Method for deducing initial magnetic pole position of permanent magnet synchronous motor
A magnetic pole position and permanent magnet synchronization technology, which is applied in the direction of motor generator control, electromechanical transmission control, electronic commutation motor control, etc., can solve the problem of easy oscillation of the addition and subtraction angle, the inability to obtain the size of the motor shaft end load, and the inability to guarantee the motor Start comfort and other issues, to achieve the effect of smooth start
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The method for inferring the initial magnetic pole position of the permanent magnet synchronous motor of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments:
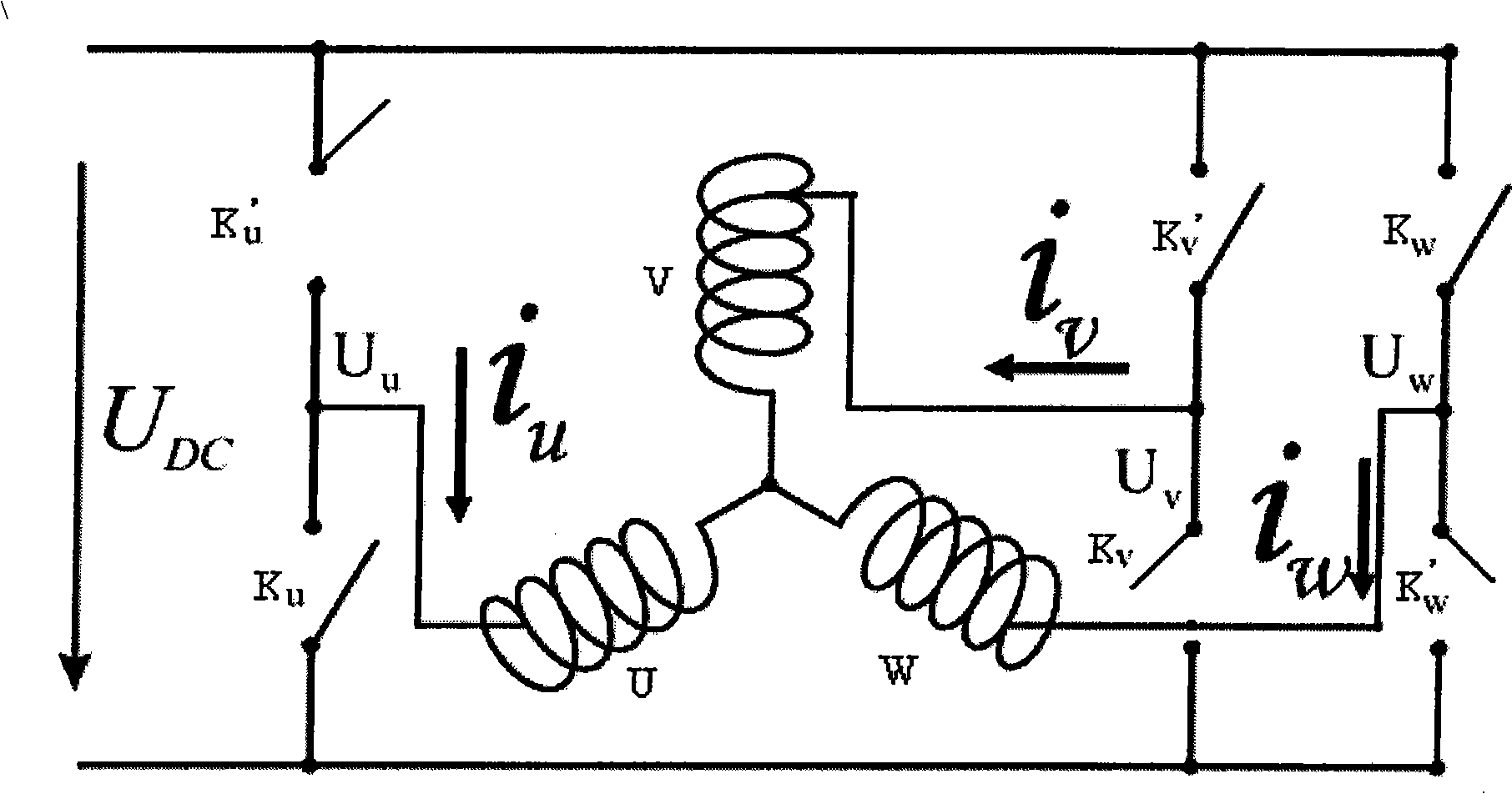
[0020] Such as Figure 11 Shown, the present invention mainly comprises following three steps:
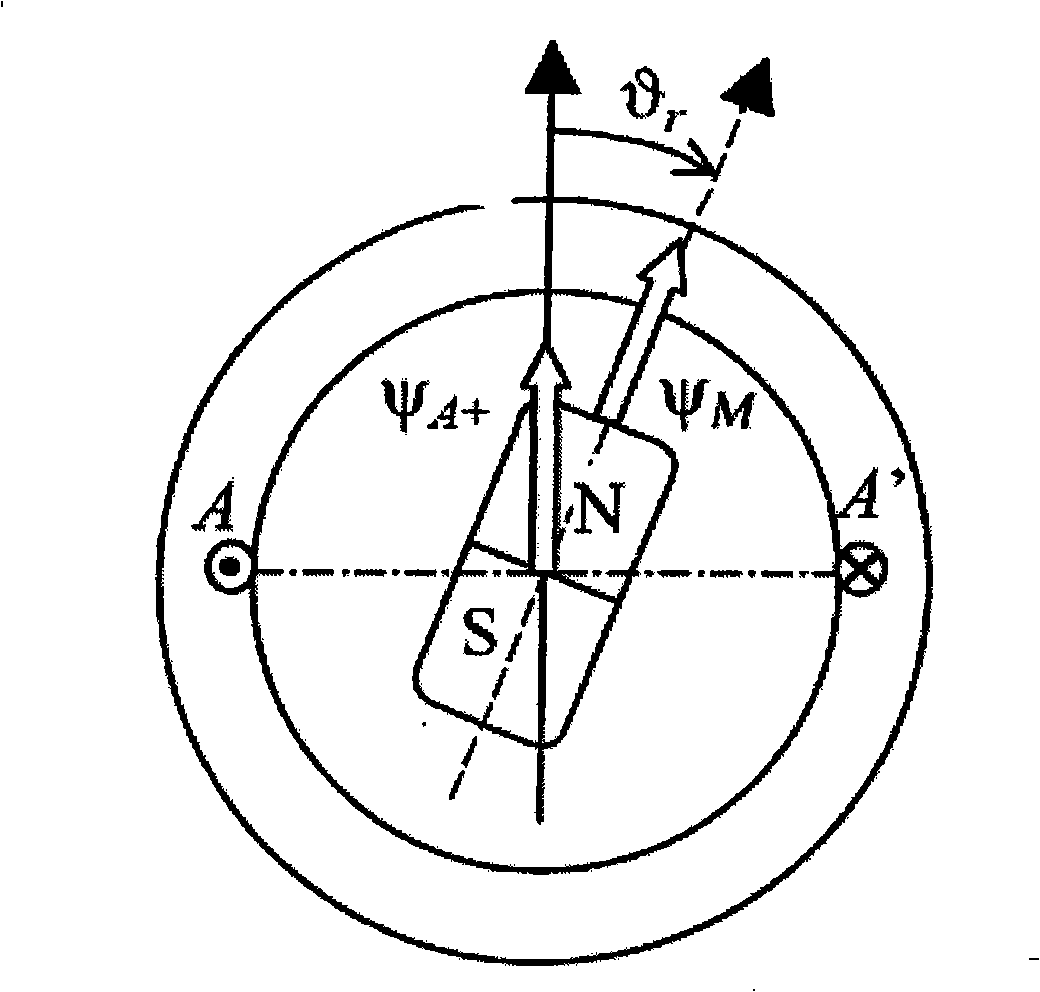
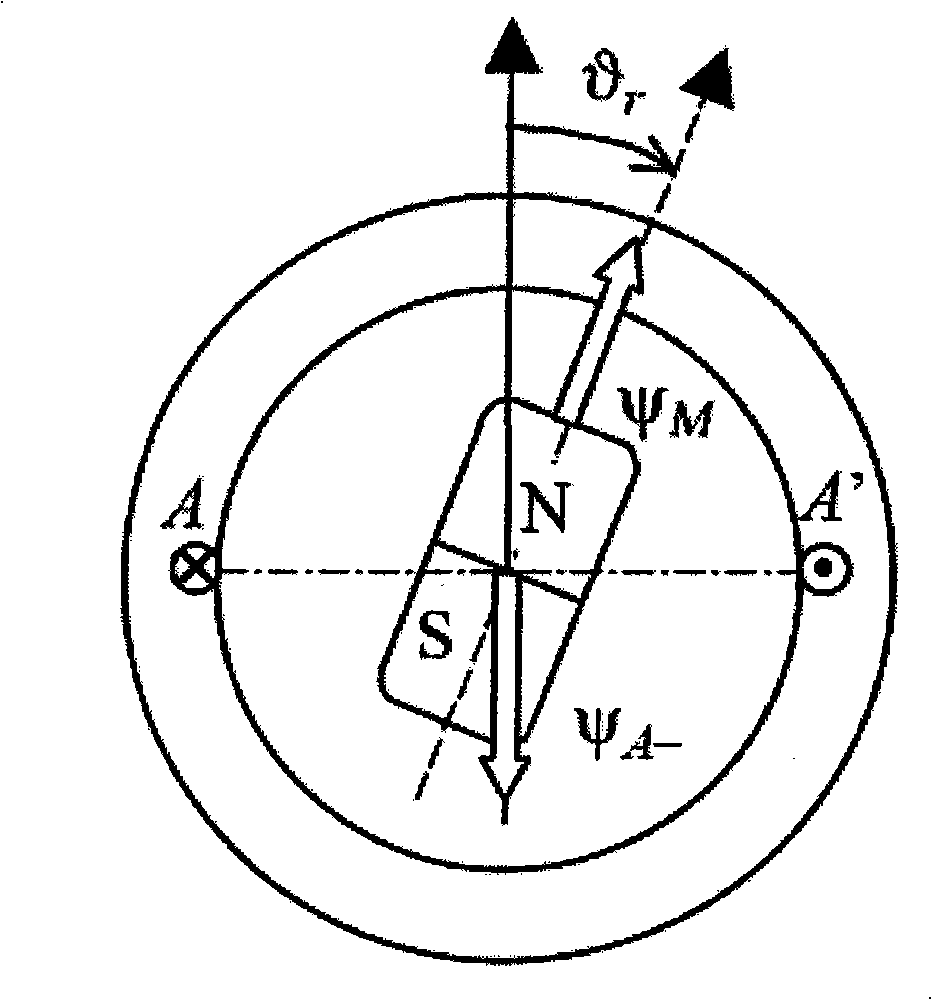
[0021] (1) In the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the rotor flux linkage can affect the flux linkage generated by the phase winding, such as figure 1 As shown, due to the saturation saliency effect, that is, when the flux linkage Ψ generated by the forward current A+ The direction of the rotor flux linkage Ψ M When the directions of the two are basically the same, the rotor flux linkage can increase the saturation degree of the stator core by affecting the phase winding (that is, the stator coil flux linkage), thereby reducing the inductance value of the phase winding; figure 2 As shown, when the reverse current produces Ψ A- The directi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com