Communication of a risk information in a multi-domain network
A risk, network layer technology, applied in the field of routing in multi-domain networks, to solve problems such as incomplete routing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
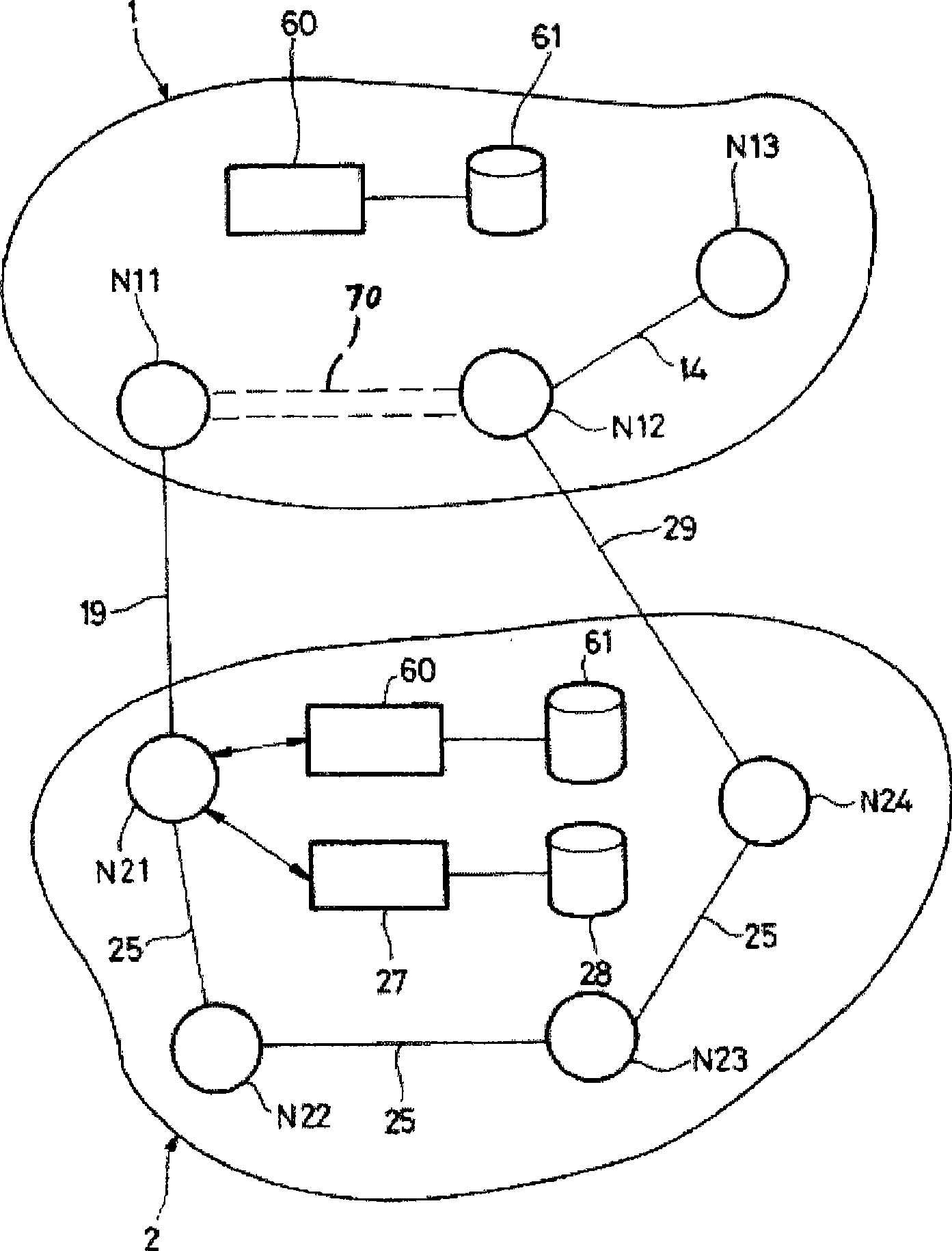
[0051] refer to figure 1 , the example communication network device includes two routing domains 1 and 2. The term "routing domain" generally refers to a collection of network elements whose address management or path computation is under the responsibility of a common entity, especially a network belonging to a single operator, autonomous system or group of autonomous systems, or an area or A set of regions.
