OFDM position location signaling utilizing mutually exclusive subsets of subcarriers
A technology for positioning signals and subsets, which is applied in the field of signaling and devices, and wireless position positioning systems, and can solve problems such as low cross-correlation, increased complexity, bandwidth time, and signal power with large differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
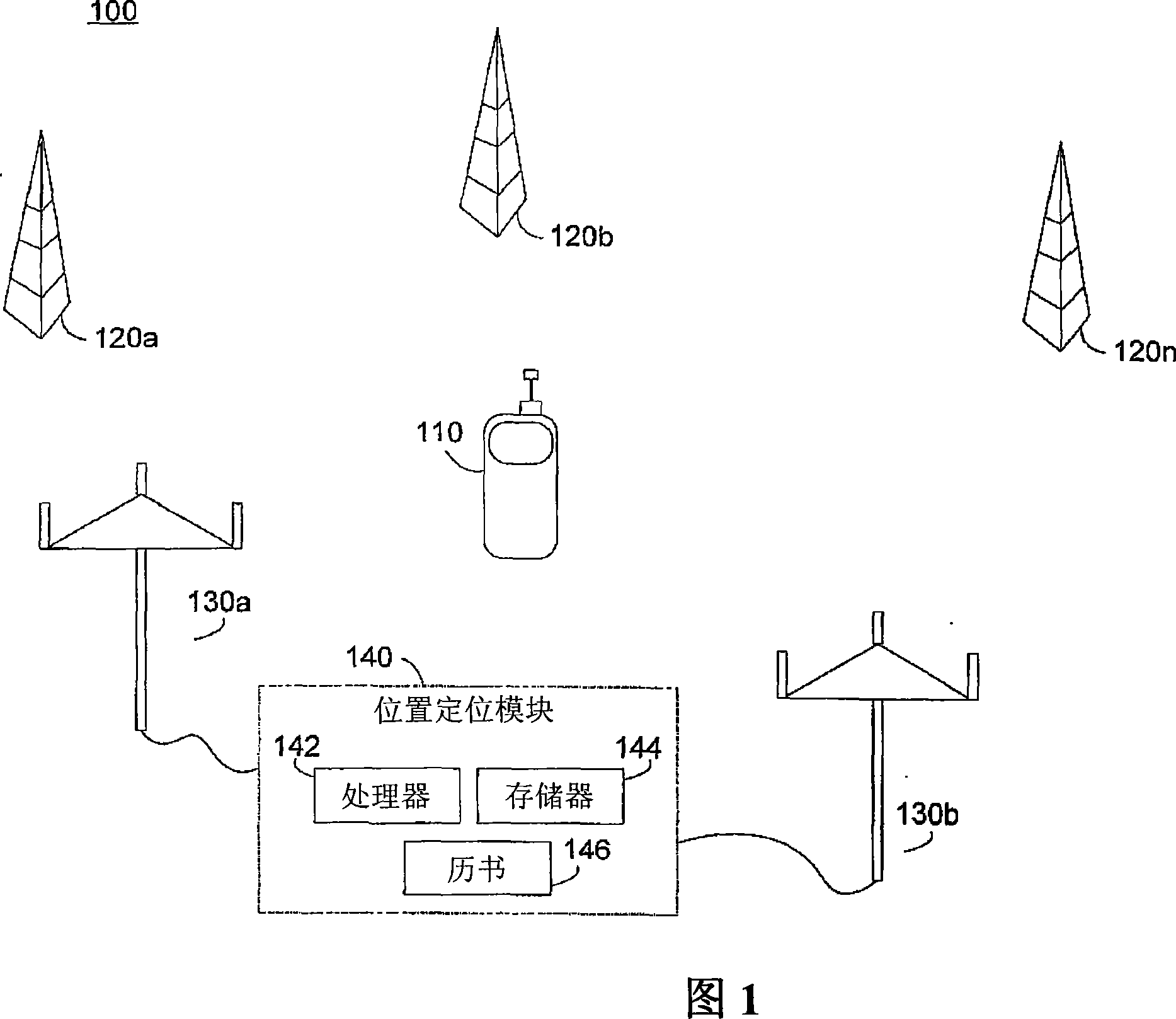
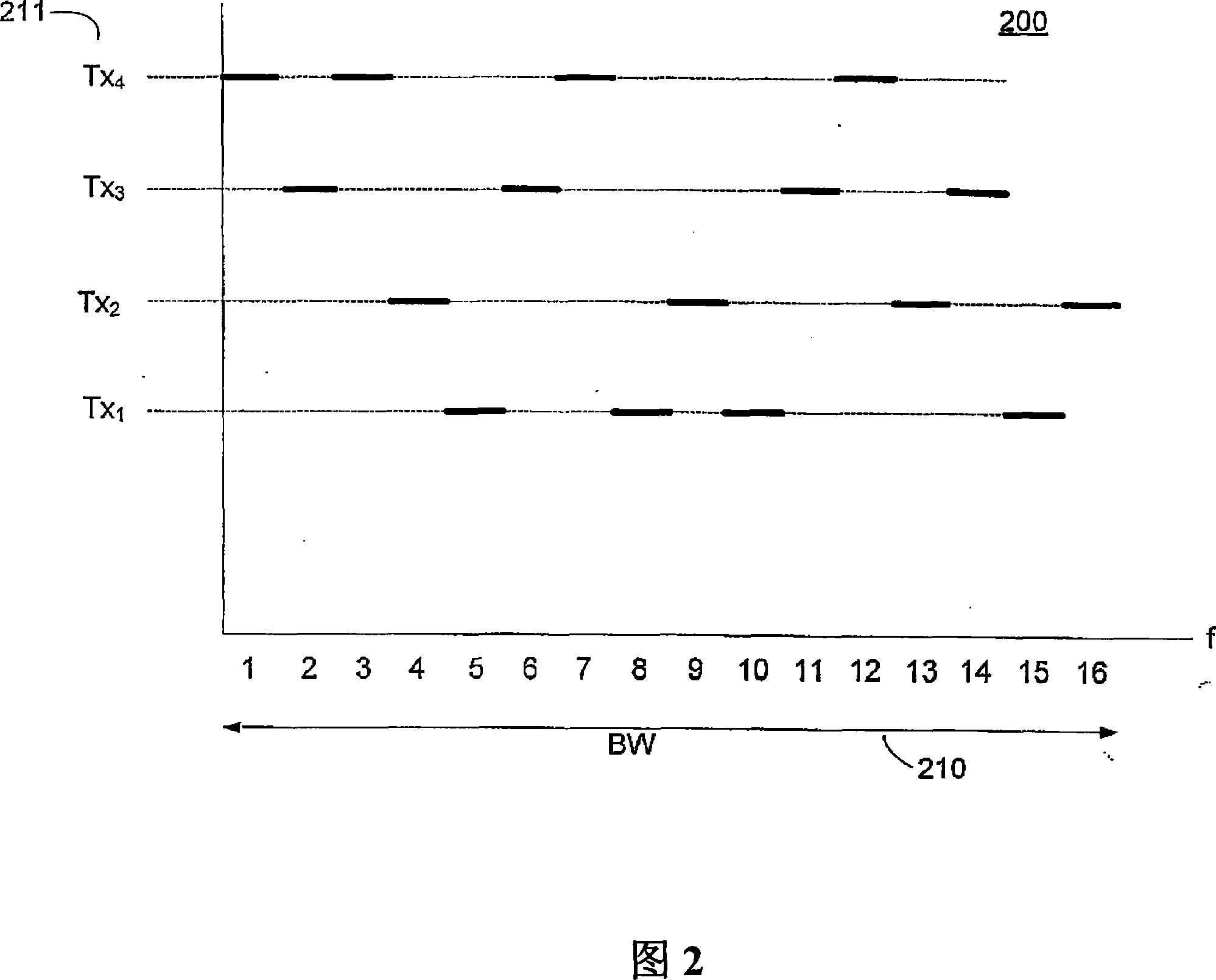
[0075] In a typical wideband broadcast system embodiment, Q = 4096 orthogonal carriers may be defined within a 5.5MHz frequency span, which just fits within a commonly allocated 6MHz TV broadcast channel. This allocation of carriers results in a carrier spacing of approximately 1.343 kHz.
[0076] If M=8 different position location signals are configured, each position location signal includes a subset with Q / M or 512 carriers. Each position location beacon 120 may be assigned one of the 8 carrier subsets.
