Method for transparently exchanging data packets and network node unit
A technology of network units and network nodes, which is applied in the direction of data exchange, electrical components, transmission systems, etc. through path configuration, and can solve the problem of not being able to identify network units.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
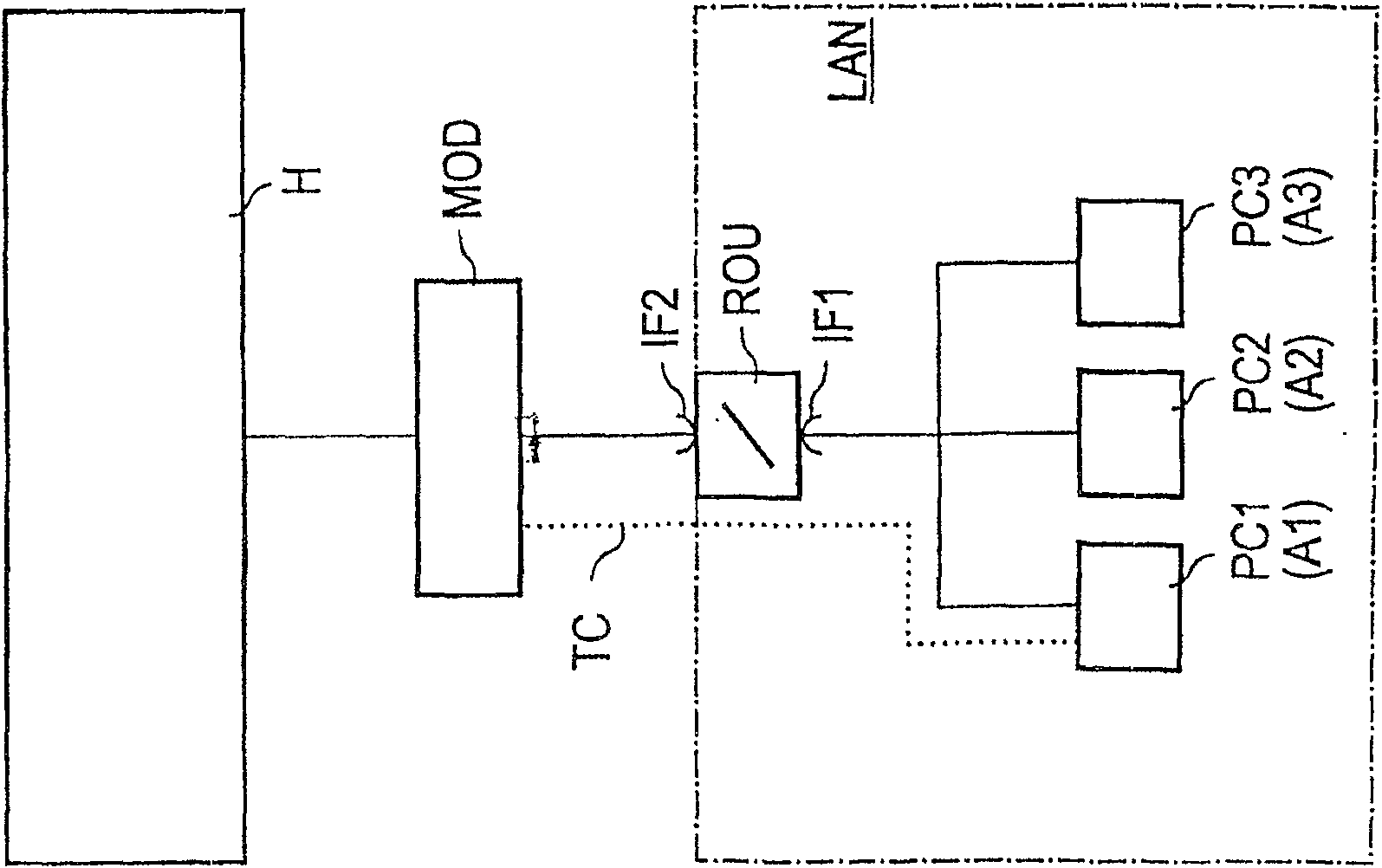
[0039] exist figure 1 A packet-oriented network LAN with a first network element PC1 , a second network element PC2 and a third network element PC3 is shown in .