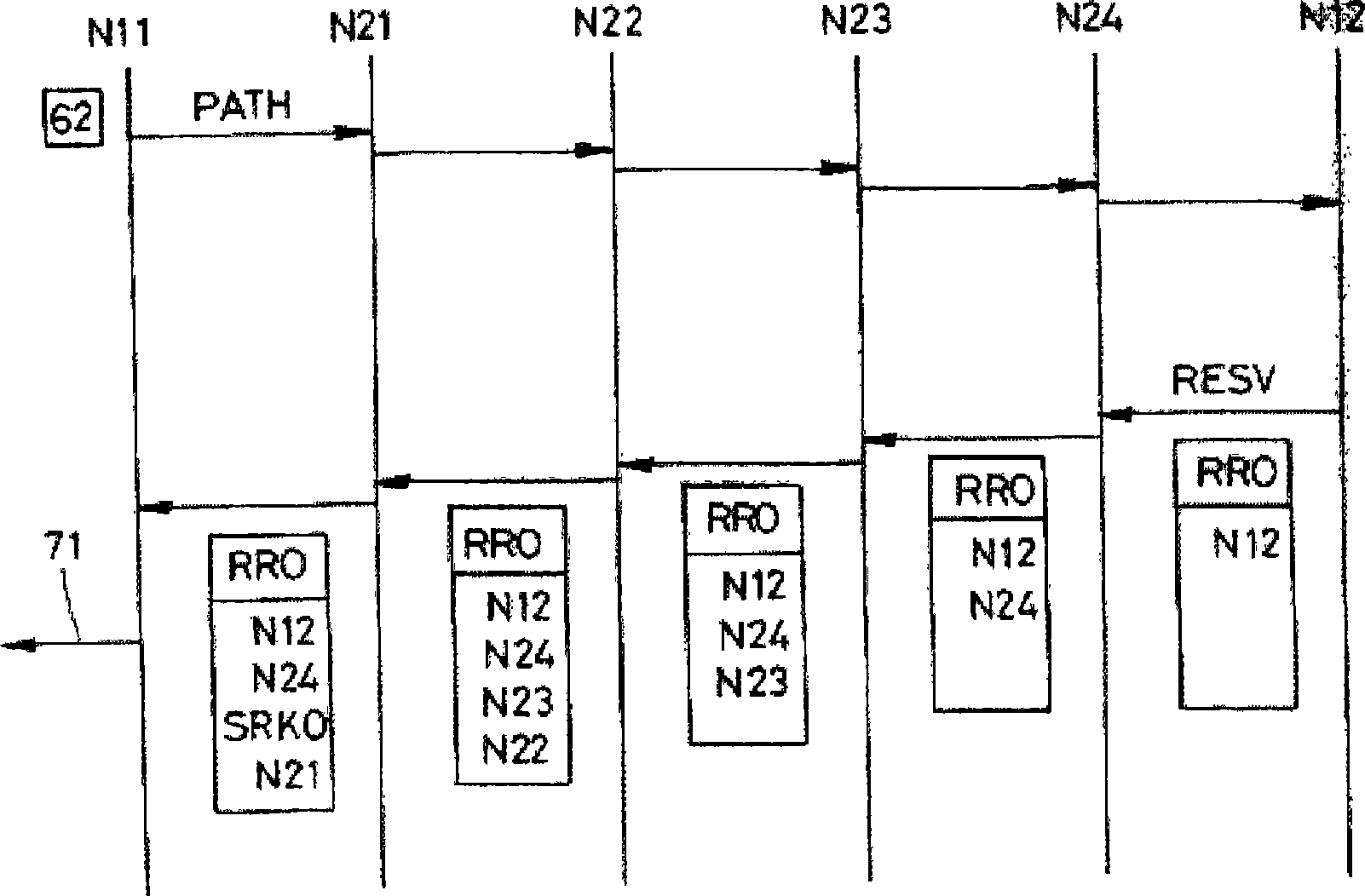
[0052] Domain 1 comprises three nodes N11, N12 and N13 which may eg be IP / MPLS routers. Intra-domain link 14 connects nodes N12 and N13. There is no intra-domain link connecting nodes N11 and N12. Nodes N11 and N12 are edge routers connecting domain 1 and domain 2 .
[0053] Domain 2 includes four nodes N21 to N24. The intra-domain link 25 connects the nodes N21 to N24. Nodes N21 and N24 are edge routers connecting domain 2 with domain 1 . The inter-domain link 19 connects the nodes N11 and N21, and the inter-domain link 29 connects the nodes N12 and N24.
[005...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com