Treatment of severe community-acquired pneumonia by administration of tissue factor pathway inhibitor (tfpi)
A technology for severe pneumonia and preparations, which can be used in drug combinations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as reducing the mortality rate of sepsis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] ala-TFPI therapy in patients with severe pneumonia
[0088] Patients with severe pneumonia were evaluated to study the possible effect of ala-TFPI treatment on a relatively homogeneous group of patients. Patients with pneumonia were identified if the investigator demonstrated that one of the sources of sepsis was pneumonia. Other sites of infection may also be present. Aspiration pneumonia (patient) was excluded due to the difficulty in distinguishing infections due to chemical sequelae. Identified pneumonia patients were then classified as culture-positive (either evidence of infection, such as cultures or Gram strains (positive)) or culture-negative (negative cultures or no cultures). The patient was treated by continuous intravenous infusion at a dose of 0.025 mg / kg / hour with a non-glycosylated ala-TFPI preparation expressed in Escherichia coli containing 300 mM L-arginine, 20 mM sodium citrate, pH 5 .5. Prepare buffer solution with osmolality of 560+ / -110mOsm. T...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Analysis of confirmed infection types in patients with severe pneumonia
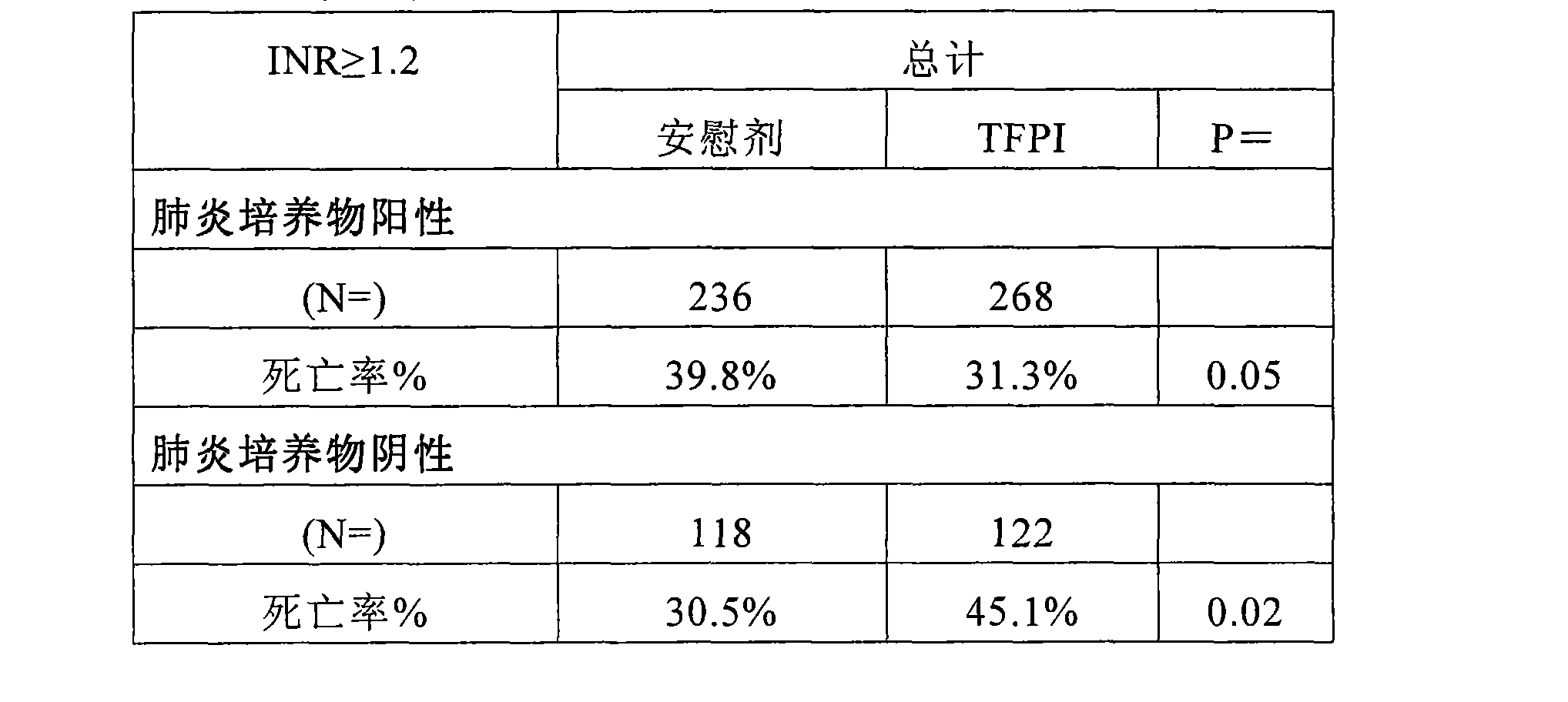
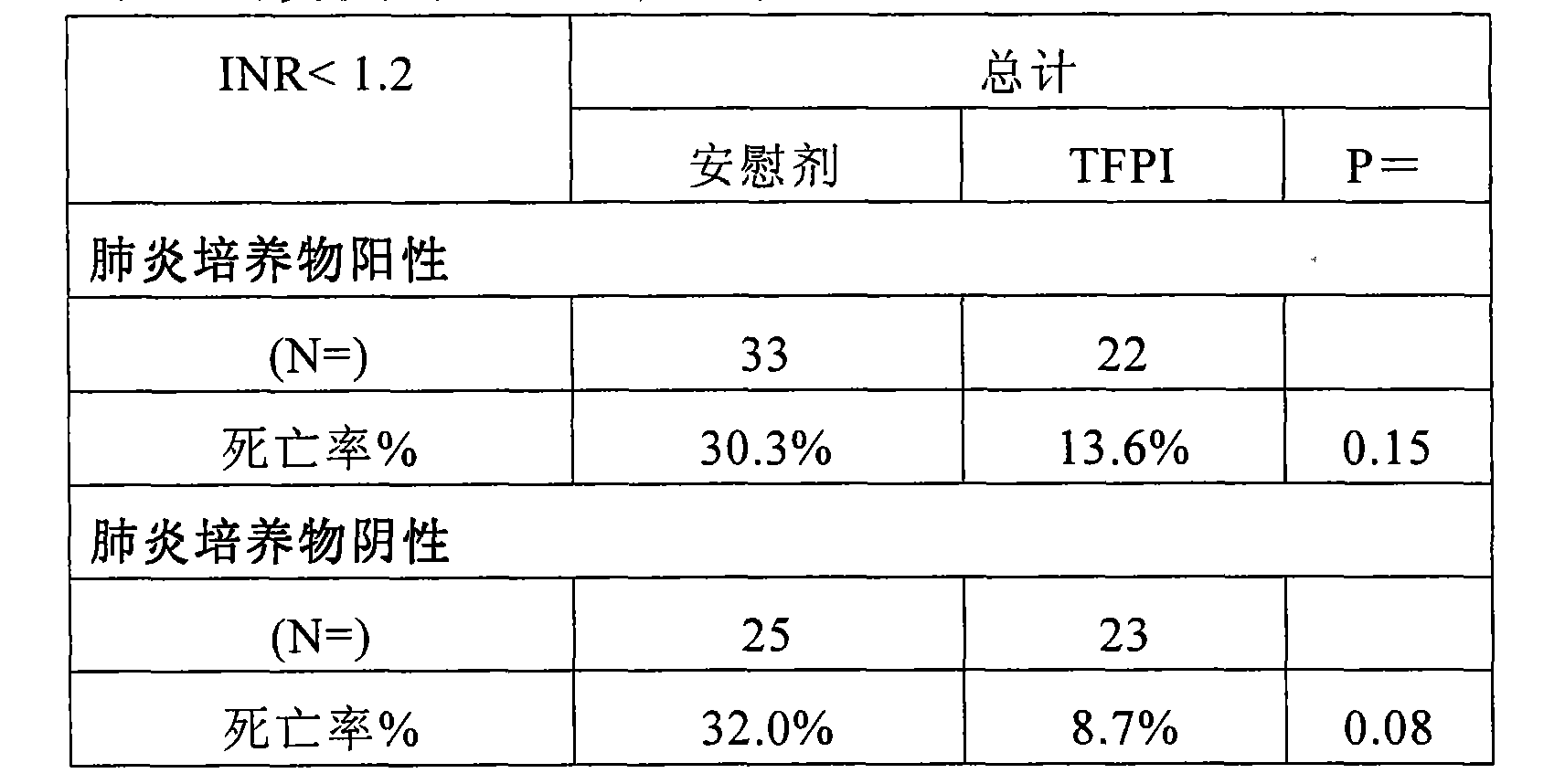
[0102] As noted above, the overall benefit of ala-TFPI treatment was observed in patients with the most established infection, ie, those with positive blood cultures. Analyzing severe pneumonia patients with confirmed infection types, ala-TFPI treatment efficacy was observed in subjects with positive blood cultures and other evidence (Table 6). Its effect was strongest in the bacteremia group, that is, the group with the highest probability of infection or the most obvious source of infection.
