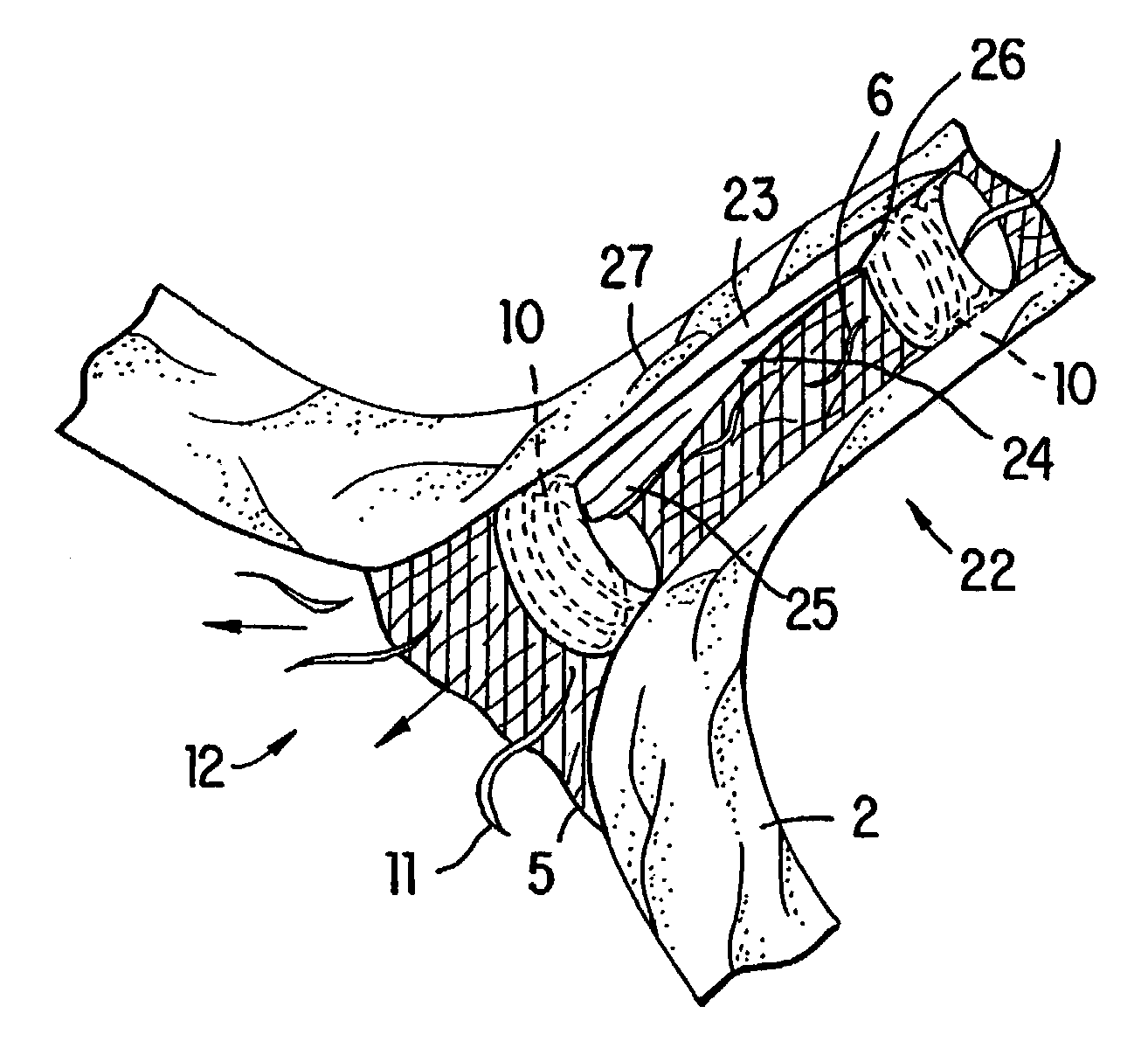
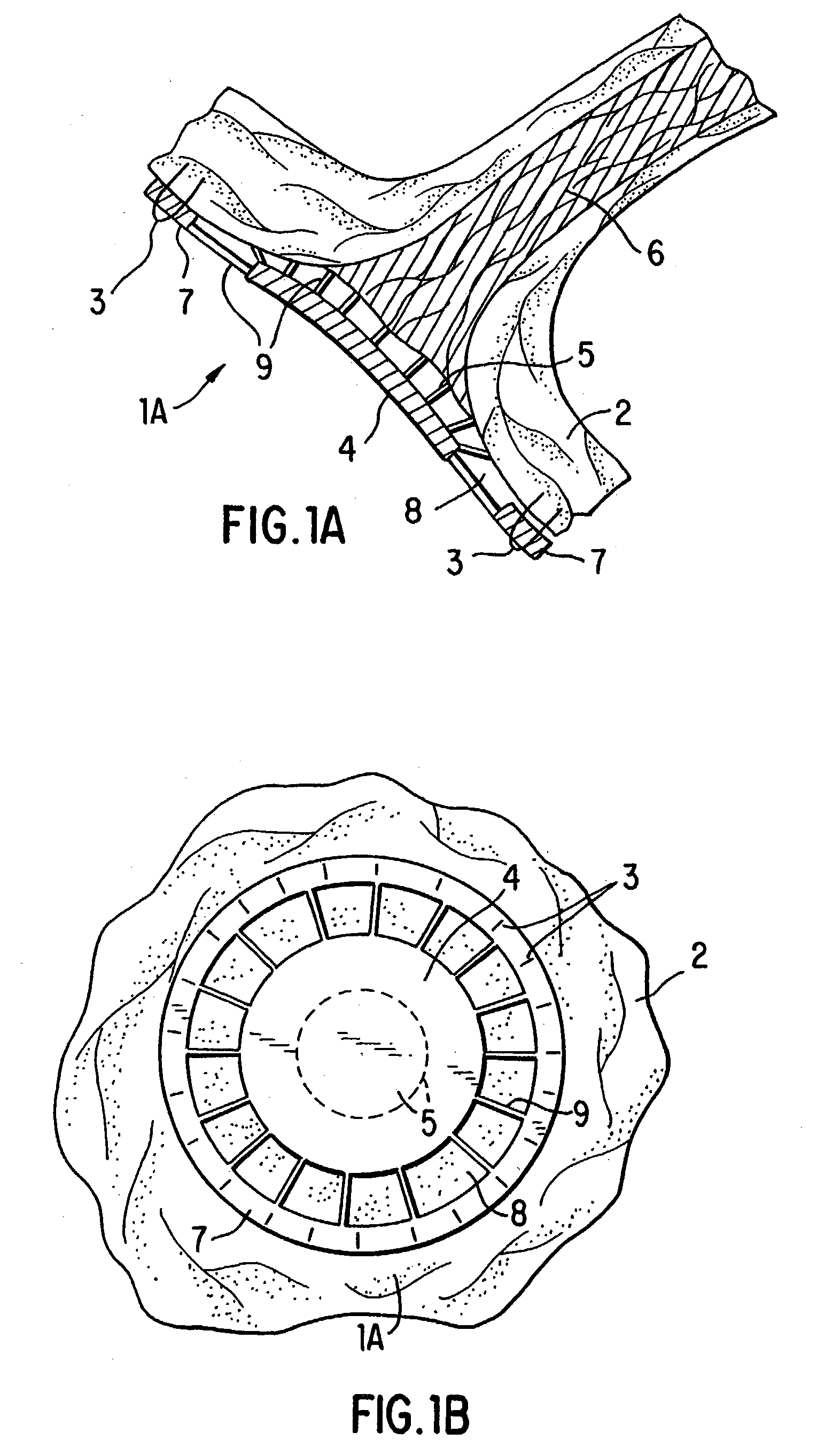
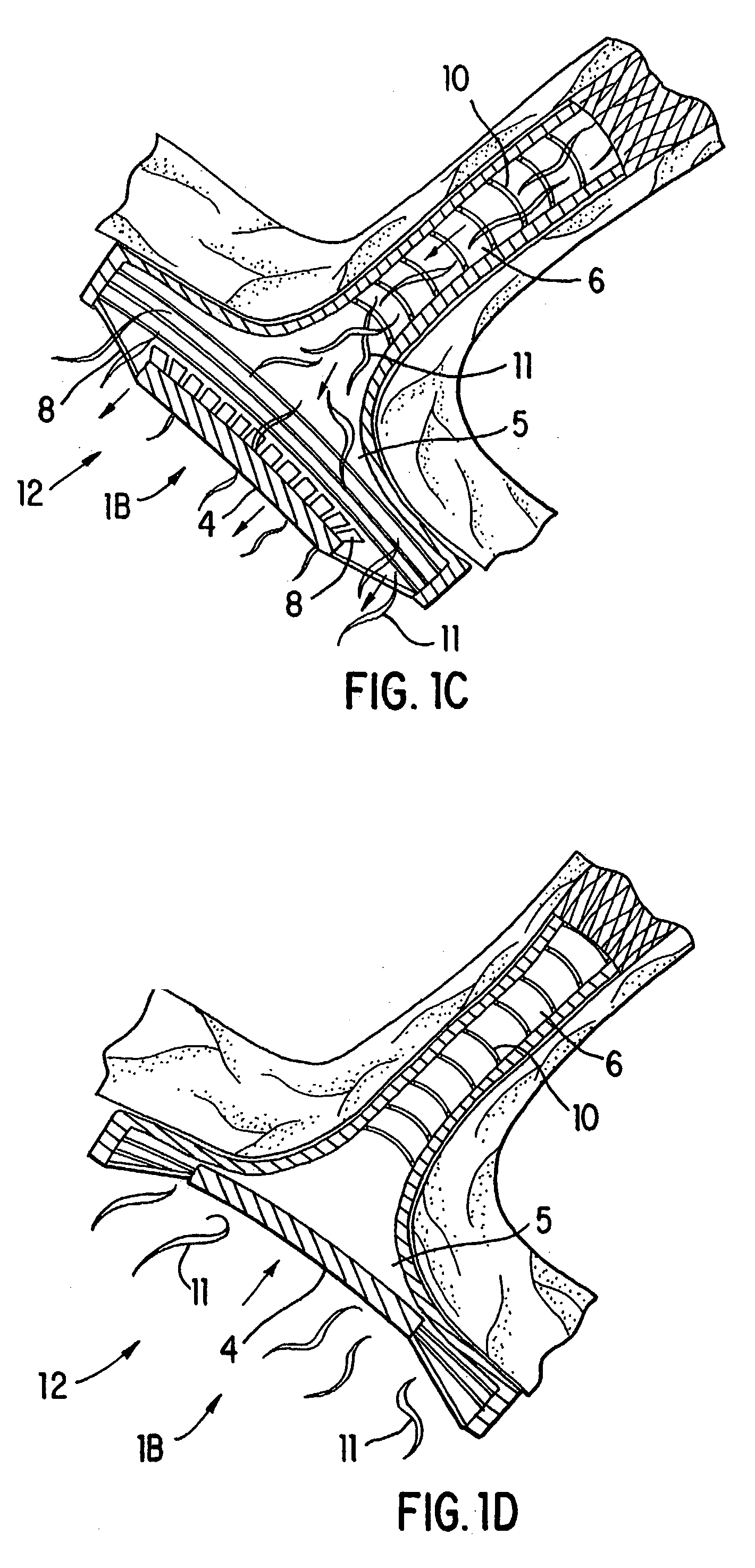
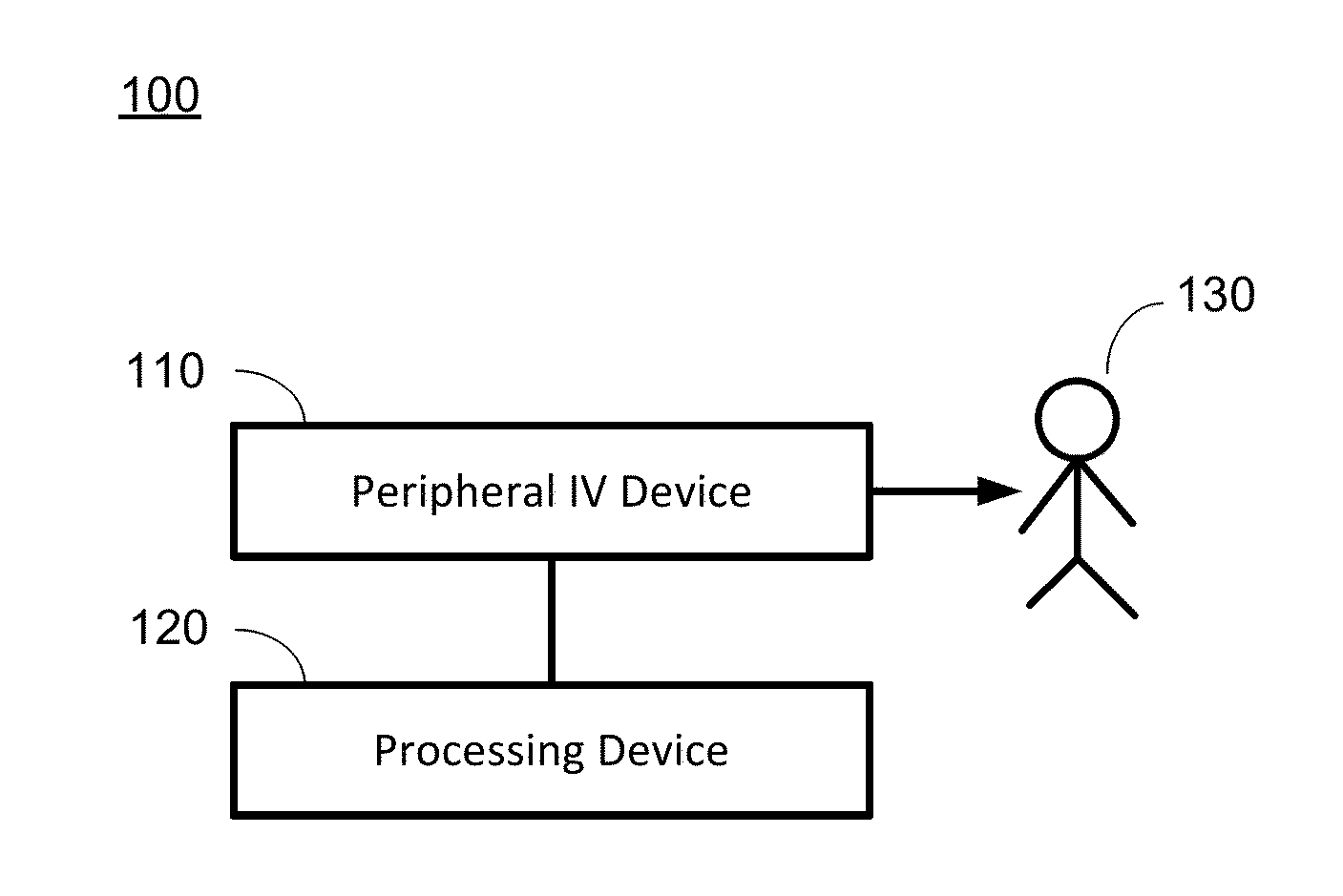
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Venous Pressures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Venous pressure is the vascular pressure in a vein or the atria of the heart. It is much lower than arterial pressure, with common values of 5 mmHg in the right atrium and 8 mmHg in the left atrium.
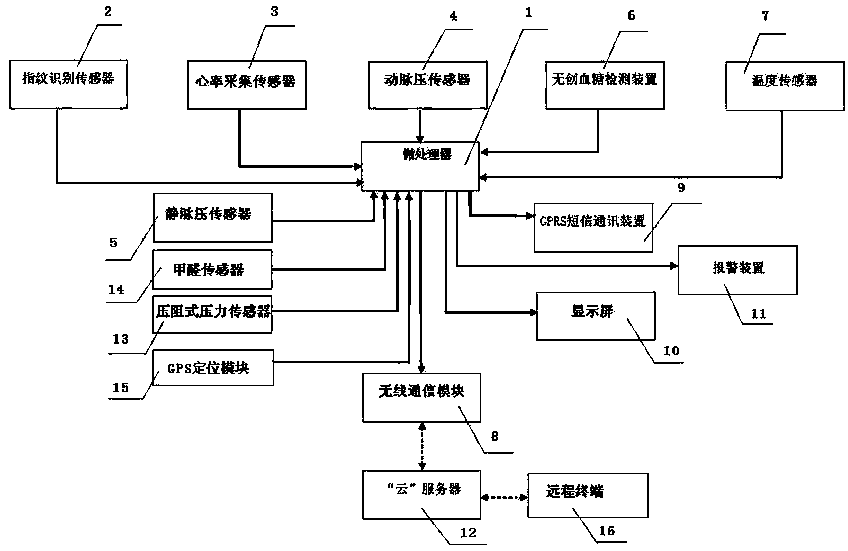
Physiological index detector
ActiveCN103393414AHigh densityImprove scalabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCurve shapeDecreased mean arterial pressure
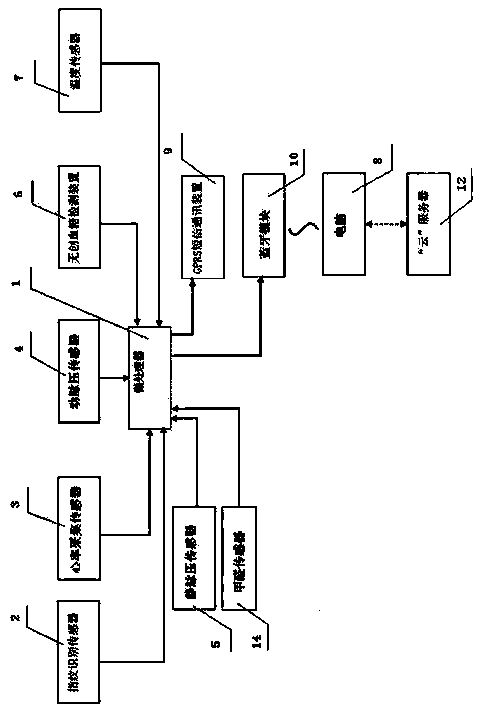
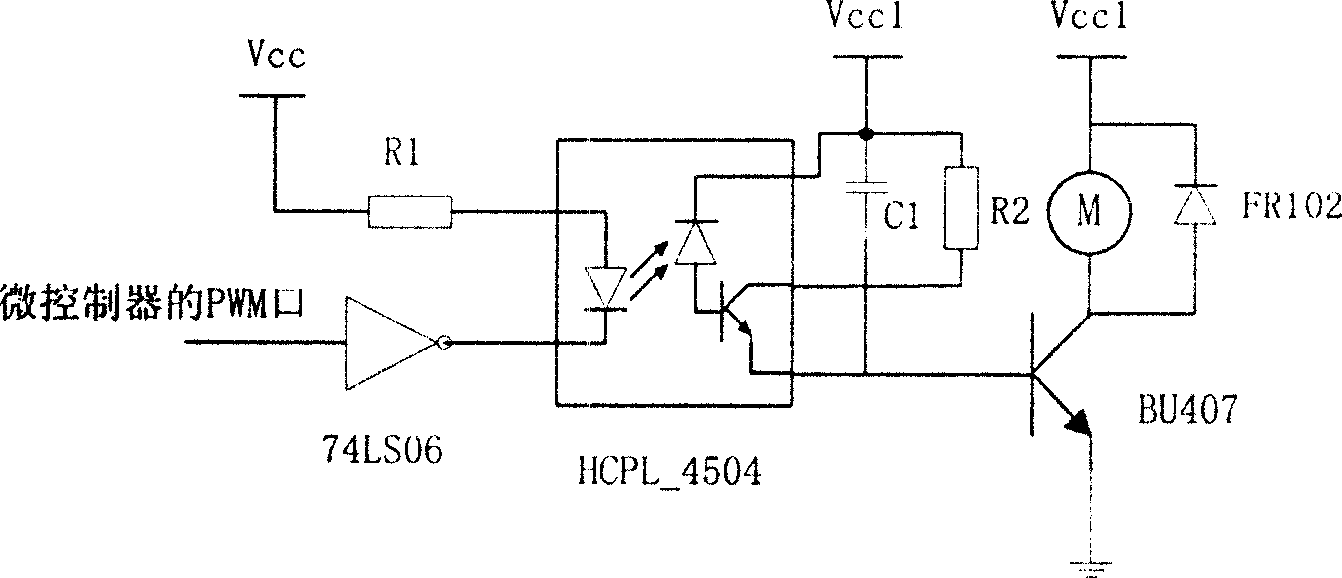
The invention discloses a physiological index detector. The physiological index detector comprises a microprocessor, a fingerprint identification sensor, a heart rate acquisition sensor, an arterial pressure sensor, a venous pressure sensor, a noninvasive blood glucose detection device, a temperature sensor, a wireless communication module, a GPRS short message communication device, a display screen and a warning device. The physiological index detector is a wristband-type structure fit to the wrist curve of the human body, components in the circuit portion are installed by using a flexible printed circuit (FPC), the FPC is mounted in the wristband-type physiological index detector in a circular arc shape, the display screen is an organic light emitting diode (OLED) which is arranged along the outer side of the wristband-type physiological index detector in an arc-shaped curve shape, and the wireless communication module transmits the acquired physiological index data of the human body to a cloud server for editing, preserving and processing. The physiological index detector is convenient to carry and measure and data are uploaded to the cloud, so that the physiological index data can be preserved for a long time, analyzed, tracked and warned.
