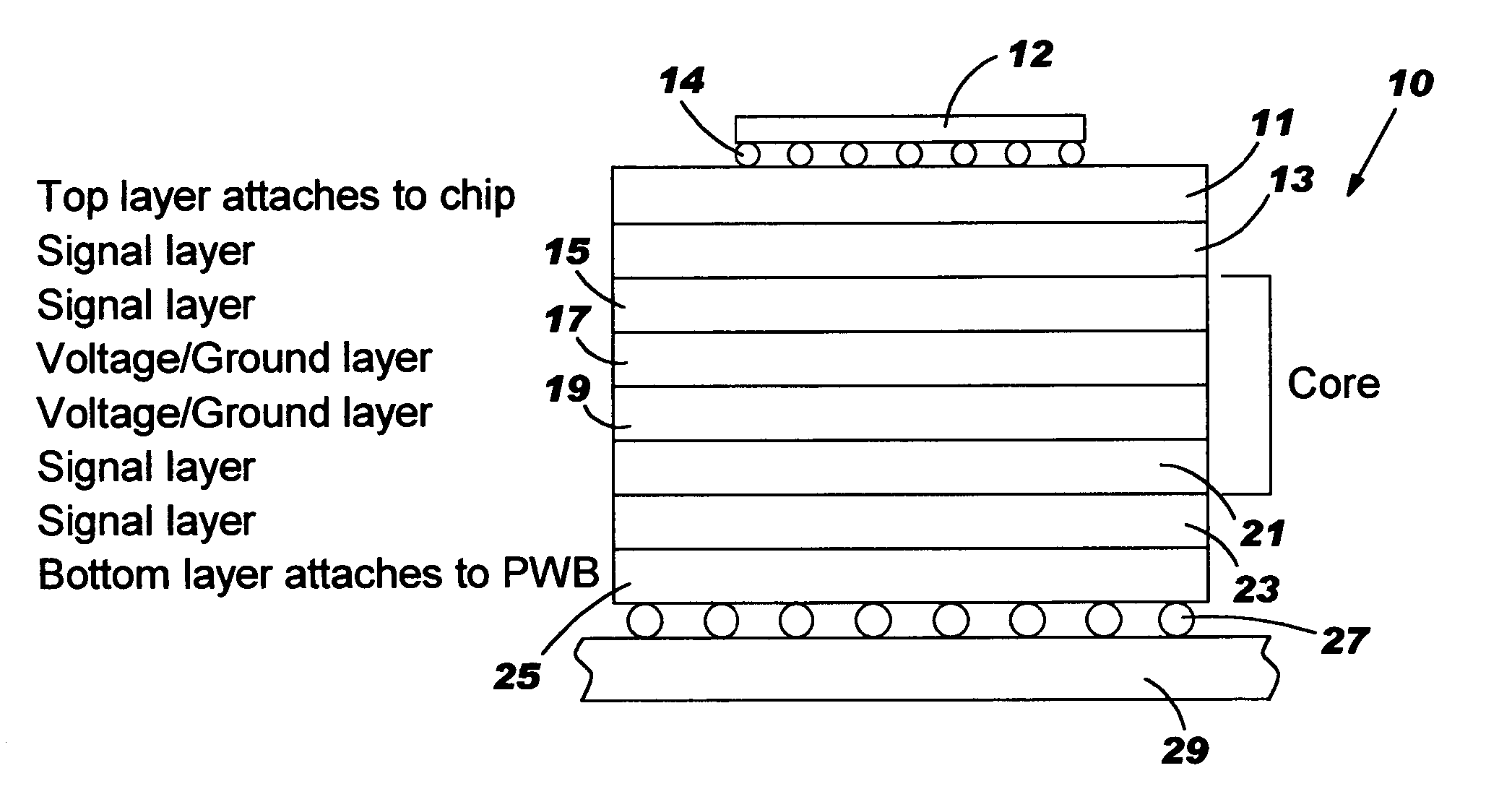
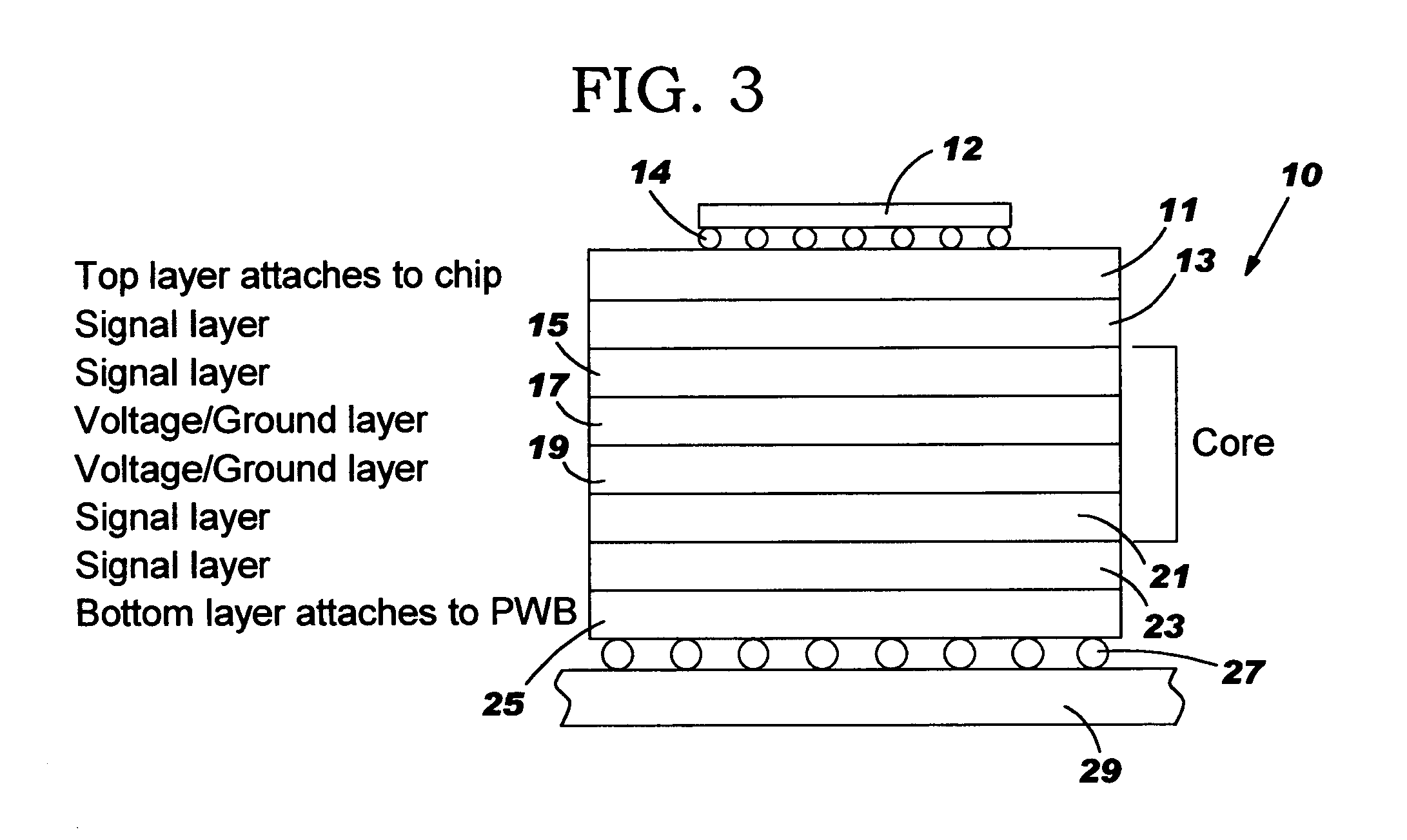
High wireability microvia substrate
InactiveUS20050104221A1Reduce chip sizeMaintaining wireability densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsSemiconductor chipHemt circuits
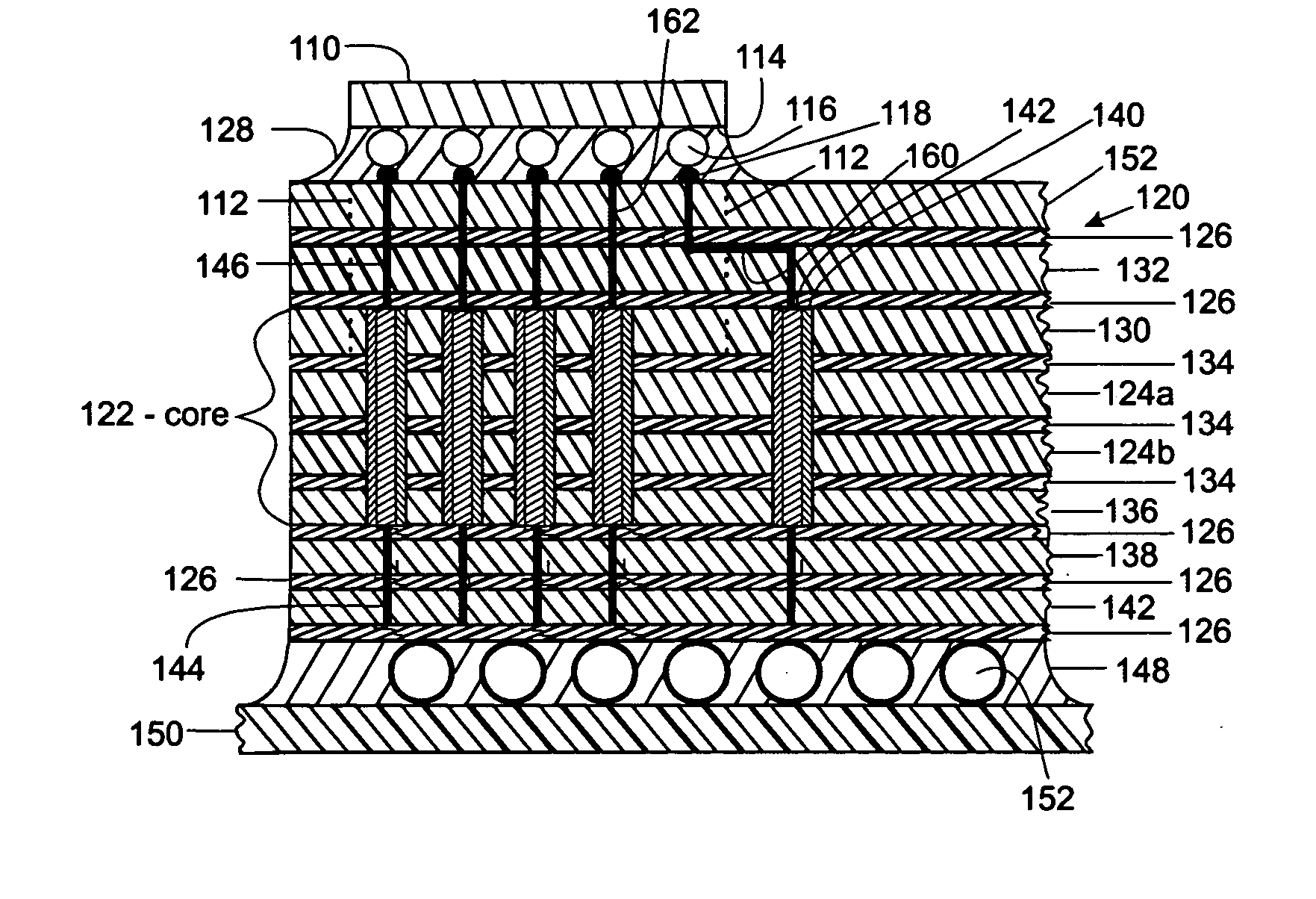
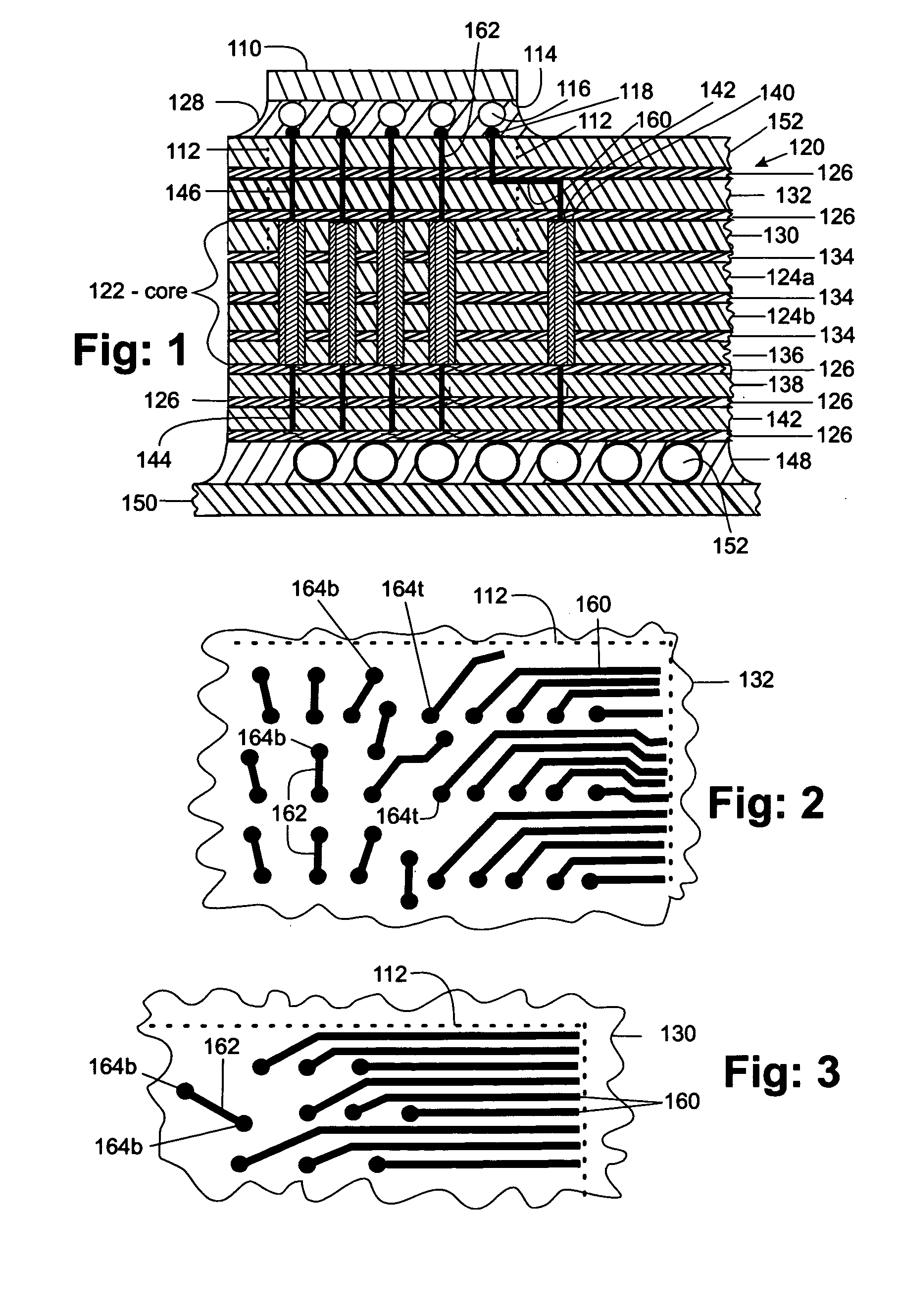
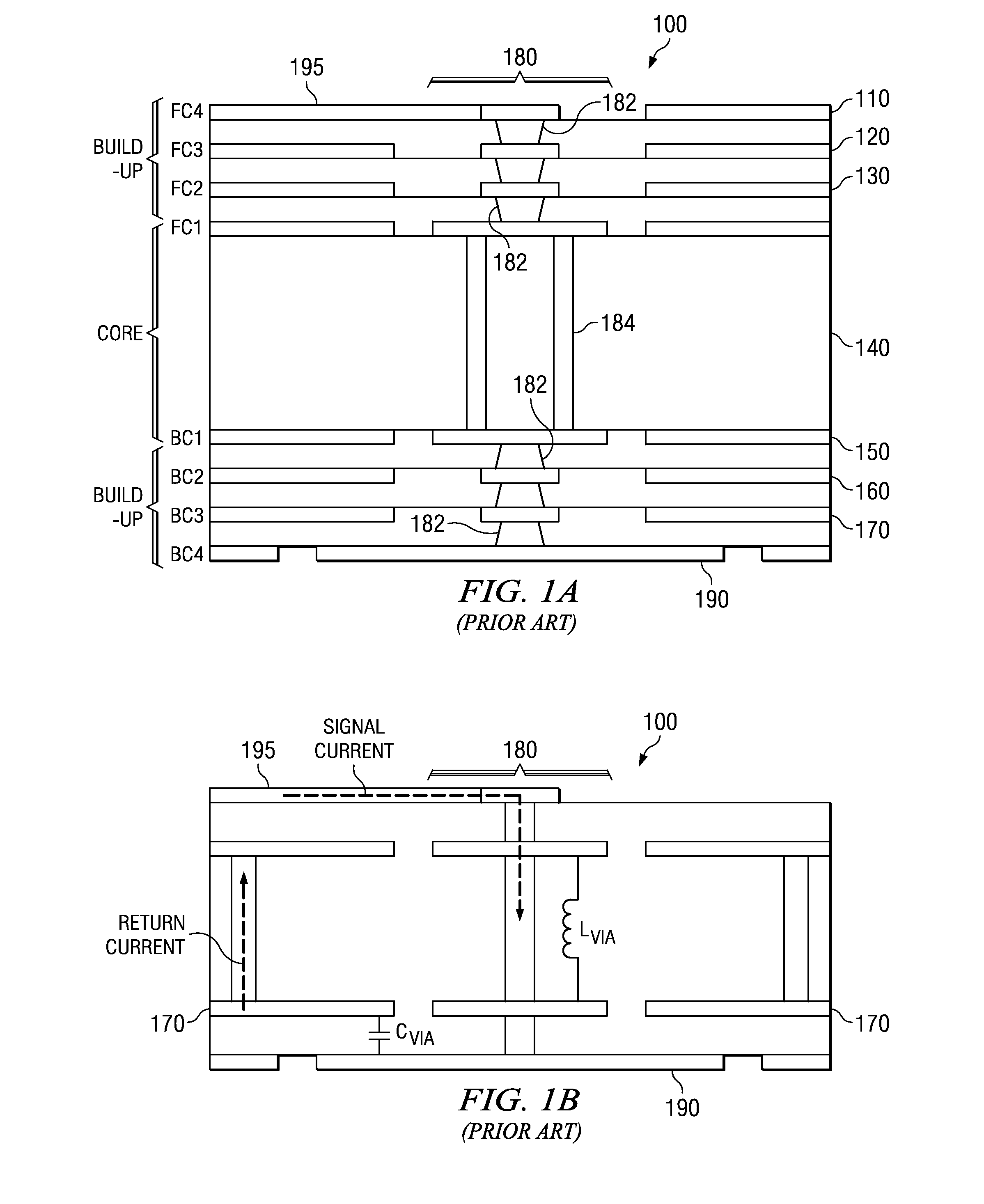
The escape of signals from a semiconductor chip to a printed wiring board in a flip chip / ball grid array assembly is improved by repositioning the signals from the chip through the upper signal layers of the carrier. This involves fanning out the circuit lines through the chip carrier from the top surface that communicates with the chip, through the core to the bottom surface where signals exit the carrier to the printed wiring board. This fanning out is achieved by making better utilization of the surface area of the signal planes between the core and the chip. The signals are fanned out on each of the top signal planes so that many more of the signals are transmitted through the vias in the core to the bottom signal planes where they can escape outside of the footprint area of the chip thereby increasing the density of circuits escaping the footprint area.
Owner:IBM CORP
Conveyorized blind microvia laser drilling system
InactiveUS7062845B2High peak powerMaterial removalCircuit board tools positioningPrinted resistor incorporationComputer moduleEngineering
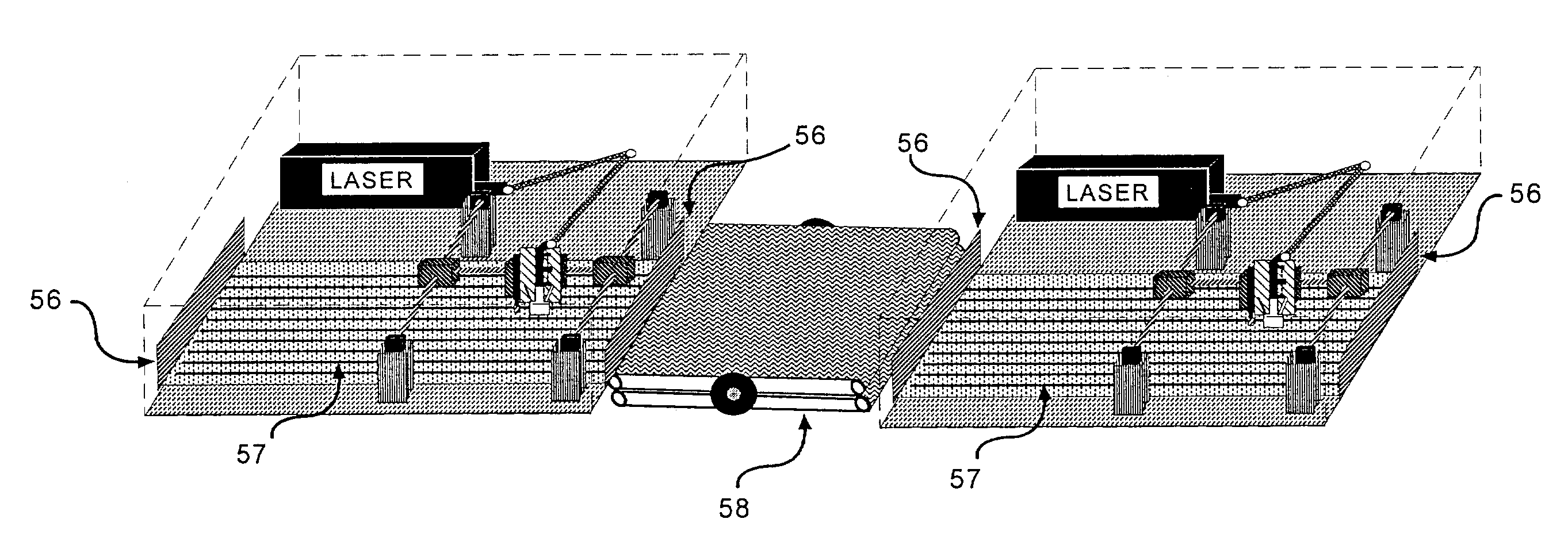
A laser drilling system for drilling blind vias in printed circuit board panels, multichip modules and chipscale packages with top and bottom surfaces and which include multiple dielectric polymer and metal layers. The system includes a first laser module comprising a laser able to form at least one via per pulse through one