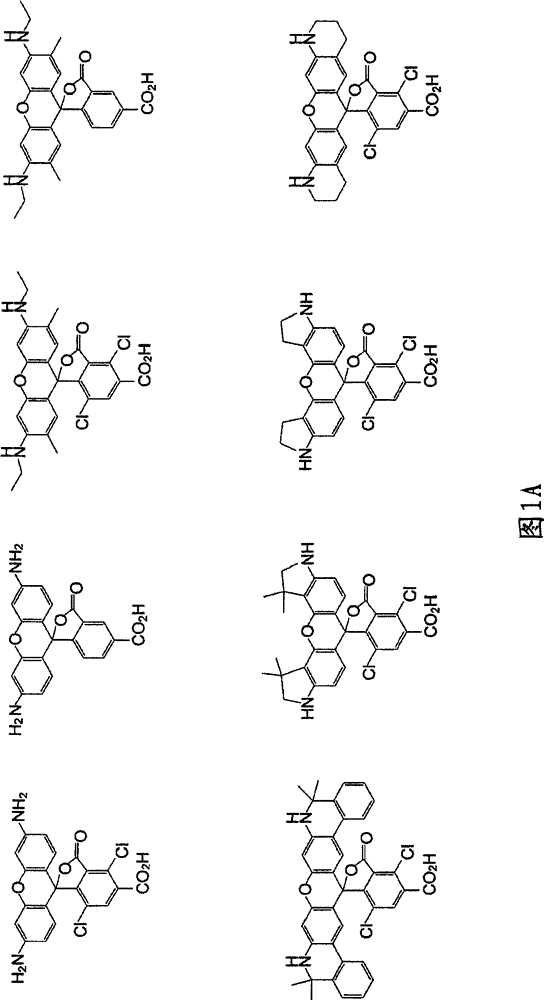
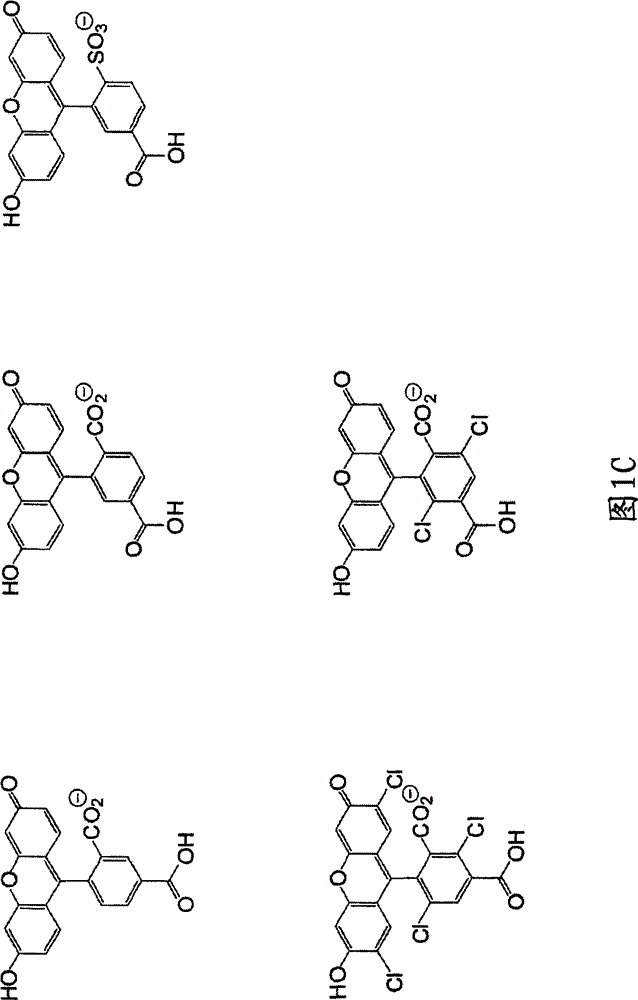
Reagents for Synthesis of Rhodamine-Labeled Oligonucleotides
An oligonucleotide, labeling technology, applied in the field of reagents for synthesizing rhodamine-labeled oligonucleotides, can solve the problems of increased steps and labor, large cost and inconvenience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0271] Example 1: Synthesis of N-protected NH-rhodamine phosphoramidite synthesis reagent
[0272] Parent NH-rhodamine dyes including carboxyl substituents at the C5- or C6-position were synthesized as described in US Patent No. 4,622,400, US Patent No. 5,750,409, US Patent No. 5,847,162, US Patent No. 6,017,712, US Patent as described in US Patent No. 6,080,852, US Patent No. 6,184,379 or US Patent No. 6,248,884. The parent NH-rhodamine dye is subsequently protected by an acetyl or trifluoroacetyl protecting group on an exocyclic amine, and the resulting N-protected NH-rhodamine dye is converted to Hydroxyl-amide derivatives and conversion of the hydroxyl functionality to phosphoramidites using standard procedures. The overall composition diagram is explained below:
[0273]
[0274] Protected with acetyl . NH-rhodamine dye acid 6 (mono-TEA salt, 1.676 mmol) was suspended in DCM (40 mL) and TEA (3.67 mL). Acetic anhydride (3.13 mL) was added, and the reaction mixture...
Embodiment 2
[0282] Example 2: Synthesis of a heterodimeric dye network
[0283] A dye network comprising O-protected fluorescein attached to N-protected NH-rhodamine was synthesized as set forth below:
[0284]
[0285] Bis-acetyl N-protected NH-rhodamine NHS ester 16 (324 mg, 0.460 mmol) was dissolved in a solution of DMF (8 mL) and DIPEA (0.3 mL). Fluorescein derivative 17 (239 mg, 0.32 mmol; synthesized as described in US Patent No. 5,800,996) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. The mixture was evaporated and then co-evaporated with MeOH (2x). The residue was dissolved in 10% MeOH / DCM (100 mL) and washed with brine solution (100 mL). The aqueous layer was extracted with 10% MeOH / DCM (50 mLx3), and the combined organic layers were dried (Na 2 SO 4 ), filtered and evaporated. The residue was purified using flash chromatography on silica using a gradient of MeOH / DCM from 10% to 30% as eluent. Appropriate fractions were evaporated to yield 2...
Embodiment 3
[0287] Embodiment 3: Synthesis of heterodimer dye network phosphoramidite
[0288] Phosphoramidite synthesis reagents comprising a heterodimeric dye network as a labeling moiety were synthesized as set forth below:
[0289]
[0290] A solution of heterodimeric dye network 19 (0.173 mmol), DIPEA (1.028 mL) and pivalic anhydride (0.702 mL) in DCM (10 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 1 day. Add H2 0 (5 mL) and continued stirring for 1 h. The reaction mixture was diluted with DCM (50 mL) and washed with H 2 O (40 mL) wash. The aqueous layer was extracted with DCM (40 mL). The combined organic layers were dried (Na 2 SO 4 ), filtered and evaporated. The residue was purified by flash chromatography on silica using a gradient of MeOH / DCM from 3% to 15% as eluent. Appropriate fractions were evaporated to yield 0.145 mmol (84%) of bis-acetyl bis-pivaloyl heterodimer dye derivative 21 (as DIPEA salt).
[0291] Dye derivative 21 (0.146 mmol) was suspended in a dissolved...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com