Digital map shape vector encoding method and position information transfer method
A technology of data encoding and location information, applied in image encoding, measuring device, image data processing, etc., can solve the problems of increasing data volume and data transmission volume, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
[0083] In the first embodiment, a method of compressing data by variable length coding will be described.
[0084] In the method of transmitting position information of a digital map according to the present invention, first, the shape of a road is represented by shape data with statistical bias. The rationale is that when compressing and encoding data, compressibility will be improved.
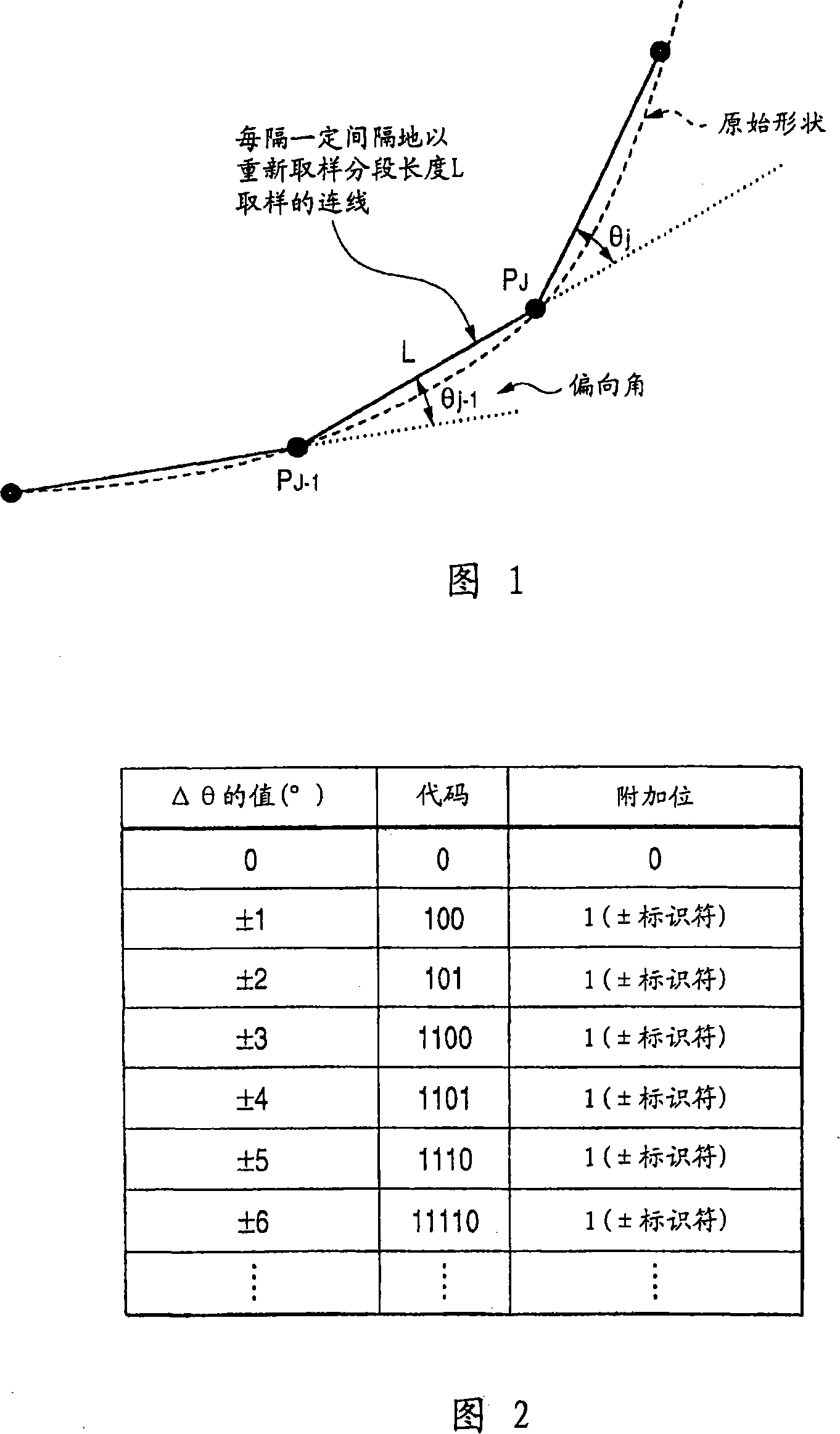
[0085] In the case where the shape of the road is represented by coordinate points arranged on the road, as shown in FIG. 41, by relative to the adjacent coordinate points (P J-1 ) The distance and angle of this two-dimensional can uniquely specify each coordinate point (P J )s position. In Figure 41, this angle is the angle Θ based on the "absolute azimuth" setting the true north (up in the figure) azimuth to 0 and specifying an angle between 0 and 360 in the clockwise direction j . Therefore, expressing coordinate points with distance and absolute azimuth is called full curvature functi...
no. 2 Embodiment
[0118] In the second embodiment, a method of compressing data using the run length method is described.
