Power converter
A power converter and power conversion technology, which is applied in the direction of output power conversion devices, electrical components, AC motor control, etc., to achieve good precision, improve operating performance, and reduce uneven rotation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
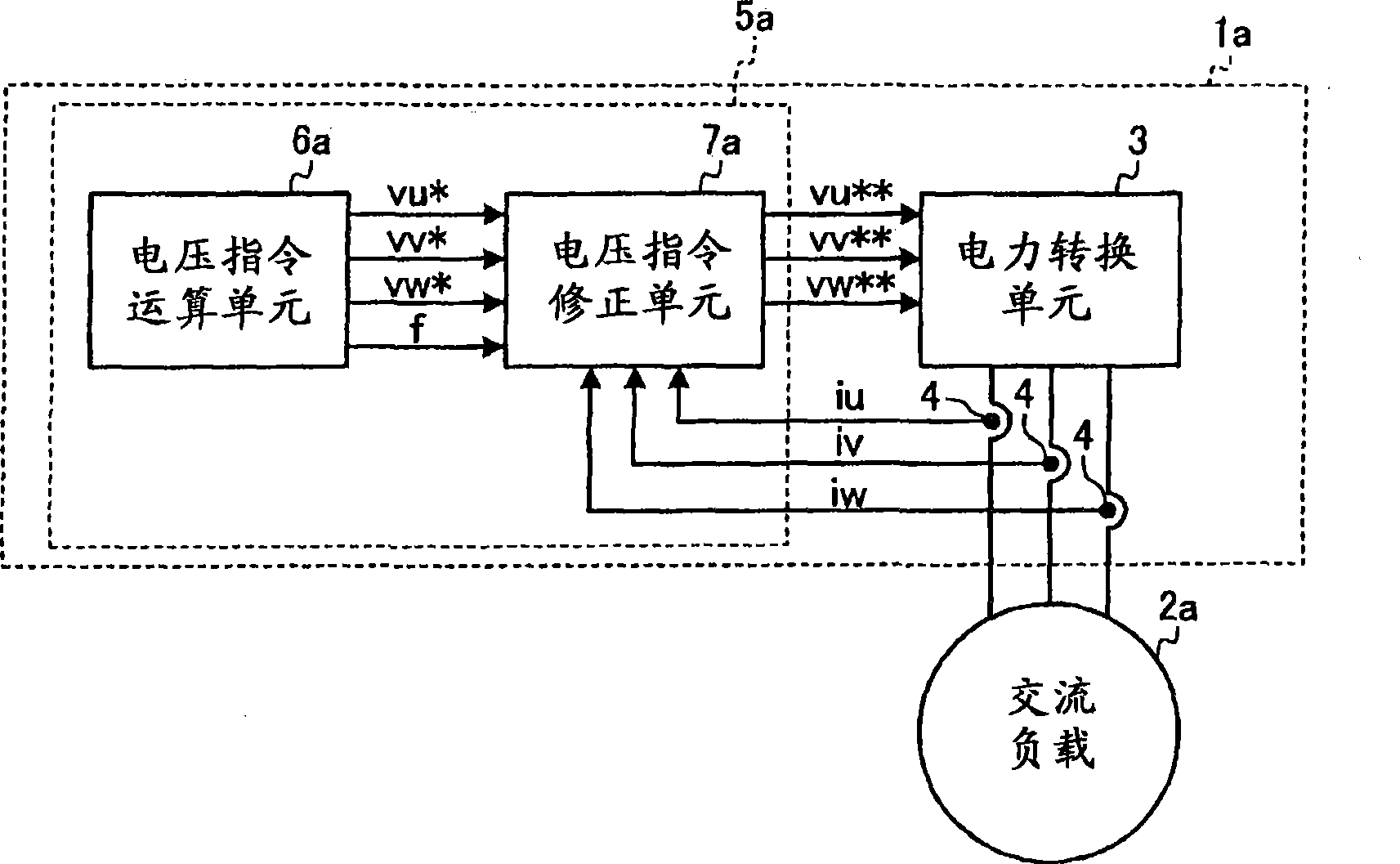
[0051] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of the power converter according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In Embodiment 1 and the following embodiments, a power converter outputting three-phase AC power is described as an example, but the content is similarly applicable to a power converter outputting single-phase AC power.
[0052] figure 1 The shown power converter 1a includes: a power conversion unit 3 connected to a three-phase AC load 2a; a current detection unit 4; AC power supply control, wherein the control device 5a is composed of a voltage command calculation unit 6a and a voltage command correction unit 7a. The voltage command correction unit 7 a is provided between the output side of the voltage command calculation unit 6 a and the input side of the power conversion unit 3 .
