Method and device for monitoring an extracorporeal blood circuit
A technology of extracorporeal blood circuit and extracorporeal circuit, which is applied in the direction of blood circulation processing, suction equipment, etc., and can solve problems such as undetectable error states
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
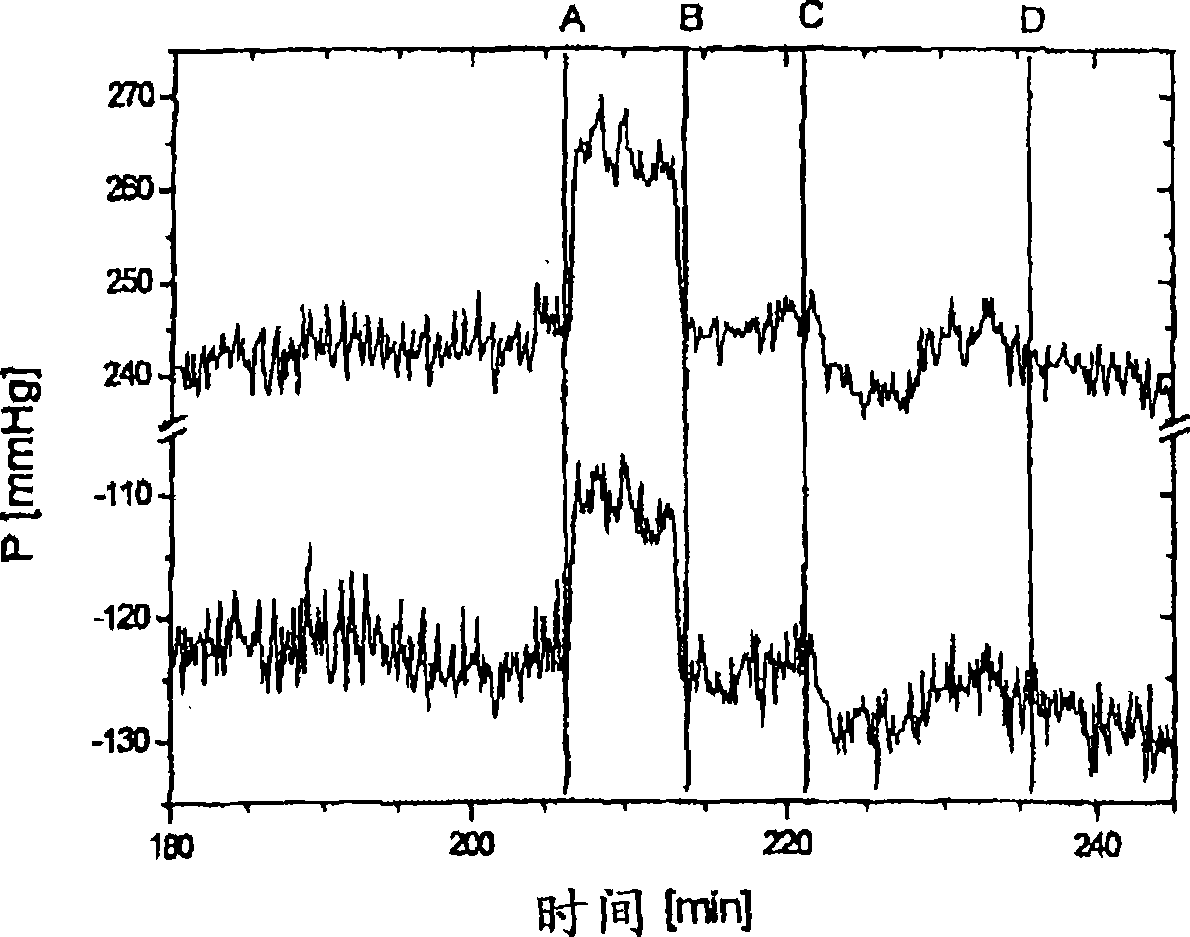
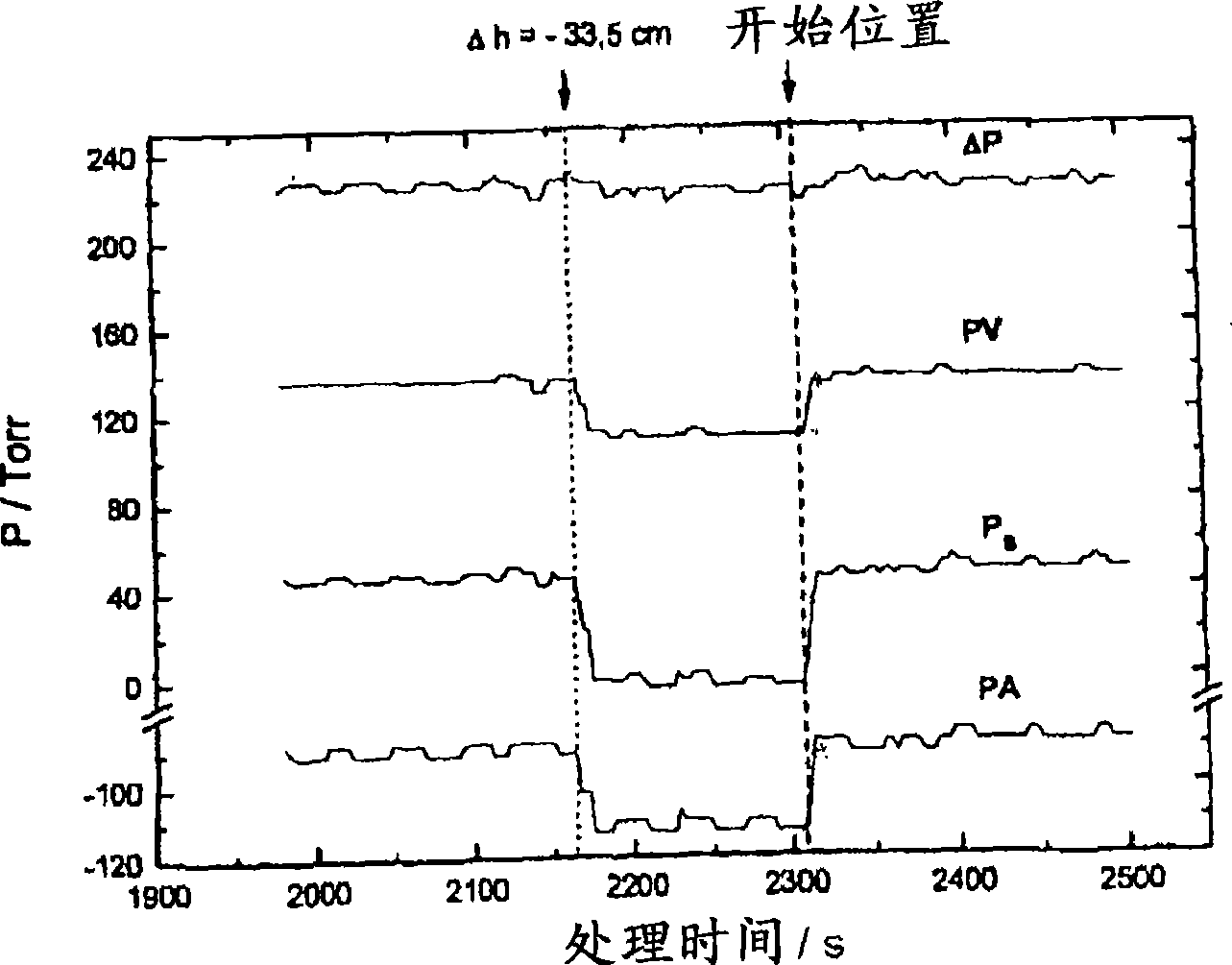
[0034] The arterial and venous pressures measured in the arterial and venous branches of the extracorporeal blood circuit include in each case the dynamic pressure in the extracorporeal circuit and the dynamic pressure in the patient's vascular access generated by the flow of the blood pump .
[0035] The dynamic pressure in the extracorporeal circuit is a function of the extracorporeal blood flow and the sum of the resistance to flow in the extracorporeal circuit. The arterial flow resistance and the venous flow resistance are different because of the different geometries of the parts through which the blood flows, so the sum of the arterial and venous pressures (hereinafter, referred to as Ps) is likewise a function of the blood flow. In known blood purification methods, the delivery rate Q of the blood pump B Usually set to a fixed value. Therefore, when the viscosity of the blood is constant, the sum of the flow resistances in the extracorporeal circuit is also constant....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com