[0119] In the example of the first embodiment, after putting Δθ j When coding to represent shape data, "0" is repeated on a straight road or a curved road with the same curvature. In such a case, the data compressibility is higher in the expression "0 repeated 20 times" than in "00000...". Here, run-length encoding is performed to compress data.
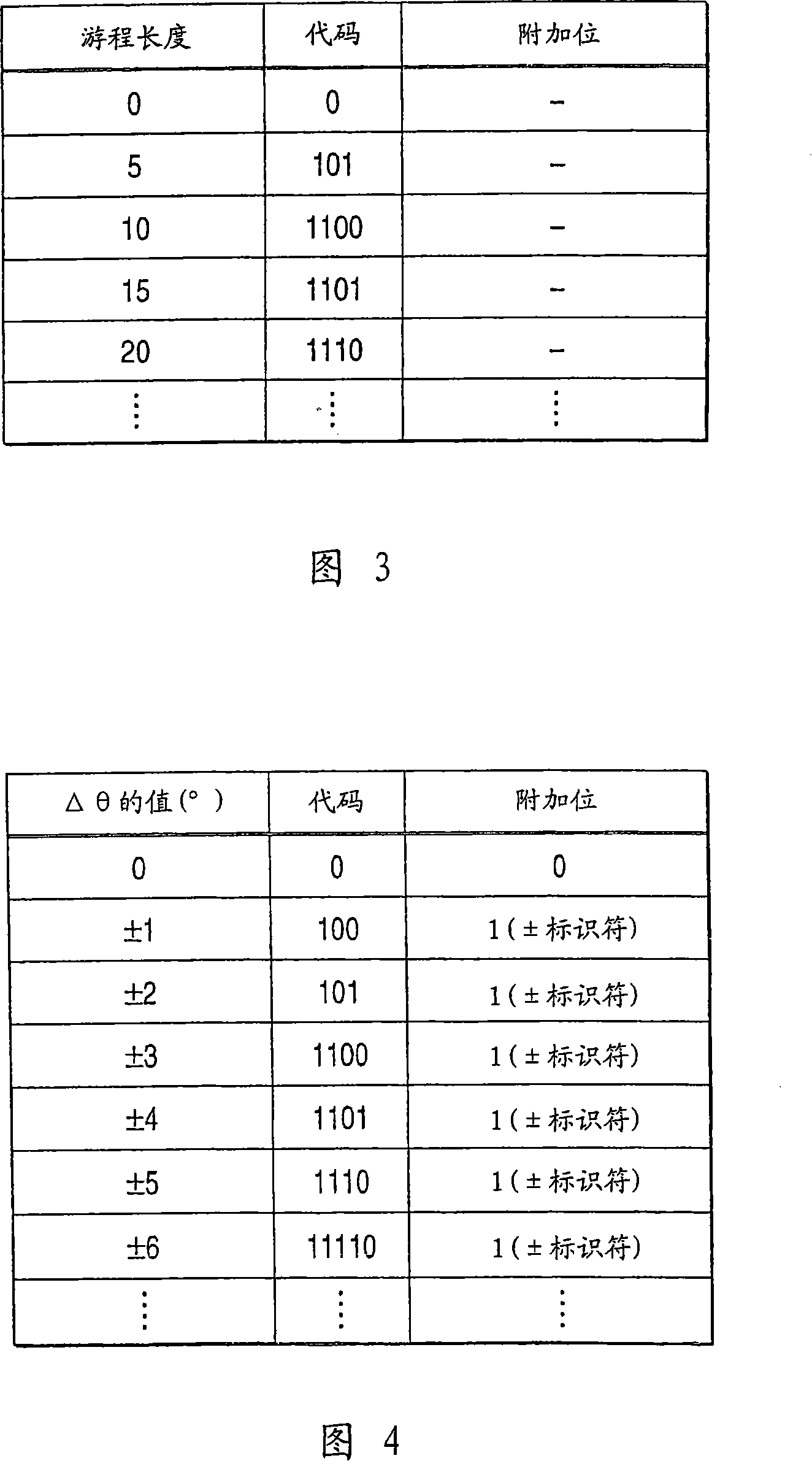
[0120] FIG. 3 shows a code table defining, for example, that the same number repeated 5 times (run length 5) is displayed as "101". FIG. 4 shows the same code table for Δθ as that in FIG. 2 .