Owner:JIANGSU HUITONG GRP
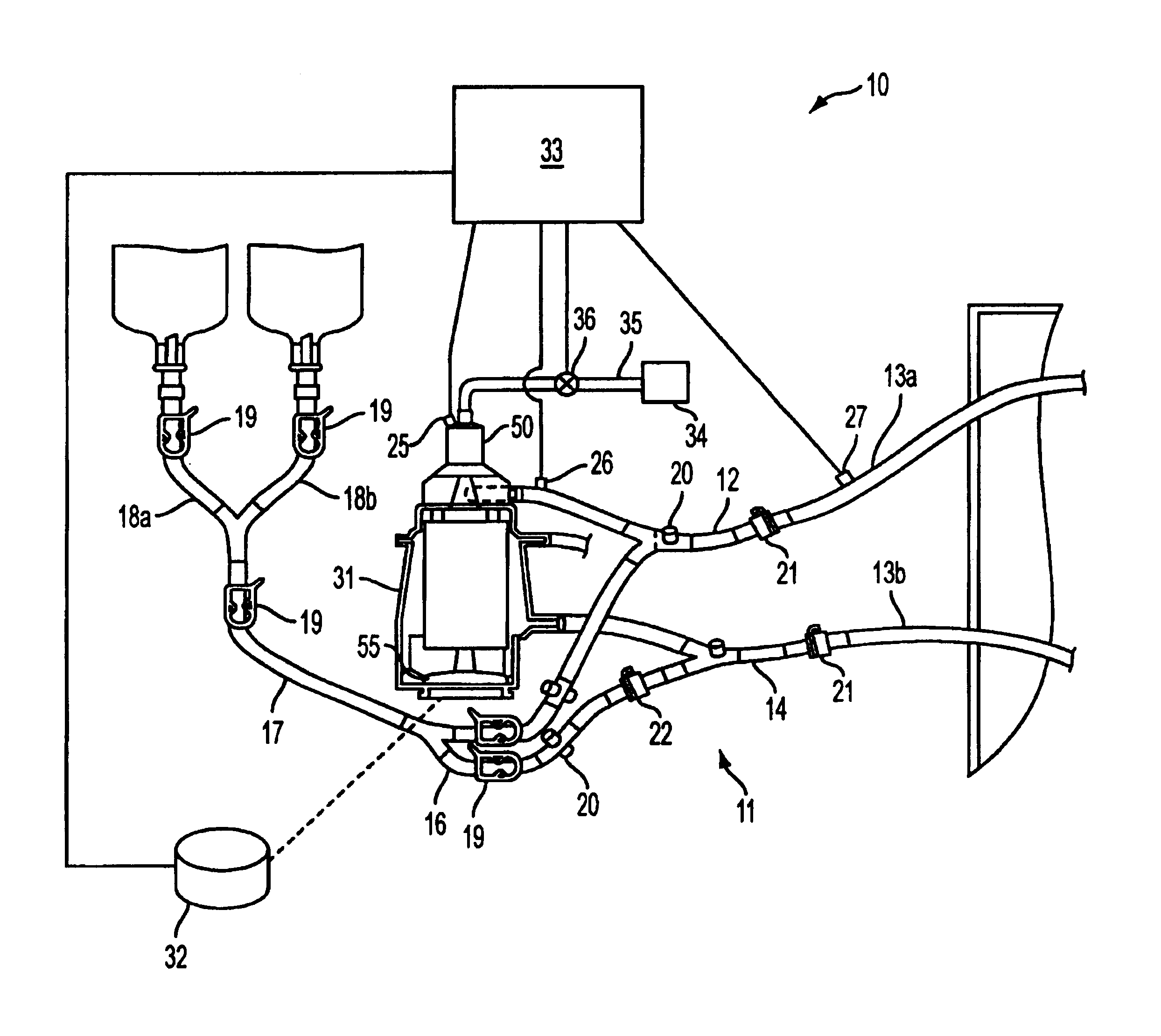
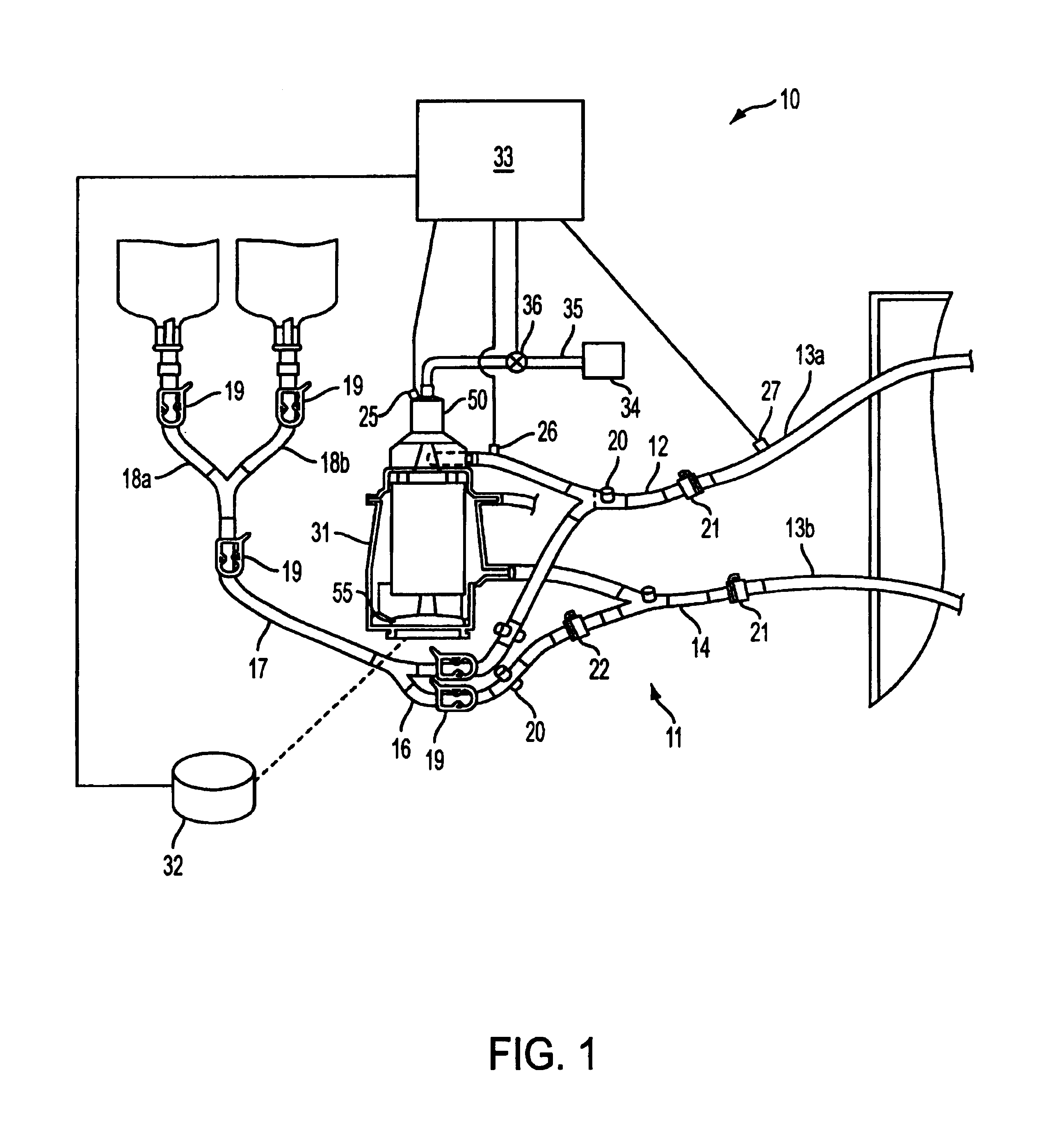
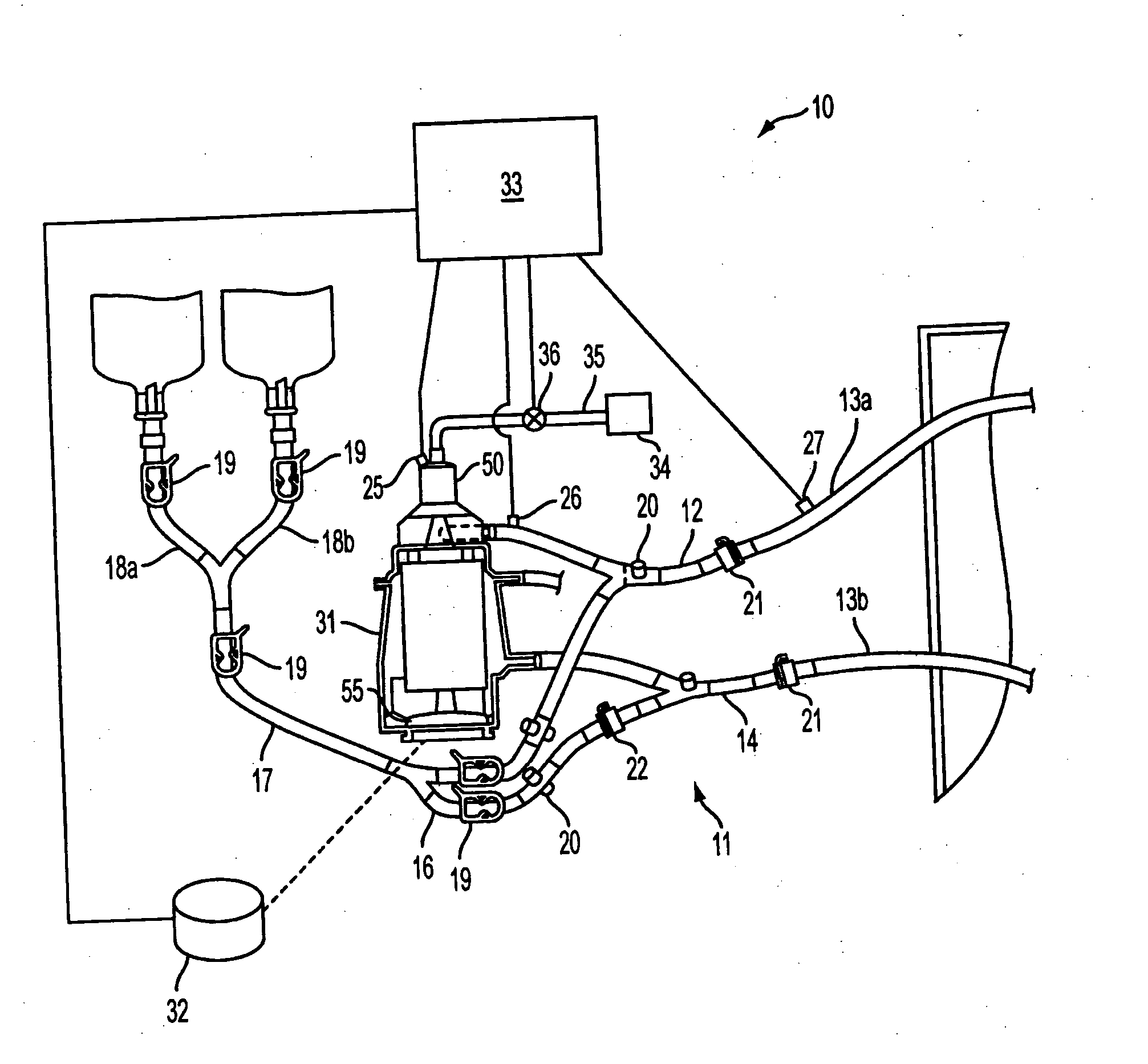
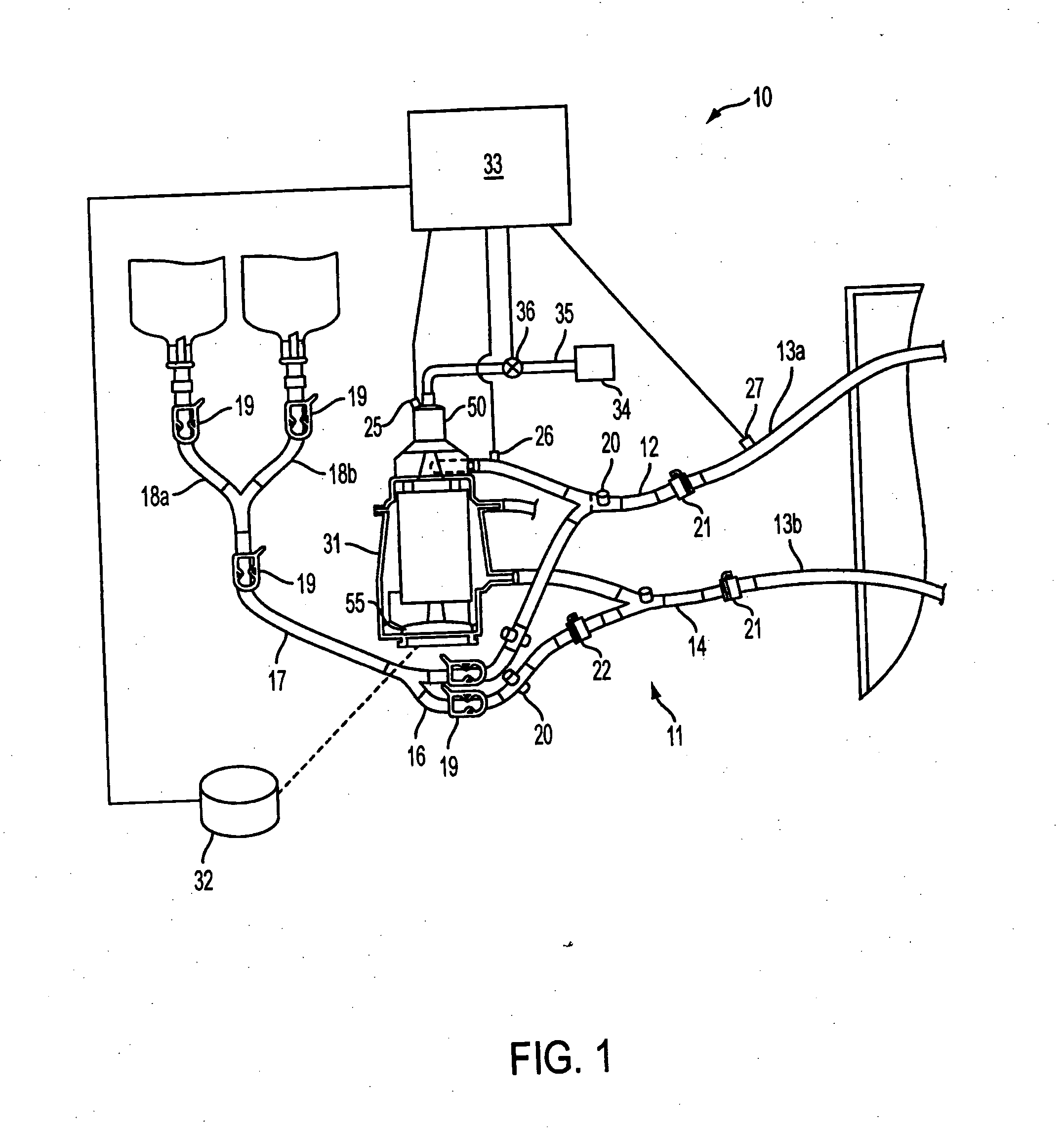
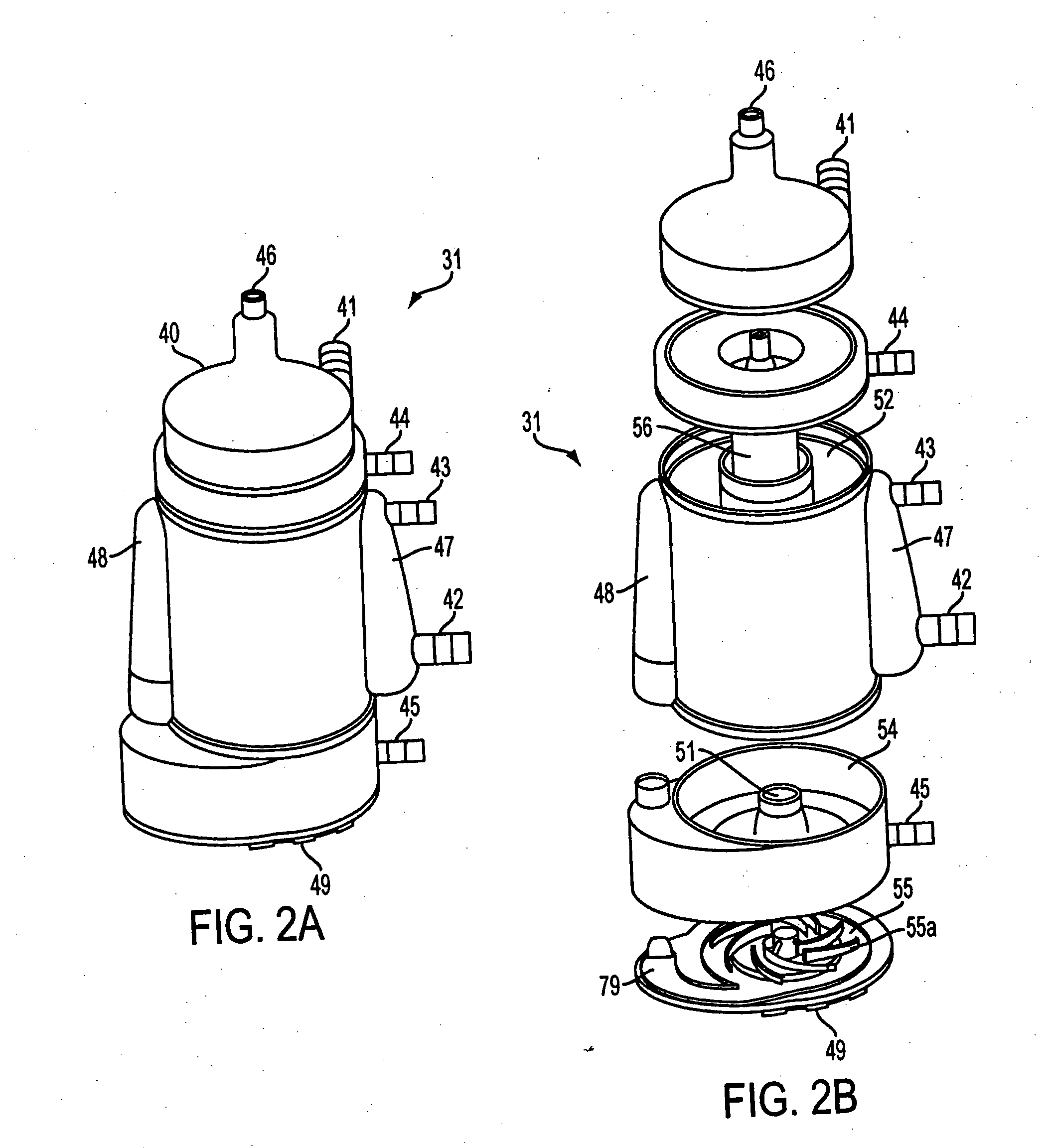
Extracorporeal blood handling system with automatic flow control and methods of use
InactiveUS7022099B2Extension of timeImprove abilitiesOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationAutomatic controlHandling system
Apparatus for processing blood in an extracorporeal circuit with automatic flow control is provided in which error conditions are sensed and system operation is modulated responsive to the error conditions. The apparatus includes an extracorporeal blood processing system, at least one sensor that senses the presence or absence of gas or monitors venous pressure, and a controller operably coupled to the blood processing system to selectively reduce pump speed or to reconfigure flow paths within the blood processing system responsive to the sensor output.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK +1
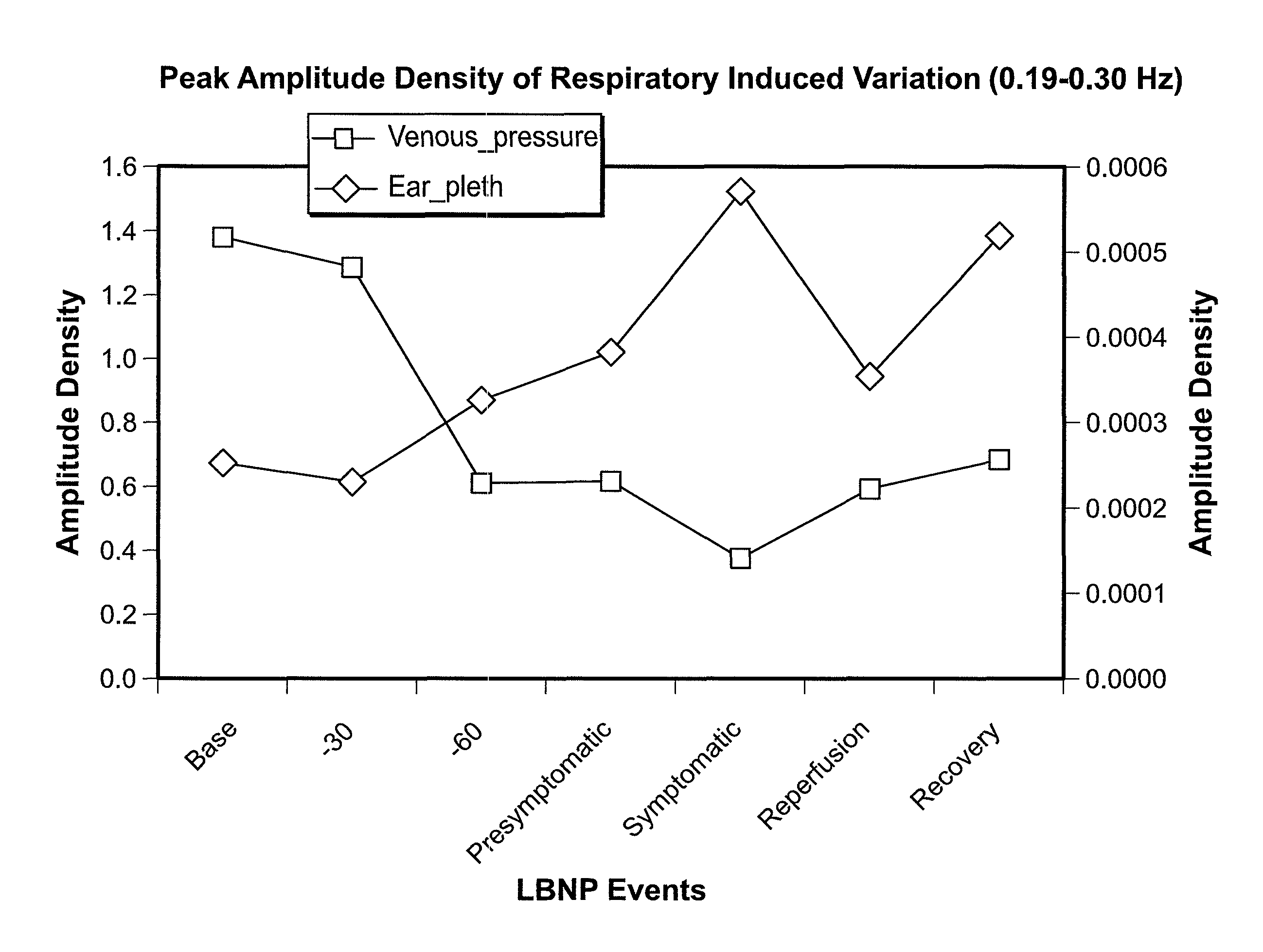
Volume Status Monitor: Peripheral Venous Pressure, Hypervolemia and Coherence Analysis
ActiveUS20100191128A1Reduce blood volumeEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterFluid replacementCoherence analysis
Systems and methods are provided for monitoring changes in blood volume using waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. In particular, the systems and methods relate to detecting ventilation-induced variation (VIV) of waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. Advantageously, the systems and methods may relate to analyzing VIV in peripheral venous pressure (PVP). Thus, the VIV of PVP may be measured, wherein decreased VIV is indicative of decreased blood volume In exemplary embodiments, such as involving spontaneous breathing, it may be necessary to account for changes in respiratory signal strength. Thus systems and methods are also provided for assessing coherence between ventilation and VIV for a flow or pressure waveform. Specifically, coherence is evaluated by comparing the waveform to a detected respiratory signal. Finally, systems and method are provided for distinguishing the impact of respiration on the PG signal during hypervolemia as compared to hypovolemia. Such systems and methods may advantageously be utilized to monitor fluid status during fluid replacement.
