Method for detecting illegally cut-in point in radio cocal network
A wireless local area network, wireless access point technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as unavoidable, data without confidentiality and privacy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
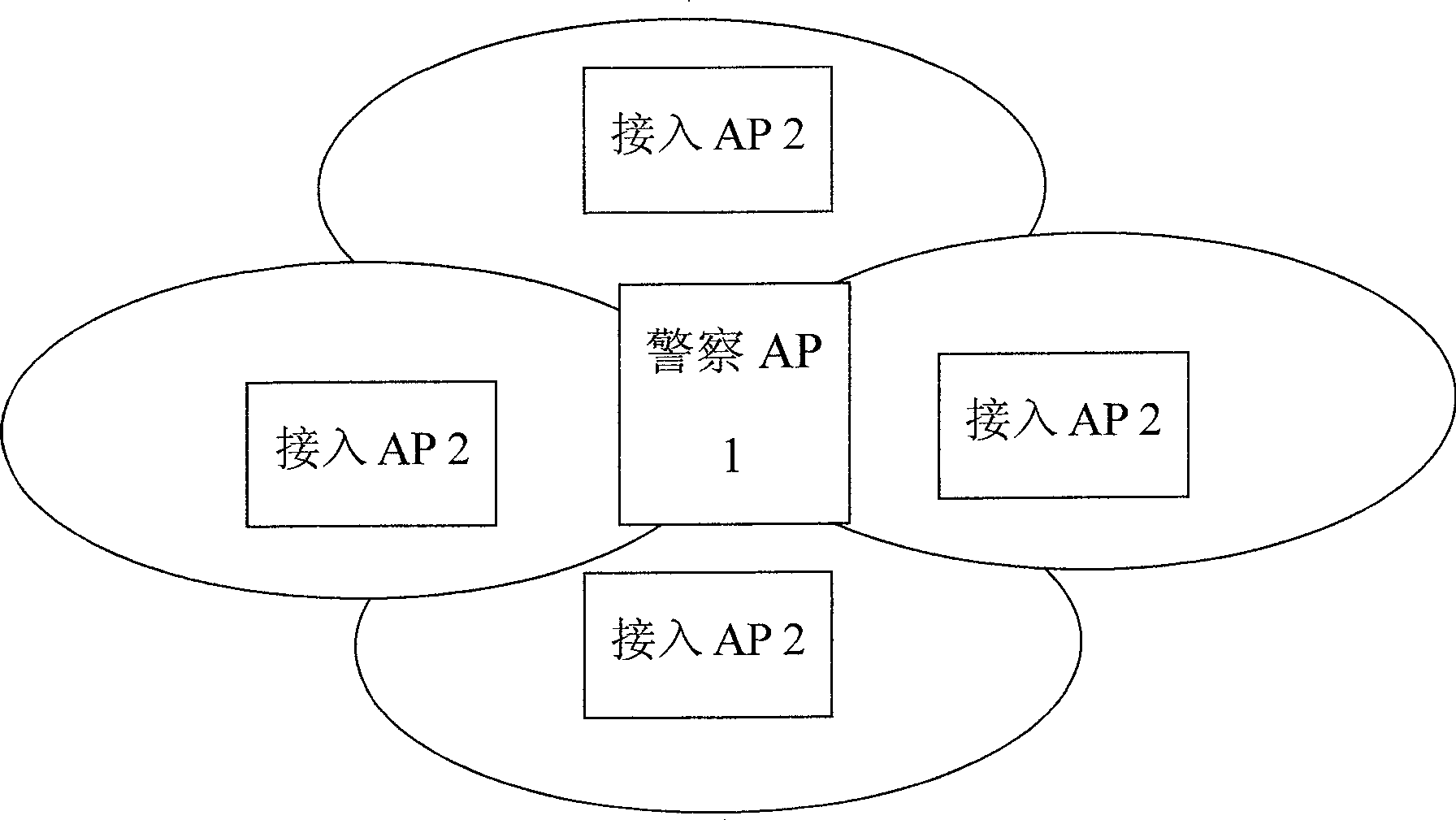
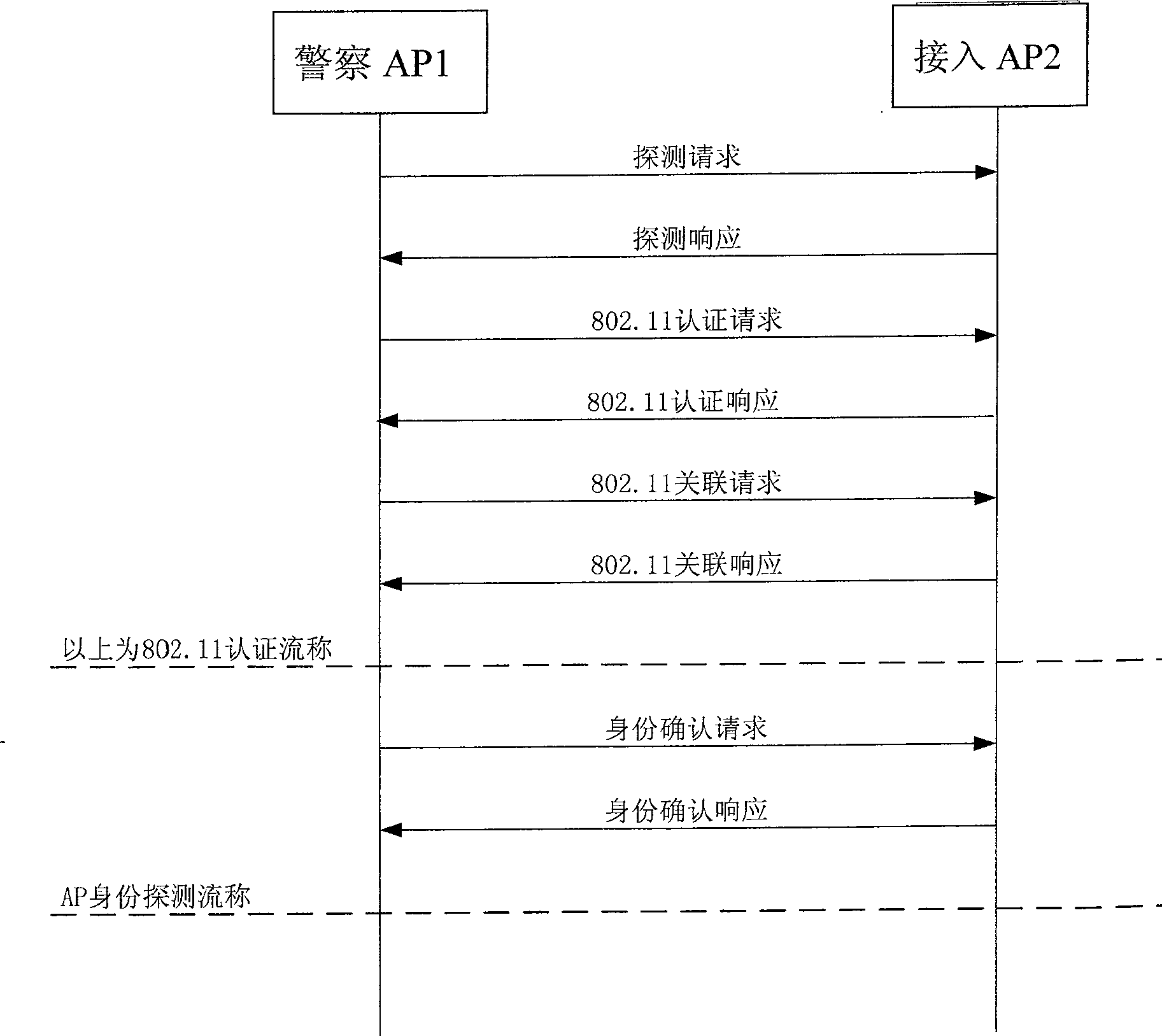
[0019] see figure 1 , two kinds of wireless access points (APs) are included in the wireless local area network of the present invention, namely the police AP1 and some access AP2s within the coverage of the police AP1, the access AP2 can issue its own identity information as required, and the police AP1 collects these information And make a judgment to confirm the legitimacy of the identity of each access AP2 in the local area network. The police AP1 will periodically scan its coverage area and perform a protocol interaction with the scanned access AP2. If the interaction is successful, it is a legal access AP. He will record the data as a backup. If the interaction is unsuccessful, it will judge It may be an illegal AP, and an alarm will be sent to the network management. In this way, in a local area network, if the access AP2 supports identity reporting, and several police AP1s with the ability to collect and report information are properly placed, when an illegal AP acces...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com