[0053] The power device elements of the upper and lower arms of the power conversion unit 3 are based on the AC voltage command input from the control de...
Embodiment approach 2
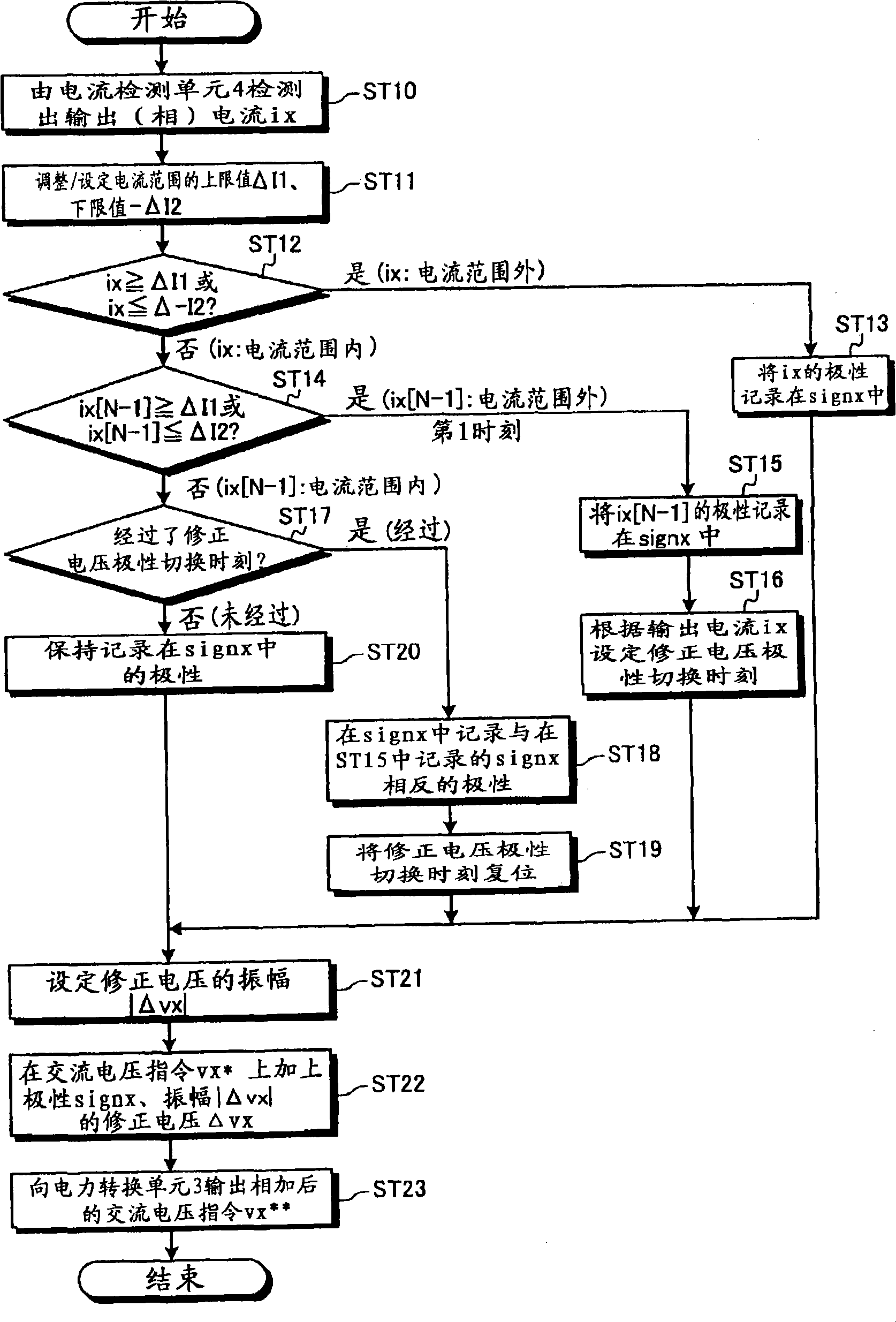
[0115] Figure 8 It is a flowchart explaining the correction operation procedure of the voltage command correction means included in the power converter according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. exist Figure 8 in, for with figure 2 Processes shown that are the same or equivalent are assigned the same reference numerals. Here, the description will focus on the part related to the second embodiment.
[0116] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the voltage command correction unit included in the power converter of Embodiment 2 is figure 2 In the shown processing procedure, in the process of shifting from ST14 to ST17, if the determination in ST14 is negative (No), the processing of ST30 is performed, and then the process proceeds to ST17.