Owner:SHELLEY KIRK H +2
Pressure measurement device
InactiveUS20060094966A1Adequate responseReduce stressCatheterIntracranial pressure measurementPressure transmissionEngineering
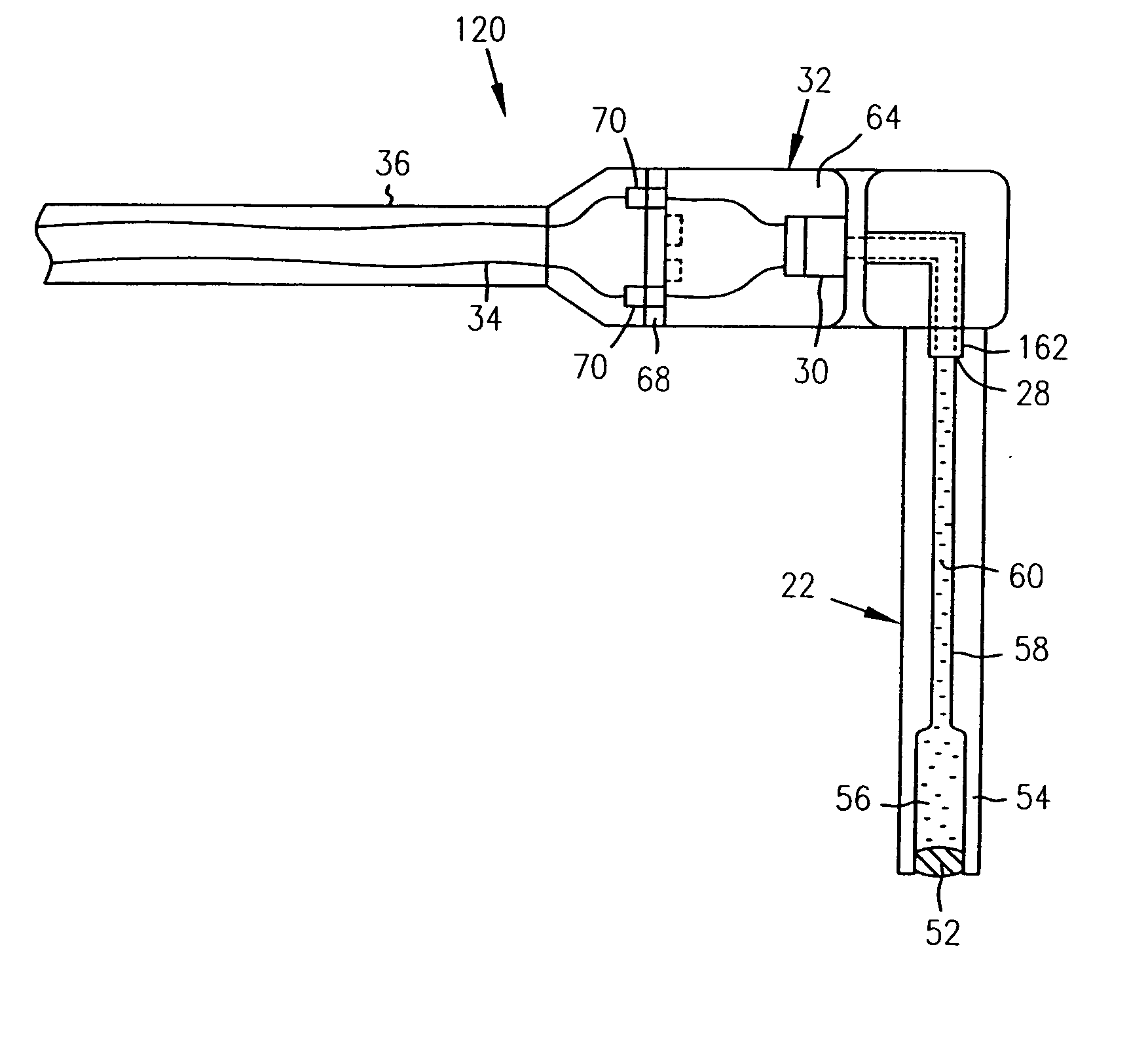
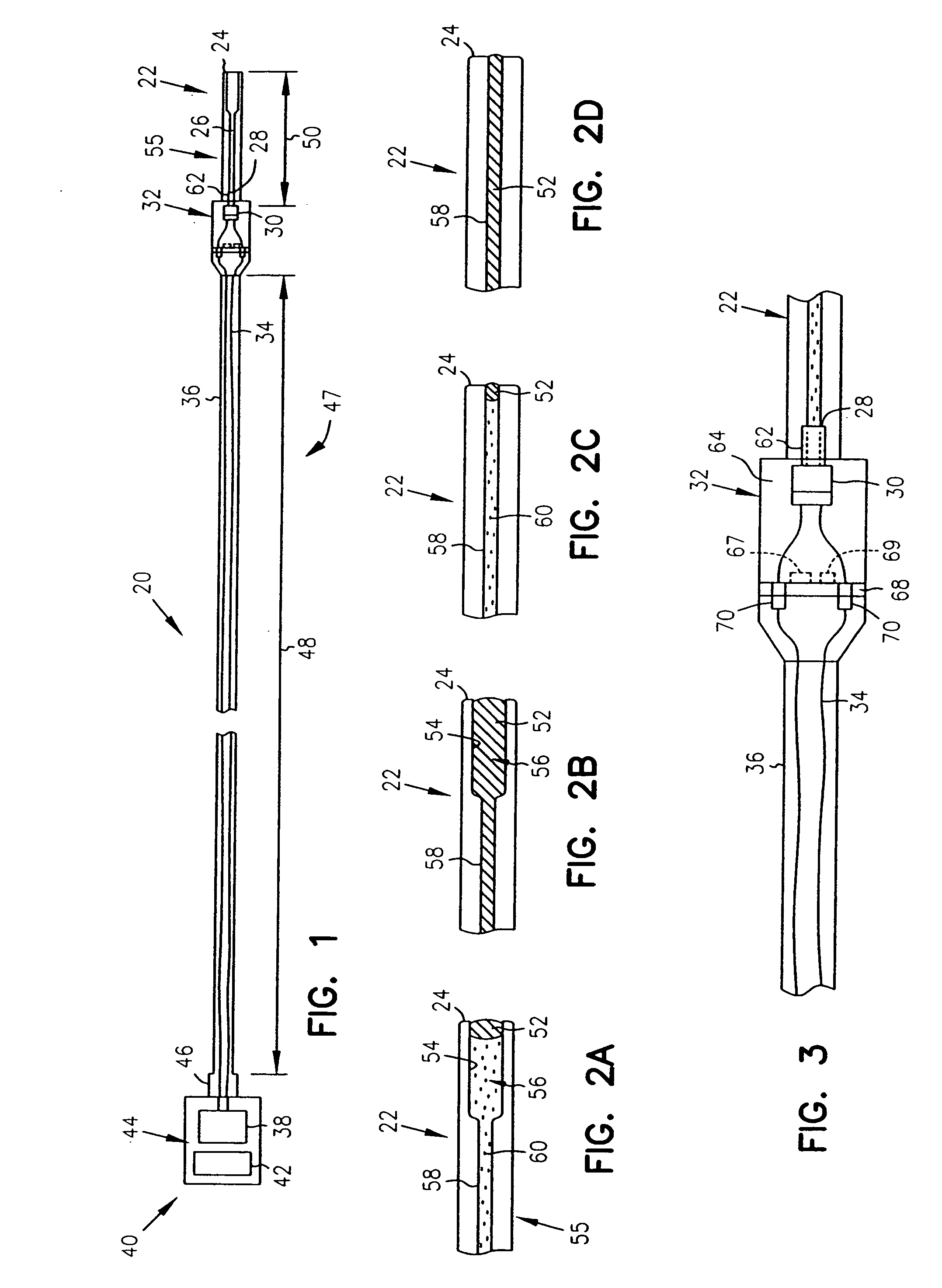
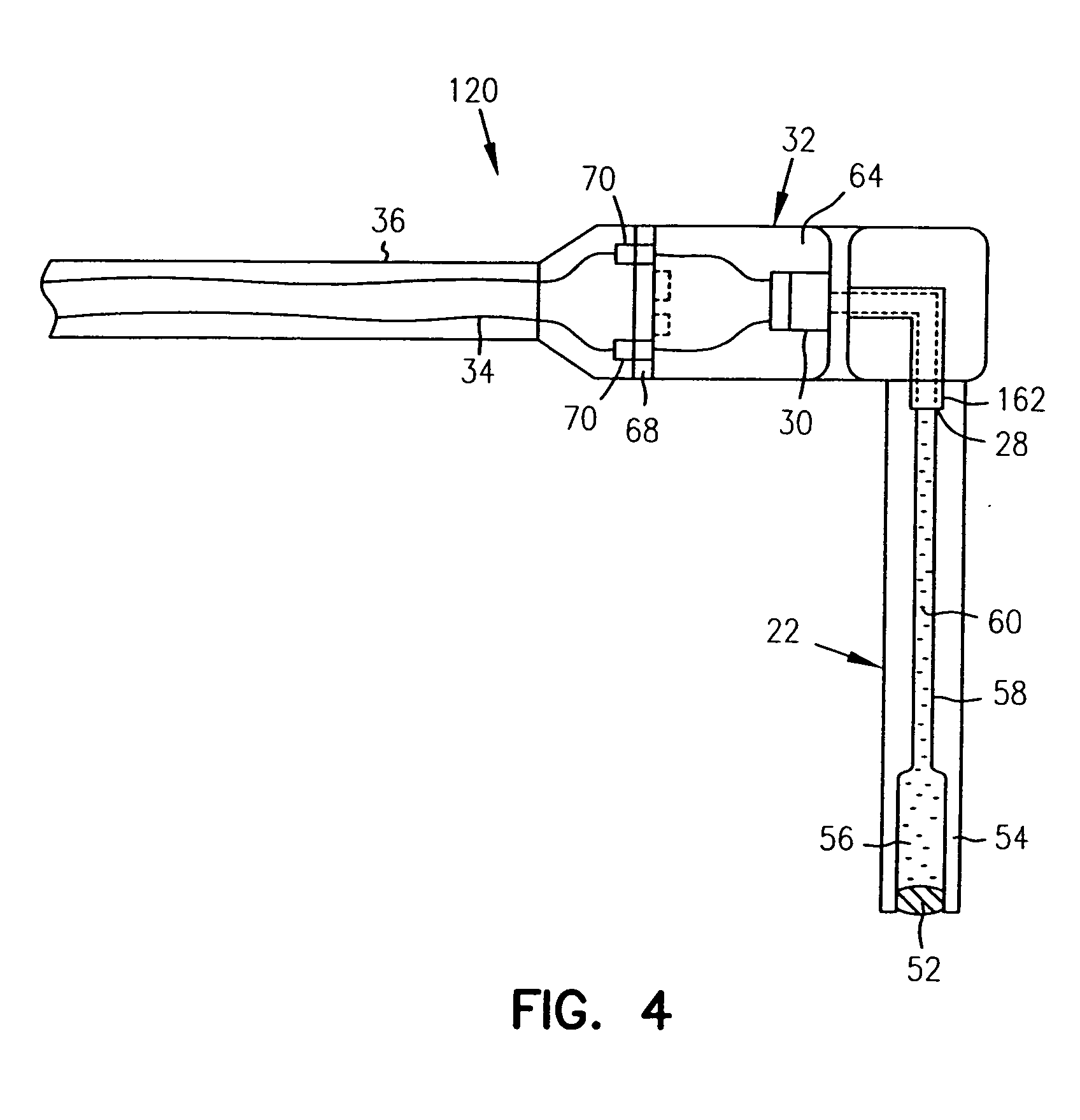
A device measures pressures in animals and humans and includes a pressure transmission catheter (PTC) filled with a pressure transmitting medium and implantable in an area in having a physiological pressure. A transducer communicates with the pressure transmitting medium to provide a pressure signal representing variations in the physiologic pressure on electrical wires. A connecting catheter carries the electrical wires to signal processing and telemetry circuitry, which transmits a telemetry signal representing the pressure signal to a receiver external to the animal or human. A housing holds the signal processing and telemetry circuitry, but the transducer is remote from the housing. The device is particularly useful in measuring venous pressure, pulmonary pressure, bladder pressure, or intracranial pressure without significant head pressure artifact and with a sufficient dynamic response. One embodiment of the PTC includes a multi-durometer stem.
Owner:DATA SCI INT
Method and device for determining blood flow in a vascular access
InactiveUS20050096578A1Easy to implementImprove reliabilityOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsExtracorporeal circulationBlood treatments
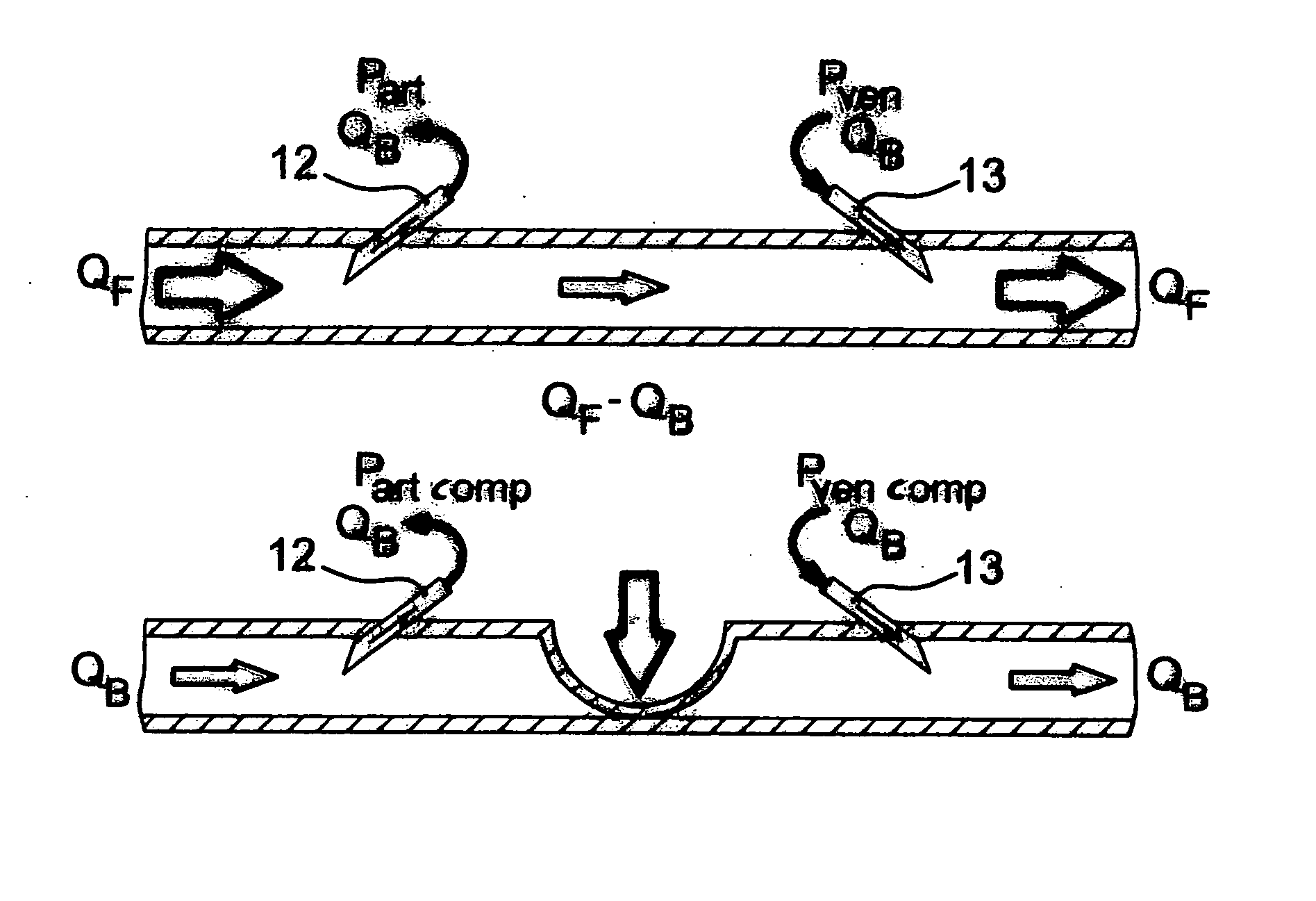
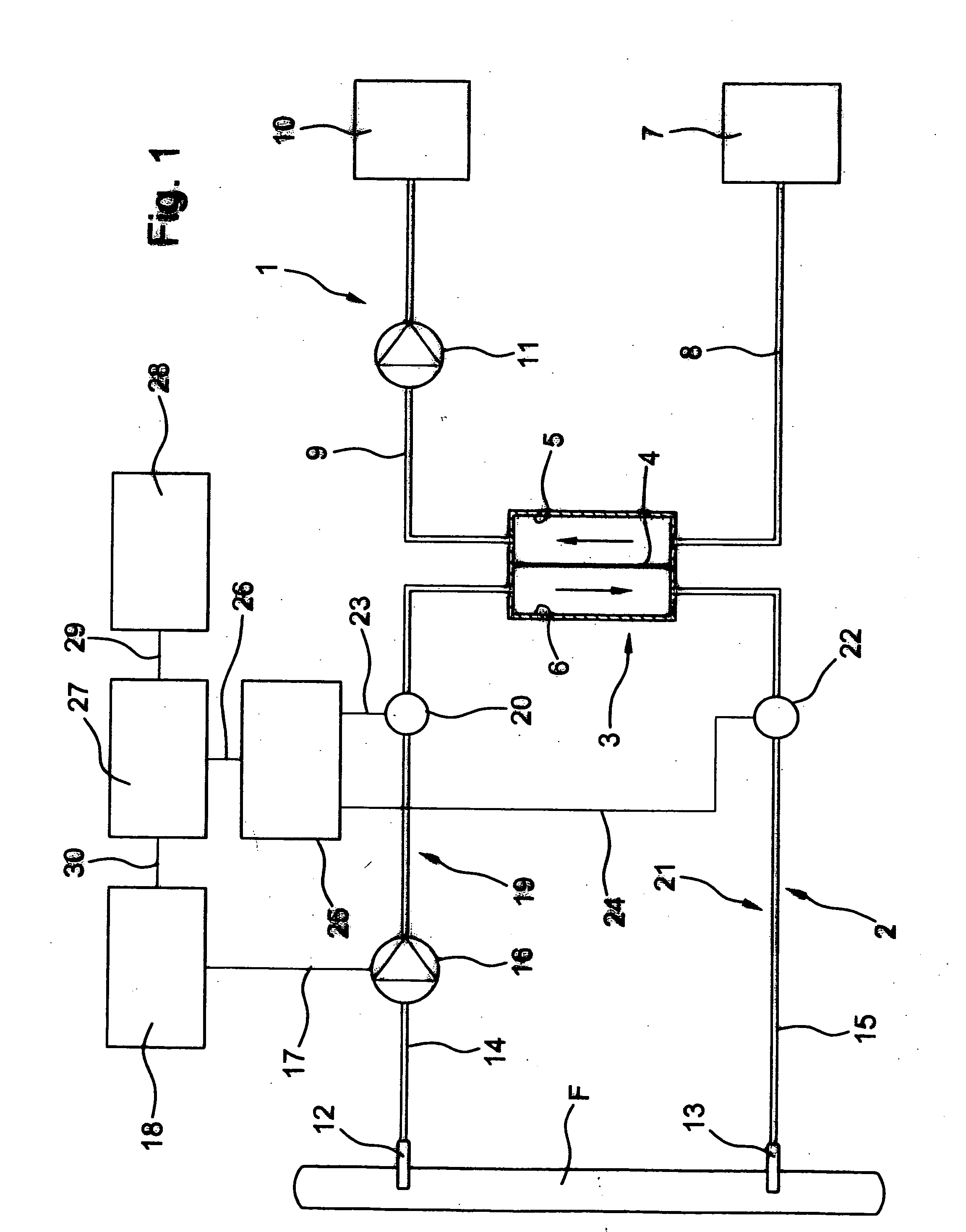
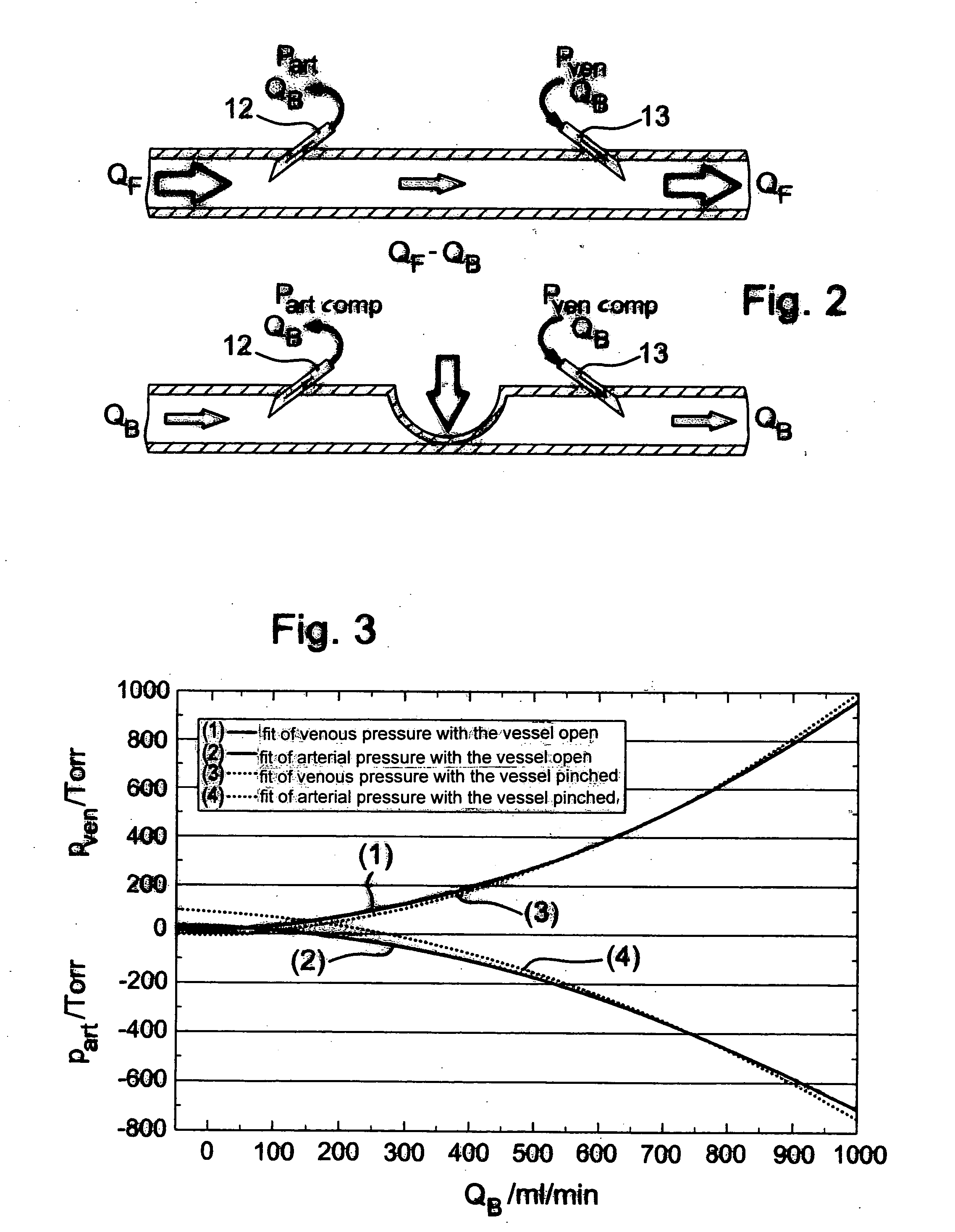
A method and a device for determining the blood flow QF in a vascular access (F) during an extracorporeal blood treatment is described, where the blood enters the blood treatment unit (3) of the blood treatment machine through an arterial branch (19) of an extracorporeal circulation loop (2) which is in fluid connection with the vascular access at an arterial connection. The blood is returned through a venous branch (21) of the extracorporeal circulation, which is in fluid connection with the vascular access at a venous connection (13). The blood flow in the vascular access is determined by measuring the pressure part, pven, in the arterial and / or venous branch of the extracorporeal circulation when the vascular access is open and interrupted, while the extracorporeal blood flow QB is varied. Then the fistula flow QF is determined from the measured values for the arterial and / or venous pressure while the vascular access is open and interrupted.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Method of detecting portal and/or hepatic pressure and a portal hypertension monitoring system
The devices and methods generally relate to vibratable sensors for measuring ambient fluid pressure, in particular implantable sensors. The devices and methods are particularly well-suited to implantation within the body of a living animal or human to monitor physiological conditions, such as portal and / or hepatic venous blood pressure, and allow frequent, remote interrogation of venous pressure using the resonance frequency of an implanted sensor. The sensor devices are relatively small compared to conventional devices for measuring fluid pressure and can be implanted in the porto-hepatic venous system, whereas conventional devices are too large. The small size of the device is accomplished by using a thick sensor membrane, compared to conventional devices, and by limiting the size of additional elements of the device relative to the size of the sensor membrane. The thicker sensor member also obviates the need for multiple sensor arrays and maintains the accuracy and robustness of the sensor device. A data capture, processing, and display system provides a pressure measurement reading, and is particularly well-suited for detecting portal hypertension in patients with liver disorders.
