A vehicle networking knowledge base representation method, device and system
A knowledge representation and Internet of Vehicles technology, applied in the field of Internet of Vehicles, can solve problems such as difficulties and shortages, and achieve the effects of fast memory operation, low space complexity, and flexible knowledge sampling methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
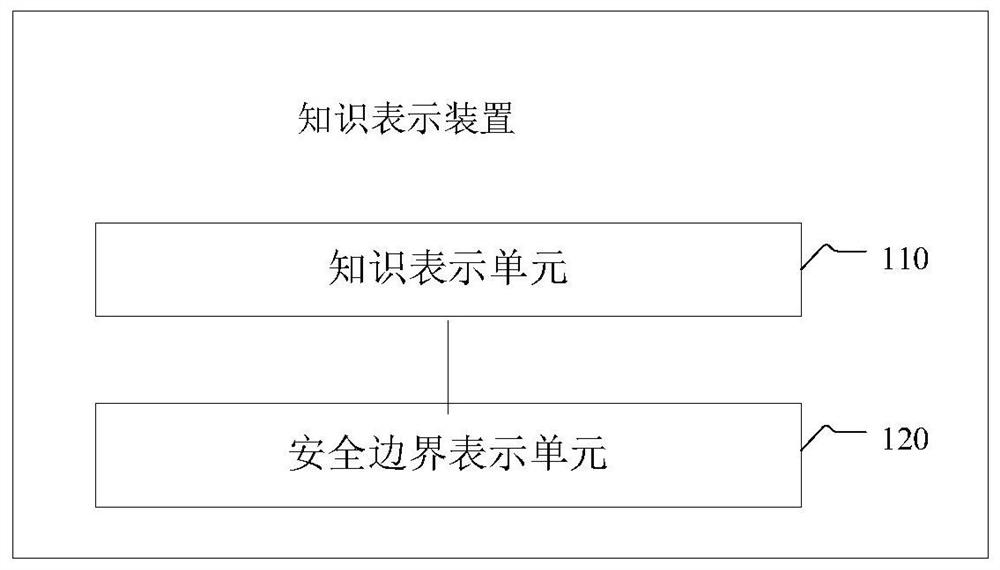
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0290] Example 1: SC-based IOV knowledge representation
[0291] ○Use SC as the carrier of knowledge on IOV multi-dimensional continuous space to perform discrete sampling and continuous deduction.
[0292] Represent an IOV knowledge f:R with a k-dimensional SC with a k'-dimensional function value k →R k’ (that is, a function with k input variables and k' output values: 1 ,…,x k >→1 ,…,y k’ >):
[0293] Any point in SC represents an input point of f;
[0294] ■Any point in SC has a k-dimensional coordinate, that is, the value of k input variables at this point;
[0295] ■Any point in SC has a k'-dimensional function value, that is, the k' output values of f at this point.
[0296] ●Discrete sampling, continuous deduction:
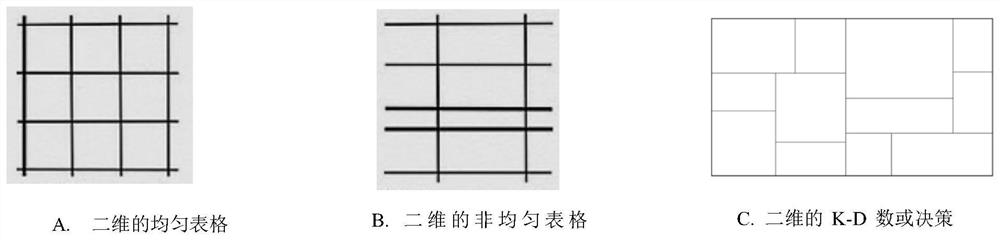
[0297] ■Discrete sampling: The vertices of SC are used as sampling points, and only the coordinates and function values are recorded at these points, and not at other points (non-sampling points).
[0298] ■Continuous deduction: Use SC units as ...
Embodiment 2
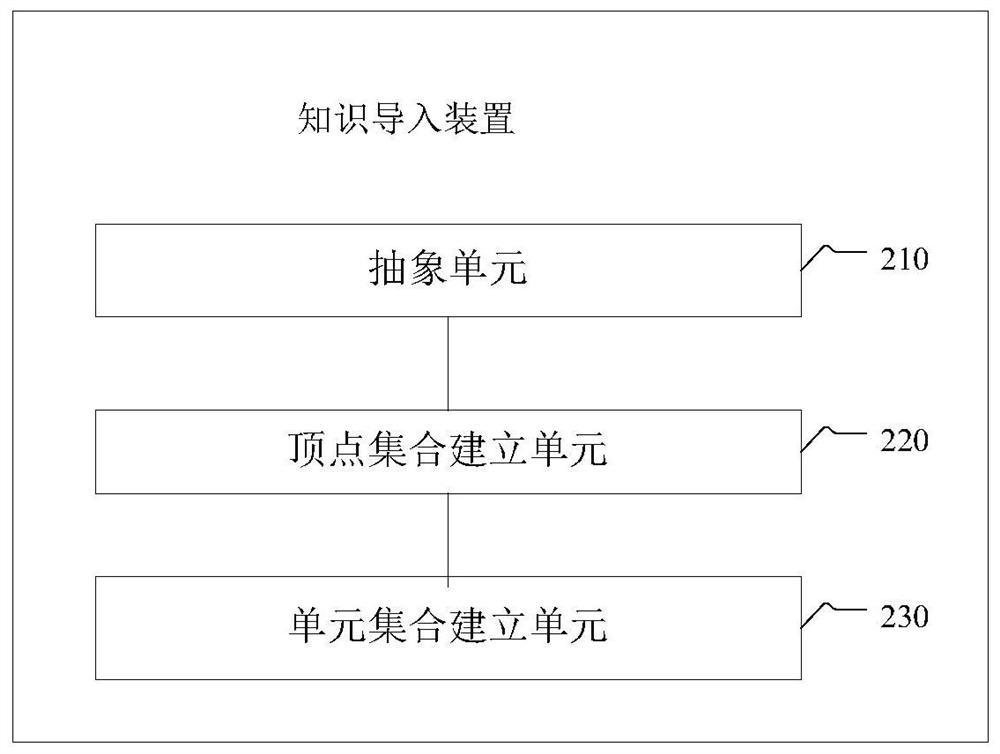
[0301] Embodiment 2: Import method of SC-based IOV existing knowledge
[0302] ○Designed a general method of importing knowledge into SC (that is, the initialization method of the knowledge base): first select the appropriate set of SC vertices (discrete sampling points), and calculate the function value on each vertex, and then establish SC units to seamlessly Connect the vertices.
[0303] ○ In particular, the existing knowledge also includes the knowledge from the rule-based IOV system, thereby realizing the re-expression and import of the existing rules (technical problem 1).
Embodiment 3
[0304] Example 3: SC-based IOV knowledge point fast location method
[0305] ○ Designed a method to speed up the search by attaching additional clues: the problem of directly searching for the target unit where a given target point is located is transformed into an indirect search process: first determine a starting unit and starting point for the search, and then start from the Starting from the starting element, along the ray from the starting point to the target point, the target element is searched linearly. In this way, the originally vast search space (the entire SC) can be reduced to a series of units penetrated by the rays, and an exponential search speedup can be obtained, thereby making up for the biggest shortcoming of the topological SC (technical problem 6).
[0306] ○The acquisition method of additional clues is designed: the entire SC space is structured and partitioned, and according to the continuity of multiple positioning, the proxy unit in the area where th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com