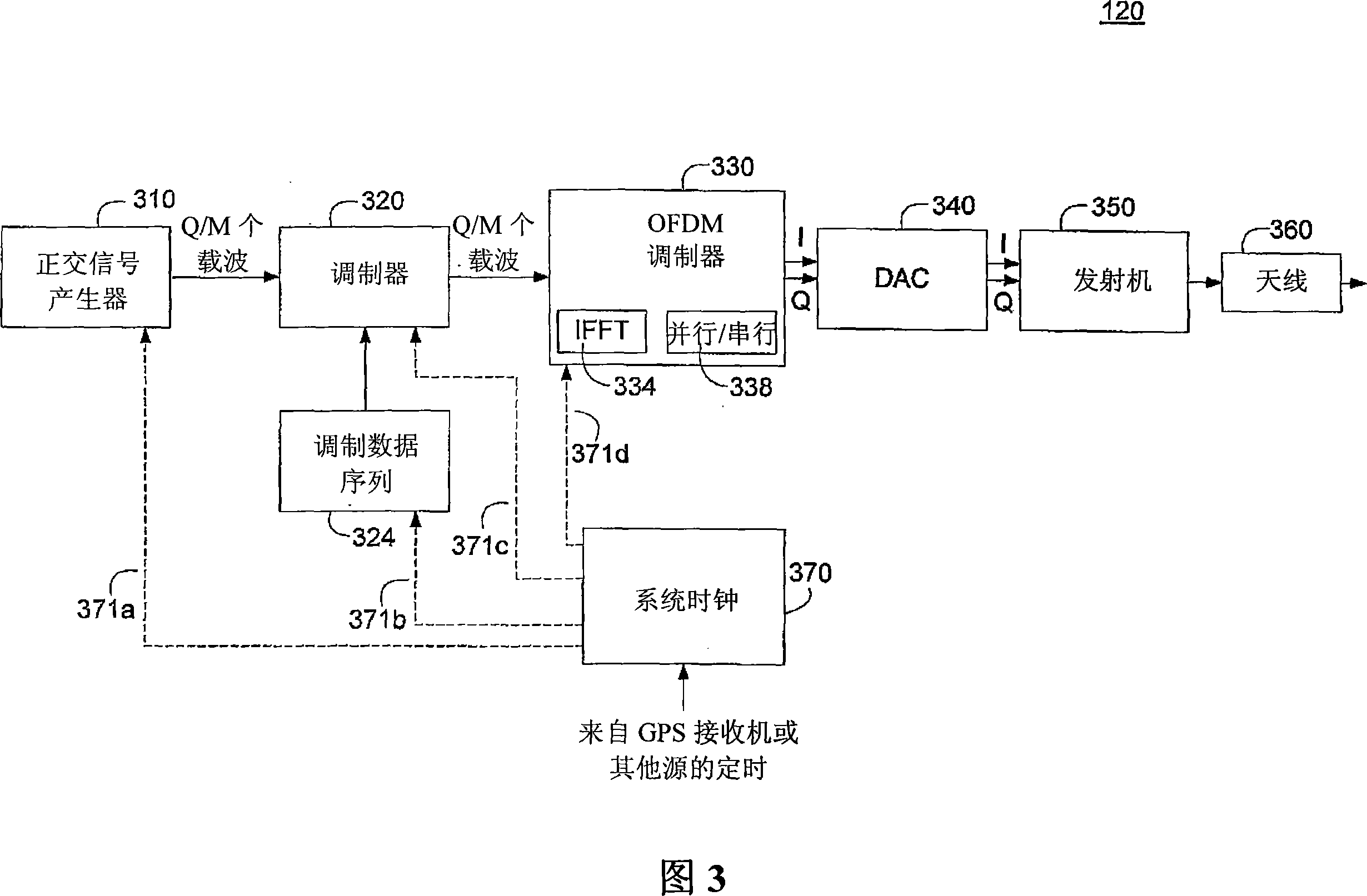
[0077] The quadrature signal generator 310 can be configured to generate at least 512 quadrature carriers required for a position location signal. The 512 quadrature carriers are then provided to the modulator 320 input. Modulated data module 324 is configured to provide a pseudo-random binary sequence to modulator 320, such as a golden code extended to 512 bits in length if desired (the full length of the golden code is 2n−1, where n is an integer, such as when n= 9 o'...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com