Station control system for a driverless vehicle
a technology of driverless vehicles and control systems, which is applied in the direction of brake systems, train hauling devices, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of position indicators and corresponding readers, unable to provide statistical variation in unique and arbitrary identifiers, and the number of polarity combinations available from such magnets. to achieve the effect of reducing the cost of driverless vehicles or carts and relatively inexpensive station control systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
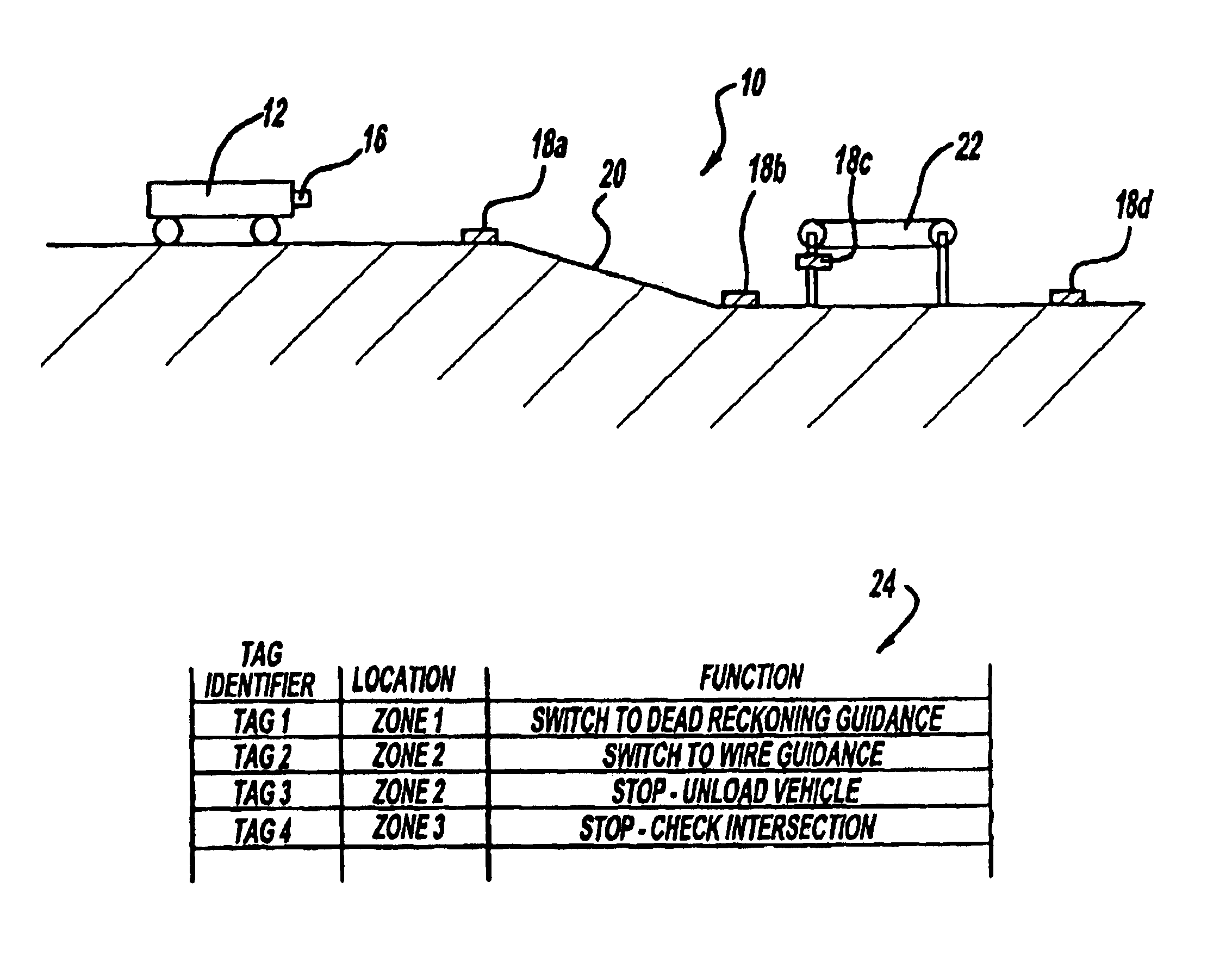
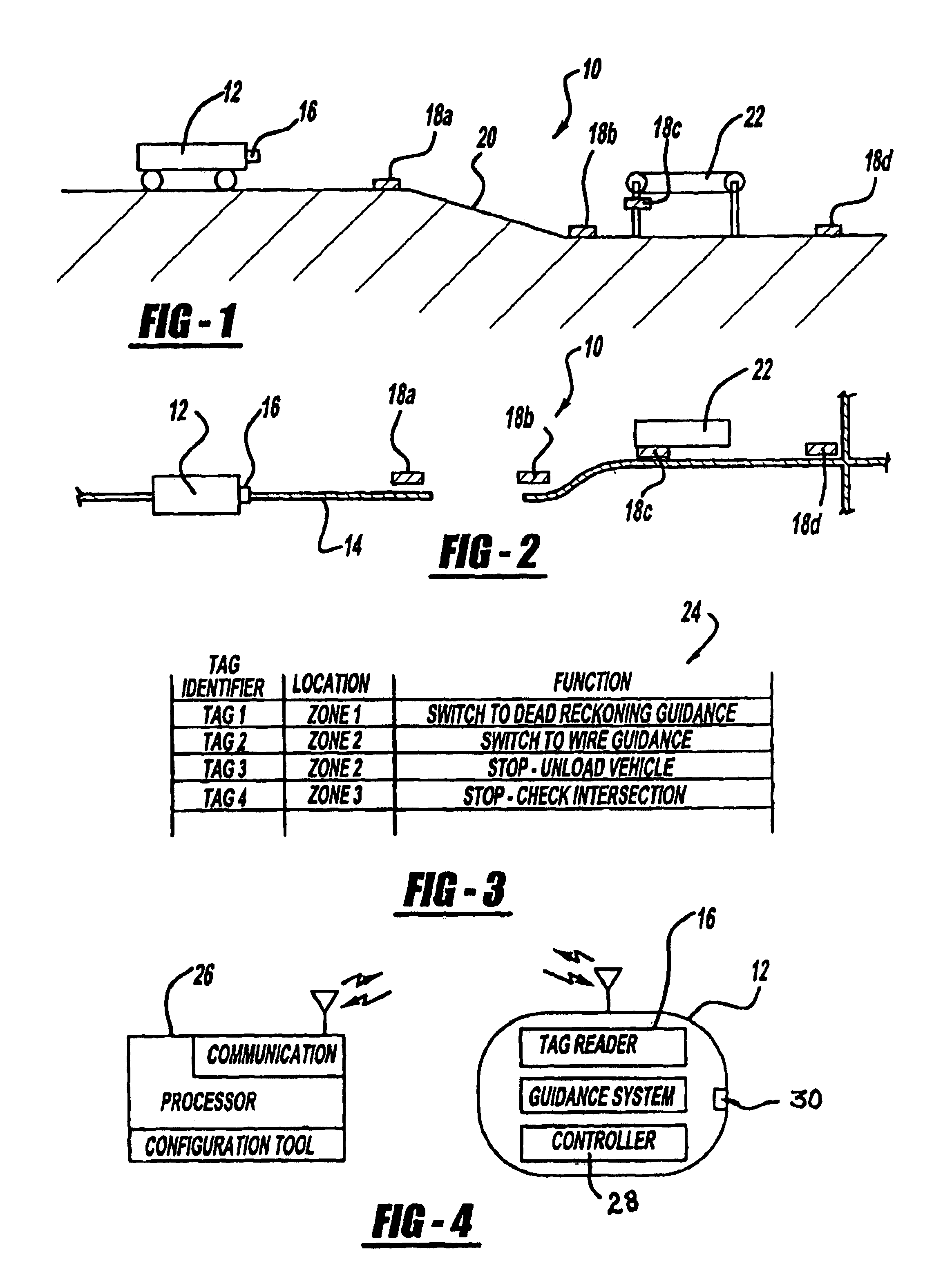
[0013]FIGS. 1 and 2 are schematic elevation and plan views, respectively, of a station control system 10 for a driverless vehicle 12 in accordance with the present invention. The driverless vehicle 12 can be controlled by any known guidance systems including an inertial guidance system, active or passive wire guidance system, optical guidance system, magnetic guidance system and the like. Notwithstanding the applicability of the present invention with a variety of guidance systems, the invention is particularly suitable for use with captive guidance systems without absolute position updates, e.g., where the vehicle senses or is otherwise constrained to move along a positive guide path. The guidance system is designed to steer and control the vehicle 12 along a guide path 14 while repeatedly monitoring the position of the vehicle 12 relative to the path 14. The present invention provides a station control system for the driverless vehicle in addition to and in cooperation with known ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com