[0040] The network units PC1, PC2, and PC3 are connected to each other and to a network node device ROU through a common transmission medium, such as Ethernet. The network node ROU has a first network interface IF1 for connection to the packet-oriented network LAN and a second network interface IF2 which connects the network node ROU to an input of a modulation / demodulation device MOD (also referred to as a modem). Packet-oriented data are also exchanged between the second network interface IF2 and the input of the modem MOD as in the packet-oriented network LAN.
[0041] In an alternative embodiment, the modulation / demodulation function is integrated into the network node device ROU, so that the use of the modem MOD becomes superfluous.
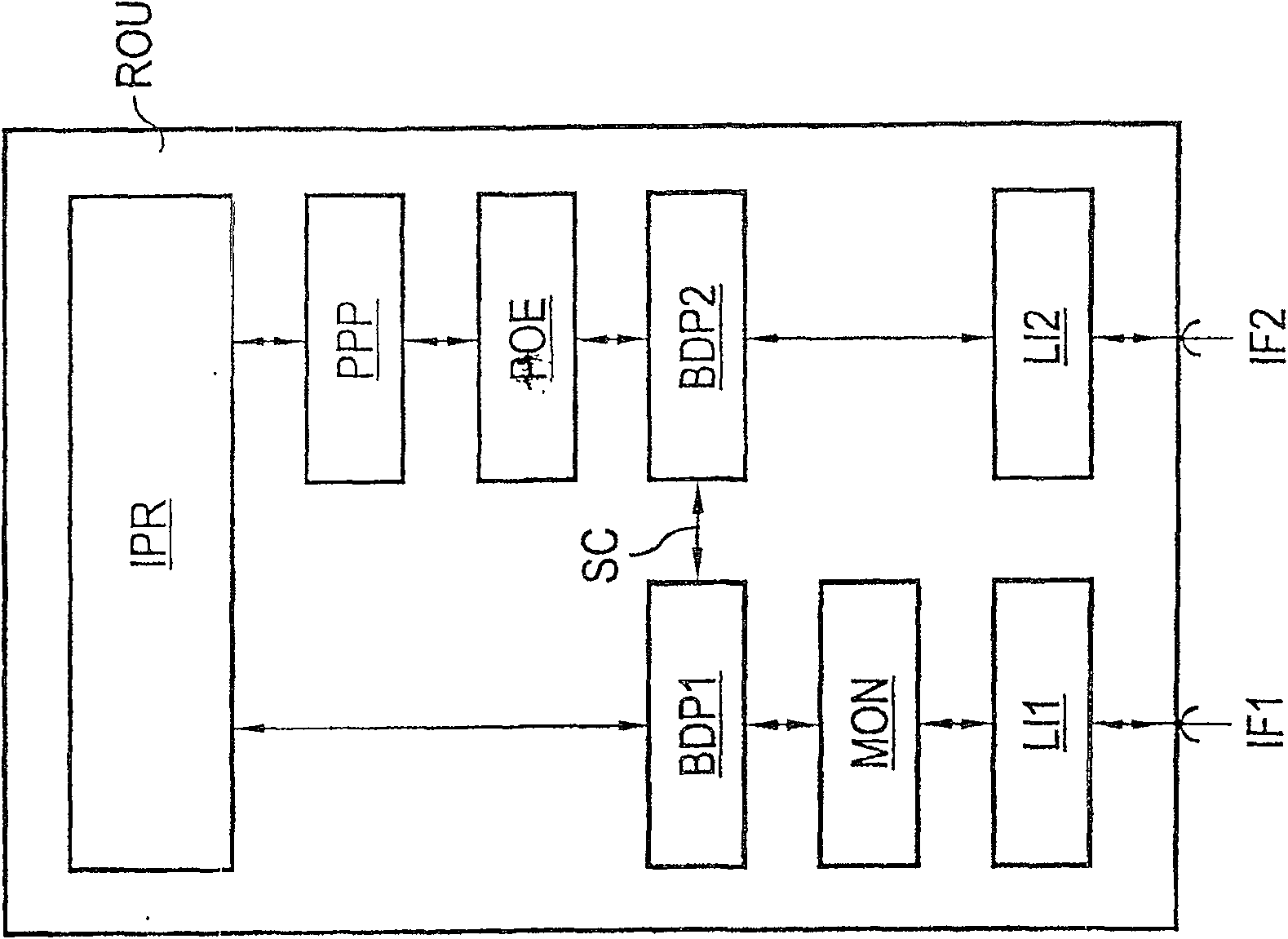
[0042] The network node device ROU is realized, for example, as a router or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com