Method for fault line selection of electric distribution network by using S transformation energy relative entropy
A technology for fault line selection and line selection method, which is applied to fault locations, electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., and can solve problems such as low accuracy and reliability, difficult detection, and easy misjudgment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
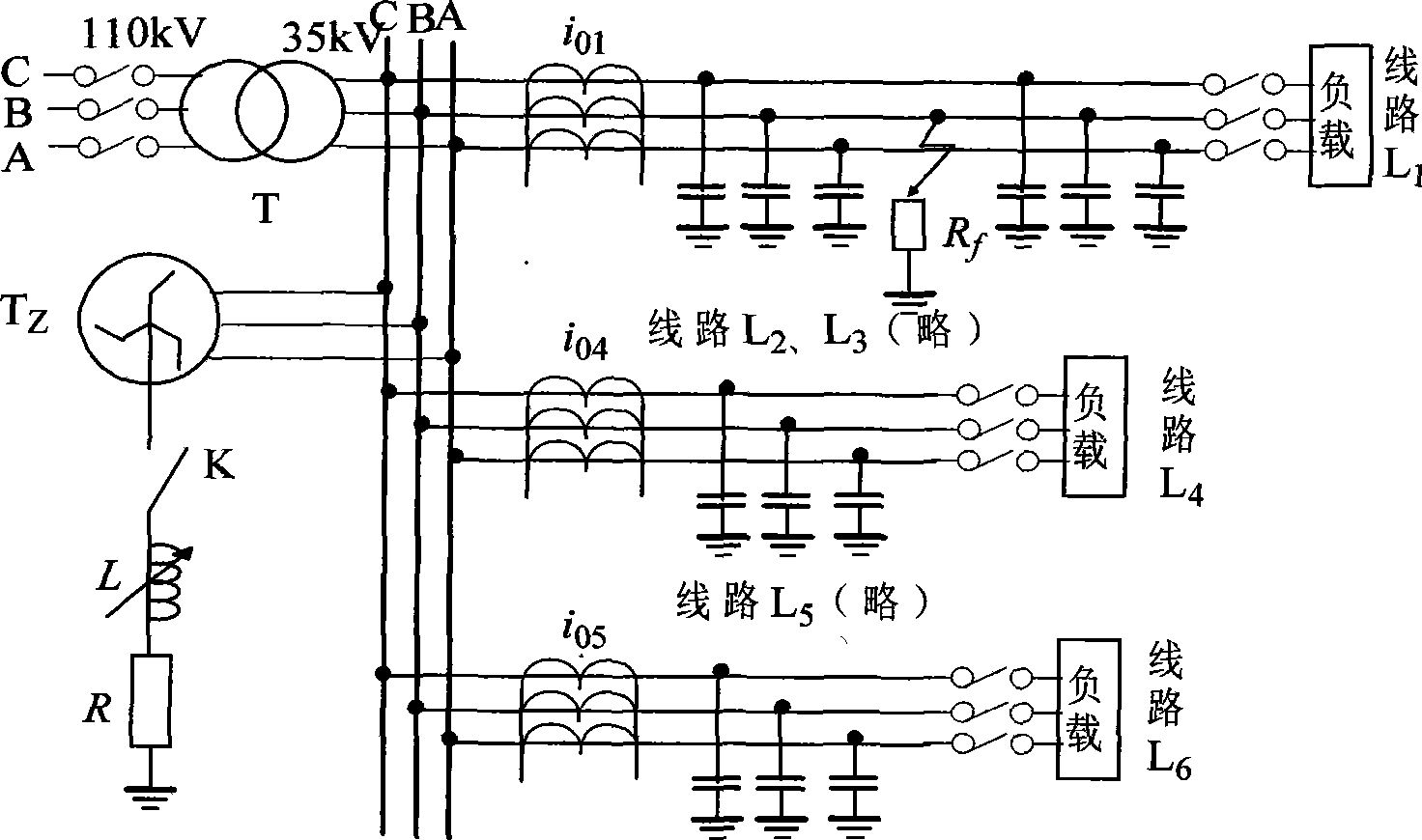
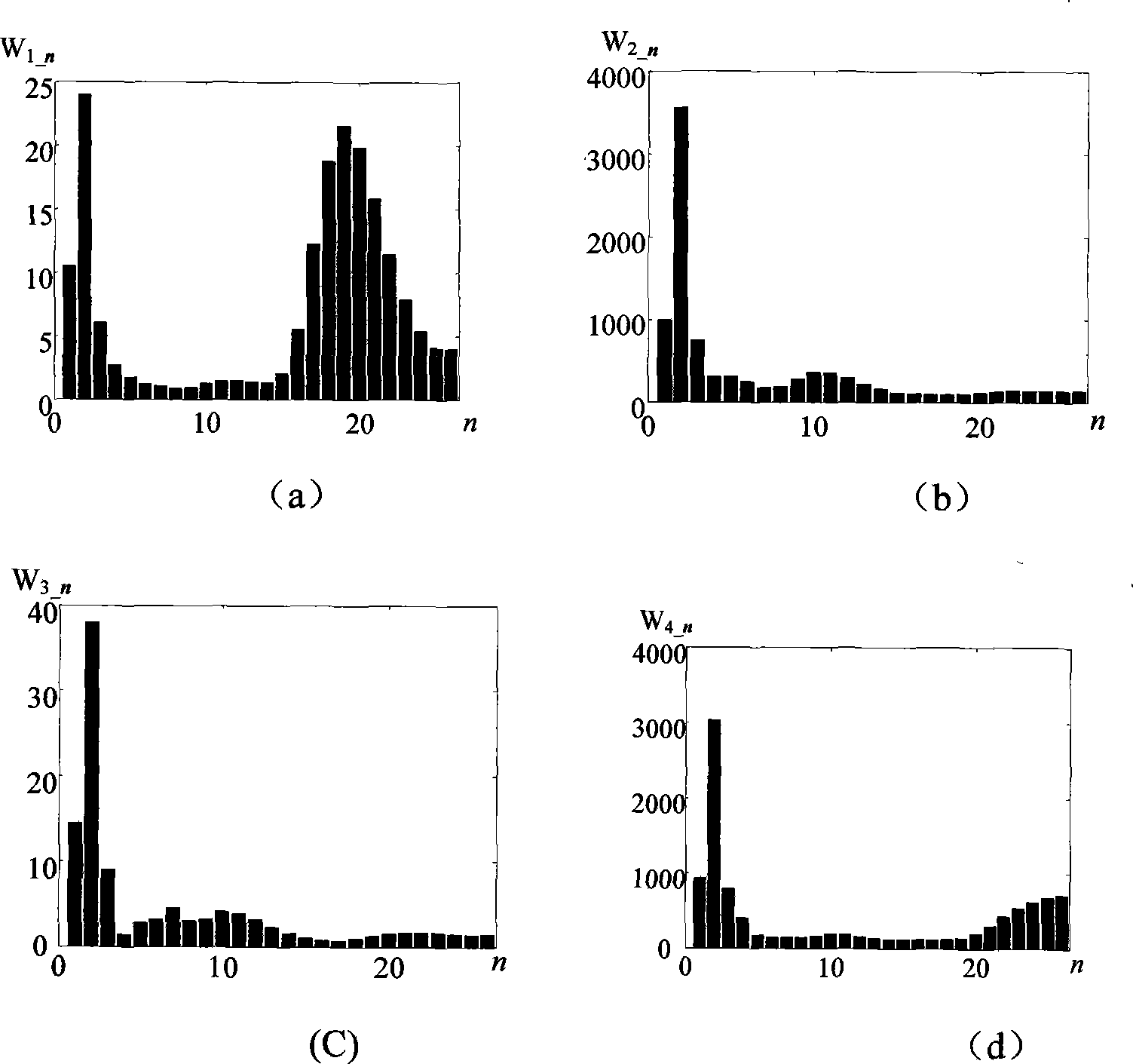
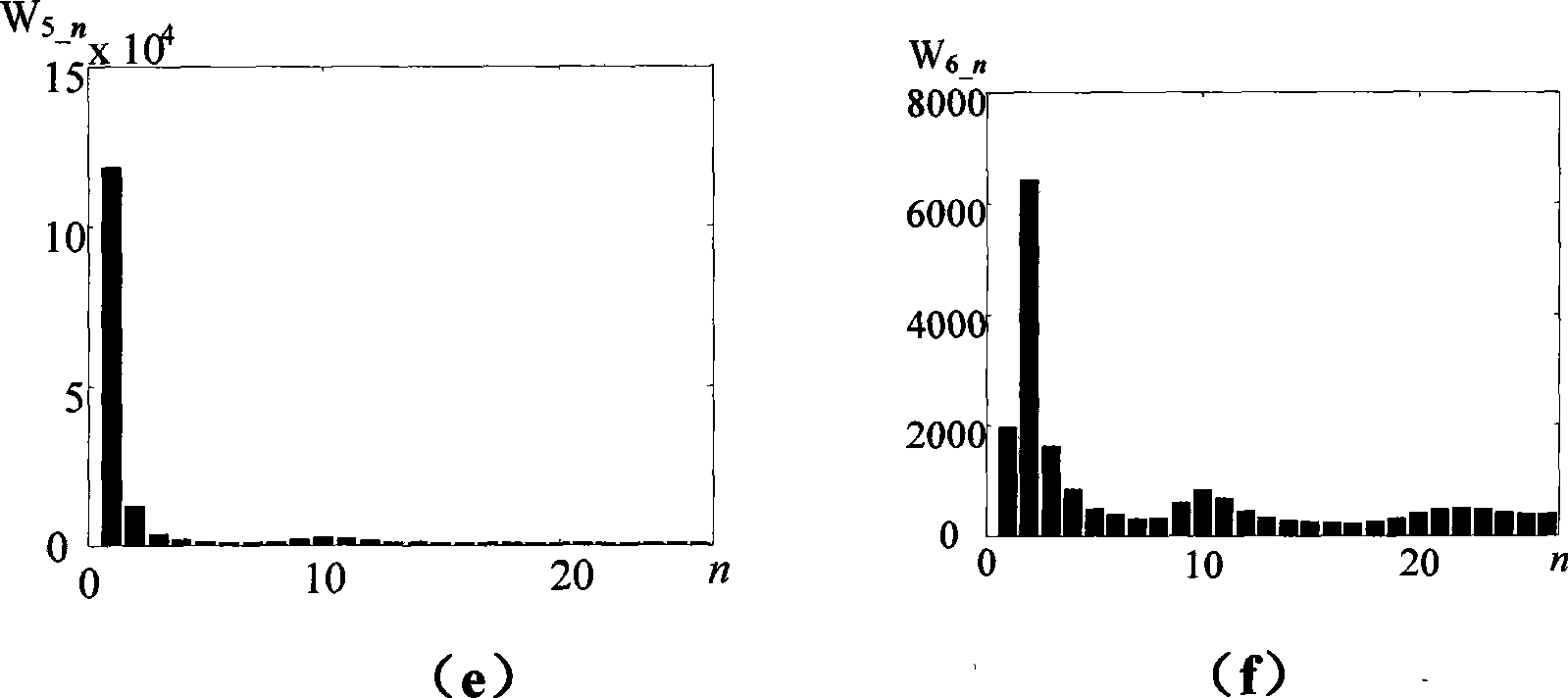
[0087] Line L 5 A single-phase ground fault occurs at a distance of 5km from the busbar, the fault closing angle is 90°, and the transition resistance is 200Ω. S-transform the zero-sequence currents of the six lines in T / 4 obtained by sampling. The sampling frequency of the original signal is 10kHz, and the length of the sampling sequence is 50 sampling points. Six complex matrices of 50×26 are obtained by S-transformation , modulo this matrix. According to the formulas (11)~(14), the S transformation energy relative entropy M of each line is obtained il , the resulting 6×6 S transformation energy relative entropy matrix M is:
[0088] M = M 11 M 12 M 13 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com