Method for selecting aggregation node in network
A node and network technology, applied in the field of selecting aggregation nodes, which can solve problems such as short lifetime
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
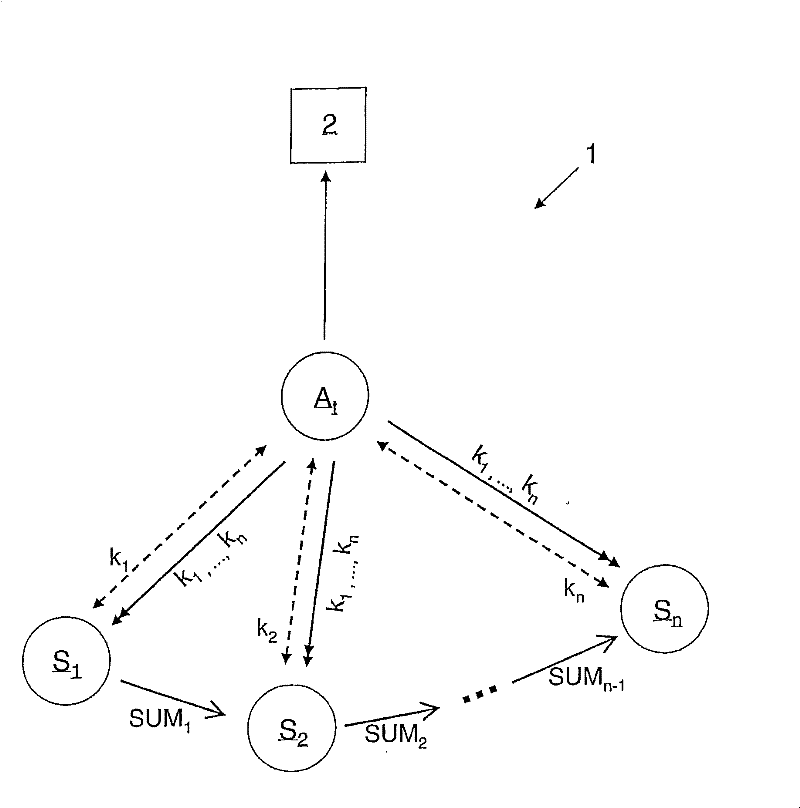
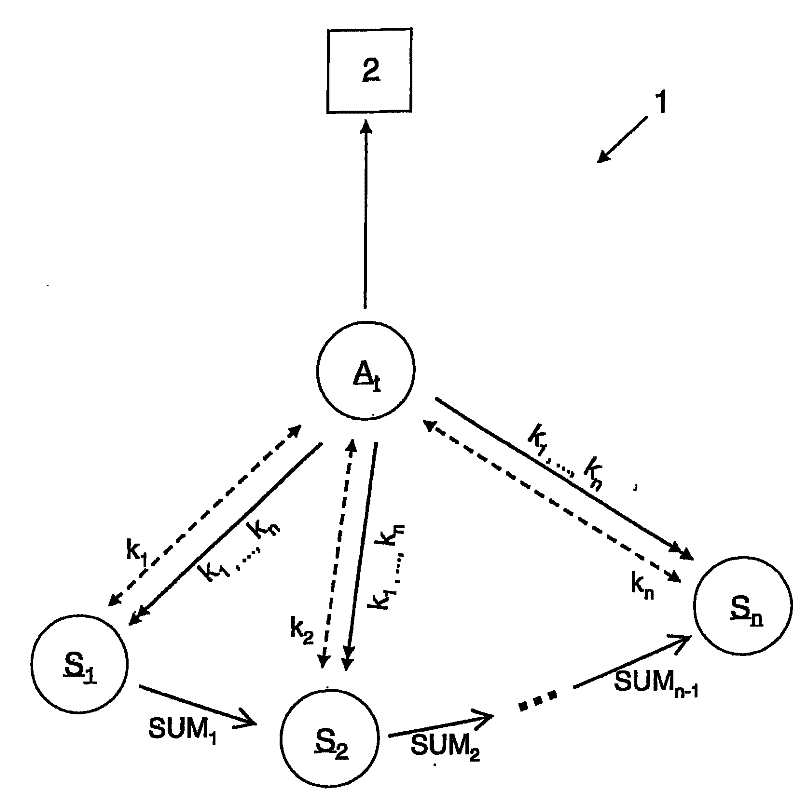
[0029] Referring in more detail to the attached drawing, the sole figure shows an application scenario of the method according to the invention. As an illustration, the figure shows a sensor network 1 with a plurality of sensor nodes using S 1 to S n These sensor nodes are marked according to their numbers. aggregation node A tFor sensor node S 1 to S n The sensed sensor data is aggregated. Usually, when sink node 2 requests, aggregation node A t Forward the collected data to the sink node 2, the sink node 2 and the sensor node S i and rendezvous node A t The difference is a specific device with sufficiently large physical resources. For clarity, only one rendezvous node A is shown in the figure t , and in A t There is no intermediate node between and sink node 2.
[0030] The sensor network 1 is shown in the state at epoch t, during epoch t, denoted by A t The sensor nodes act as aggregation nodes. At the beginning of the next period t+1, the protocol starts ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com