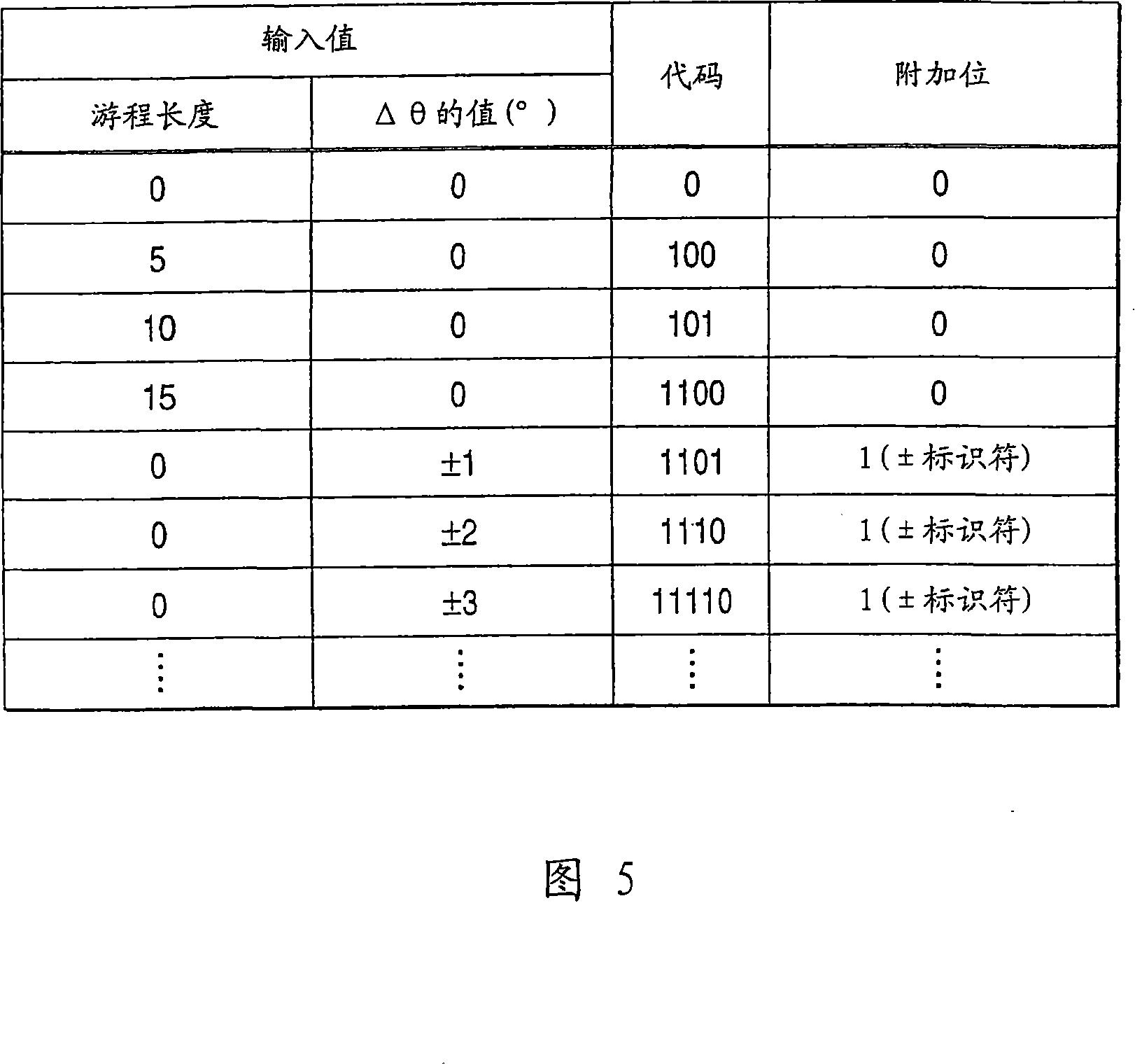
[0121] For example, the data array is determined as run length → Δθ → run length → Δθ → . . . When Δθ is "0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -2, -2, 0, +3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ,0,0,0,-1..",
[0122] The run length encoding can be represented by "101.0_0.1011_0.1011_0.0_0.11000_1101.0_0.1001.."→"10100101101011000110001101001001..." (32 ...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0127] In the third example, a description will be given of an apparatus that executes the position information transmitting method according to the present invention.
[0128] FIG. 6 shows an example of a device, a location information transmitter / receiver exchanging information on the occurrence of events on a road with another device 30 .
[0129] The apparatus includes an offline processing section for generating a code table to be used for compressing and encoding road shape data in an offline state; and an online processing section 10 for transmitting traffic information using the code table data generated by the offline processing section 20 . Off-line processing section 20 includes digital map database 22; Storage section 21 is used to store traffic information in the past; Code table calculation section 23 is used to generate code table data to be used for compression and encoding; With code table database, it is used to store such Generated code table data.
[0130]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com