Pre-stressed rack of intrahepatic portacaval shunt
A venous shunt and prestressing technology, which is applied in the field of medical equipment, can solve the problems of accidental right atrium cardiac tamponade, lower portal vein pressure, difficult access, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing trauma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
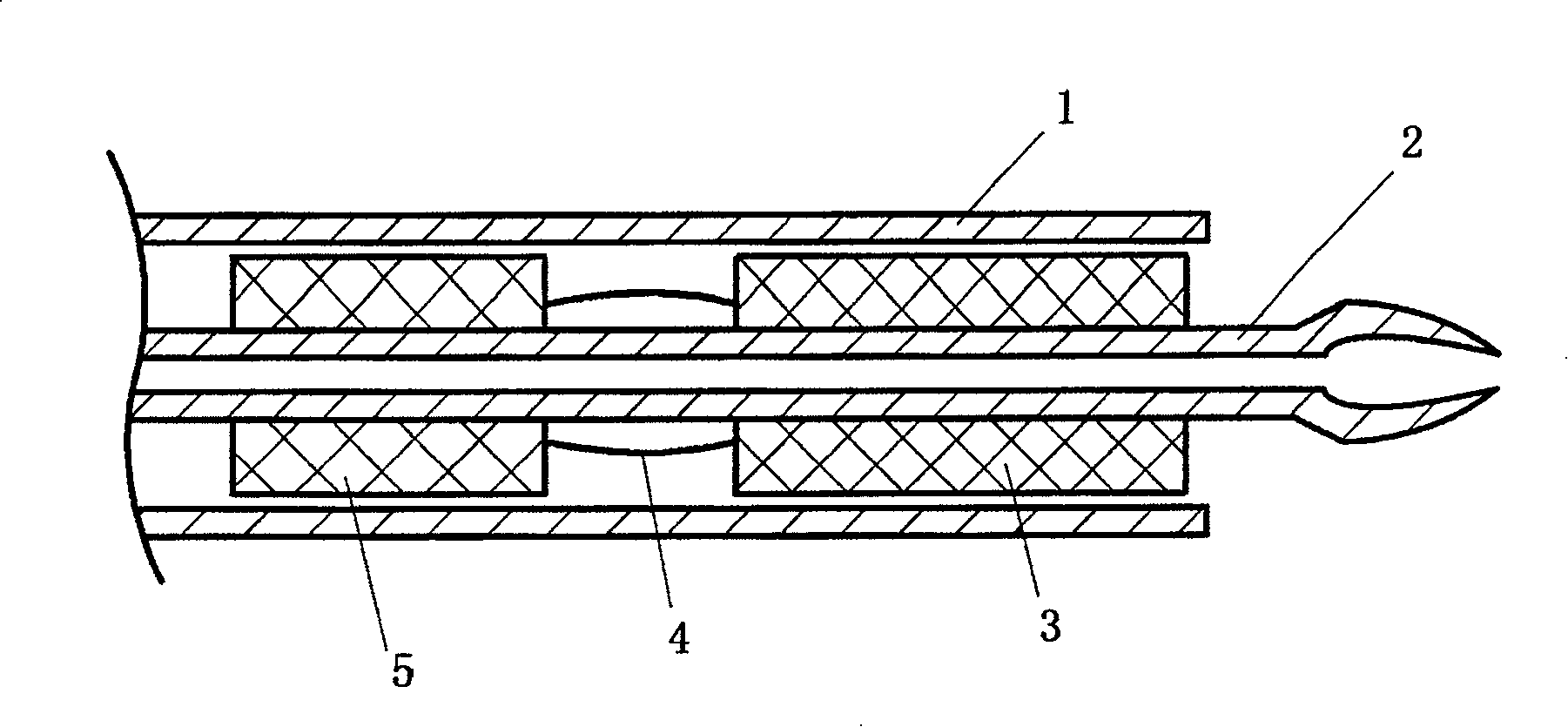
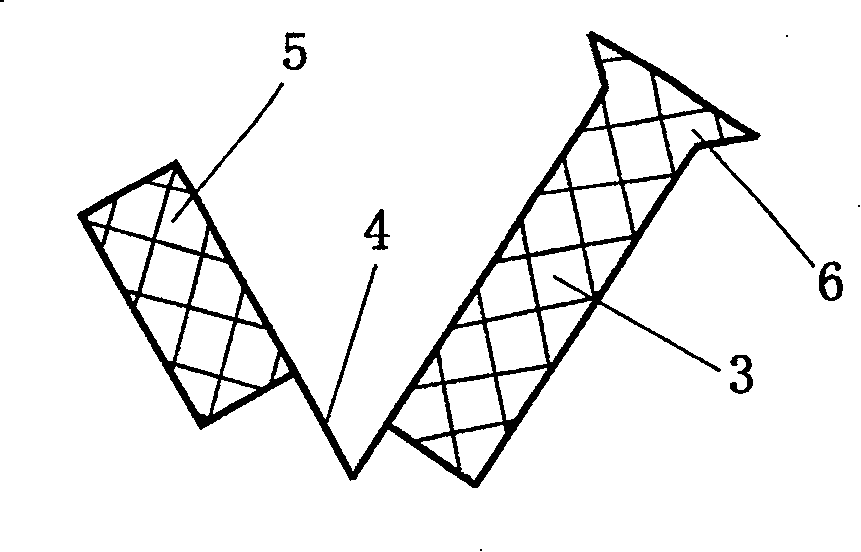
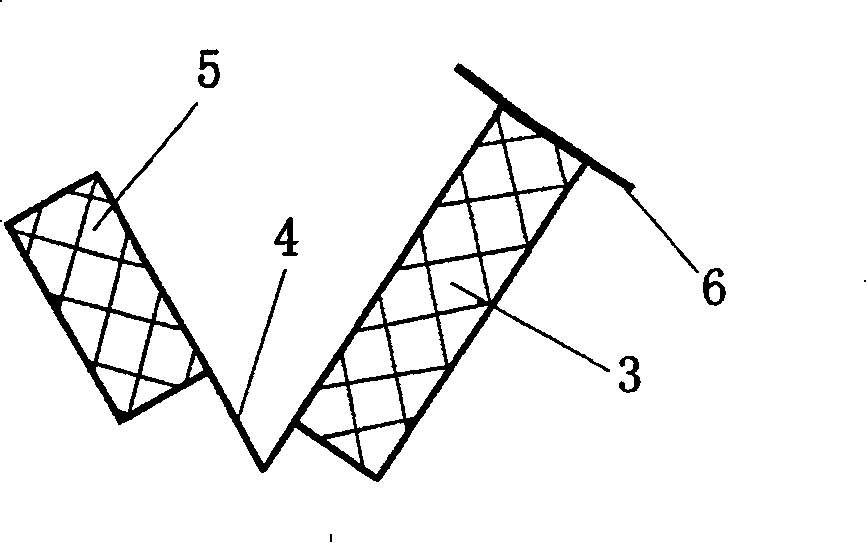
[0023] like figure 1 , Figure 2a and Figure 2b As shown, the prestressed stent for intrahepatic portocaval shunt of the present invention includes two parts, the main stent 3 and the auxiliary stent 5, and two or more nickel-titanium alloys are passed between the main stent 3 and the auxiliary stent 5 The wires 4 are connected. The main support 3 and the auxiliary support 5 are special-shaped network tubular structures woven from metal wires of the same material.
[0024] like figure 1 As shown, in this example, the diameters of the main bracket 3 and the auxiliary bracket 5 are both 8-10mm, the length of the main bracket 3 is 3-5cm, and the length of the auxiliary bracket 5 is 1.5cm. Two or more nickel-titanium alloy wires with an angle of 80° are connected in 4 phases. In clinical practice, different specifications and sizes can be designed according to the size of the liver volume caused by different races or different etiologies. The weaving and The formed stent is c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com