Extracorporeal blood handling system with automatic flow control and methods of use
a technology of automatic flow control and extracorporeal blood, which is applied in the field of extracorporeal blood handling system, can solve the problems of significant patient injury, depletion of reservoir and air supply, and the inability to meet the needs of patients, so as to increase the time available for operators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Overview of a Preferred Blood Handling System
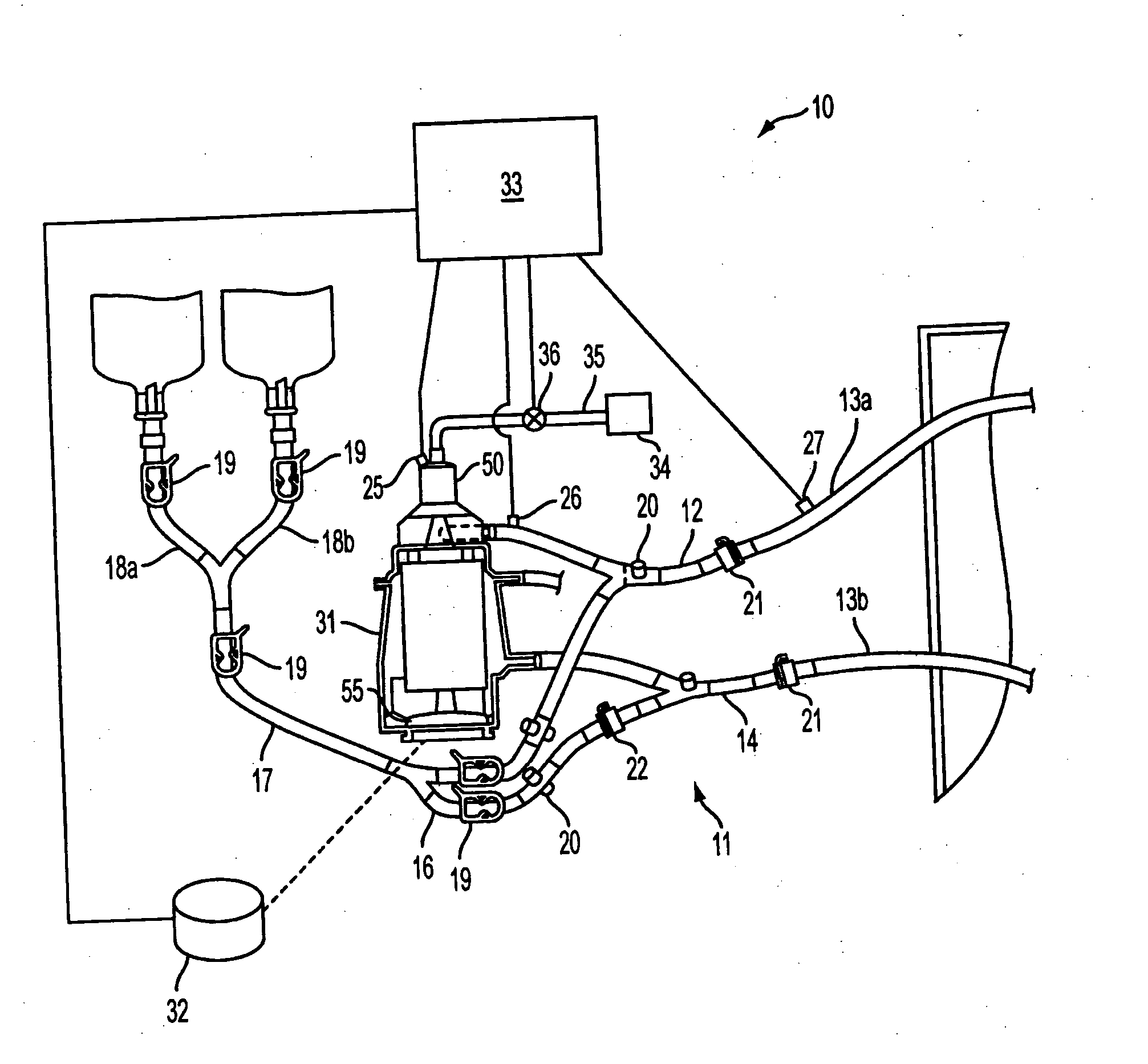