[0103] Table 6. Mortality by (different) culture status and pneumonia status
[0104]
[0105]
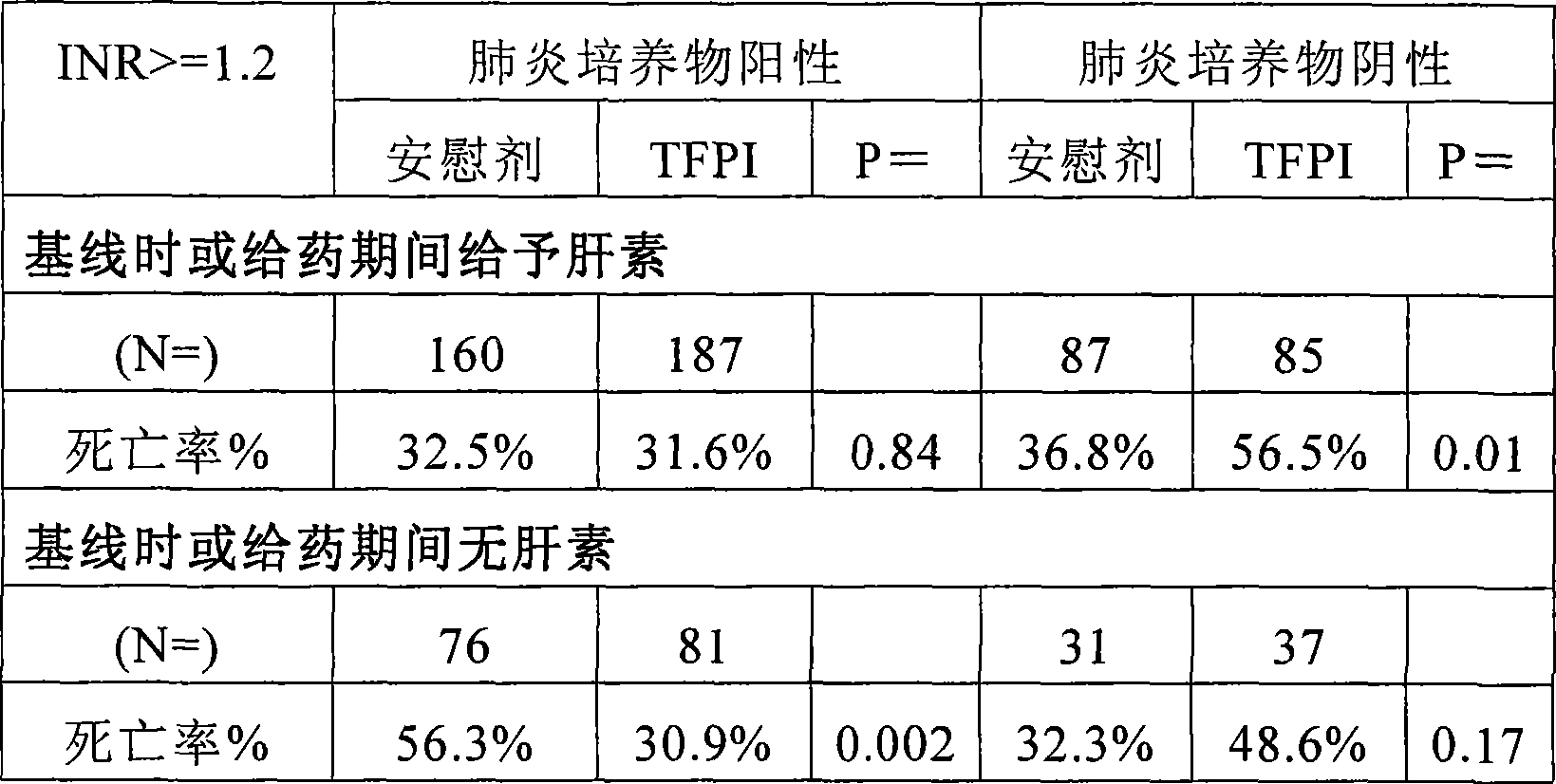
[0106] As shown above, patients with proven infection (blood + "other" evidence) benefited from TFPI treatment when heparin was not used. Drug efficacy in the pneumonia group most likely contributed to this result (Table 7). This finding seems to indicate that the benefit of endogenous anticoagulants i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com