Owner:MICROTECH MEDICAL TECH
System for management and prevention of venous pooling
A monitoring system comprises sensors adapted to be worn by a user, and, a processor linked with the sensor. The processor receives sensor data and processes this data to determine user posture data including data indicative of vertical distance between level of the user's heart and ankle. Based on the posture data together with a value for degree of user chronic venous insufficiency and / or blood density, generate an estimate of user static venous pressure while the user is static, without calf muscle pump activity. The processor also processes the sensor data to determine if there is calf muscle pump activity, and generates an estimate of user active venous pressure according to the static venous pressure estimate, rate of calf muscle activity, and a value for degree of user chronic venous insufficiency. The processor may generate the venous pressure estimate in real time, and may control an NMES device accordingly.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY +1
Method and devices for decreasing elevated pulmonary venous pressure
The present invention relates to the implantation of one or more prosthetic valve(s) in the pulmonary vein(s) of a subject as a means of decreasing or preventing an increase in pulmonary venous pressure. The present invention accordingly provides for novel treatment strategies for the treatment of medical disorders associated with elevated pulmonary venous pressure, including congestive heart failure, as well as for prosthetic pulmonary vein valves and their delivery systems. Expandable as well as fixed-dimension non-expandable pulmonary vein prosthetic valves for implantation by a variety of surgical and percutaneous procedures are also described.
Owner:SHAKNOVICH ALEXANDER
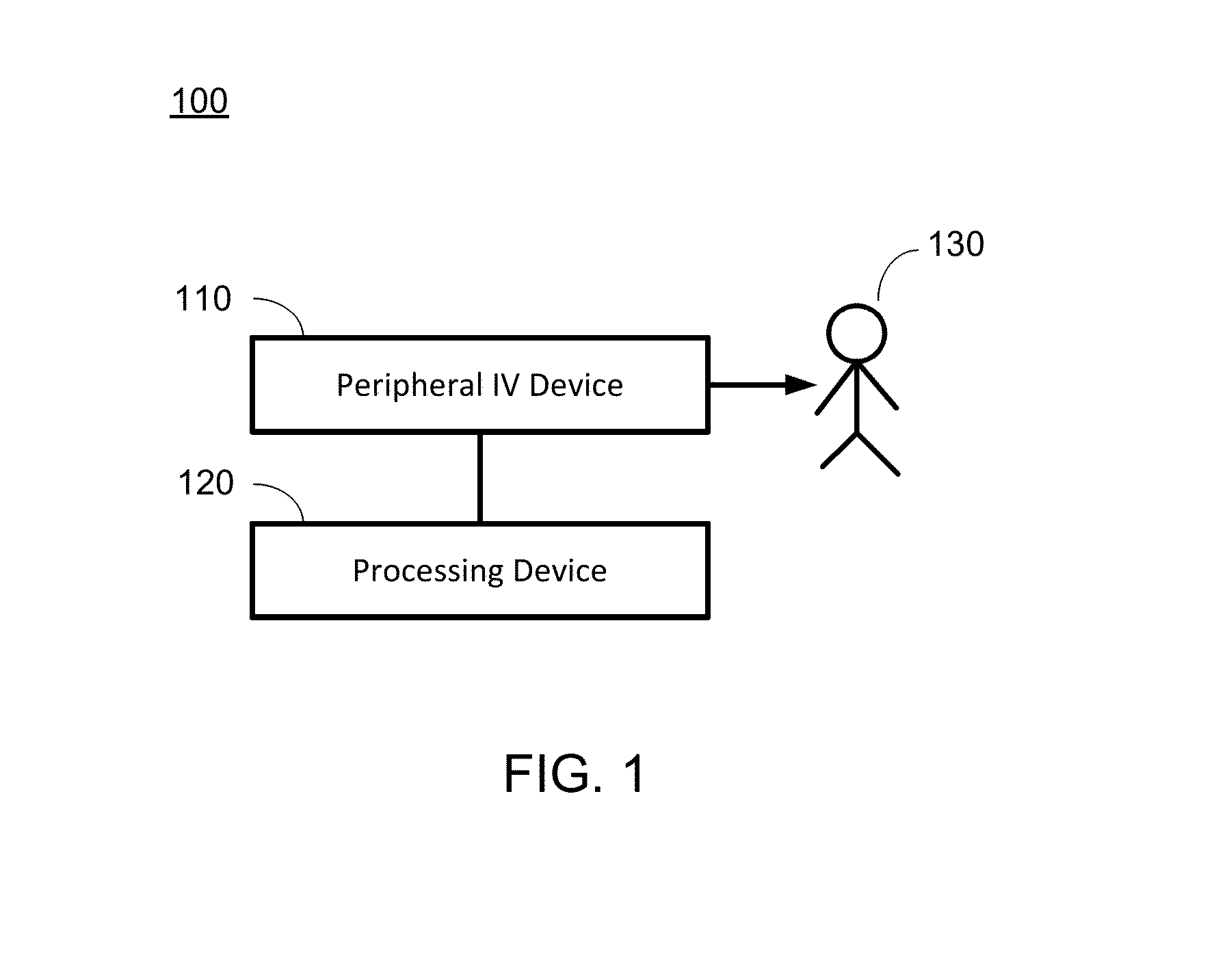
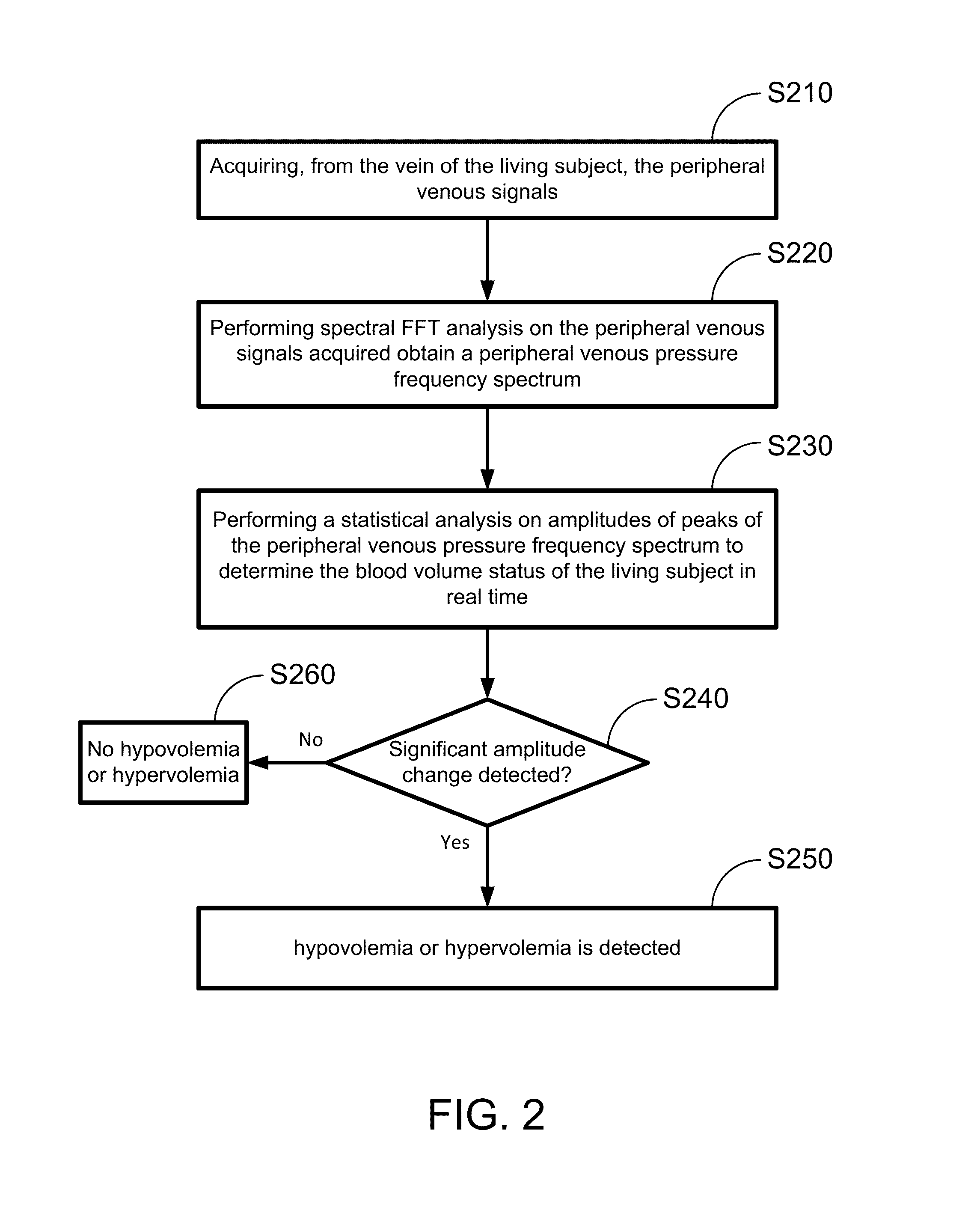
Hypovolemia/hypervolemia detection using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis (PIVA) and applications of same
Aspects of the invention relates to systems and methods for hypovolemia and / or hypervolemia detection of a living subject using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis. In one embodiment, the method includes: acquiring, from a vein of the living subject, peripheral venous signals; performing a spectral analysis on the acquired peripheral venous signals to obtain a peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum; and performing a statistical analysis on amplitudes of peaks of the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum to determine the blood volume status of the living subject in real time. Specifically, at least two peaks, respectively corresponding to a first frequency and a second frequency, are obtained on the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum. Amplitude change of the second peak is used to determine the blood volume status of the living subject. Hemorrhage may be detected when a significant amplitude decrease is detected from the second baseline peak to the second peak.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