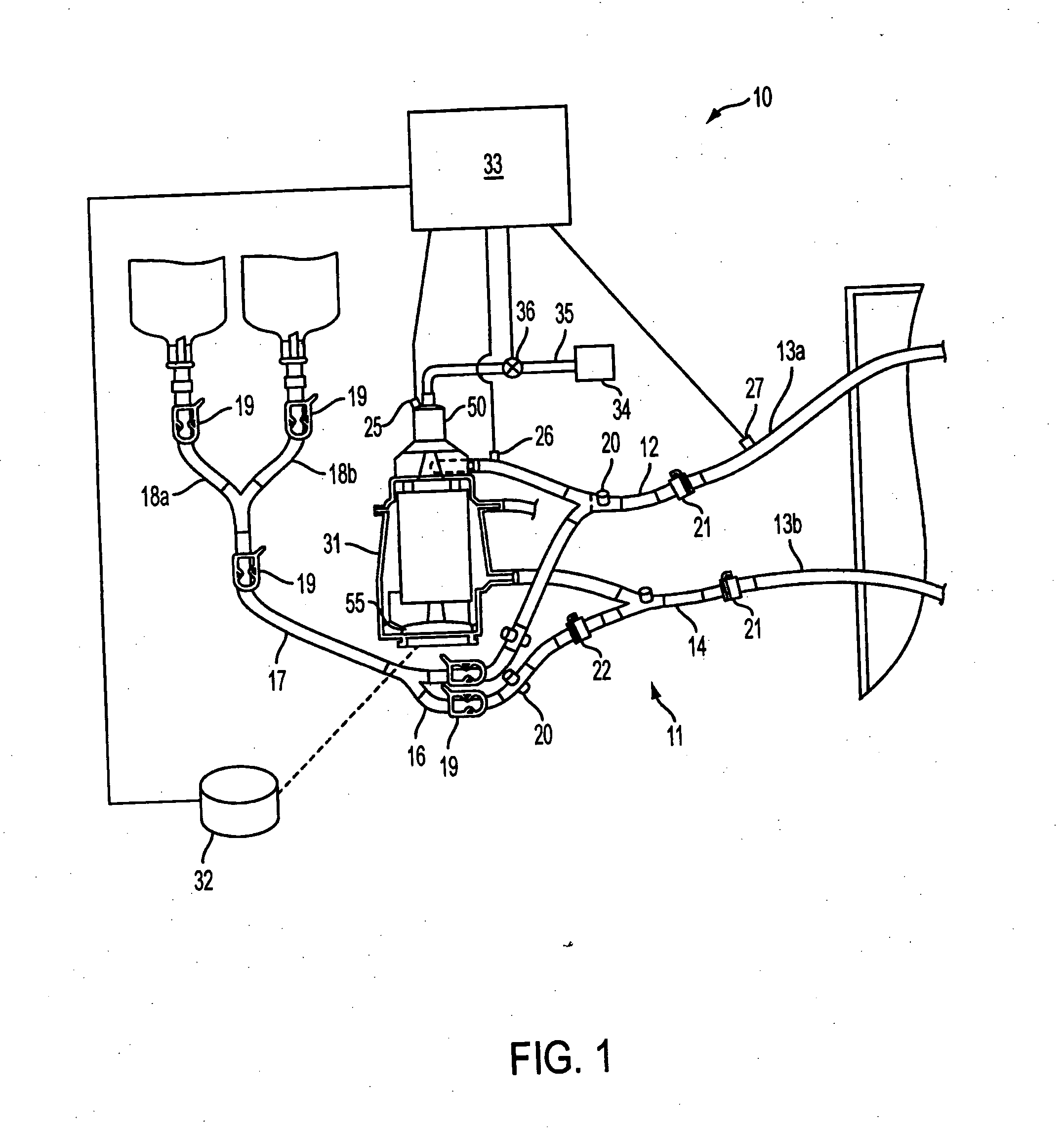
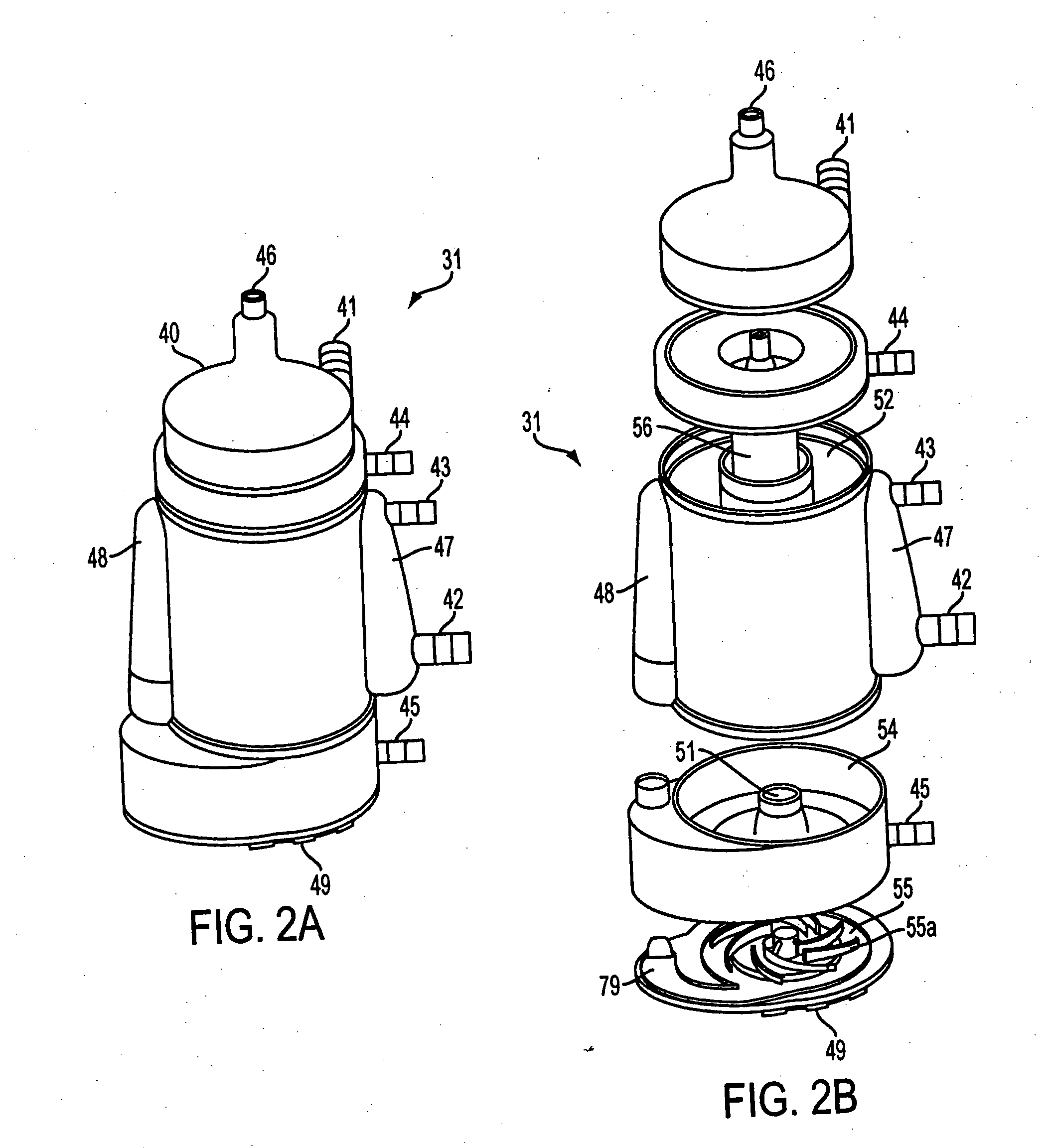
[0046] Referring to FIG. 1, a preferred extracorporeal blood handling system 10 suitable for use with the automatic flow control system of the present invention is described. Extracorporeal blood handling system 10 is designed to maintain a patient on full or partial bypass support, for example, during a coronary artery bypass graft procedure, in either a full-bypass or beating heart (partial bypass) mode of operation, or open heart repair procedure, typically with full-bypass mode of operation.
[0047] Extracorporeal blood handling system 10 includes an extracorporeal blood circuit 11 having a perfusion circuit comprising venous line 12, perfusion line segments 13a, 13b and arterial line 14, and a priming / reservoir circuit comprising line 16, priming line 17, and segments 18a and 18b. The ends of perfusion line segments 13a (venous), 13b (arterial) are shown extending into the sterile field as they would appear during use, where they ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com