or more polymer layers. The vias are circular or non-circular in shape. An articulated arm is adapted to move at a speed of about 200 inches per second and at an acceleration of about 5 g's or more. A beam delivery unit is attached to the articulated arm and a conveyor adapted to move panels at a constant speed. The first laser module positioned on a separate track from the conveyor moves at a faster rate than the conveyor to drill the top surface. A second laser module is positioned to move on another separate track from the conveyor movable at a faster rate so as to drill the bottom surface.
Owner:MARGER JOHNSON & MCCOLLOM P C
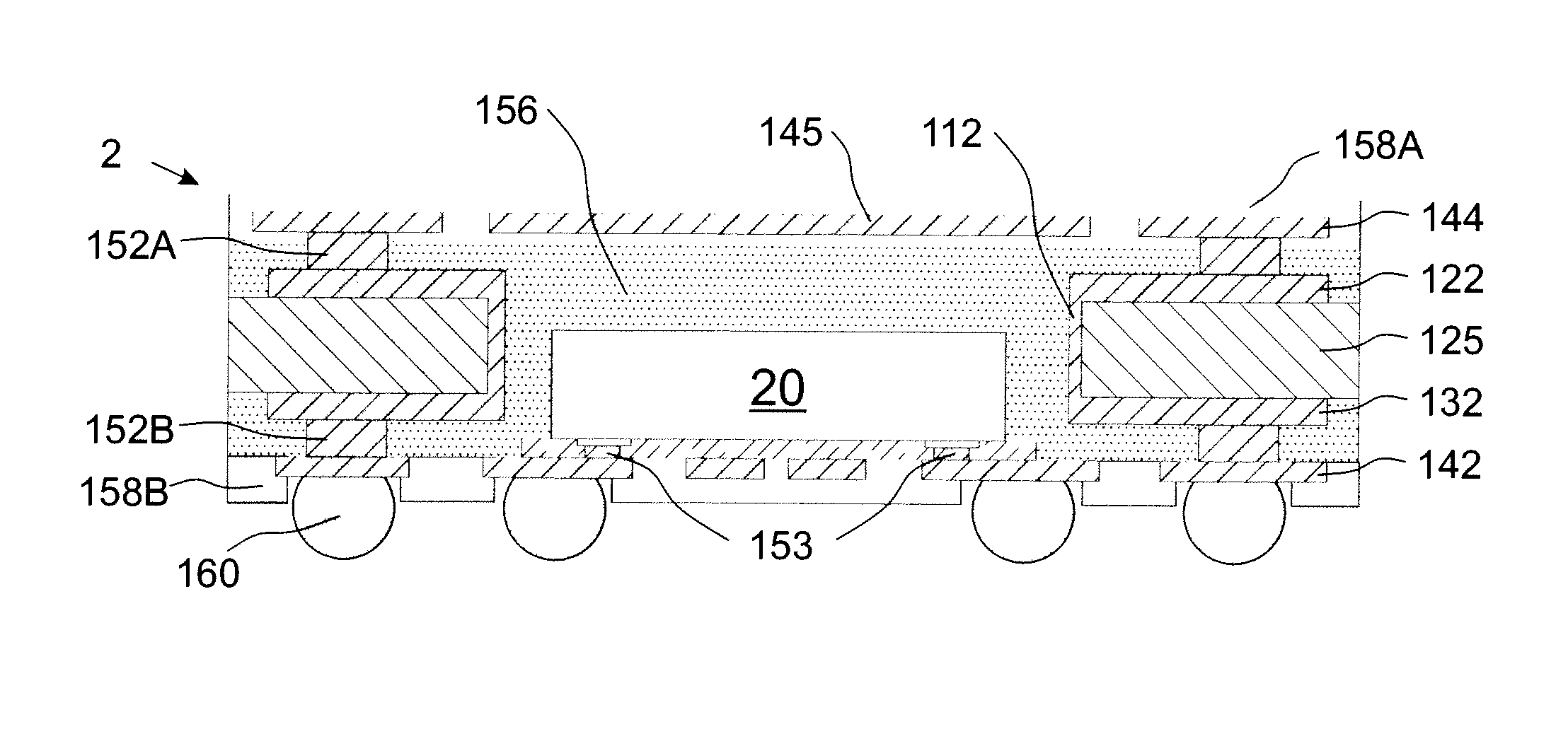
Heat dissipation approach in chip on board assembly by using stacked copper microvias
The present disclosure discusses an improved optical transceiver. The optical transceiver of the present disclosure includes an optical transmitter and an optical receiver coupled to an area of a printed circuit board that includes a plurality of thermal microvias. The thermal microvias are coupled to a heat sink or other heat dissipater and provide a path from the components of the optical transceiver to the heat dissipater for heat to travel.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Electrolytic copper plating solutions
InactiveUS20060183328A1Effective platingEnhanced brightener concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuit manufactureCopper platingElectrolysis
The present invention provides inter alia copper electroplating compositions, methods for use of the compositions and products formed by the compositions. Electroplating compositions of the invention contain an increased brightener concentration that can provide effective copper plate on difficult-to-plate aperture walls, including high aspect ratio, small diameter microvias.