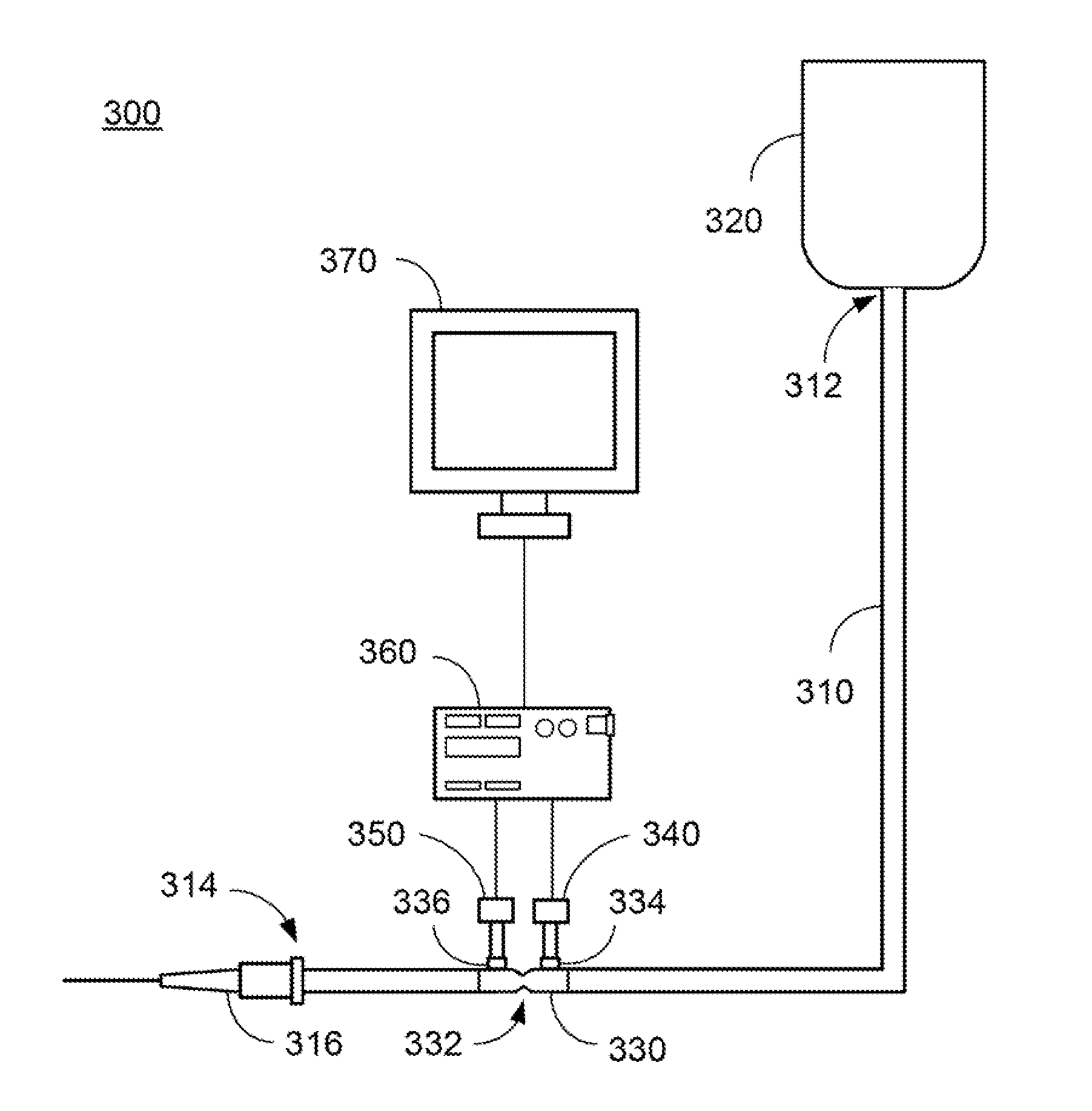
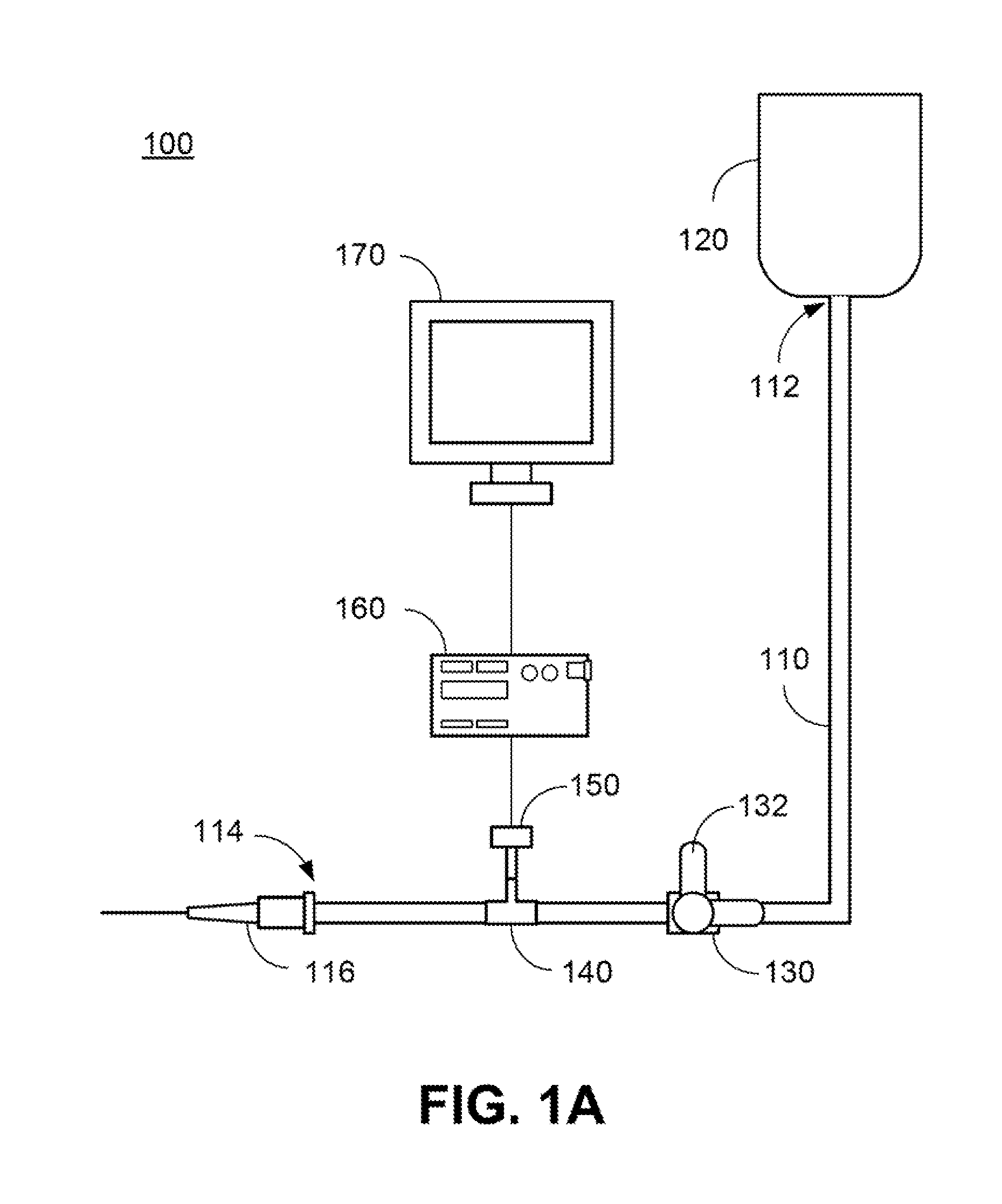
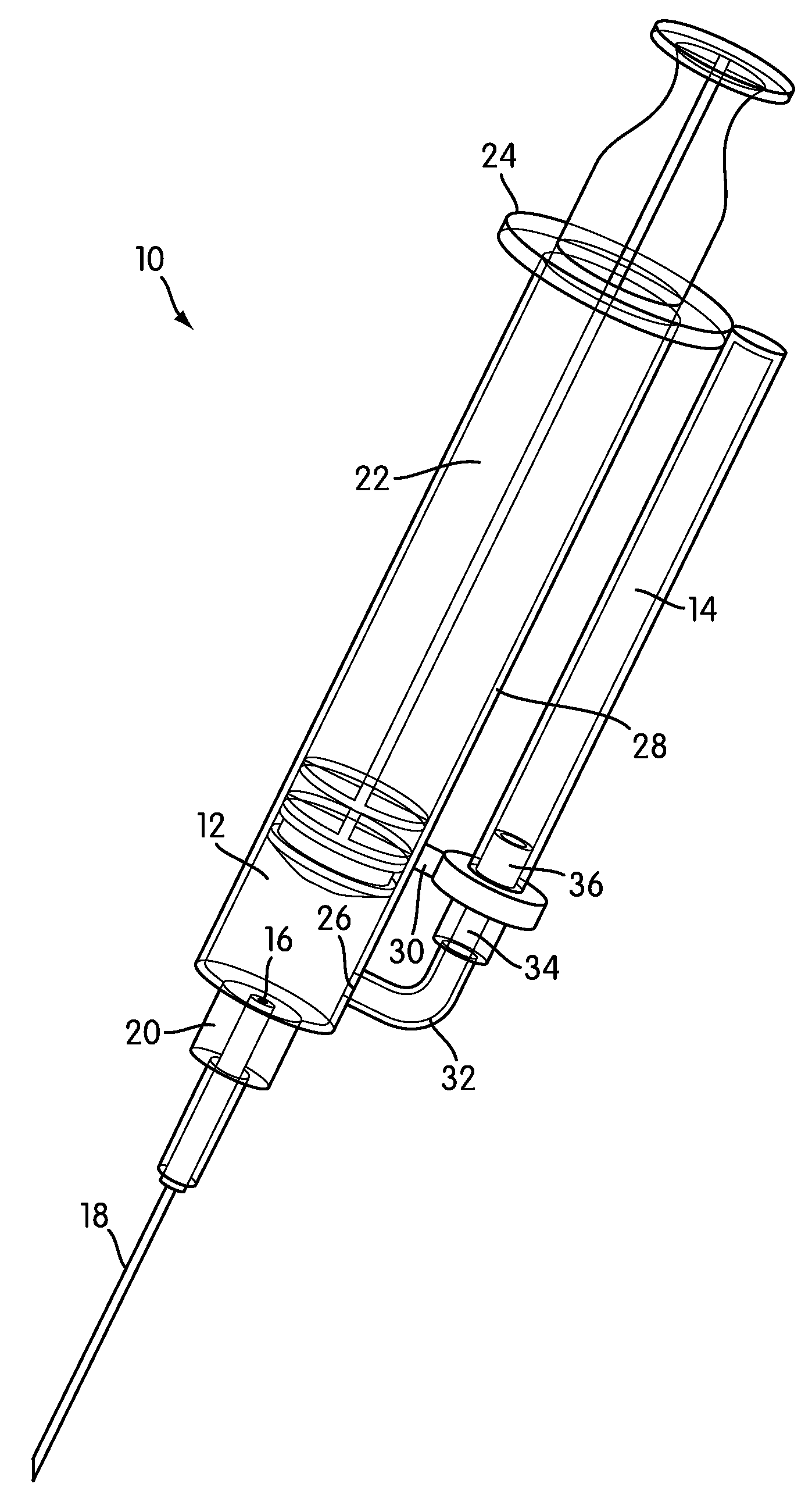
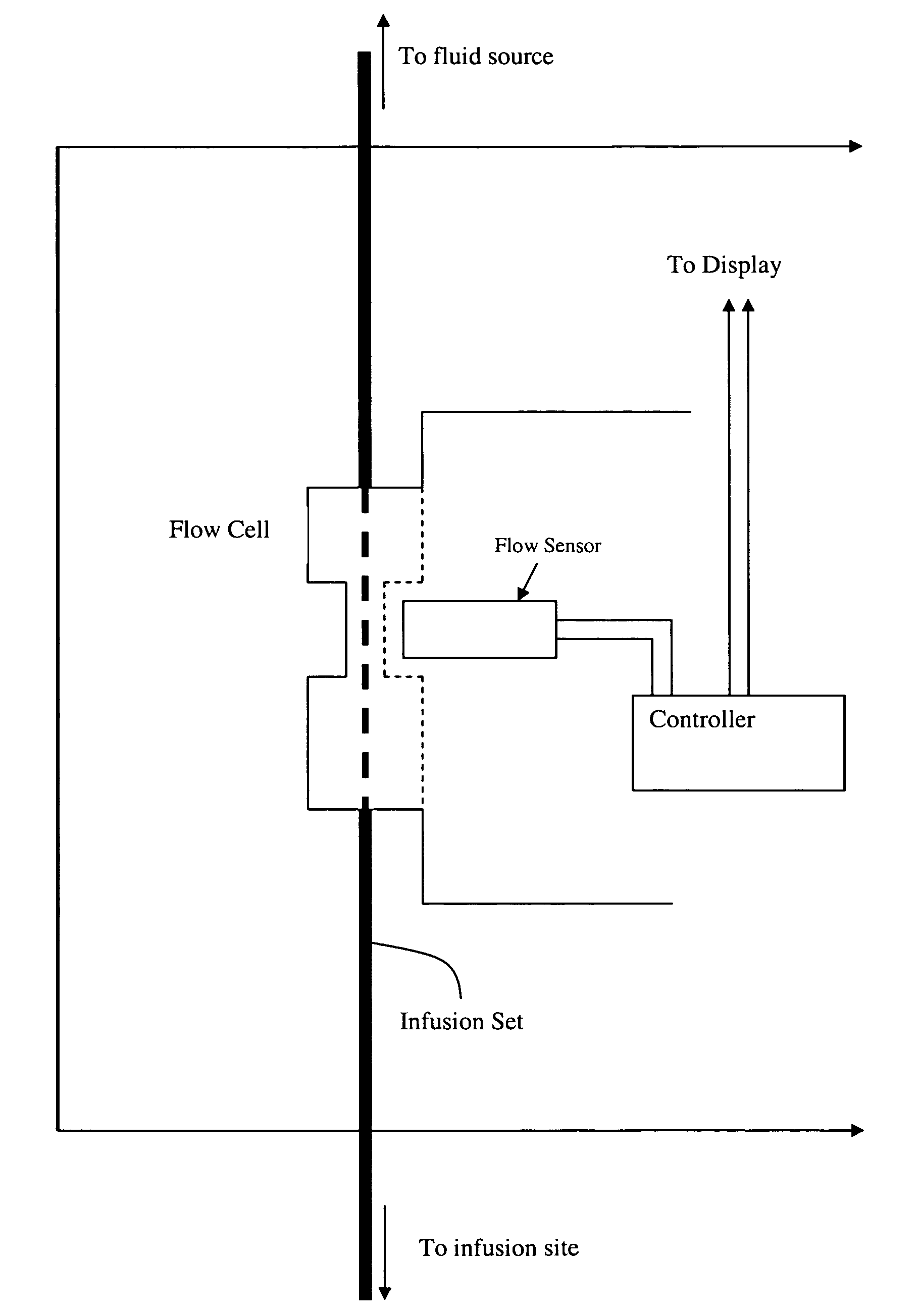
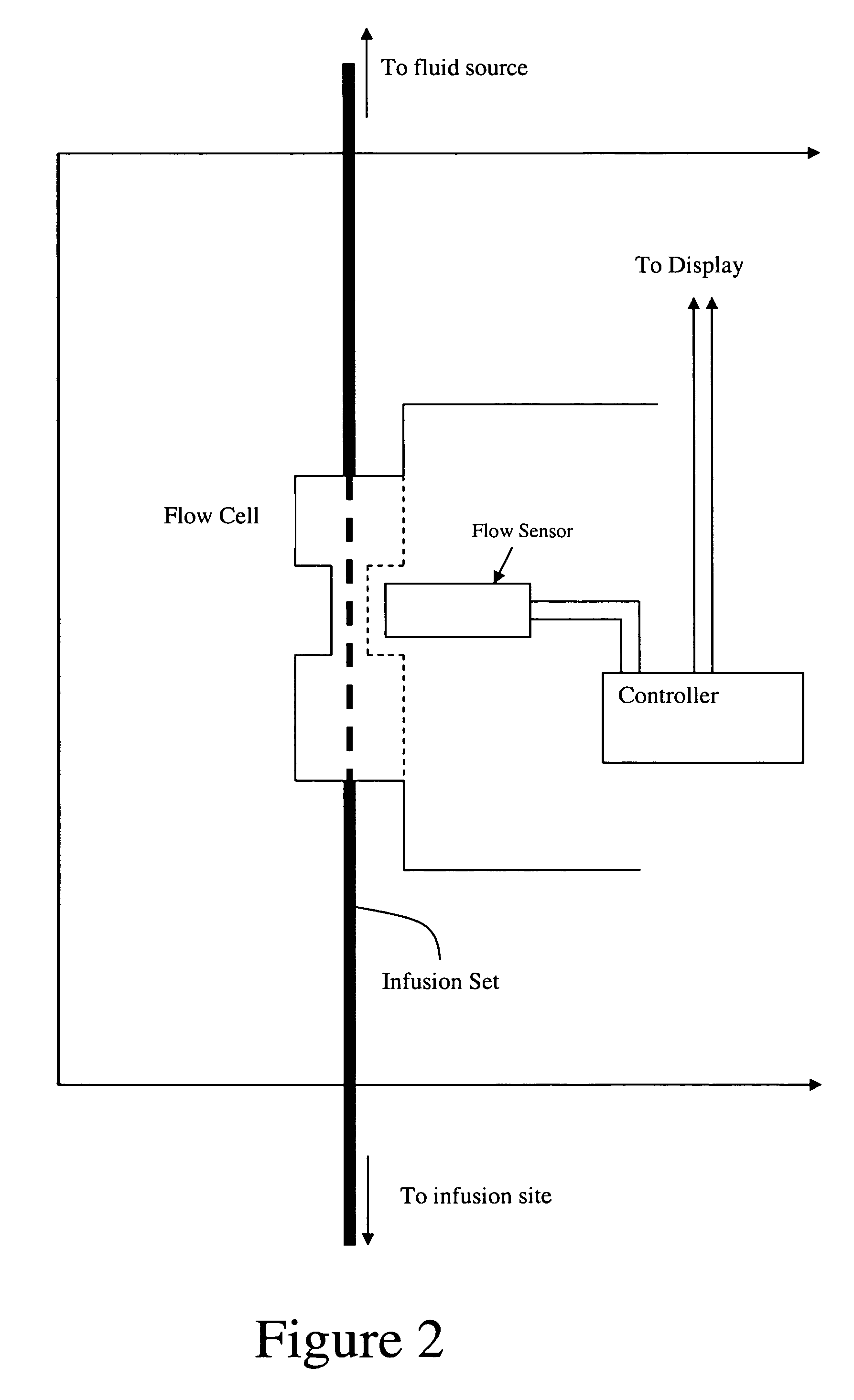
Apparatus and methods for measuring peripheral venous pressure and applications of same
In one aspect, an apparatus for measuring peripheral venous pressure includes a tubing having two ends with one end connectable to a fluid source and the other end connectable to a vein, a fluid controlling device configured to have an on position and an off position, and at least one pressure sensor configured to measure fluid pressures therein. When the fluid controlling device is in the on position, fluid flow in the tubing is allowed to pass through the fluid controlling device, such that the at least one pressure sensor measures both a fluid pressure from the fluid source and a distal venous pressure from the vein. When the fluid controlling device is in the off position, no fluid flow in the tubing is allowed to pass through the fluid controlling device, such that the at least one pressure sensor measures the distal venous pressure from the vein only.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Measuring Blood Flow and Venous Capacitance
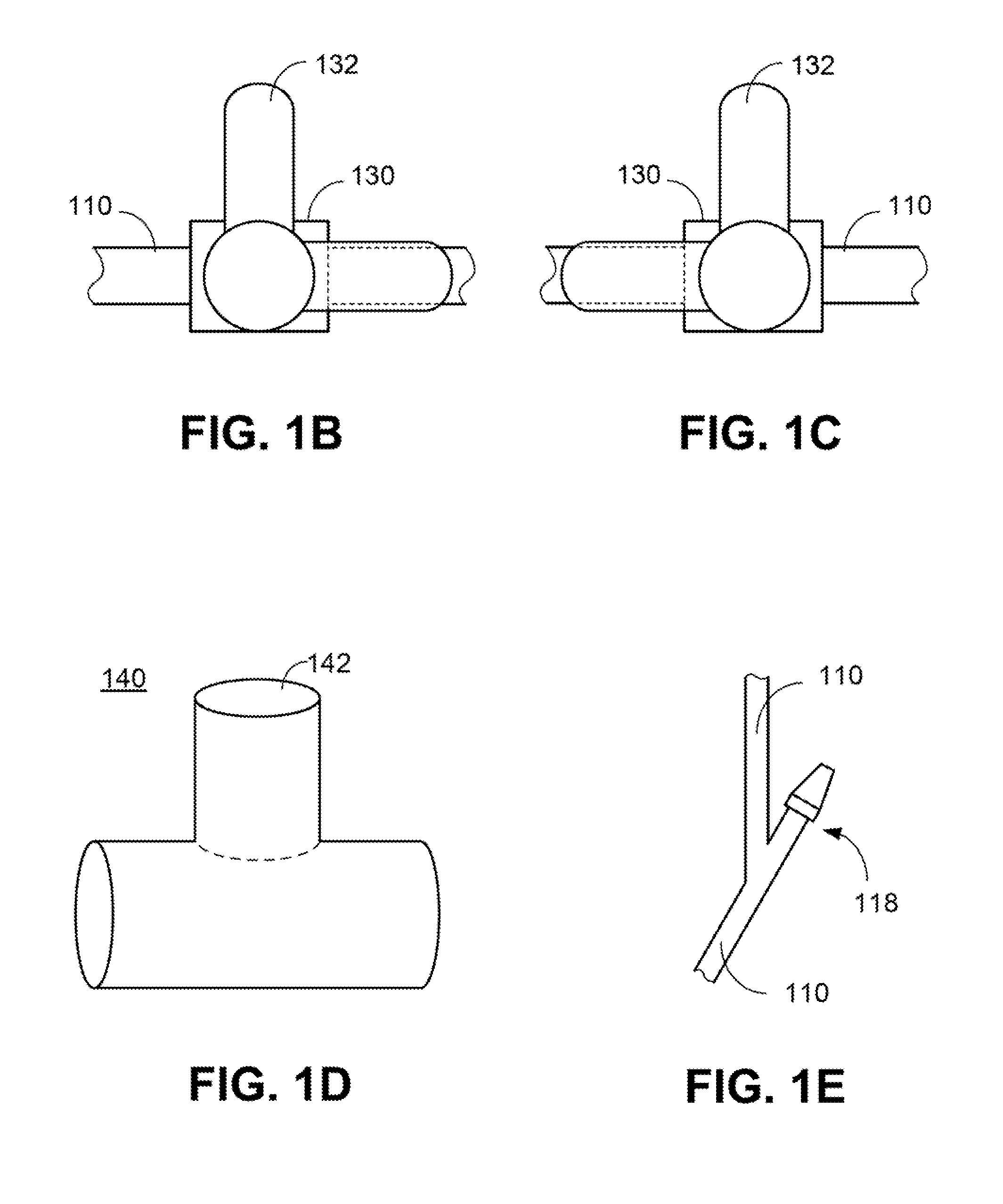
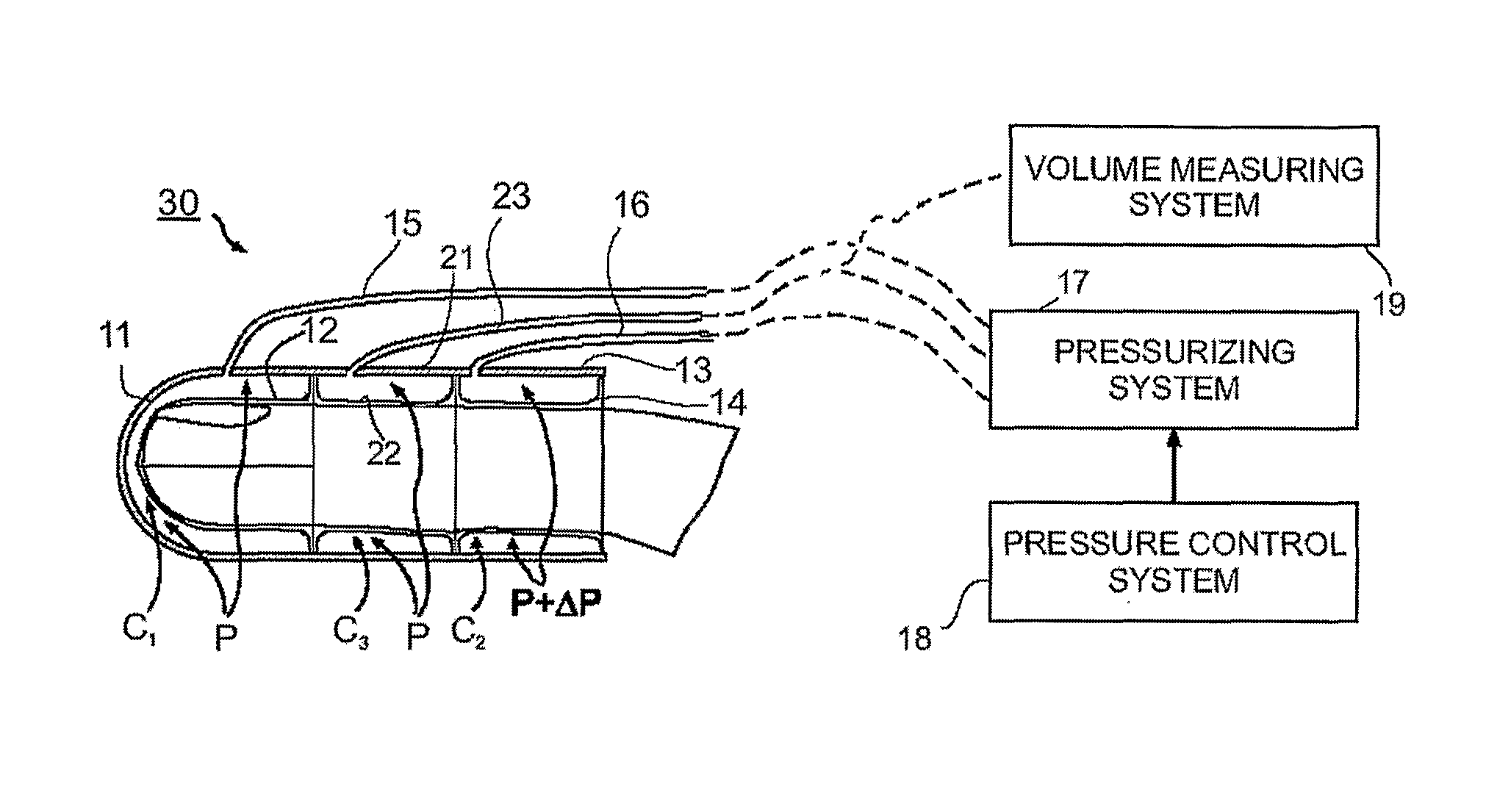
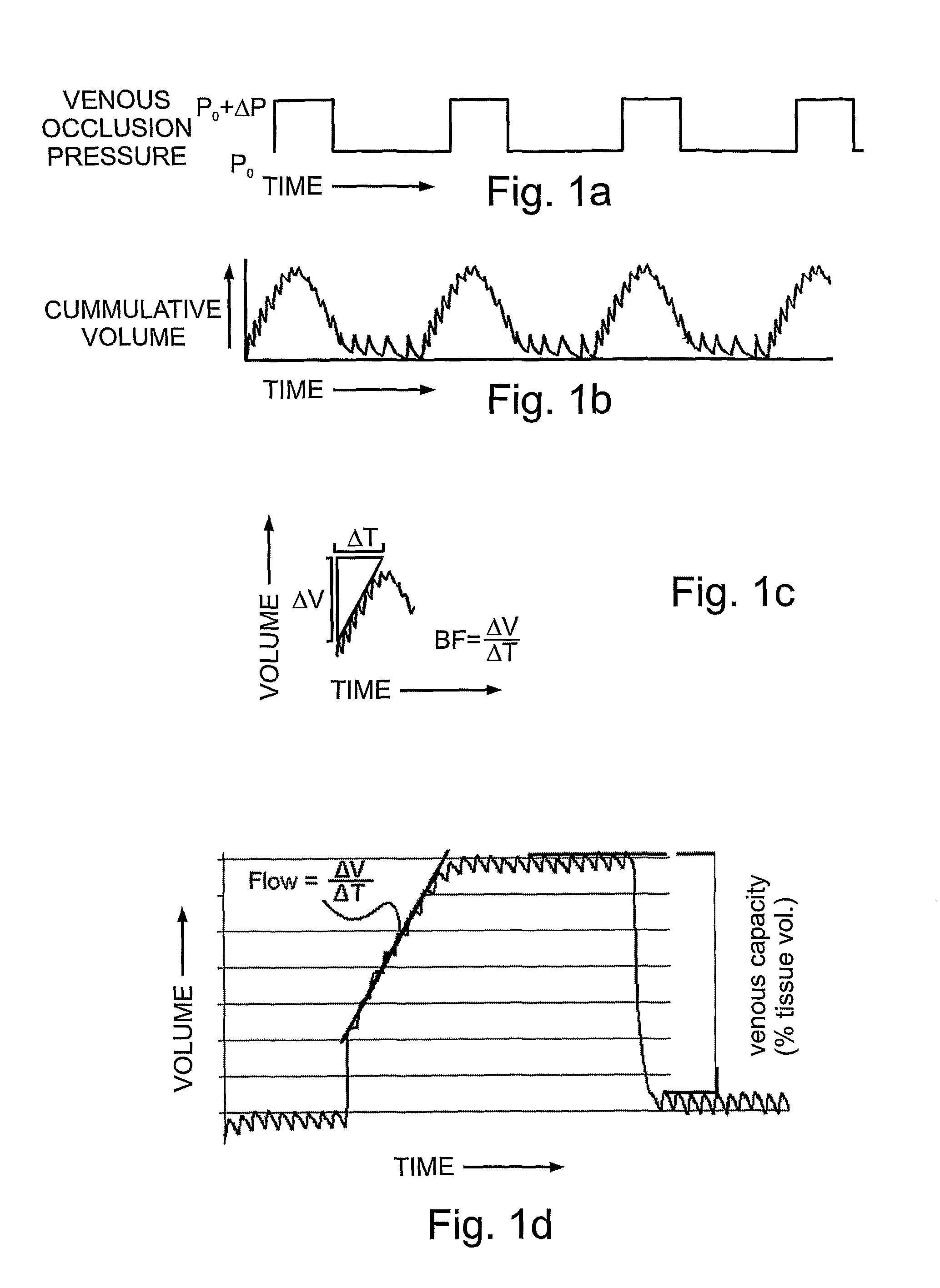
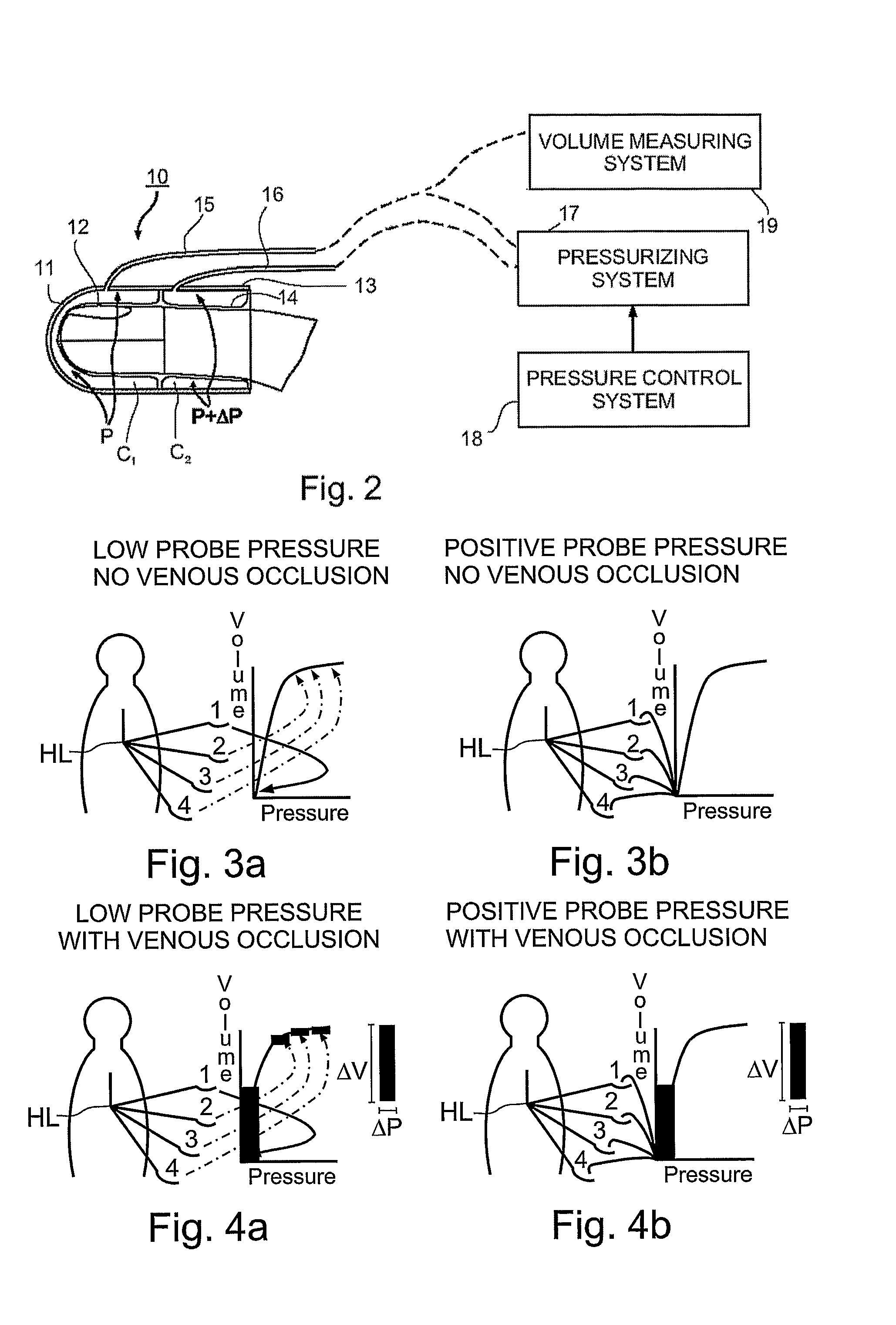
Non-invasively measuring a physiological parameter by applying to a subject's body part a venous occlusion plethysmographic device including a first section having a first fluid chamber and at least a second region having a second fluid chamber to engage a first region of the body part and a second region of the body part, proximal of the first region; pressurizing the first chamber to a pressure sufficient to compensate for hydrostatic pressure added to the inherent venous pressure at the maximal vertical lowering level of the body part relative to the subject's heart level; intermittently raising and lowering the pressure in the second fluid chamber to a pressure above or equal to the pressure in the first chamber, but below the arterial blood pressure; measuring changes in volume of the first region of the body part; and utilizing the measured volume changes to provide a measure of the physiological parameter.
