System and methods for network reachability detection
An autonomous system and boundary technology, applied in the direction of transmission system, digital transmission system, data exchange network, etc., can solve problems such as lack of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
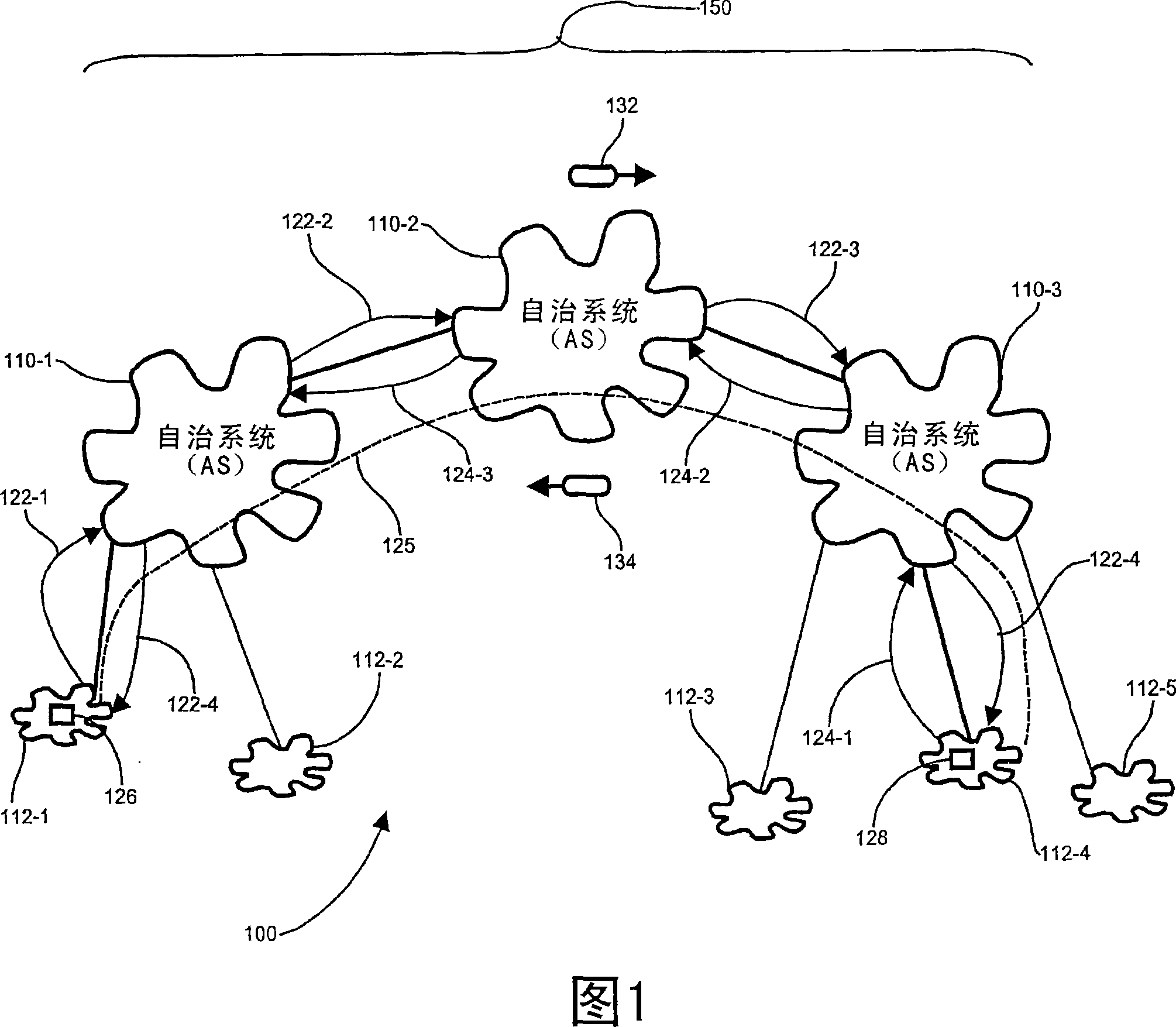
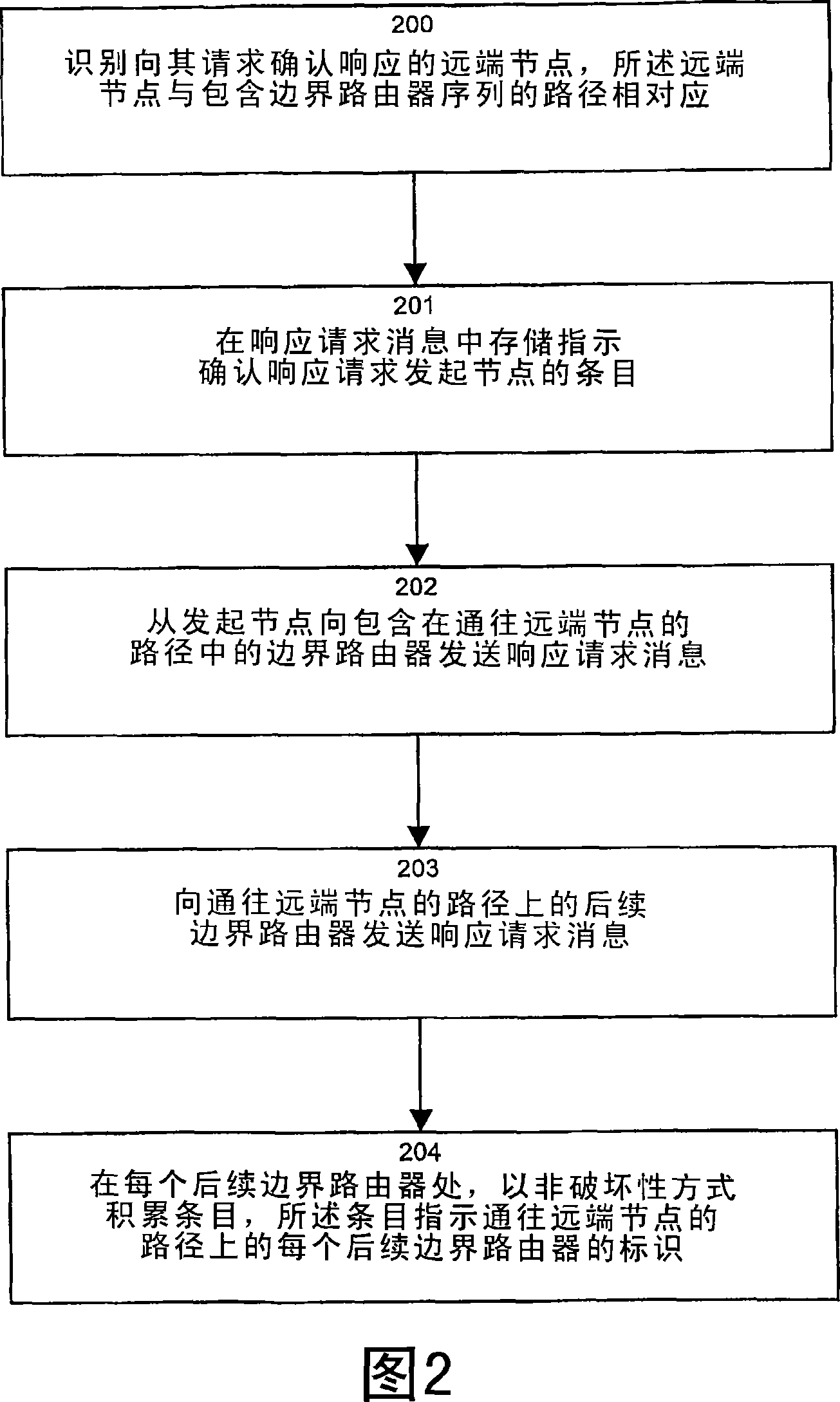
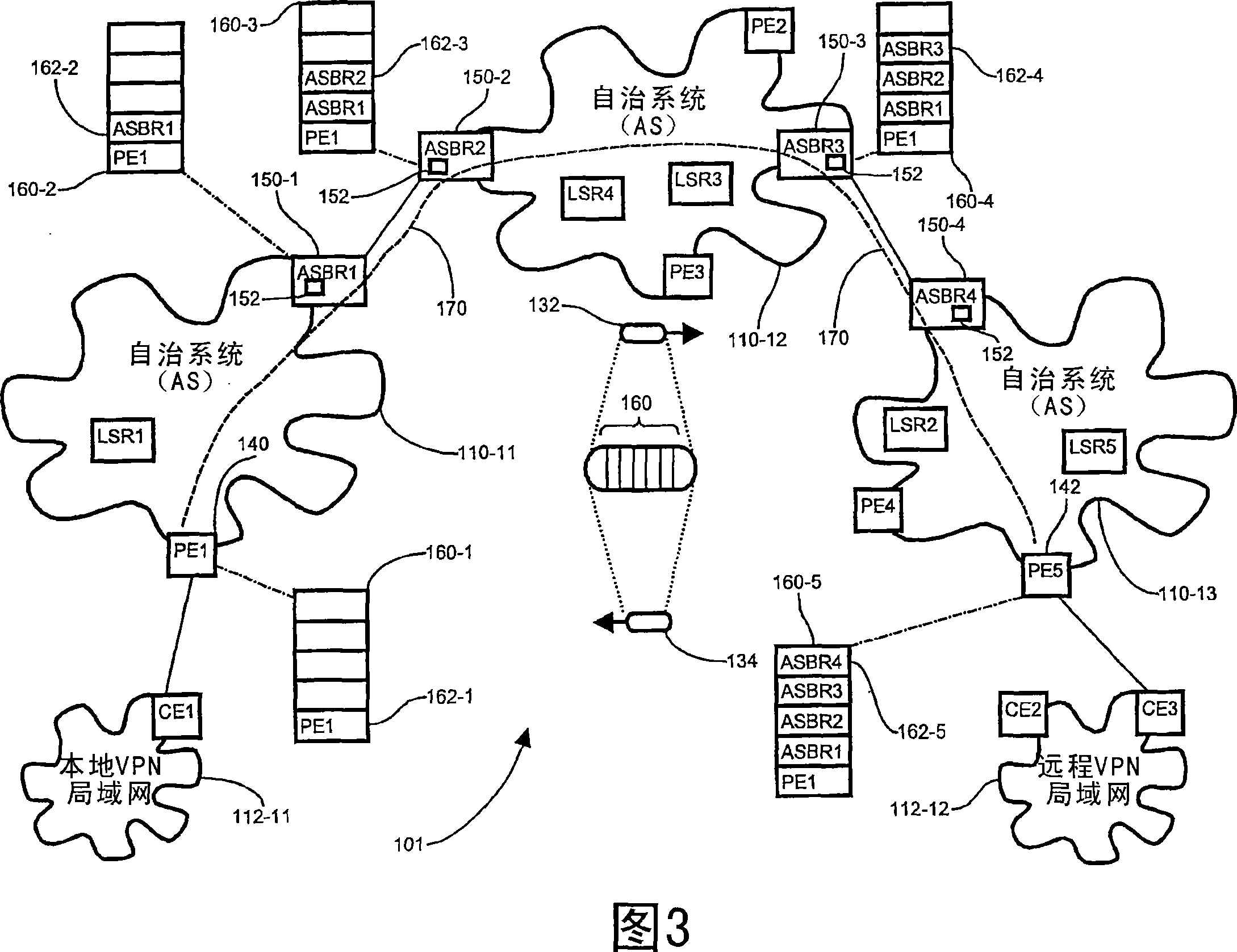
[0031] Pinging remote nodes on routes or paths across autonomous systems using LSP routing encounters the problem that the identity of the ping originator may not be recognized outside the source AS. Due to the difficulty of propagating addresses within an AS outside the local AS, the traditional ping command does not extend outside the AS. Traditional MPLS ASBRs and other LSRs incorporate this ping message using a time-to-live (TTL) attribute, usually as part of the MPLS header. Each ASBR sets the TTL to 1 or introduces a route warning label, indicating that the ping message is intercepted before leaving the originating AS. Setting the TTL to 1 ensures that the packet is not propagated outside the source AS. So, there is no way to perform traditional ping commands outside of ASBR. Therefore, since traditional ASBRs using LSP routing cannot provide return path routing information for ping commands issued to remote ASs, VPN subnets (i.e., CE or PE routers), or other destinati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com