Owner:BARSTAD LEON R +6
Integral capacitance for printed circuit board using dielectric nanopowders
InactiveUS20010040007A1Adhesive processes with surface pretreatmentPrinted circuit aspectsCapacitanceSputtering
A method for producing integral capacitance components for inclusion within printed circuit boards. Hydrothermally prepared nanopowders permit the fabrication of a very thin dielectric layers that offer increased dielectric constants and are readily penetrated by microvias. Disclosed is a method of preparing a slurry or suspension of a hydrothermally prepared nanopowder and solvent. A suitable bonding material, such as a polymer is mixed with the nanopowder slurry, to generate a composite mixture which is formed into a dielectric layer. The dielectric layer may be placed upon a conductive layer prior to curing, or conductive layers may be applied upon a cured dielectric layer, either by lamination or by metallization processes, such as vapor deposition or sputtering.
Owner:TPL INC
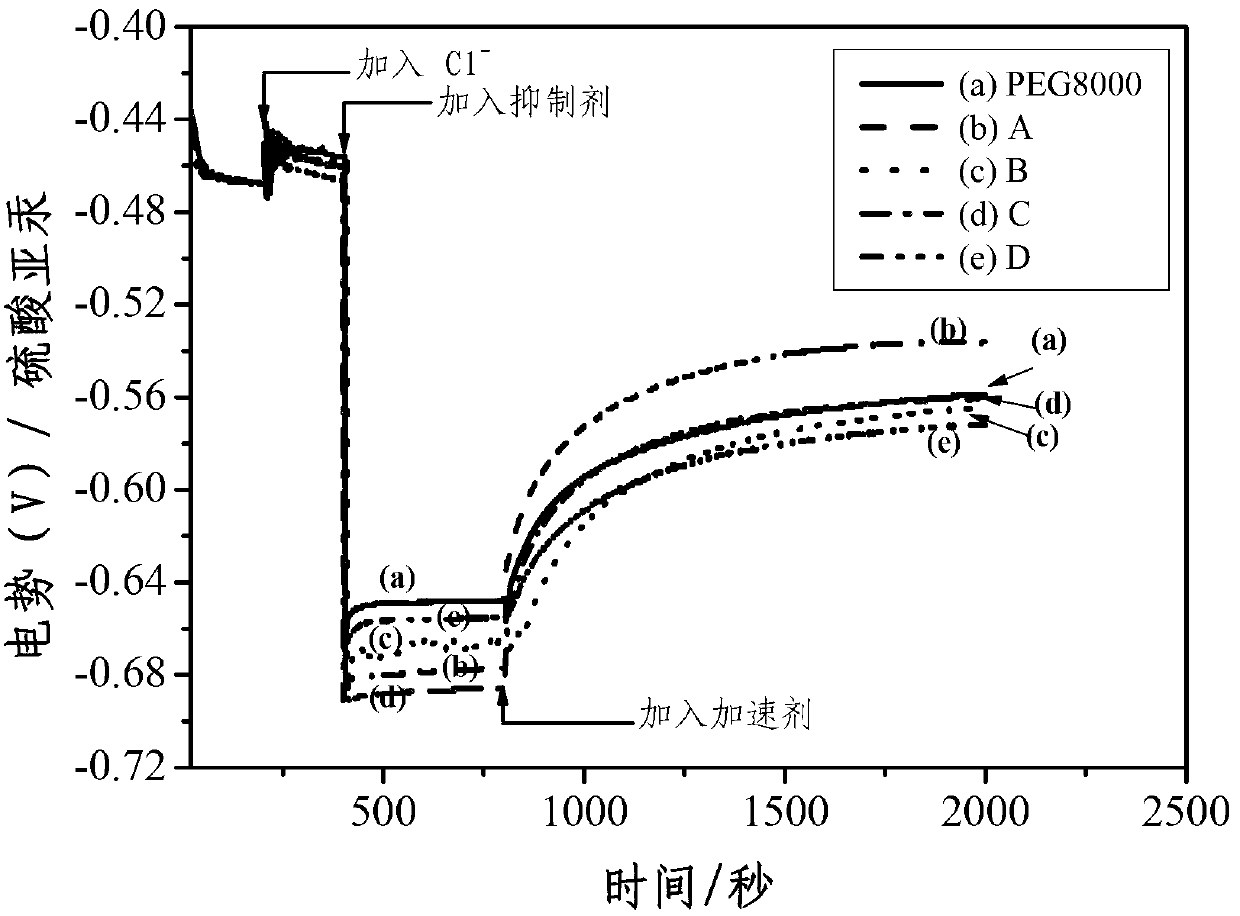
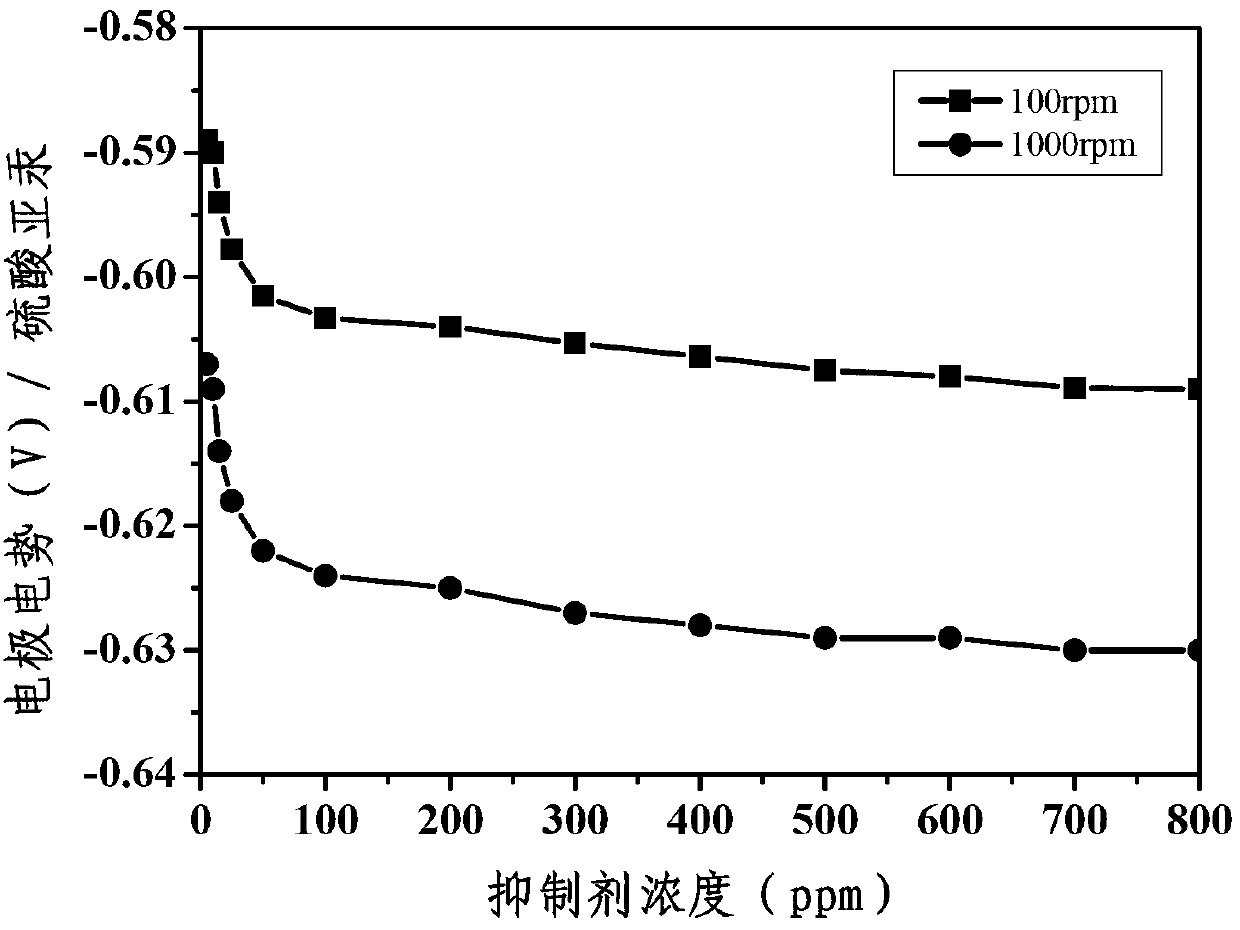
Electrocoppering solution for filling blind microvia
InactiveCN102995076AStable in natureExtended service lifeLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSulfonateJanus green
The invention relates to an electrocoppering solution for filling blind microvia. Materials of block polyether, poloxamers, amine block polyether or polyvinylpyrrolidone and the like are added into the electrocoppering solution to be used as an inhibitor so as to realize a synergistic effect with an accelerator of sodium 3, 3'-dithiodipropane sulfonate or 3-sulfhydryl group-1-propanesulfonate, a leveling agent of janus green and the like and chloride ions, so that the non-voidance, seamless and perfect electrocoppering filling of the blind microvia with different ratios of pit-depth to pit-diameter for an electroplating technology is realized. The electrocoppering solution has the advantages of stable quality, long service life, large concentration operation windows for various additives, small copper surface area thickness and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Electronic module with feed through conductor between wiring patterns
ActiveUS20100308452A1Solve the thickerImprove routing efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionElectrical conductorElectrical connection
Owner:IMBERATEK LLC
A method for microvia filling by copper electroplating with TSV technology for 3D copper interconnection at high aspect ratio
InactiveUS20160190007A1Improve accuracyHigh aspect ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSulfonateVolumetric Mass Density
A method for microvia filling by copper electroplating with a TSV technology for a 3D copper interconnection at a high aspect ratio, which includes: Step 1: formulating an electroplating solution of a copper methyl sulfonate system, Step 2: wetting the microvias of the TSV technology by means of an electroplating pre-treatment, Step 3: charging into the grooves, completing the ultra-low current diffusion, so that the copper ions and the additives are rationally distributed at the surface and the interior of the microvias of the TSV technology, Step 4: connecting the wafer for the TSV technology to the cathode of a power source, fully immersing the electroplating surface of the wafer in the electroplating solution, and electroplating with a step-by-step current method of rotating or stirring the cathode, the current density of the plating conditions is 0.01-10A / dm2 and the temperature is 15-30° C., Step 5: after the electroplating, washing the wafer completely clean with deionized water, and drying it by spinning or blowing. The method for microvia filling by copper electroplating with a TSV technology for a 3D copper interconnection at a high aspect ratio has a high via-filling speed, a thin copper layer on the surface, no risk of creating voids and cracks, and can achieve the complete filling of microvias having an aspect ratio of more than 10:1 which are extremely difficult to fill.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINYANG SEMICON MATERIALS
Microvia-superfilling copper plating technology
InactiveCN104109886ASimplify device configurationReduce consumptionJewelleryCopper platingFilling rate
The invention discloses a microvia-superfilling copper plating technology. The microvia-superfilling copper plating technology comprises the following steps of a, carrying out activation treatment on a blind hole plate to be plated in a dilute sulphuric acid solution for 1-10min, carrying out water washing and drying, vertically fixing the blind hole plate to be plated to the middle of a Hull cell having the volume of 1500mL, and putting phosphor-containing copper plates as anodes having phosphor content of 0.04-0.065% at two ends of the cell, b, preparing a plating solution, c, switching on a power supply, carrying out electroplating at current density of 0.5-2ASD for 5-30min, increasing current density to 0.5-4ASD, carrying out electroplating for 10-20min, wherein the whole electroplating process is finished in a static state, then switching off the power supply, taking out the blind hole plate as a cathode, flushing the blind hole plate by distilled water, and blow-drying the blind hole plate by cold air to obtain a sample. Under the condition of absolutely no forced convection of the plating solution, the microvia-superfilling copper plating technology does not increase surface copper thickness and guarantees a high microvia-filling rate of the blind hole device.