Owner:ITAMAR MEDICAL LTD
Extracorporeal blood handling system with automatic flow control and methods of use
InactiveUS20060009728A1Extension of timeImprove abilitiesOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesAutomatic controlHandling system
Apparatus for processing blood in an extracorporeal circuit with automatic flow control is provided in which error conditions are sensed and system operation is modulated responsive to the error conditions. The apparatus includes an extracorporeal blood processing system, at least one sensor that senses the presence or absence of gas or monitors venous pressure, and a controller operably coupled to the blood processing system to selectively reduce pump speed or to reconfigure flow paths within the blood processing system responsive to the sensor output.
Owner:CARDIOVENTION
Venous-arterial detector and pressure indicator
Owner:DEVICE EVOLUTIONS
Flashback blood collection needle
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Decellularized anti-calcification heart patch and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104998299ASuitable degradation cycleSlightly altered collagen structureProsthesisActive agentHeart chamber
The invention relates to a preparation method of a decellularized anti-calcification heart patch. The method mainly comprises the steps that raw material pericardial tissue is degreased through an organic reagent and processed by a mixed solution of a high salt, a surface active agent and alkali, and finally sterilization treatment is performed to obtain the decellularized anti-calcification heart patch. According to the obtained heart patch, due to the special decellularized anti-calcification technology, the collagenous fiber three-dimensional pore structure of the raw materials is reserved, meanwhile, cells contained in the materials are effectively removed, and the immunogenicity is lowered; the materials can guide cells to grow in the materials, scar tissue generation is reduced, and the good anti-calcification ability is achieved; the excellent mechanical property is achieved, arterio-venous pressure difference between heart chambers can be resisted, and the repair effect is ensured. The preparation method is applicable to atrial septal defects, ventricular septal defects, aortic stenosis and the like caused by the congenital heart disease.
Owner:SHAANXI BOYU REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
Construction method of radiology-based hepatic venous pressure gradient calculation model
ActiveCN107945878AIncrease operational difficultyInvasive riskMedical simulationImage enhancementBurden of diseaseHepatic veins
The invention provides a construction method of a radiology-based hepatic venous pressure gradient (rHVPG) calculation model. An advantageous hepatic vein pressure gradient calculation model can be constructed on this basis, and a new approach is provided to calculate the early noninvasive indexes of patients with portal hypertension. The invention also provides a rHVPG calculation system. The method can overcome many limitations of an existing noninvasive measurement method. The rHVPG calculation system is feasible, and is expected to provide a new idea for the noninvasive measurement of portal pressure, and plays an active role in improving the quality of life of patients with portal hypertension and reducing the burden of disease in families and society.
Owner:祁小龙
Wireless mouse
InactiveCN103412658AStrong computing powerSolve the problem that it is impossible to track various indicators of users for a long timeSpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingGeneral Packet Radio ServiceHuman body
The invention discloses a wireless mouse which comprises a mouse body, a micro processor, a fingerprint recognition sensor, a heart rate collecting sensor, an arterial pressure sensor, a venous pressure sensor, a noninvasive blood glucose detecting device, a temperature sensor, a general packet radio service (GPRS) short message communication device and a bluetooth module. The micro processor transmits collected human body fingerprints, heart rate, arterial pressure, venous pressure, blood glucose and body temperature signals to a computer in a bluetooth mode, and the computer sends the collected human body physical sign data to a cloud server to be edited, stored and processed. Various sensors are arranged on the wireless mouse, and physical indexes can be monitored at any time. The wireless mouse is connected with the cloud server through a network, collected data is uploaded to the cloud server to be stored, data analysis is conducted by using strong computing capacity of cloud computing, and the problem that various indexes of a user can not be tracked for a long time is solved successfully.
Owner:JIANGSU HUITONG GRP
Radiomics-based hepatic venous pressure gradient (rHVPG) calculation model construction method
ActiveCN107480675AIncrease operational difficultyInvasive riskImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineQuality of life
The invention provides a radiomics-based hepatic venous pressure gradient (rHVPG) calculation model construction method, on this basis, a more advantageous hepatic venous pressure gradient calculation model can be constructed, and a new way is provided for the calculation of the early stage non-invasive index of a patient with portal hypertension. The invention also provides a radiomics-based hepatic venous pressure gradient calculation system. The invention overcomes the many limitations of current non-invasive measurement methods. The rHVPG calculation system proposed by the invention is feasible, is expected to provide a new idea for noninvasive measurement of portal pressure, and plays a positive role in improving the quality of life of the patient with portal hypertension and alleviating the disease burden of families and society.
Owner:祁小龙
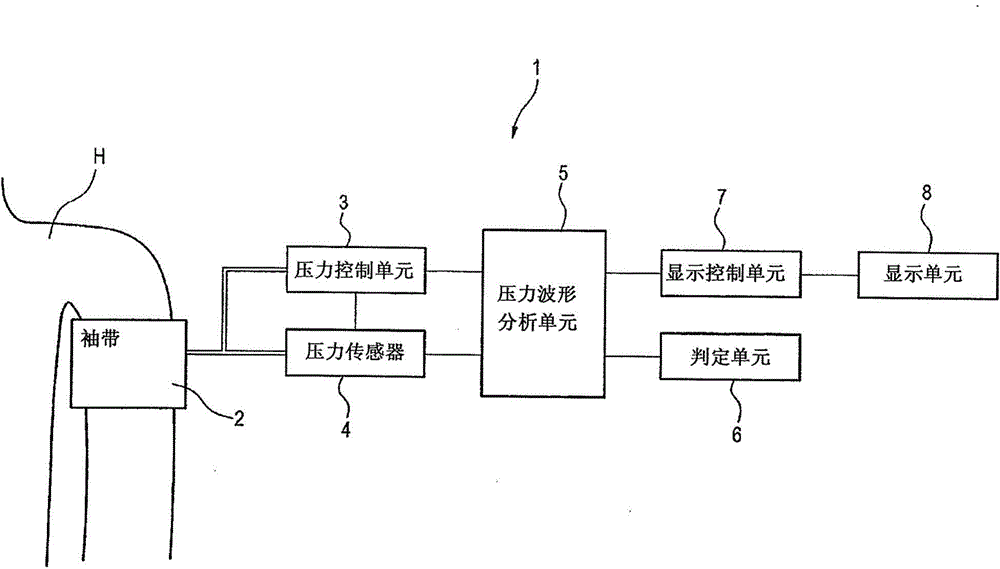
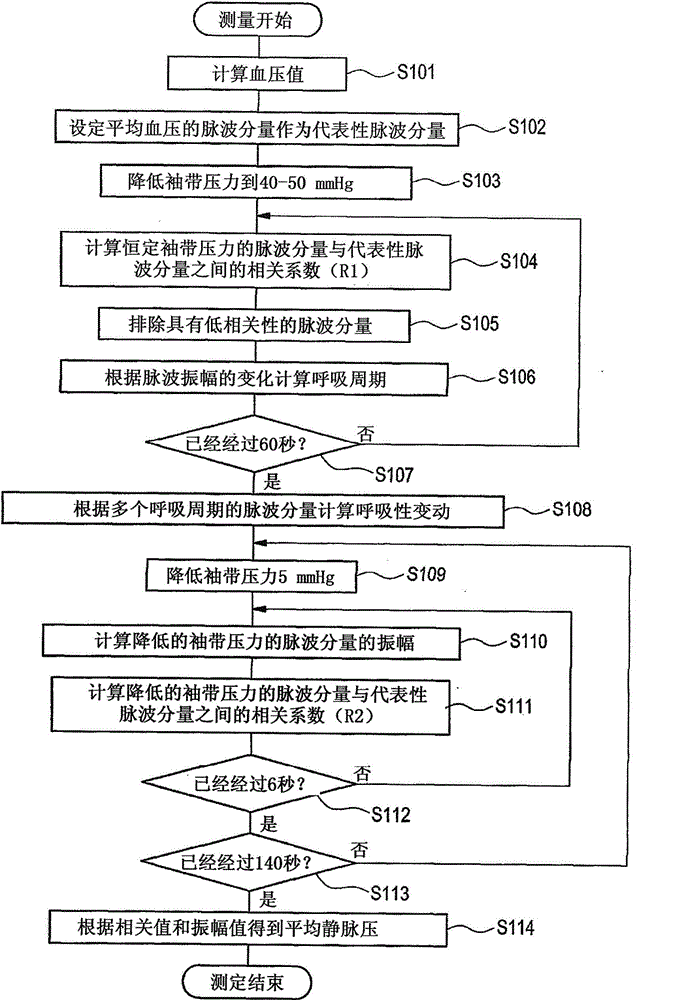
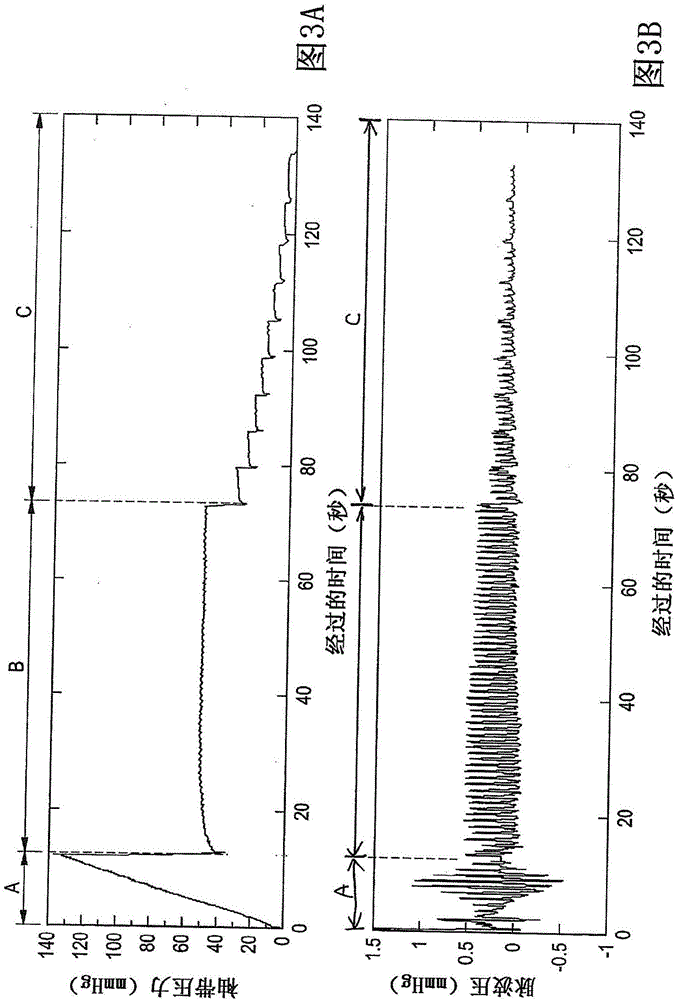
Blood pressure measuring apparatus and blood pressure measuring method
InactiveCN104873182ASimple and correctly evaluatedAccurate assessmentEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsVeinPulse wave
A blood pressure measuring apparatus (1) includes a pressure control unit (3) that controls an applied pressure applied to a region of a living body in which a vein and artery exist by a cuff (2) mountable to the region, a detection unit (4) that detects pressure waveforms in which pulse wave components from the region overlap with the applied pressure, and an analysis unit (5) that obtains a respiratory variation on the waveform of artery and a venous pressure based on the pressure waveforms detected by the detection unit (4) through one-time blood pressure measurement. The analysis unit (5) obtains the respiratory variation on the waveform of artery based on data of a first pressure waveform in a first process, and the venous pressure based on data of a second pressure waveform in a second process and the data of the first pressure waveform.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY +1
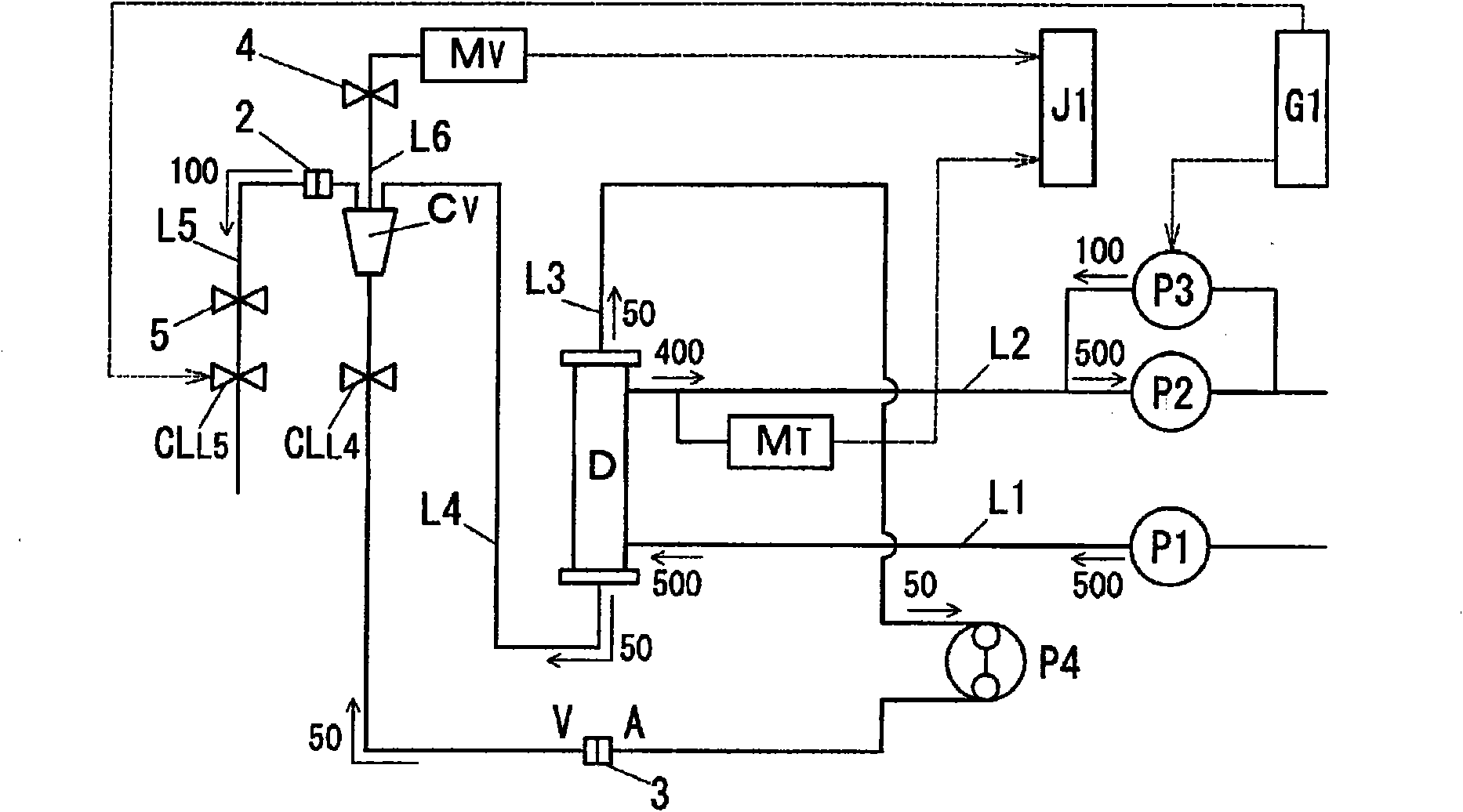
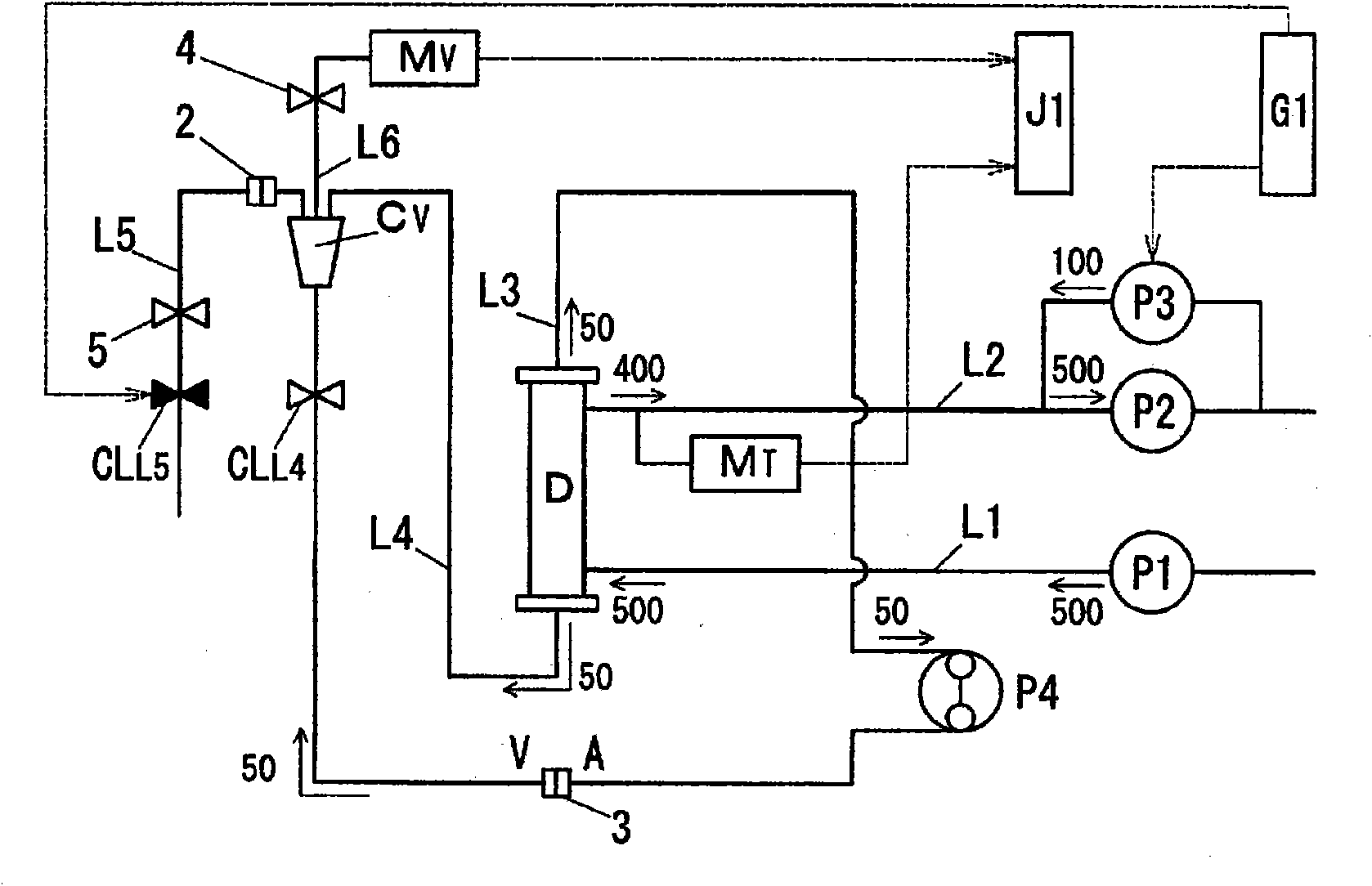
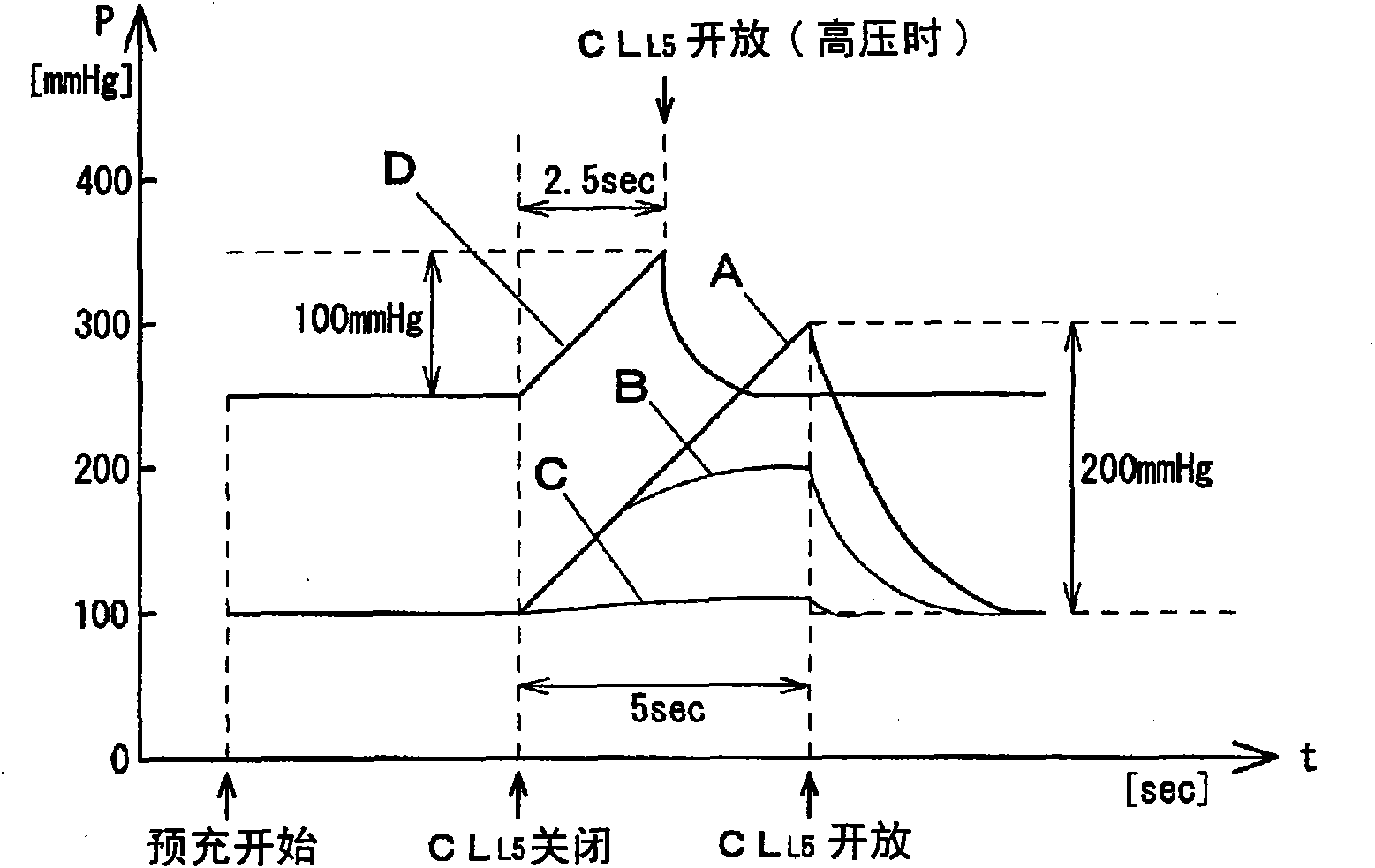
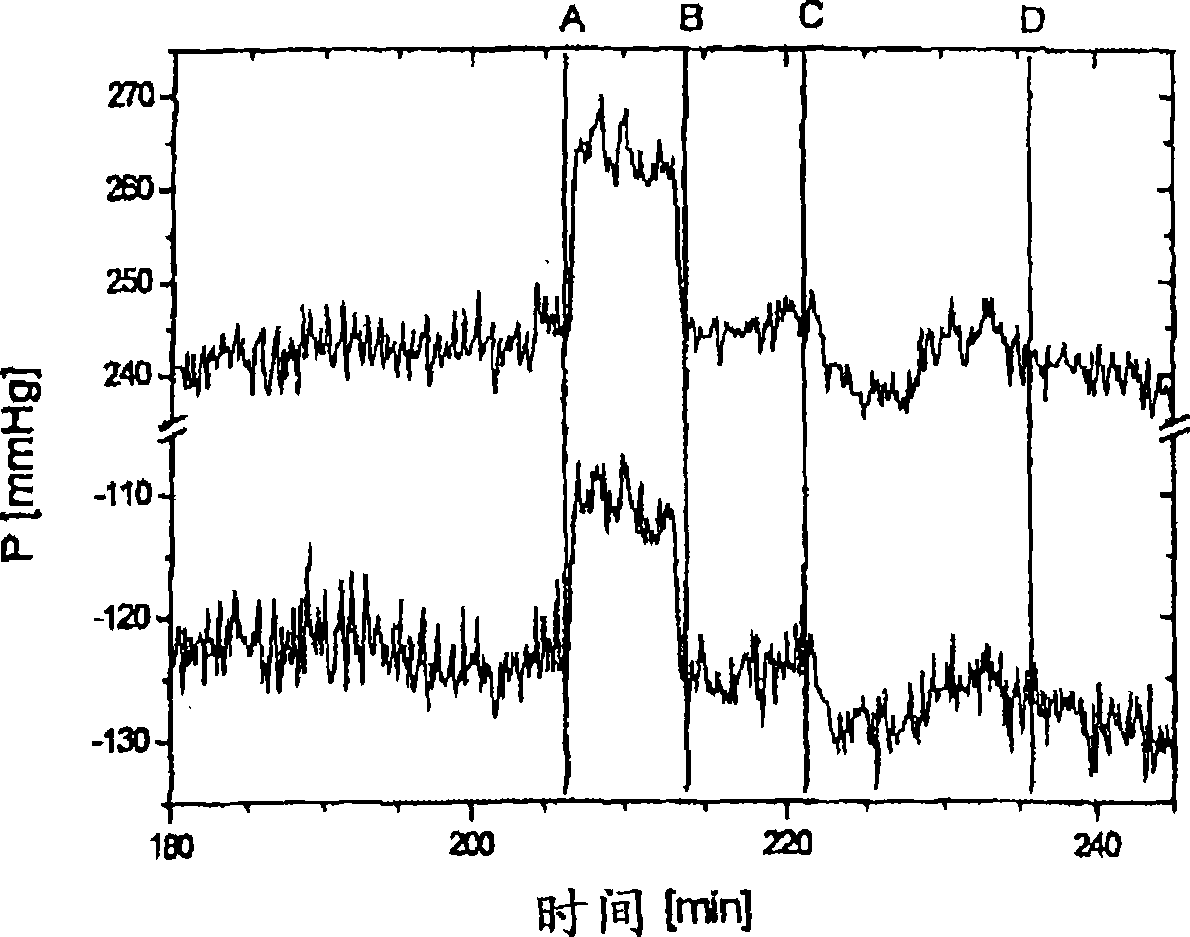
Hemodialysis apparatus