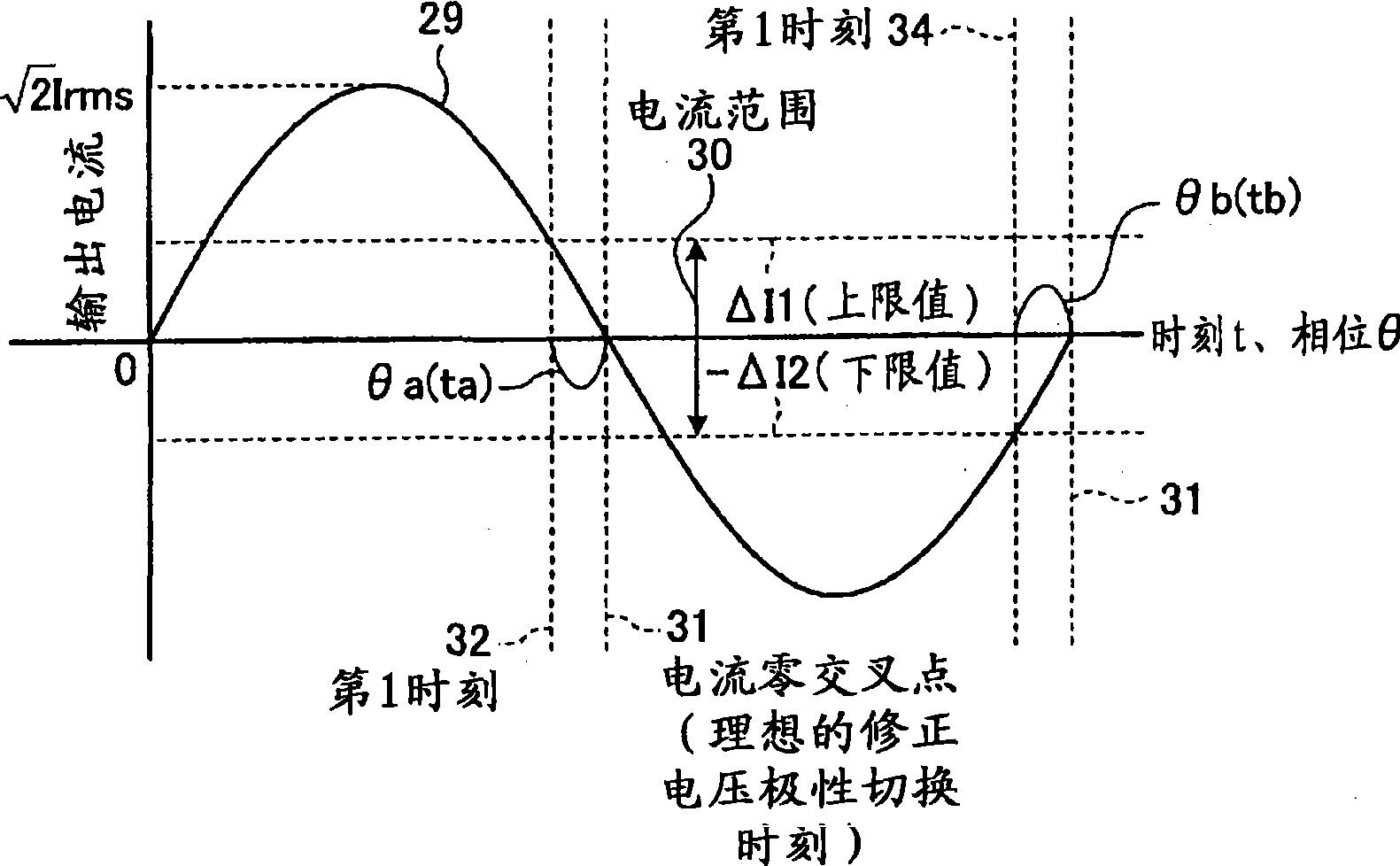
[0117] In ST30, if referring to Figure 7 For explanation, in the period (2) from the first time 32 to the correction voltage polarity switching time 38 , the correction process of the correction voltage polarity switching time 38 i...
Embodiment approach 3
[0124] Figure 9 It is a flowchart explaining the correction operation procedure of the voltage command correction means included in the power converter according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. exist Figure 9 in, for with figure 2 Processes shown that are the same or equivalent are assigned the same reference numerals. Here, the description will focus on the part related to the third embodiment.
[0125] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the voltage command correction unit included in the power converter of Embodiment 3 is figure 2 In the shown processing procedure, in the process of shifting from ST14 to ST17, if the determination in ST14 is negative (No), the processing of ST40 is performed, and then the process proceeds to ST17.
[0126] In ST40, if referring to Figure 7 For explanation, in the period (2) from the first time 32 to the correction voltage polarity switching time 38 , the correction process of the correction voltage polarity switching time 38 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com