Owner:SUR PRECISION METAL TECH
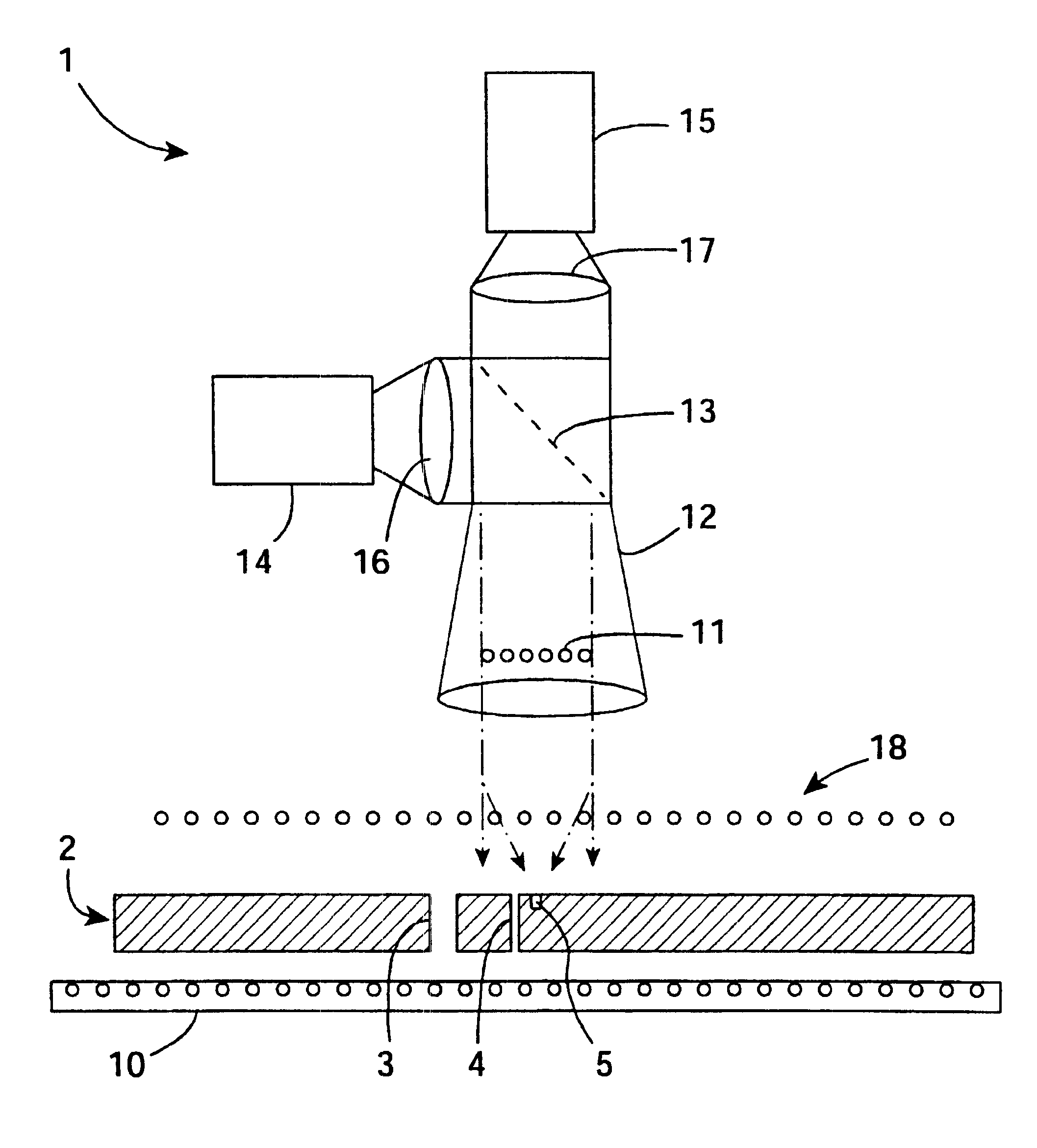
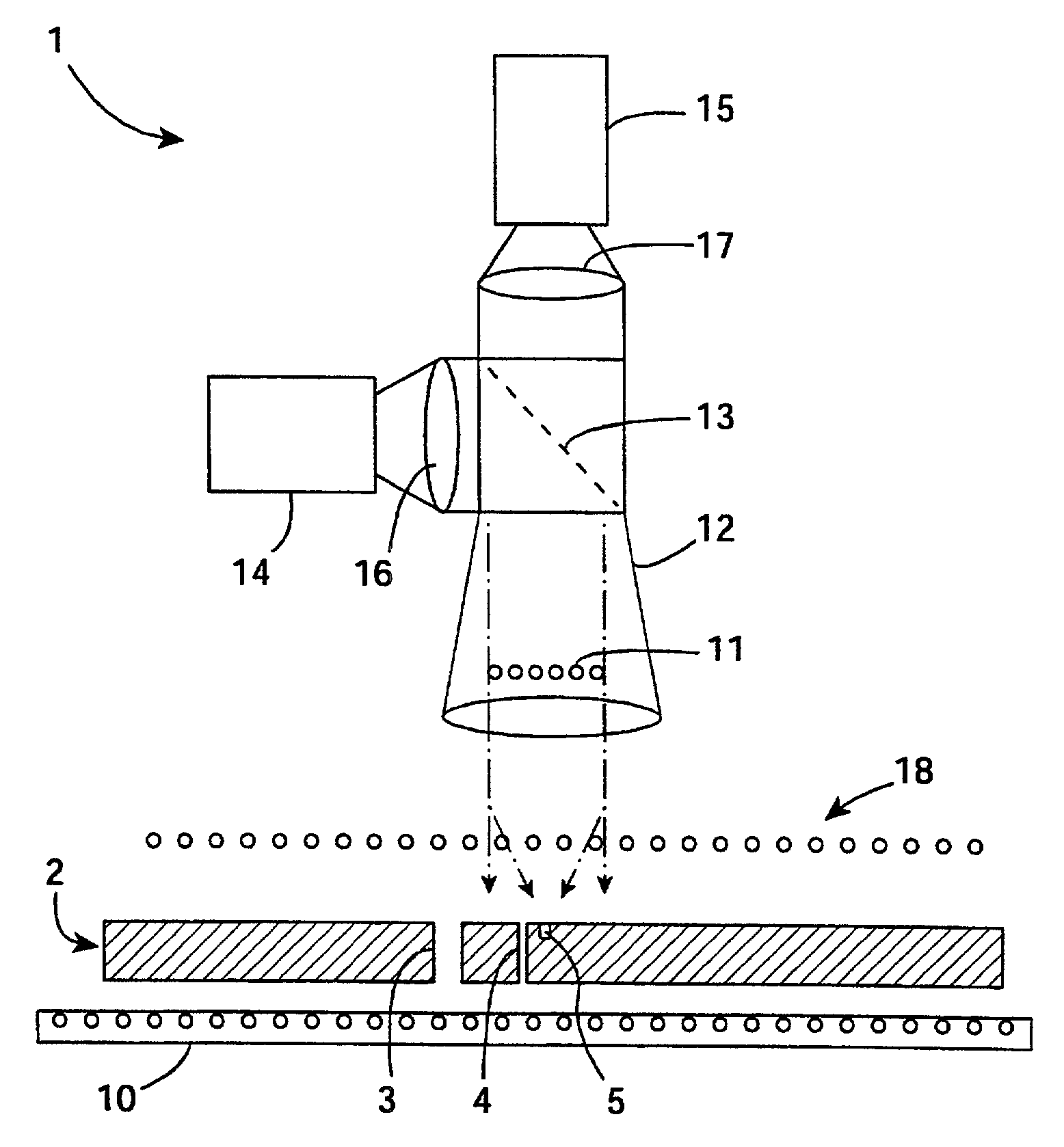
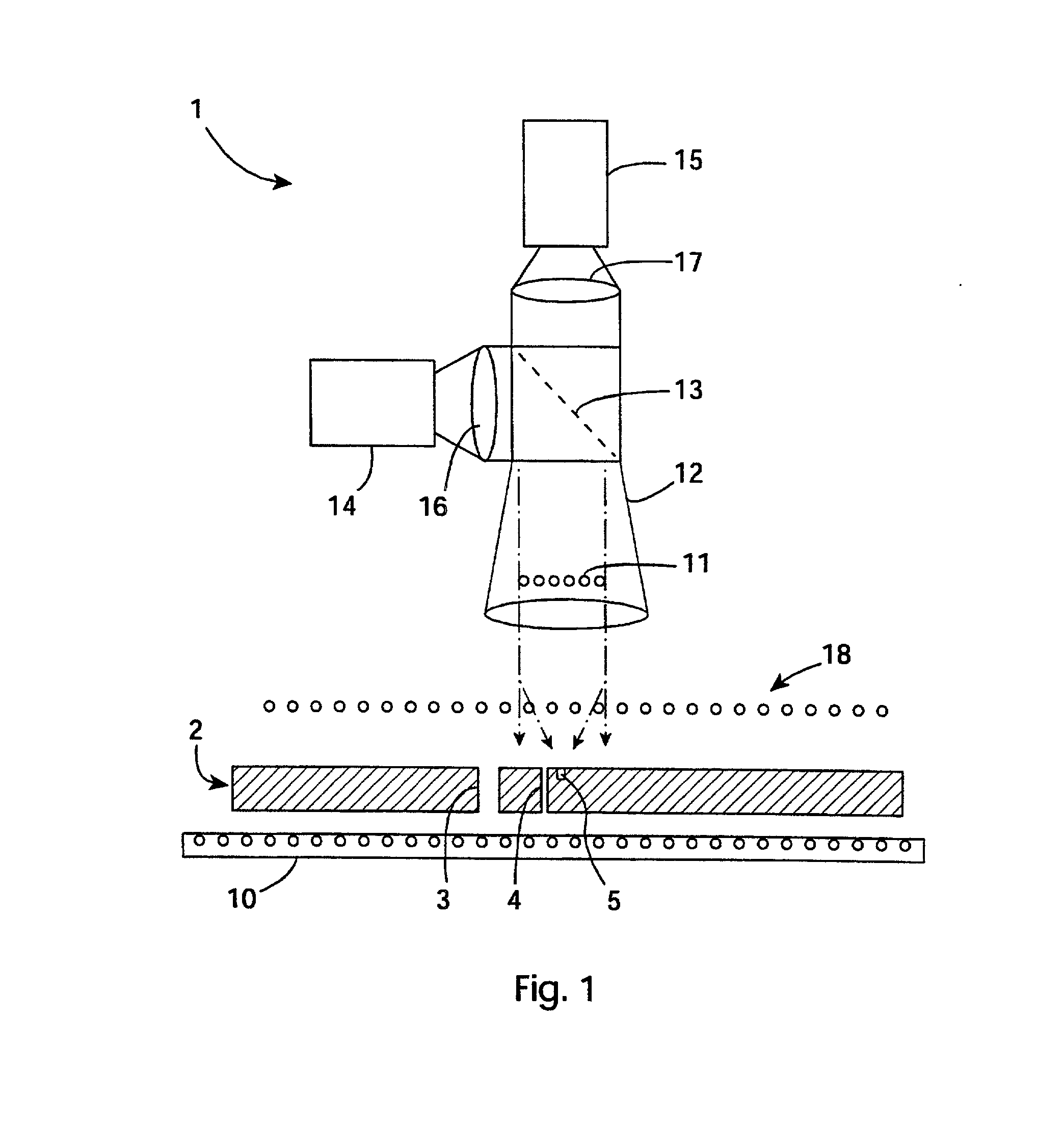
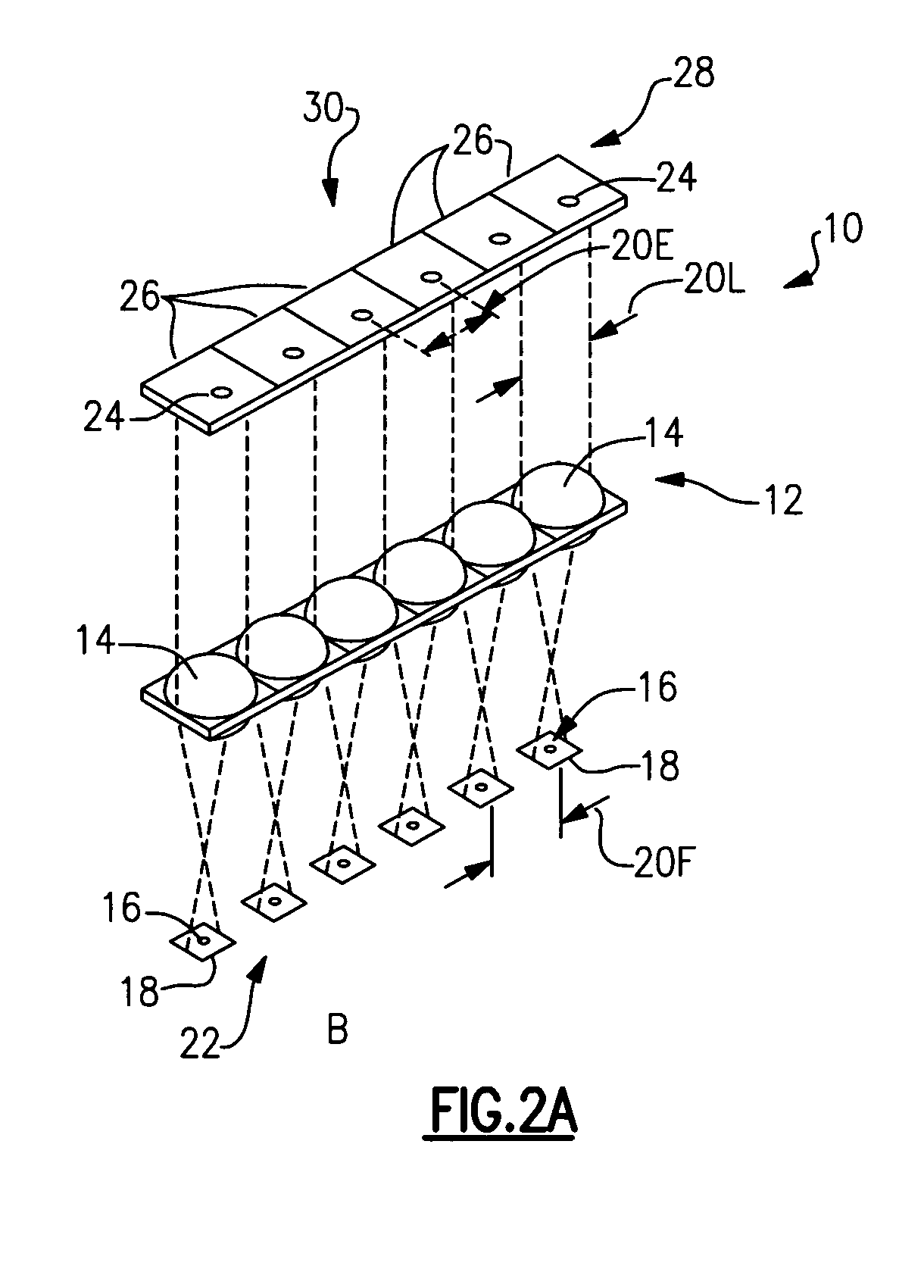
Microvia inspection system
InactiveUS6697154B2Image enhancementTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsLed arrayImage resolution
A system has a projection lens directing on-axis light and low level LEDs directing light to blind microvias. A high resolution camera captures blind microvia images and an image processor recognizes defects according to classifications according to reflected light area and centroid position. The lens is telecentric for particularly effective image capture in blind microvias. The system also has an array of 6000 back lighting LEDs providing illumination for capture of images by a camera. These images are analyzed by the image processor to detect defects such as blocked through microvias.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Hyperbga buildup laminate
InactiveUS20050099783A1Printed circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricElectronic structure
A method and structure for forming an electronic structure that comprises a redistribution structure on a circuitized substrate. The redistribution structure includes N dielectric layers (N≧2) and N metal planes formed in the following sequence: dielectric layer 1 on a metallic plane that exists on a surface of the substrate, metal plane 1 on dielectric layer 1, dielectric layer 2 on dielectric layer 1 and metal plane 1, metal plane 2 on the dielectric layer 2, . . . , dielectric layer N on dielectric layer N-1 and metal plane N-1, and metal plane N on the dielectric layer N. Metal planes or metallic planes may include signal planes, power planes, ground planes, etc. A microvia structure, which is formed through the N dielectric layers and electrically couples metal plane N to the metallic plane, includes a microvia or a portion of a microvia through each dielectric layer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
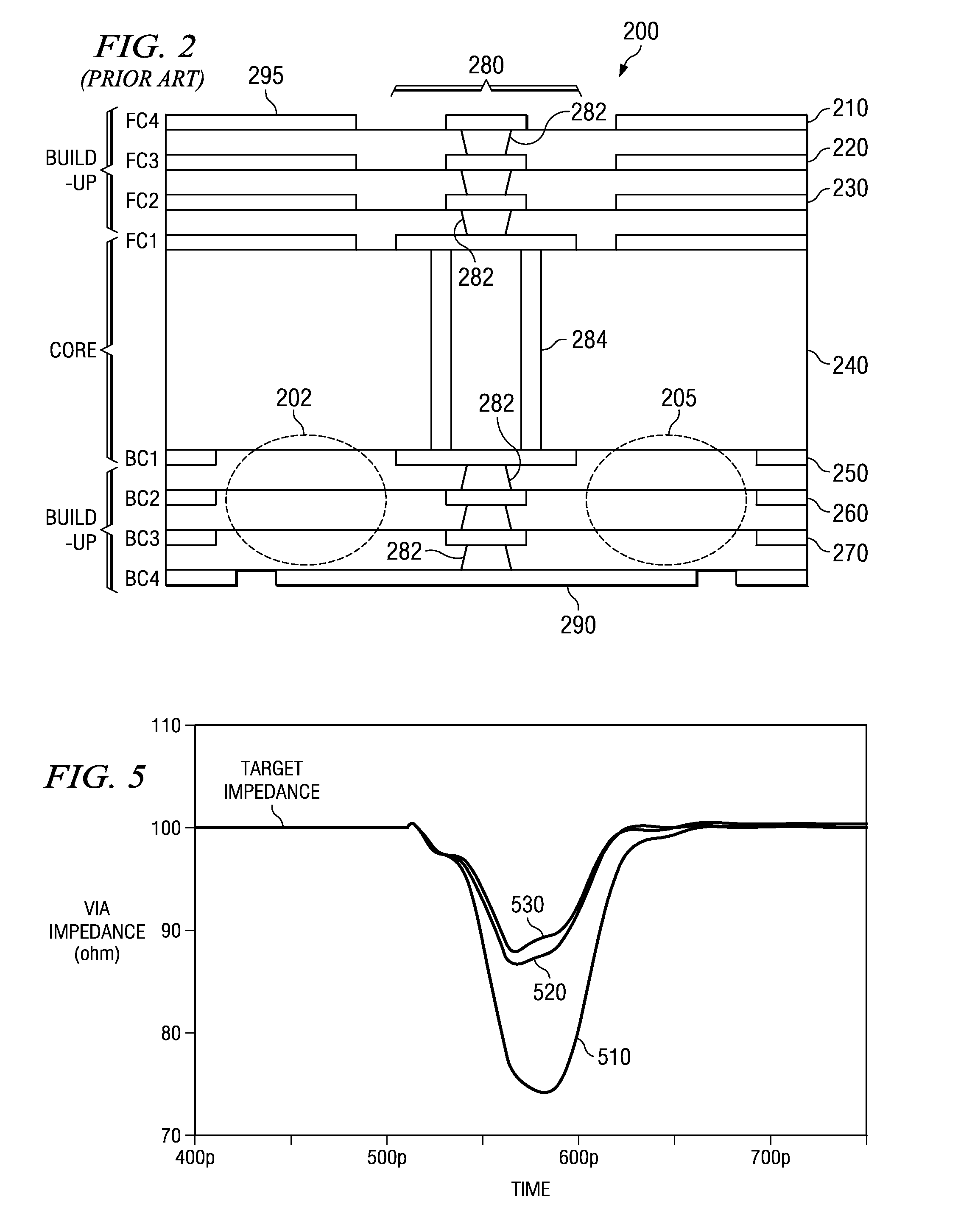
Electrically Optimized and Structurally Protected Via Structure for High Speed Signals
InactiveUS20080073796A1Reducing via capacitanceReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionCapacitanceMicrovia
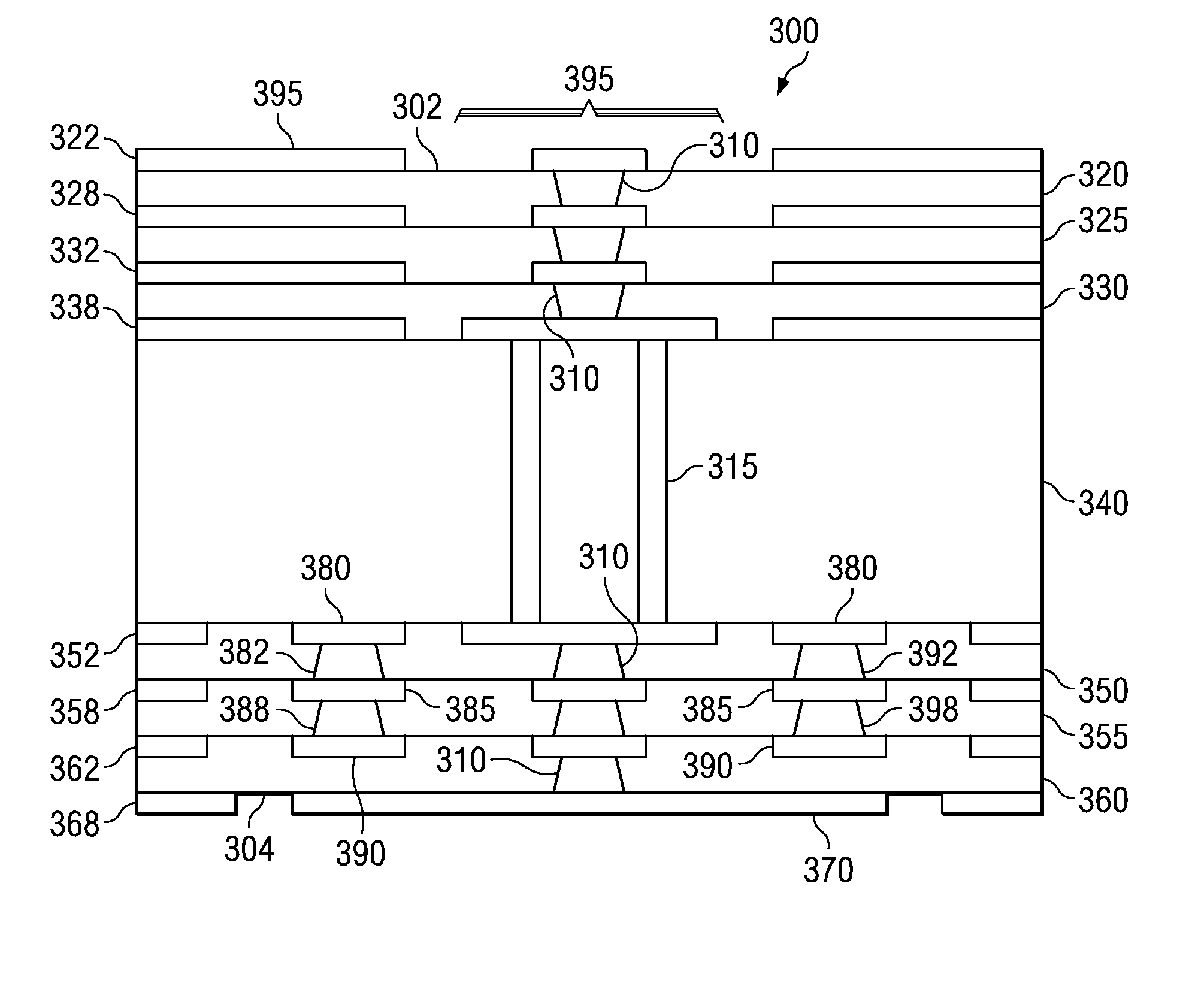