ActiveCN101848740APositive judgment of normalityReduce the burden onDialysis systemsMedical devicesFiltrationHaemodialysis machine
A hemodialyzer not causing any medical malpractice such as air inclusion or blood loss during hemodialysis by detecting even a minute connection failure, if any. The hemodialyzer comprising a hemodialyzer (D), a dialyzing fluid supply line (L1), a dialyzing fluid discharging line (L2), an arterial blood line (L3), a venous blood line (L4), first fluid sending means (P1), second fluid sending means (P2), third fluid sending means (P3), a blood pump (P4), a venous chamber (Cv), an overflow line (L5), a venous pressure monitor line (L6), dialyzing fluid pressure measuring means (MT), venous pressure measuring means (Mv), clamps (CLL4, CLL5), control means (G1) which closes the clamp (CLL5) when a predetermined time has elapsed from the start of the priming, allows the third fluid sending means (P3) to operate in the reverse filtration direction or in the water removing direction simultaneously with the closure of the clamp (CLL5), and then opens the clamp (CLL5) when a predetermined time has elapsed, and judging means (J1) which judging the normality of the circuit connection after comparing a variation of the dialyzing fluid pressure or the venous pressure while the clamp (CLL5) is closed with a predetermined reference value.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
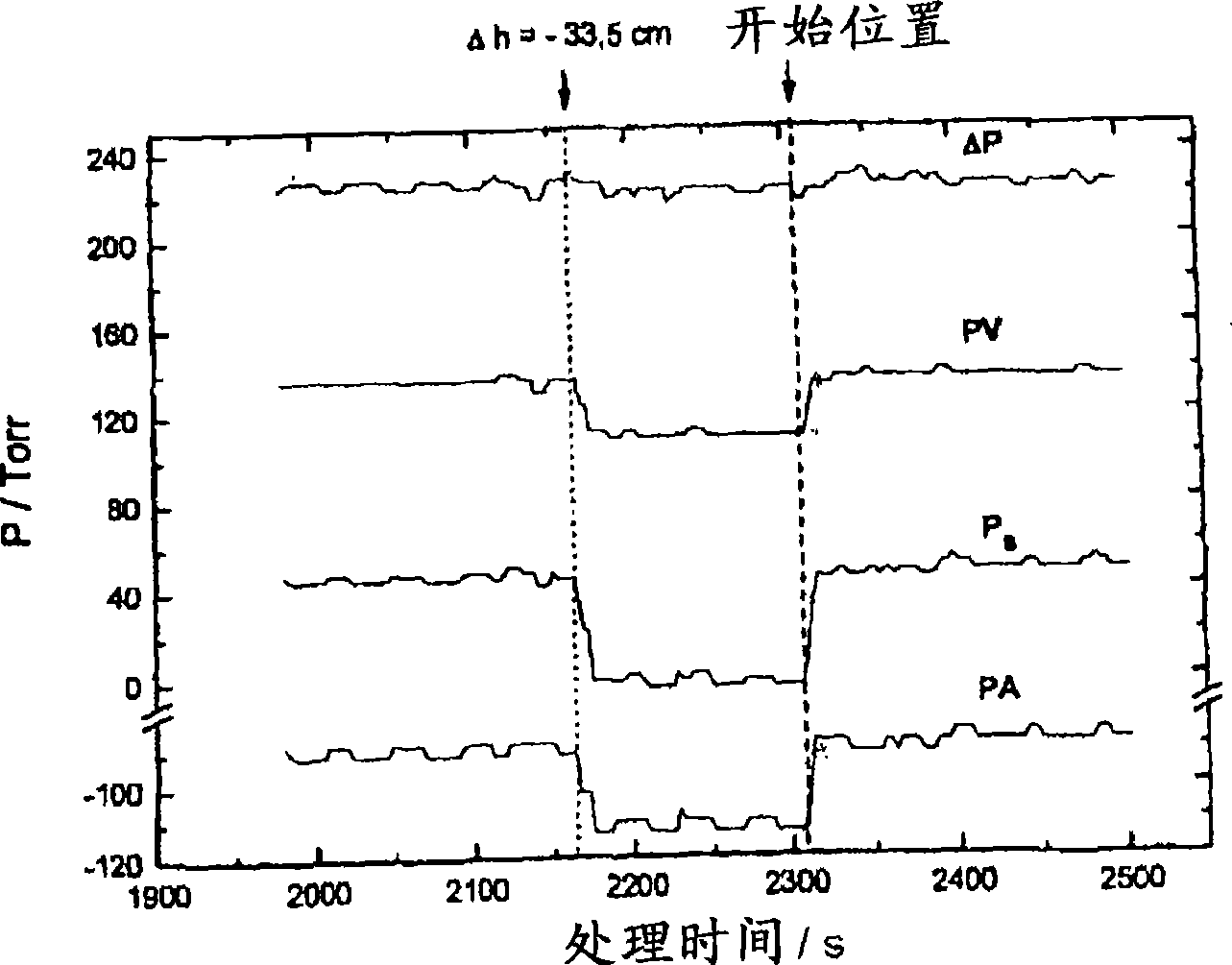
Method and device for monitoring an extracorporeal blood circuit
To monitor an extracorporeal blood circuit during an extracorporeal blood treatment, the arterial pressure and venous pressure in the arterial branch and venous branch of the extracorporeal circuit are measured by means of pressure sensors (18, 19), and the sum Ps and the difference deltaP of the arterial pressure and / or venous pressure measured at the same time are formed. A possible error state is indicated when the sum Ps and / or difference deltaP lie outside predetermined limit value windows A and B. To reduce the susceptibility to error, a check is preferably also made to ascertain whether the two above conditions are satisfied for n successive measurements.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Anti-blood return medical infusion set
The invention discloses an anti-blood return medical infusion set and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The anti-blood return medical infusion set comprises a cork puncture unit, a Murphy's pipe, an intravenous infusion needle and an infusion tube; a liquid-stopping device is arranged at the infusion pipeline between the cork puncture unit and the intravenous infusion needle; the anti-blood return medical infusion unit also comprises a volume reduction anti-blood return hose with elasticity lower than the infusion tube; two ends of the volume reduction anti-blood return hose are connected with the infusion tube between the liquid-stopping device and the intravenous infusion needle; when the anti-blood return medical infusion unit is used for infusion, the vertical distance between the lower end part of the volume reduction anti-blood return hose and the port of the intravenous infusion needle is not smaller than the height of a medical cylinder corresponding to the human body venous pressure. The anti-blood return medical infusion set is simple in structure, excellent in anti-blood return effect, and capable of changing the anti-blood return time of the anti-blood return medical infusion set by changing the hardness and / or the length of the volume reduction anti-blood return hose.
Owner:GUANGZOU YOUAN MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Intelligent ECMO treatment device based on rolling type blood pump and control method of system
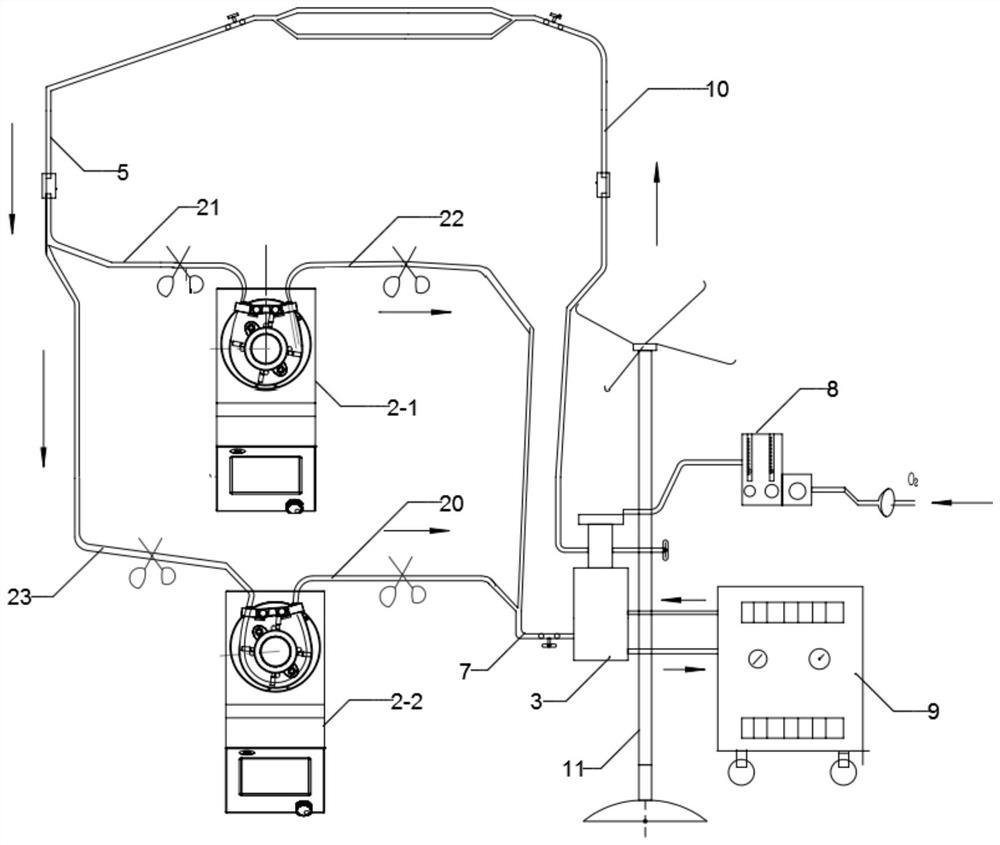
PendingCN114470377AAdded pressure monitoring structurePrecise control of perfusion pressureDialysis systemsBlood pumpsVeinArterial catheter
The invention provides an intelligent ECMO treatment device based on a rolling type blood pump and a control method of a system.The intelligent ECMO treatment device comprises a vein cannula, the rolling type blood pump, a membrane lung and an arterial cannula, the vein cannula is connected to an inlet of the rolling type blood pump through a first connecting pipe, and the rolling type blood pump is connected to an outlet of the artery cannula through a second connecting pipe; a venous pressure sensor is arranged on the first connecting pipe; an outlet of the rolling type blood pump is connected to an inlet of the membrane lung through an arteriovenous bridge tube, an artery overpressure sensor is arranged on the arteriovenous bridge tube, the membrane lung is further connected with an air and oxygen mixer and a temperature changing device, an outlet of the membrane lung is connected to the arterial cannula through a second connecting tube, and the arterial cannula is connected with the air and oxygen mixer through a second connecting tube. The venous pressure sensor and the artery overpressure sensor are respectively connected with the rolling type blood pump through the central processing unit. According to the invention, the perfusion pressure can be intelligently and accurately controlled, and finally constant-flow perfusion is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN WELCOME MEDICAL EQUIP
Flashback blood collection needle
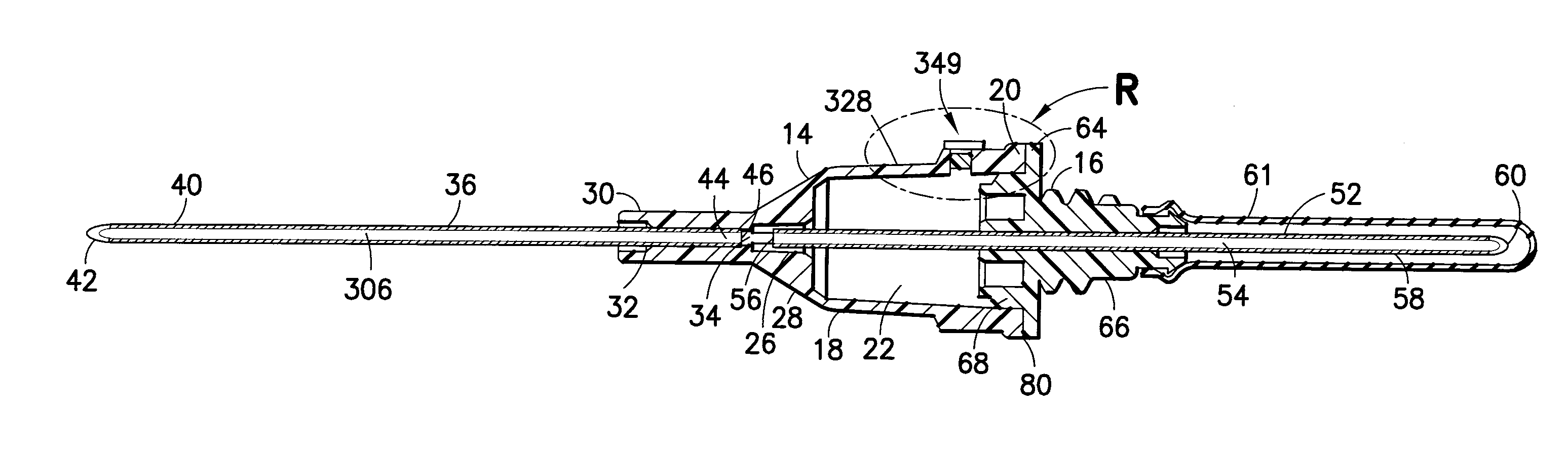
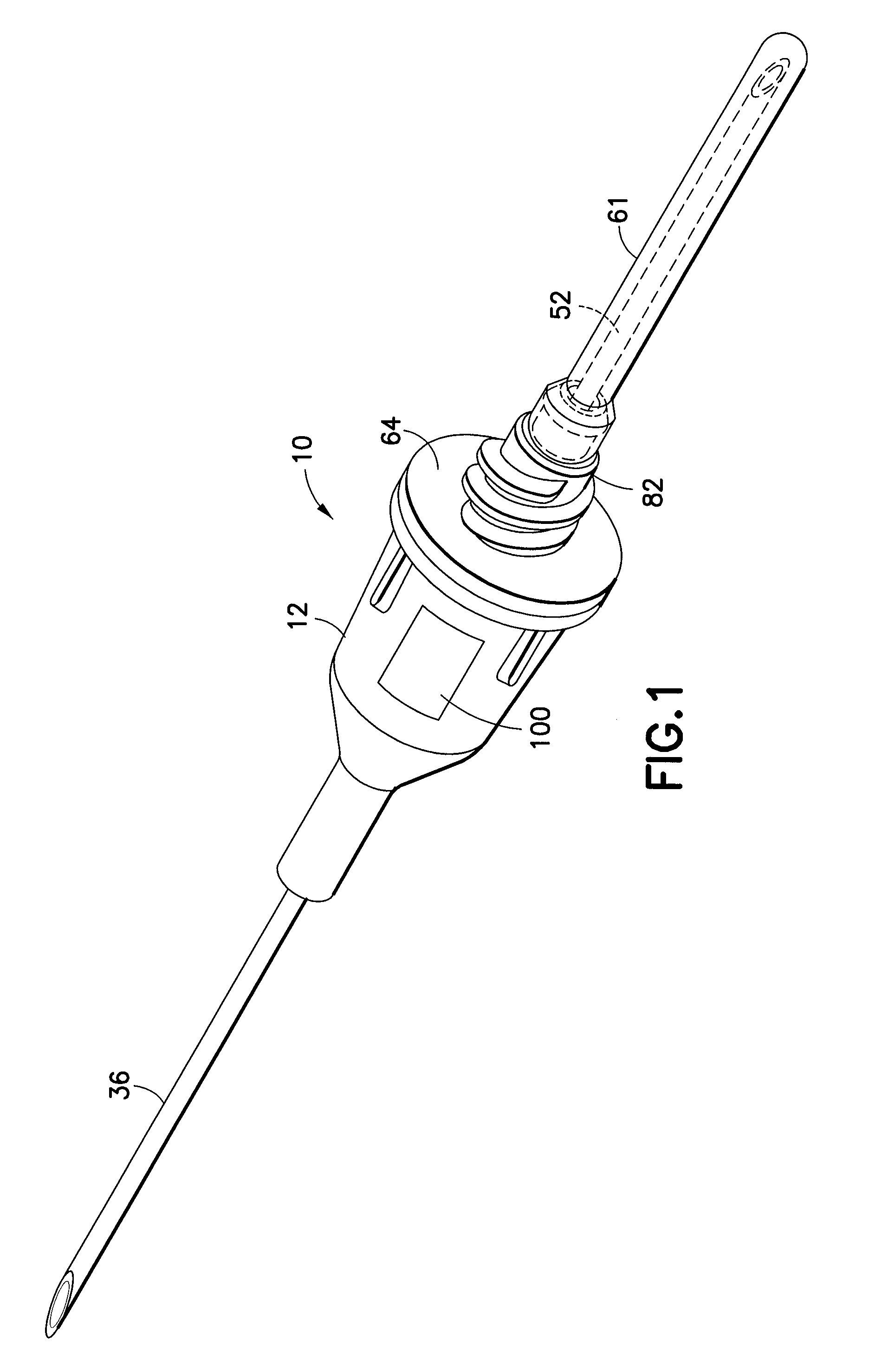
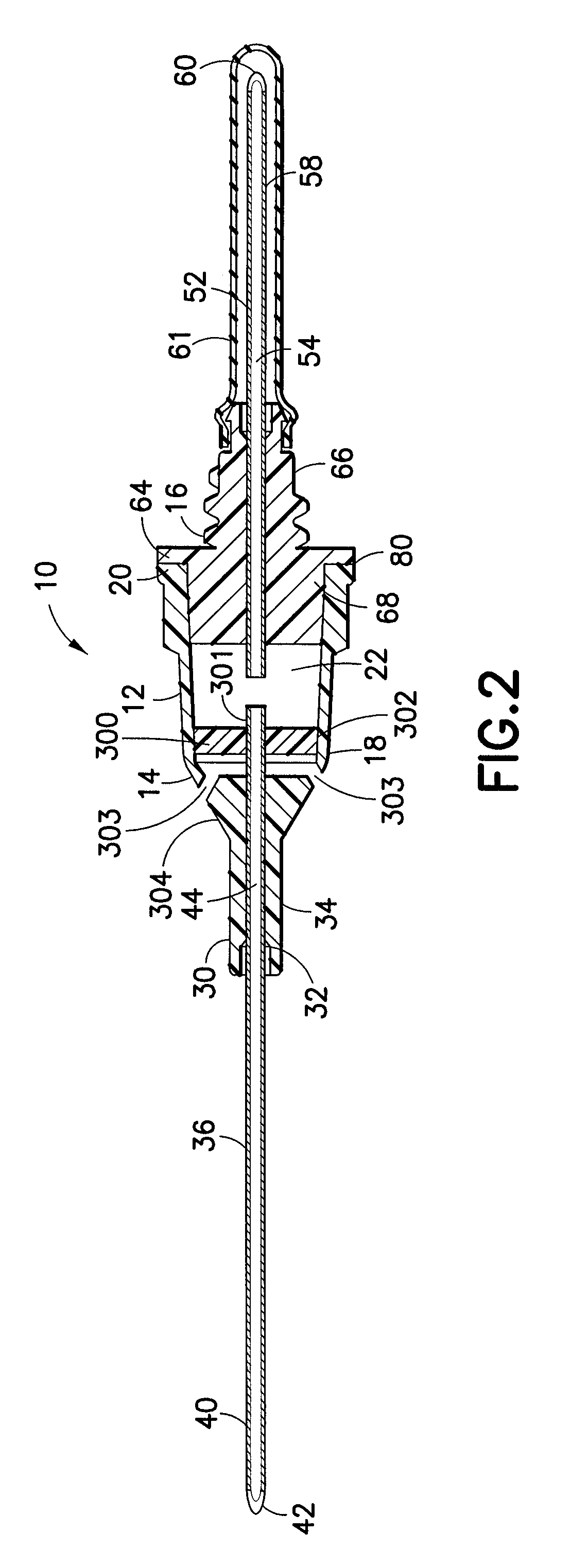
The invention is a self-venting blood collection needle assembly for the extraction of at least one fluid sample into an evacuated container for laboratory testing, this blood collection needle assembly providing a clear or translucent flashback chamber for blood to flow into, for visualization by the user to confirm successful vein entry. The self-venting mechanism permits escape of air during use, and which, typically, also prevents an outflow of fluid, such as blood. Thus, air under venous pressure will be allowed to escape from the blood collection needle assembly until blood reaches the venting mechanism.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Volume status monitor: peripheral venous pressure, hypervolemia and coherence analysis
Systems and methods are provided for monitoring changes in blood volume using waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. In particular, the systems and methods relate to detecting ventilation-induced variation (VIV) of waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. Advantageously, the systems and methods may relate to analyzing VIV in peripheral venous pressure (PVP). Thus, the VIV of PVP may be measured, wherein decreased VIV is indicative of decreased blood volume In exemplary embodiments, such as involving spontaneous breathing, it may be necessary to account for changes in respiratory signal strength. Thus systems and methods are also provided for assessing coherence between ventilation and VIV for a flow or pressure waveform. Specifically, coherence is evaluated by comparing the waveform to a detected respiratory signal. Finally, systems and method are provided for distinguishing the impact of respiration on the PG signal during hypervolemia as compared to hypovolemia. Such systems and methods may advantageously be utilized to monitor fluid status during fluid replacement.