An electrically optimized and structurally protected micro via structure for high speed signals in multilayer interconnection substrates is provided. The via structure eliminates the overlap of a contact with the reference planes to thereby reduce the via capacitance and thus, the via impedance mismatch in the via structure. As a result, the via structure is electrically optimized. The via structure further comprises one or more floating support members placed in close proximity to the via within a via clearance area between the via and the reference planes. The floating support members are “floating” in the sense that they are not in electrical contact with either the via or the reference planes. Thus, they are not provided for purposes of signal propagation but only for structural support. The floating support members may be connected to one another by way of one or more microvia structures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
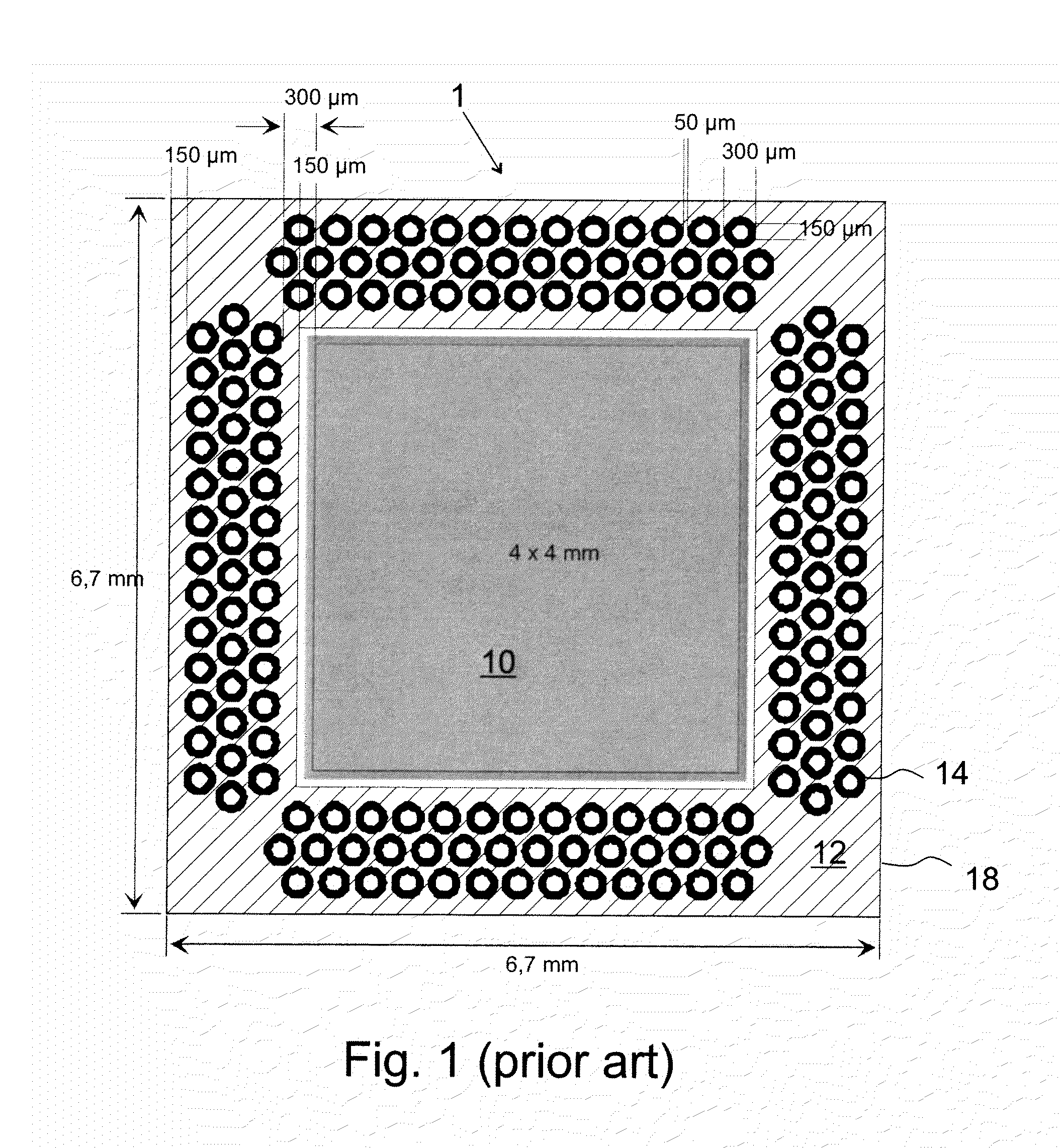
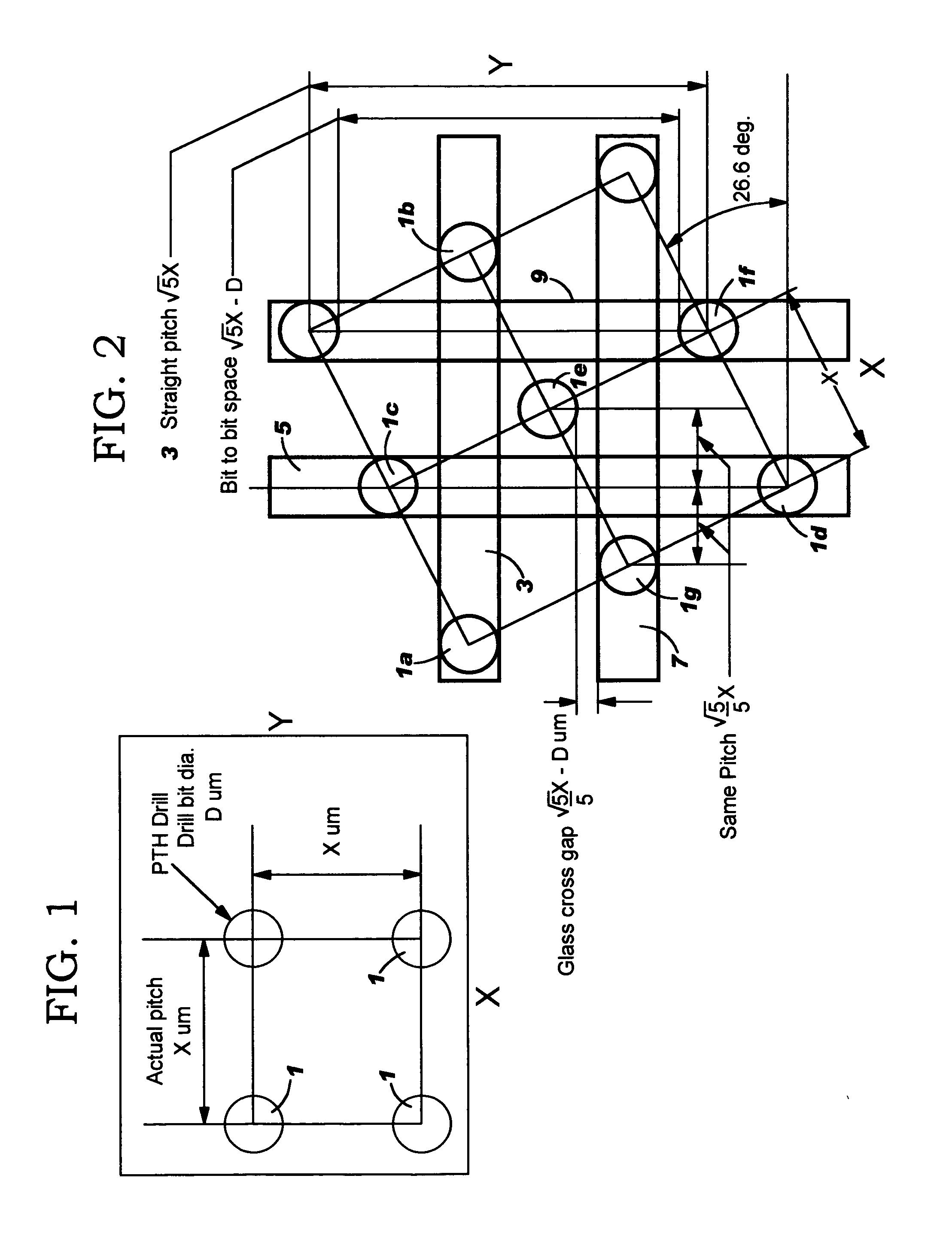
High density microvia substrate with high wireability
InactiveUS20050093133A1Without riskHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsGlass fiberGrid pattern
The density of plated thru holes in a glass fiber based chip carrier is increased by off-setting holes to positions in which fibers from adjacent holes will not connect. Elongated strip zones or regions having a width approximately the diameter of the holes and running along orthogonal columns and rows of holes, parallel to the direction of fibers, define regions of fibers that can possibly cause shorting between holes. Rotating a conventional X-Y grid pattern of equidistant holes so as to position, for example, alternate holes in one direction between the elongated strip zones running in the opposite direction significantly increases the distance between holes along the elongated strip zones running in each direction. The holes are positioned between elongated strip zones with sufficient clearance to compensate for variations in the linear path of fibers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Microvia inspection system
A system (1) has a projection lens (12) directing on-axis light and low level LEDs (18) directing light to blind microvias (5). A high resolution camera (14) captures blind microvia images and an image processor recognizes defects according to classifications (54-59) according to reflected light area and centroid position. The lens (12) is telecentric for particularly effective image capture in blind microvias (5). The system also has an array of 6000 back lighting LEDs (10) providing illumination for capture of images by a camera (15). These images are analyzed by the image processor to detect defects such as blocked through microvias.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
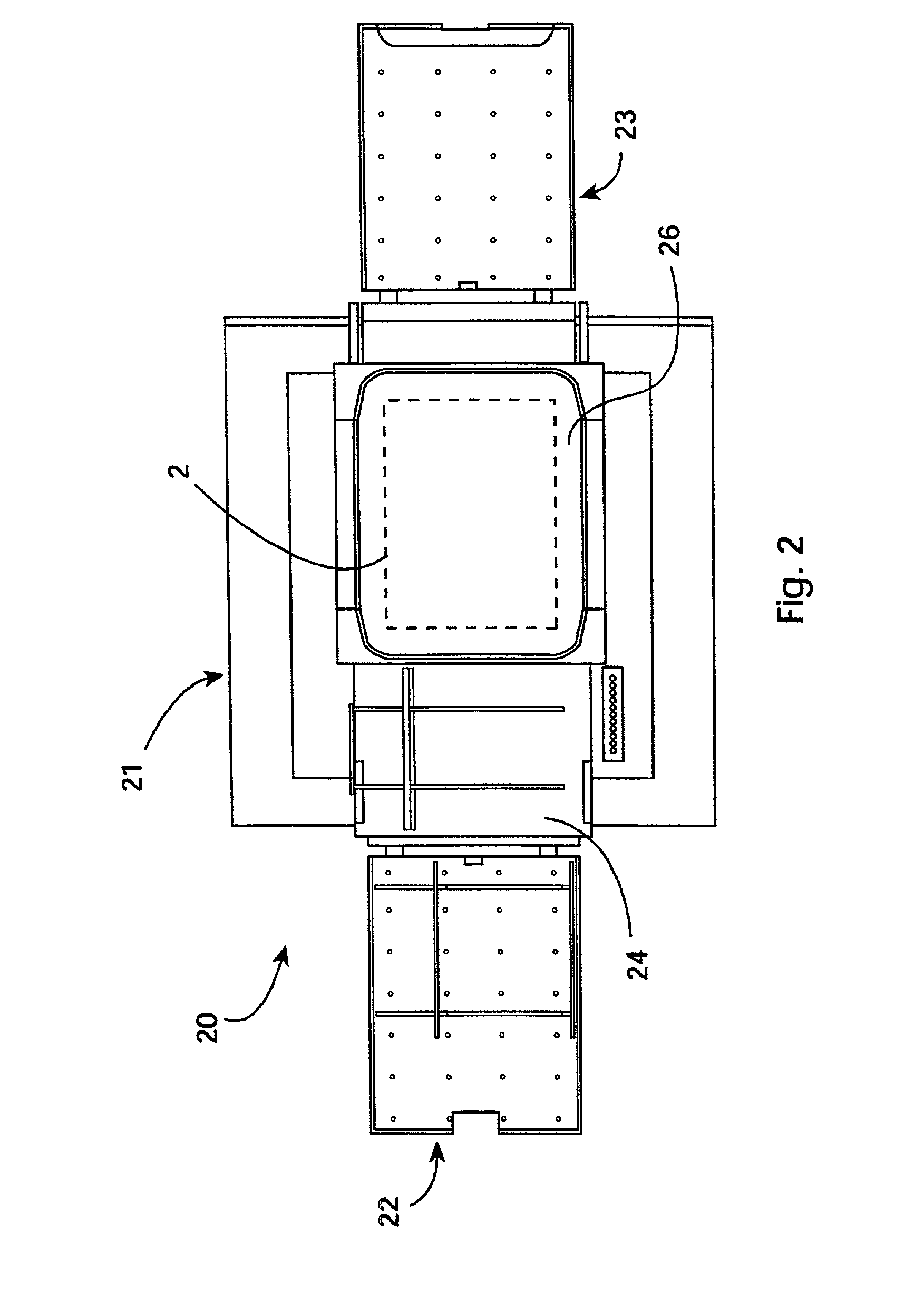
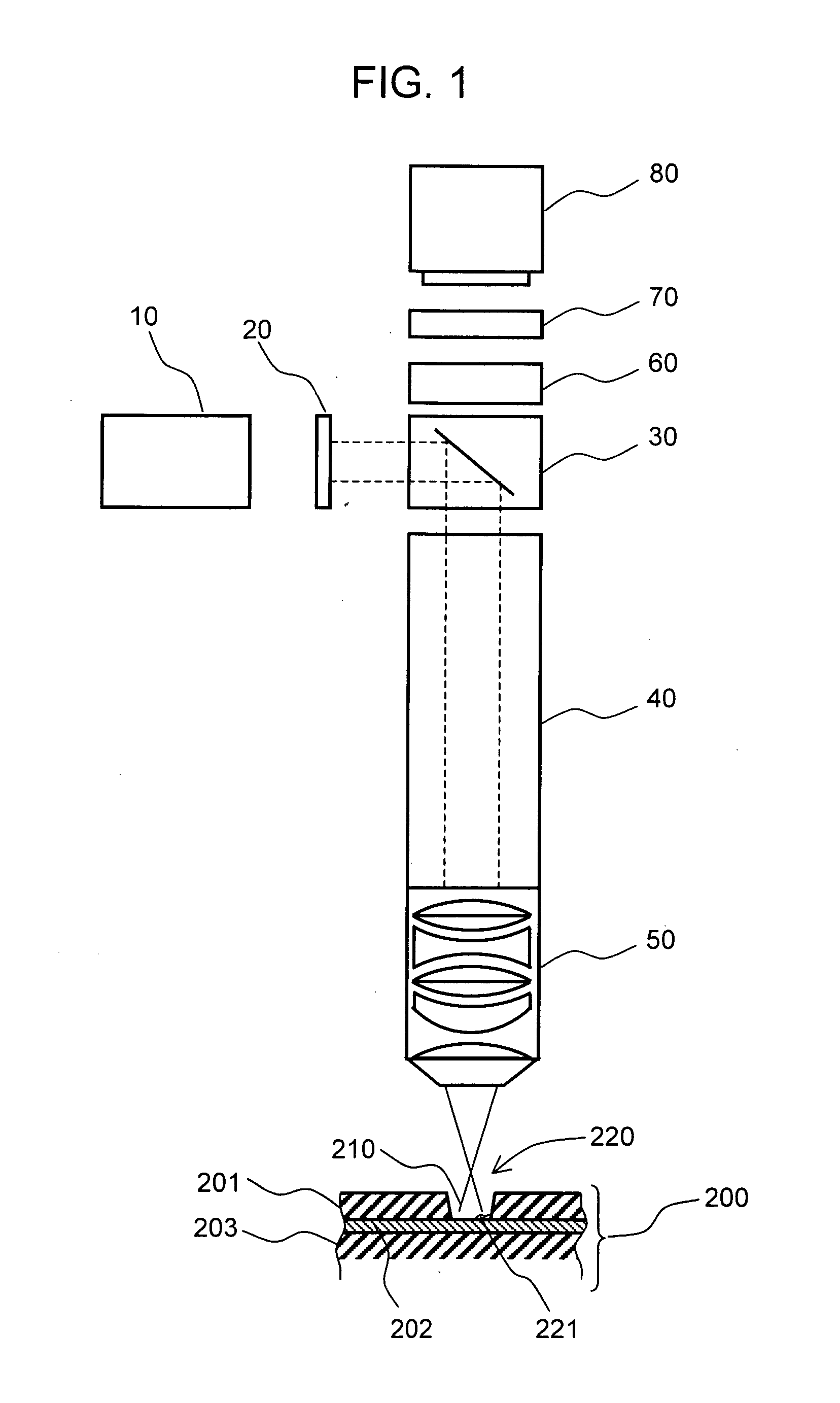
Apparatus and methods for the inspection of microvias in printed circuit boards
InactiveUS7372632B2Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionTarget surfaceField of view
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
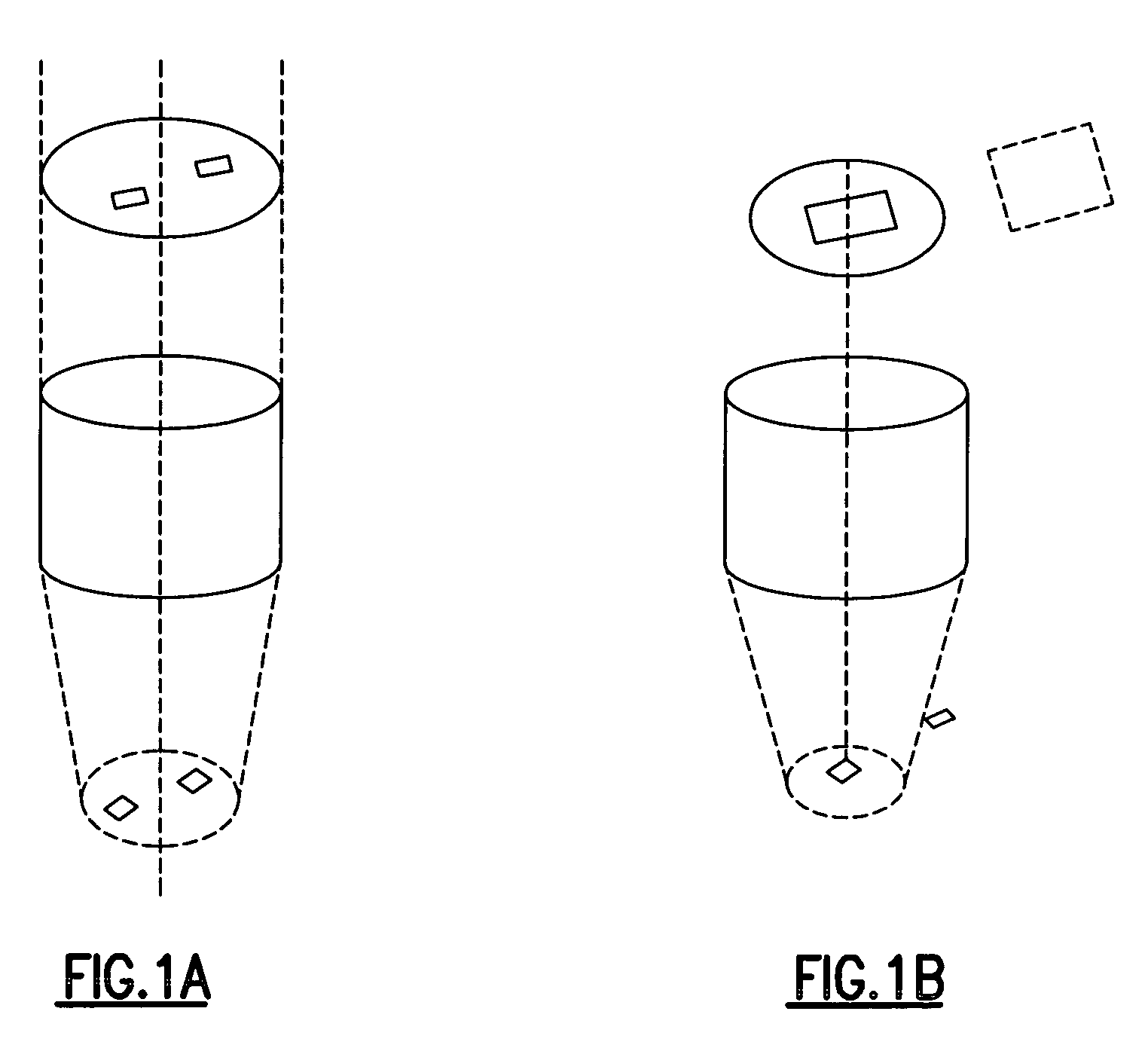
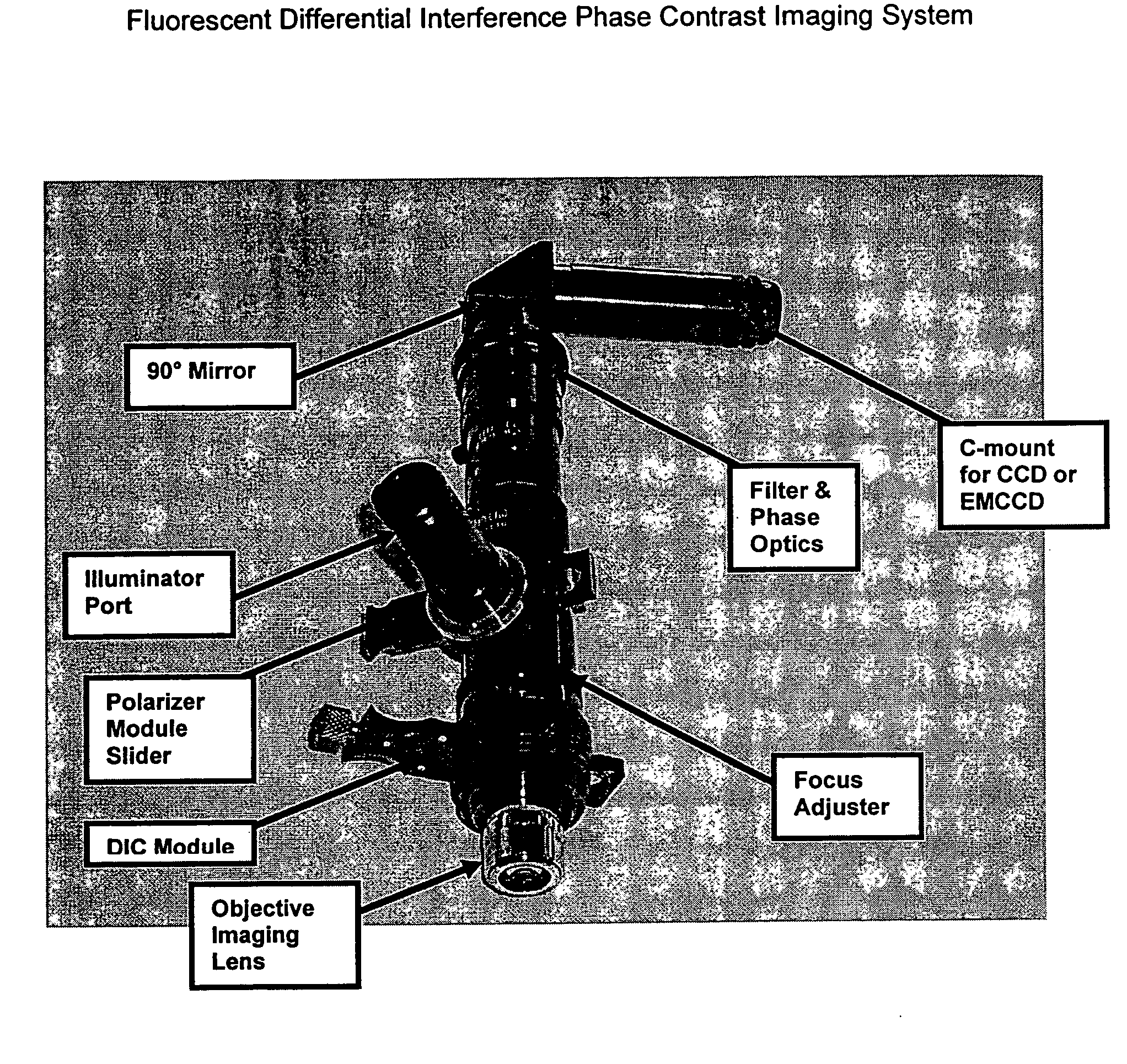
Inspection method and apparatus for partially drilled microvias
ActiveUS20080144921A1Better signal to noise ratioGood signalMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionFluorescenceImaging analysis
Inspection of partially drilled microvias by fluorescence based optical imaging techniques, selective coaxial illumination and multivariable off-axis illumination and the use of comparative image analysis and the transformation of back reflected radiation by means of an integrated fluorescing plate mounted to the surface of a CCD or EMCCD array.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
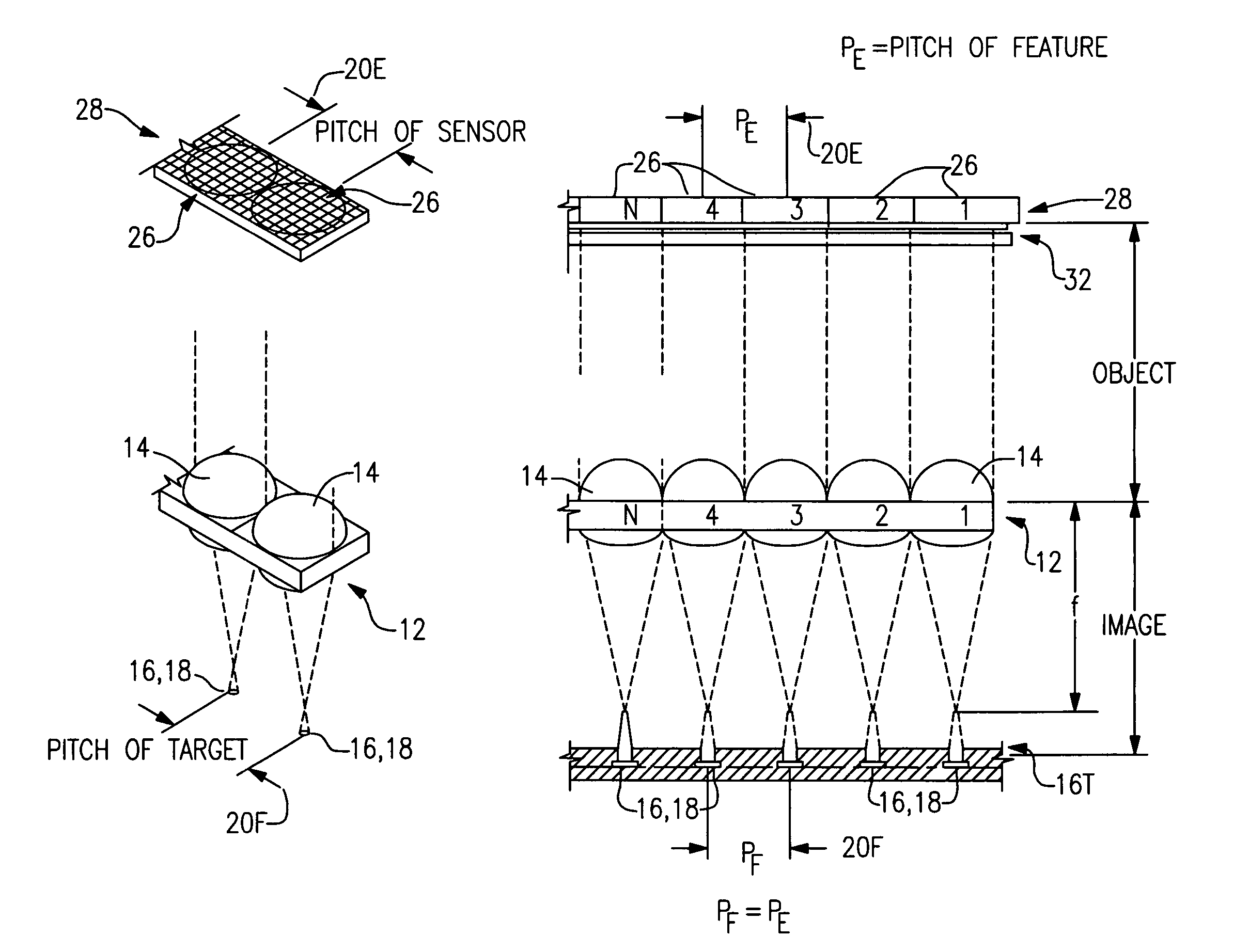
Apparatus and methods for the inspection of microvias in printed circuit boards
InactiveUS20080074749A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionTarget surfaceField of view
An imaging method and imaging system for inspecting features located at a known inter-feature pitch on portions of a target surface. The system includes a lens array having a plurality of lenses wherein the lenses of the lens array have an inter-lens pitch and an inter-field of view pitch corresponding to the inter-feature pitch, and an array of imaging elements having an inter-element pitch corresponding to the inter-feature pitch, whereby the imaging system images only field of view areas of the target surface containing features.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
Fiber laser based production of laser drilled microvias for multi-layer drilling, dicing, trimming of milling applications
InactiveUS7602822B2Additive manufacturing apparatusLaser using scattering effectsLight beamOptoelectronics
Fiber lasers and methods for constructing and using fiber lasers for micro- / nano-machining with output beams including stacked pulses and combinations of continuous wave, pseudo-continuous wave and pulse sequence components.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
Conductive dome probes for measuring system level multi-GHZ signals
ActiveUS7797663B2Final product manufactureCross-talk/noise/interference reductionReflection lossHigh density