Owner:SHELLEY KIRK H +2
Remaining needle
ActiveCN104922759AIncrease the scope of applicationImprove practicalityInfusion needlesValvesVeinElastic compression
A remaining needle comprises a remaining hose, a remaining needle seat, an extension hose seat, an extension hose connected between the remaining needle seat and the extension hose seat and a liquid stopping clamp arranged on the extension hose. The front portions of an upper contact and a lower contact located on a pressing touch portion of the liquid stopping clamp between a clamp piece and a clamp seat of the liquid stopping clamp are provided with at least one elastic compression device which has elasticity and larger clamping area and can form continuous positive pressure on the extension hose. According to the remaining needle, due to the fact that the liquid stopping clamp structure with at least two clamping positions is adopted, not only can the clamp piece of the liquid stopping clamp reliably clamp the extension hose to form liquid stopping, but also the continuous positive pressure compression device is utilized to continuously extrude the extension hose at the remaining needle seat end in a large area to enable the extension hose to generate larger deformation, liquid in an extruding pipe enters the remaining hose to play a continuous positive pressure action, therefore, blood return caused by springback siphon of the extension hose due to the liquid stopping clamp can be effectively avoided, the blood can be effectively prevented from flowing back to the remaining hose due to venous pressure fluctuation in blood vessels, and the purpose of preventing thrombus can be achieved.
Owner:ZHANJIANG JIANLIYUAN MEDICAL PROD
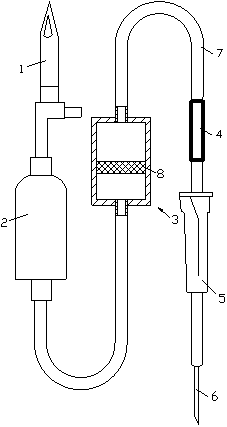
Non-wound esophageal varix venous pressure analyser
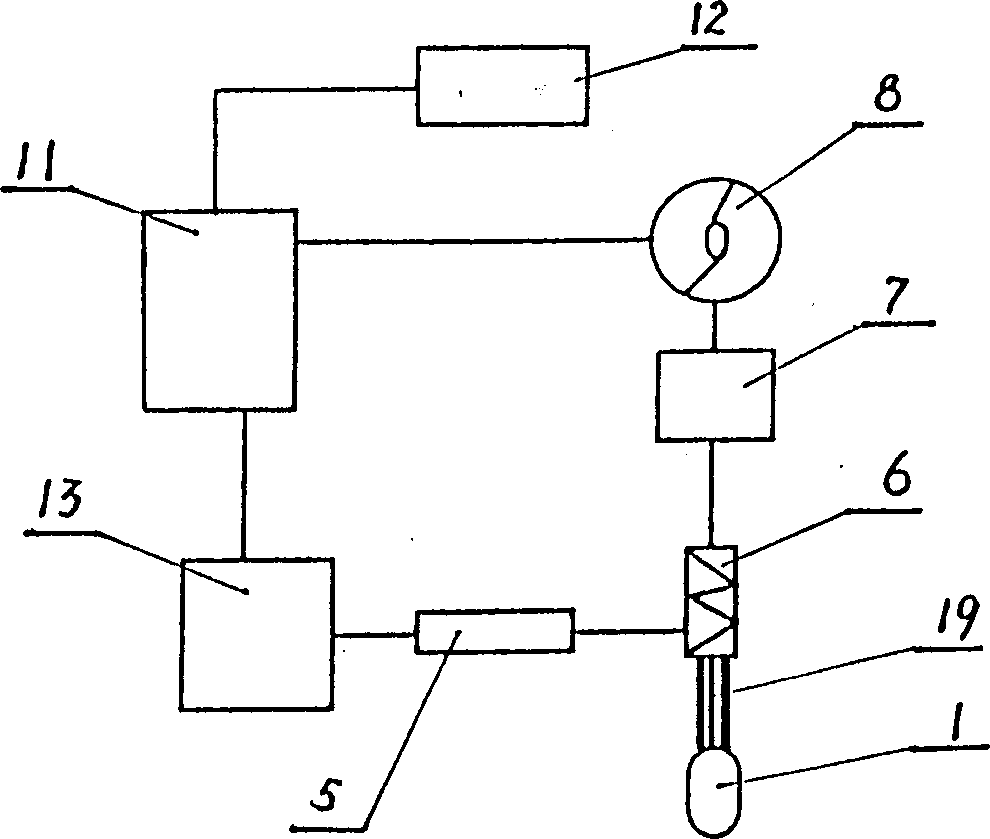
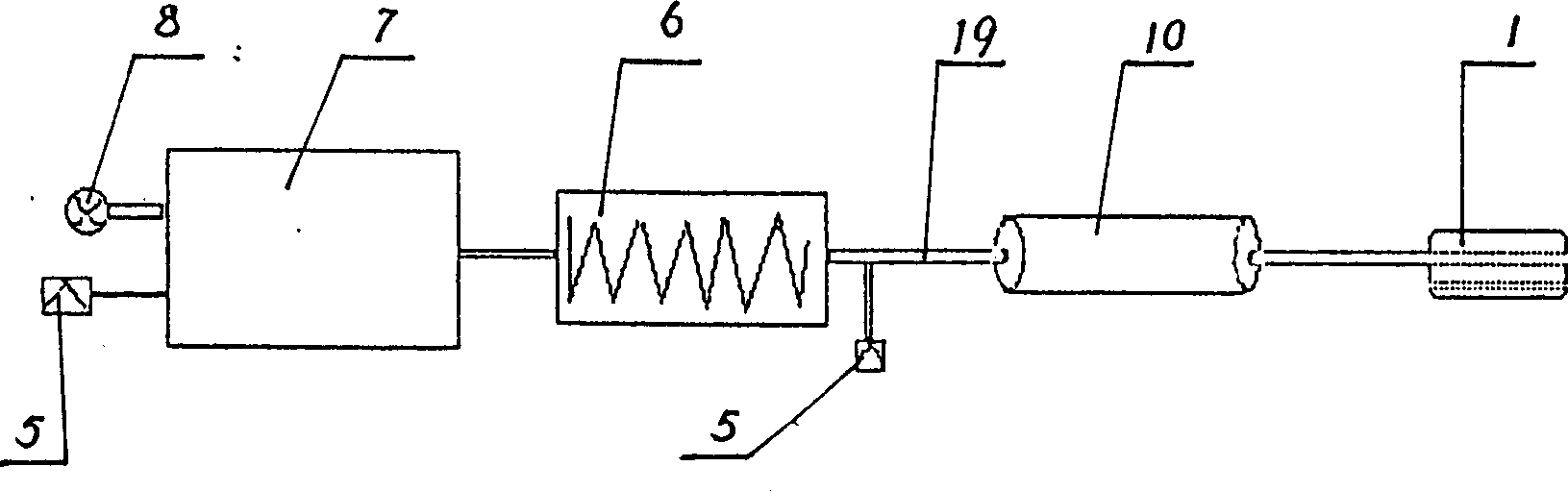
InactiveCN1709200ASolution to short lifeReduce economic pressureCatheterAngiographyMicrocontrollerMeasuring instrument
The present invention discloses a non-invasive esophageal varicose vein pressure measuring instrument. It includes PC machine, communication circuit, microcontroller, drive circuit, air pump, first pressure sensor, second pressure sensor, A / D converter, air tank and probe. Besides, said invention also provides the connection mode of all the said components.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Infiltration detection system
InactiveUS20070112329A1Quick checkAccurate placementMedical devicesIntravenous devicesVeinIV Infusion
An IV infusion system capable of detecting infiltration / extravasation events is described. Flow rate changes due to venous pressure variations are measured; infiltration / extravasation events are detected when these flow rate patterns are altered when infusion is not into a vein.
Owner:SAGE BURTON H JR
Testing meter of venous pressure for varicose esophagus in computer vision, and testing process
InactiveCN1795817AAvoid subjective errorOvercome the deficiency of subjective judgment of esophageal varices pressureCatheterAngiographyInternal pressureVein
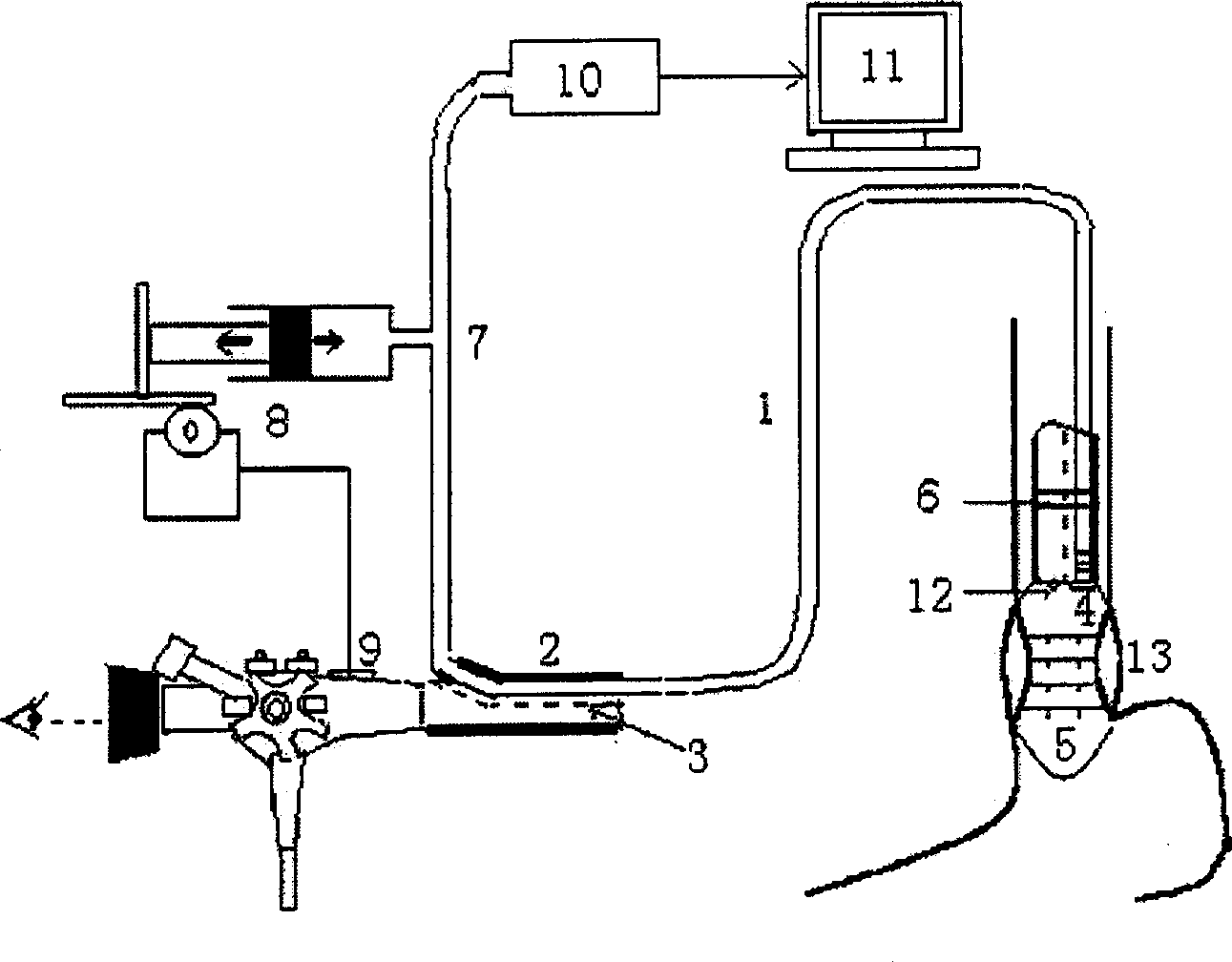
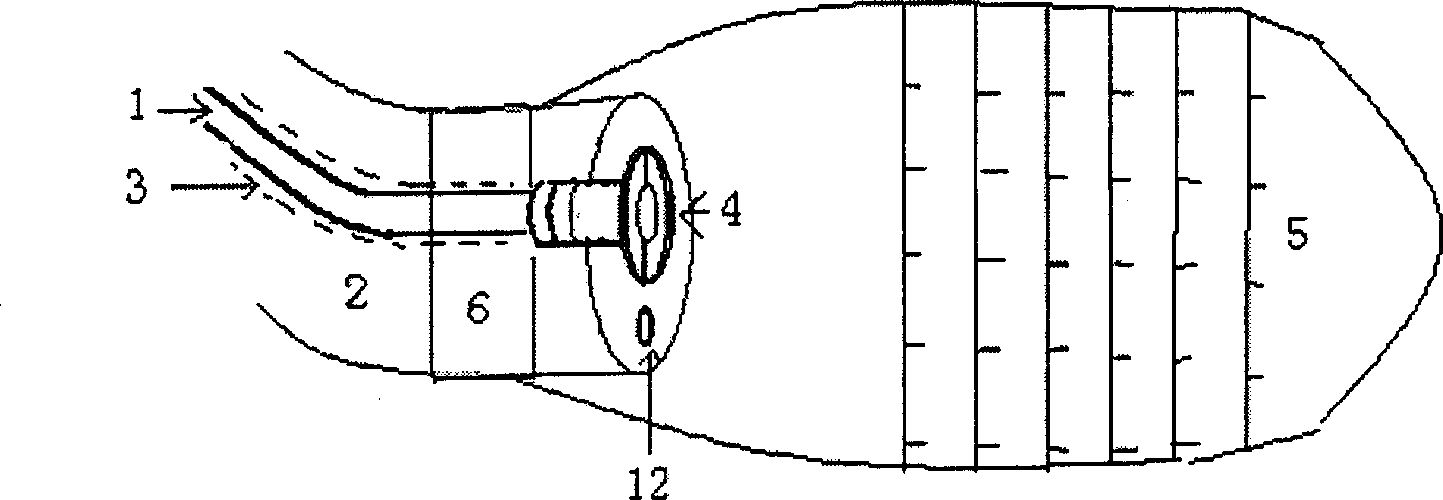
A computer visualized method for measuring the pressure of esophageal varicovein includes such steps as introducing an air bag into esophagus by use of electronic gastroscope, recording the deformations of said air bag by a camera head on the front end of electronic gastroscope, transmitting them to computer for tracking the deformation while synchronously transmitting internal pressure change of air bag to the computer, analyzing the relation between the pressure of air bag and the dynamic image of esophageal varicovein pressure amplitude, and measuring the pressure of air bag, which is just the pressure of esophageal varicovein when the pressure amplitude change of esophageal varicovein is relatively stable. Its system is also disclosed.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV +1
Method and device for measuring venous pressure without wound
InactiveCN1390523AAccurate pressure measurementAccurate measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyVeinAir pump
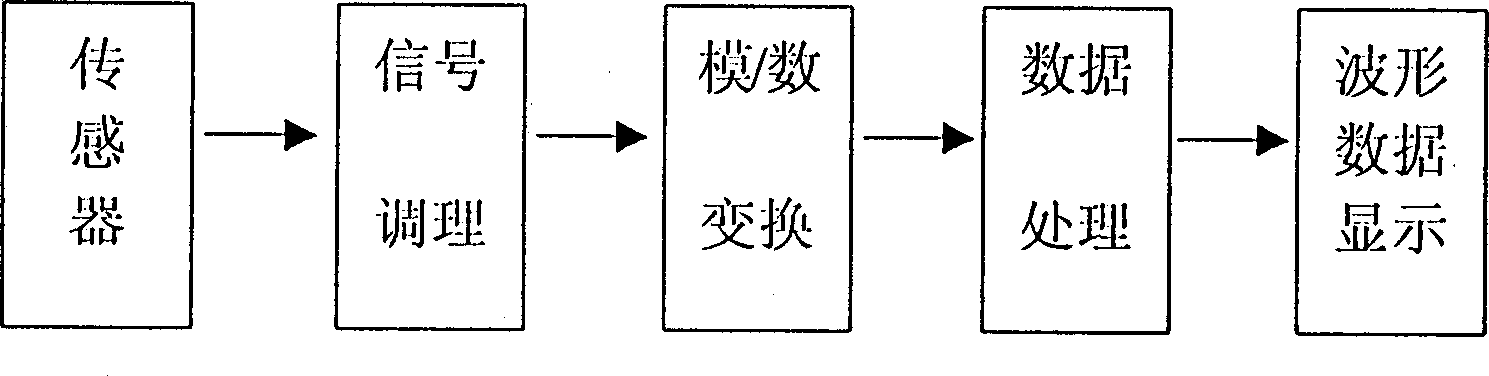
A method and equipment for measuring venous pressure without wound is disclosed. Said equipment is composed of air channel including air pump, air sensitive probe consisting of guide tube and capillary tube, circuit unit consisting of amplifier and A / D converter, and data processing unit consisting of computer and display. Said method features that the venous pressure is sensed by air sensitive probe and then transmitted via sensor to amplifier, A / D converter and computer sequentially. The result is displayed in waveform and numerals modes. Its advantages are simple method and high correctness.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com