Methods and apparatus for accessing a high speed signal routed on a conductive trace on an internal layer of a printed circuit board (PCB) using high density interconnect (HDI technology) are provided. The conductive trace may be coupled to a microvia (μVia) having a conductive dome disposed above the outer layer pad of the μVia. In-circuit test (ICT) fixtures or high speed test probes may interface with the conductive dome to test the high speed signal with decreased reflection loss and other parasitic effects when compared to conventional test points utilizing plated through-hole (PTH) technology.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Selective passivation of exposed silicon
InactiveUS6905953B2Thickness is easy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAtmospheric temperatureConductive materials
A method for applying a passivation layer selectively on an exposed silicon surface from a liquid phase solution supersaturated in silicon dioxide. The immersion is conducted at substantially atmospheric temperature and pressure and achieves an effective passivation layer in an abbreviated immersion time, and without subsequent heat treatment. In one embodiment, rapid coating of a wafer back side with silicon dioxide permits the use of a high-speed electroless process for plating the bond pad with a solder-enhancing material. In another embodiment, the walls of via holes and microvia holes in a silicon body may be passivated by immersion in the supersaturated solution prior to plugging the holes with conductive material.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method for fabricating electrical connecting element
InactiveUS6954986B2Efficient and reliableEasily bridgedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
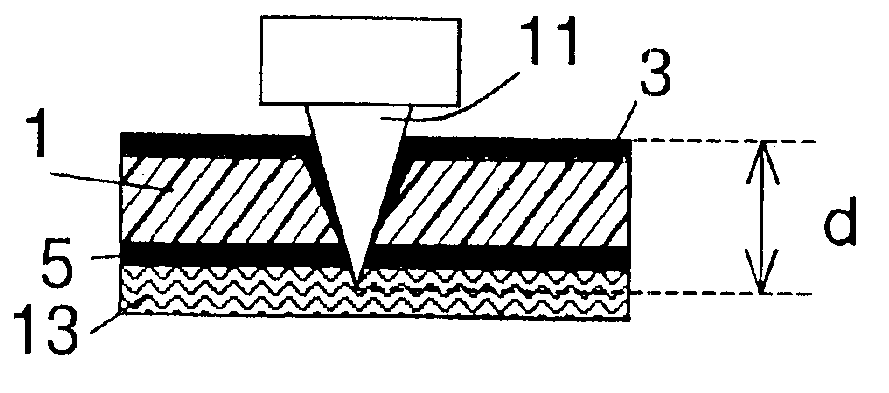
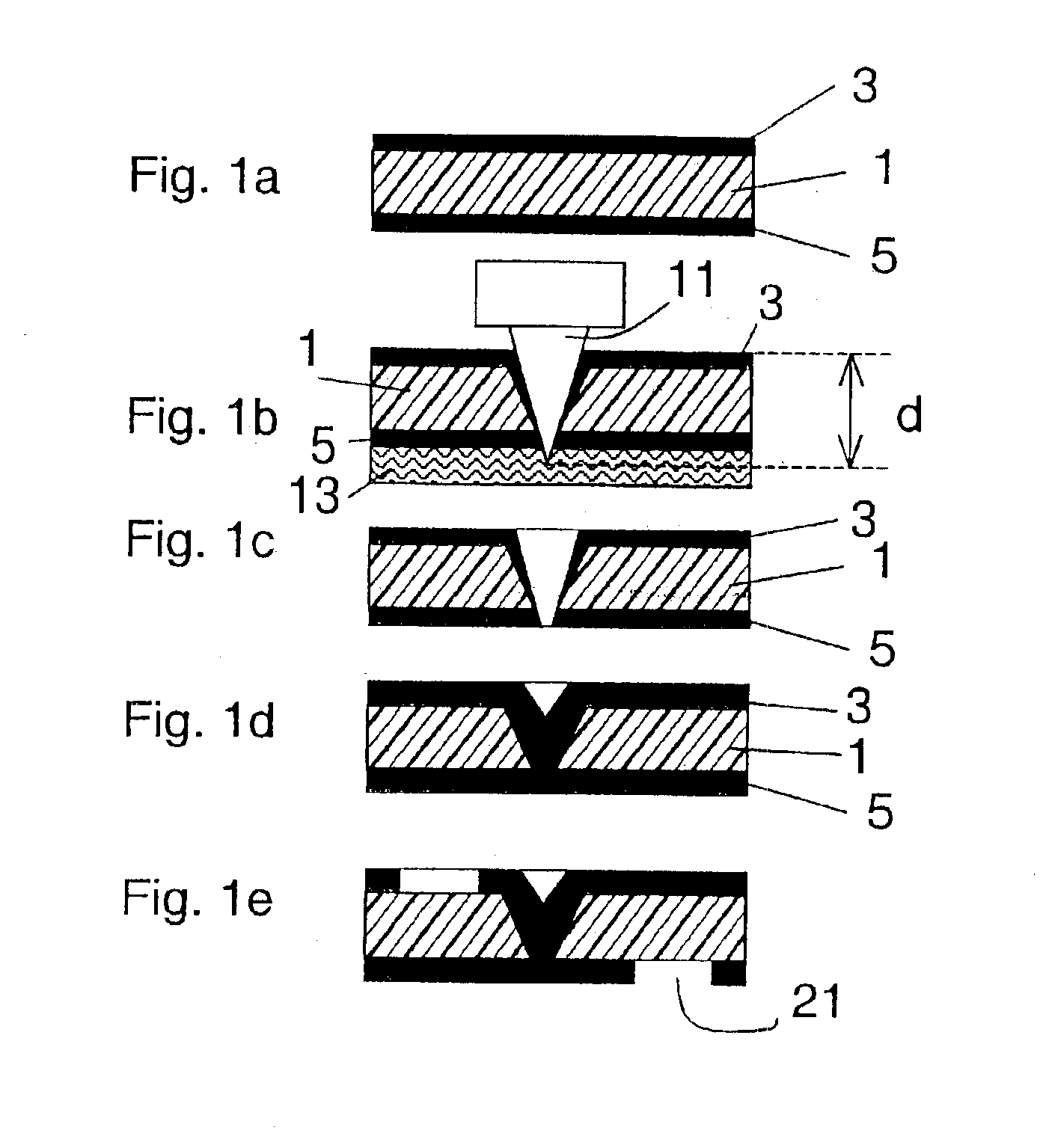
A method for manufacturing electrical connecting elements or semifinished products. Microvias are formed in a dielectric substrate layer by piercing a substrate layer (1) through a first conducting layer (3), which essentially covers an entire side of the substrate. The perforation depth (d) is at least equal to the total thickness of the substrate and the first conducting layer. The conductor material of the first conducting layer (3), during the piercing step, is deformed so that it partially covers the wall of the hole fabricated by the piercing process. Plating the first conducting layer with additional conductor material bridges the little remaining distance between the conductor material and the opposite side of the substrate layer.
Owner:DYCONEX PATENTE
Composite build-up material for embedding of circuitry
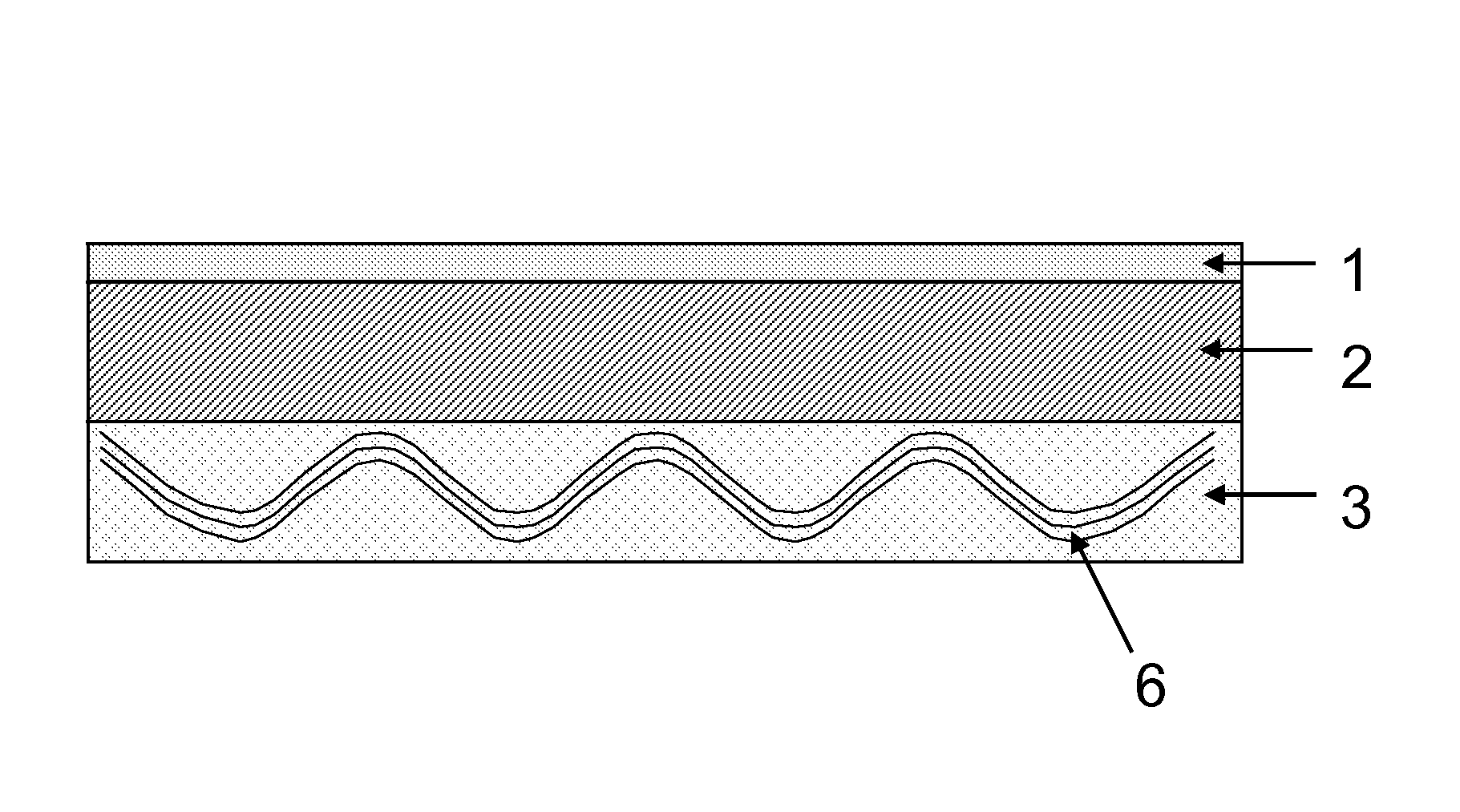
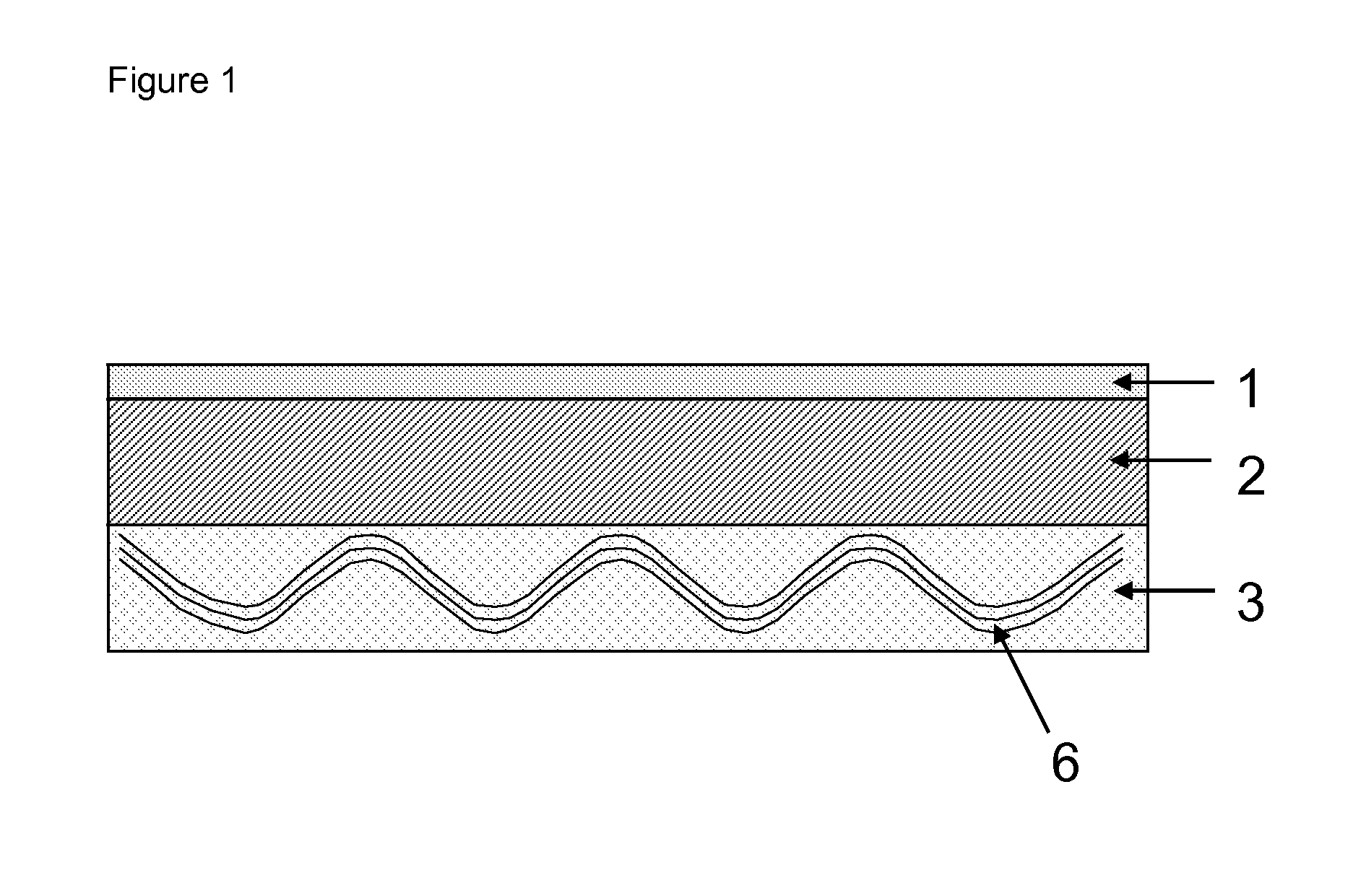
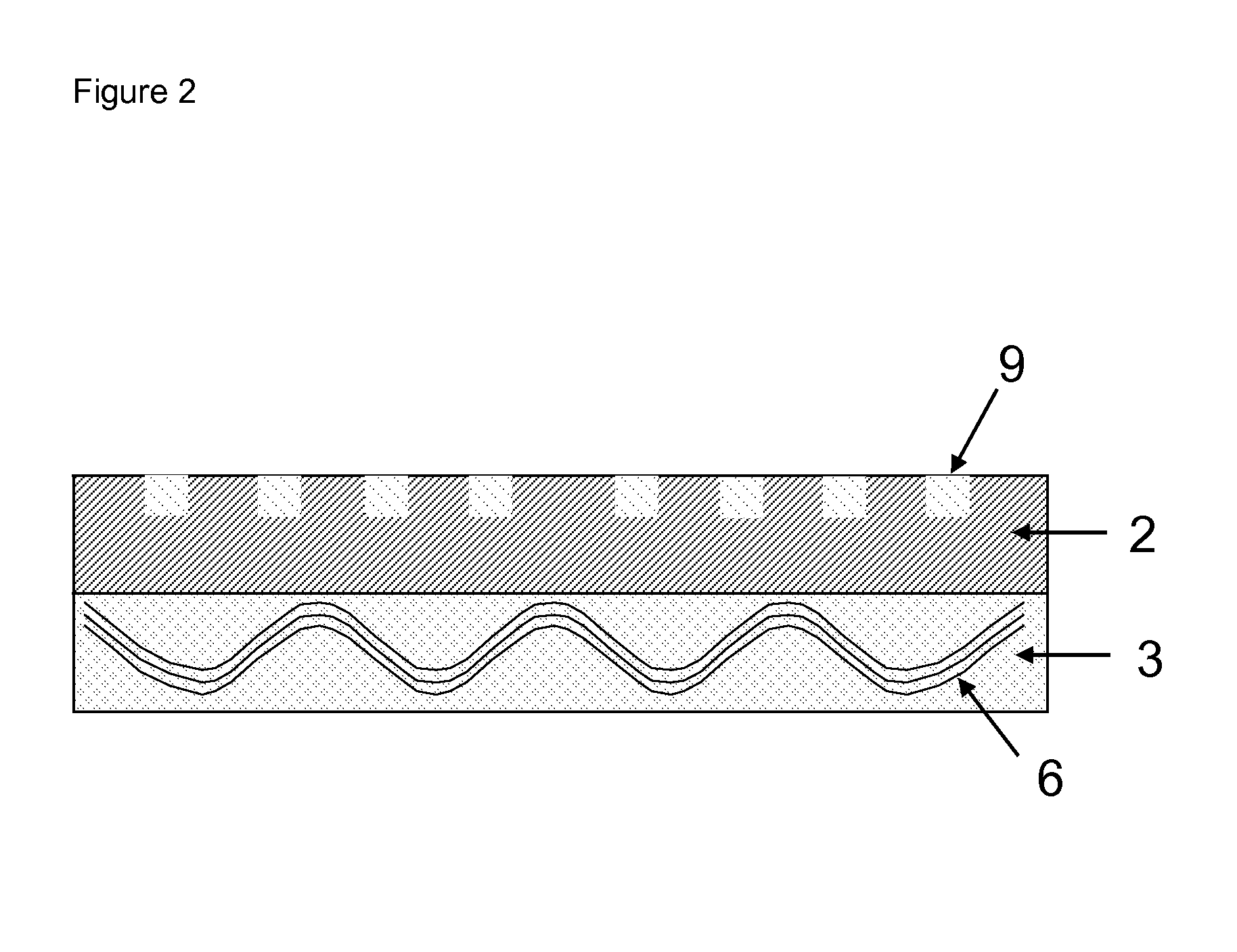
InactiveUS20130199825A1Low VOC contentGood dimensional stabilityPrinted circuit liquid treatmentLight absorption dielectricsEngineeringMicrovia
Disclosed are composite build-up materials for the manufacture of printed circuit boards, IC substrates, chip packages and the like. The composite build-up materials are suitable for embedding circuitry such as microvias, trenches and pads. The composite build-up materials comprise a carrier layer (1), a resin layer without reinforcement (2), and a resin layer with reinforcement (3). The circuitry (9) is embedded into the resin layer without reinforcement (2).
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com