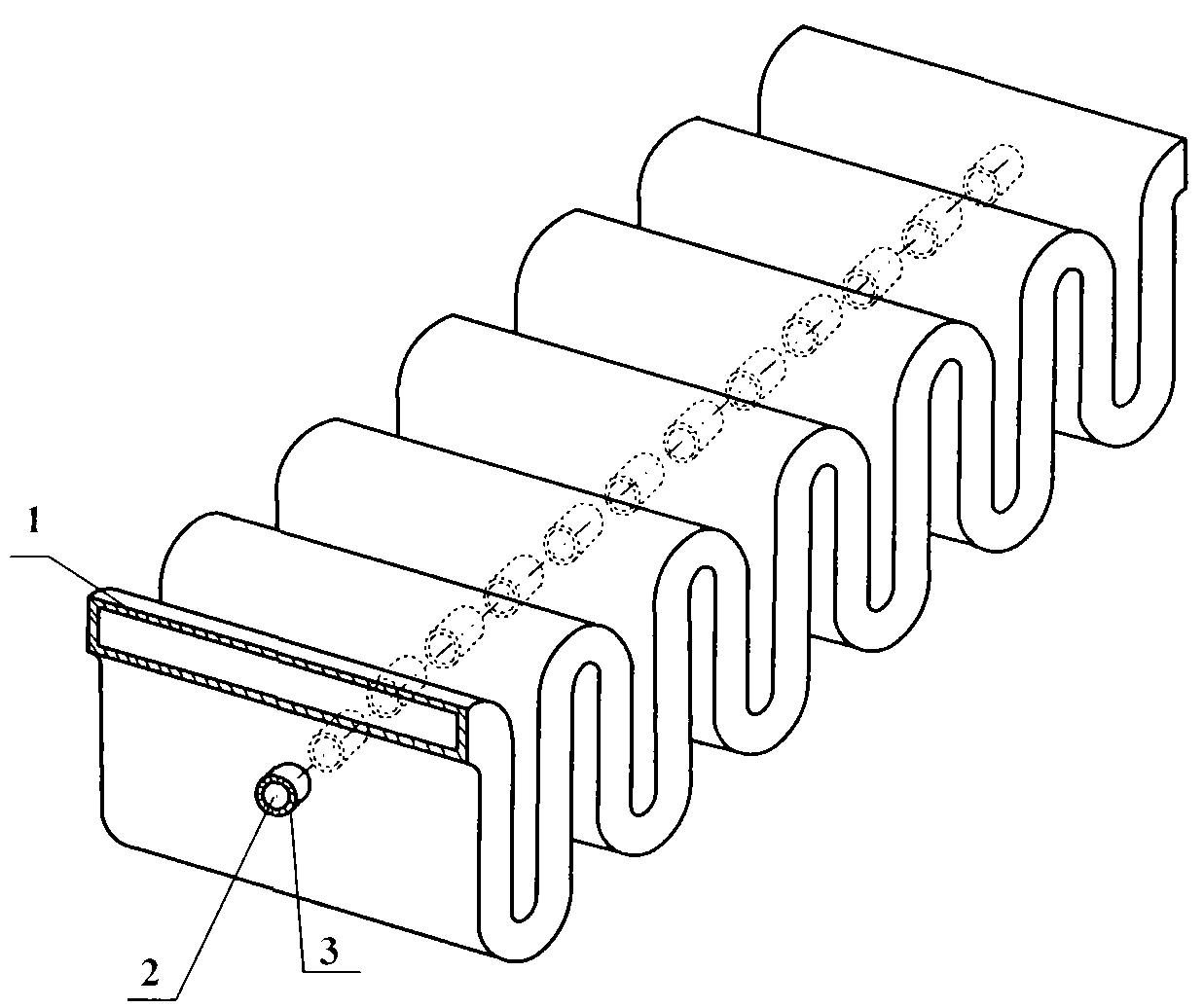
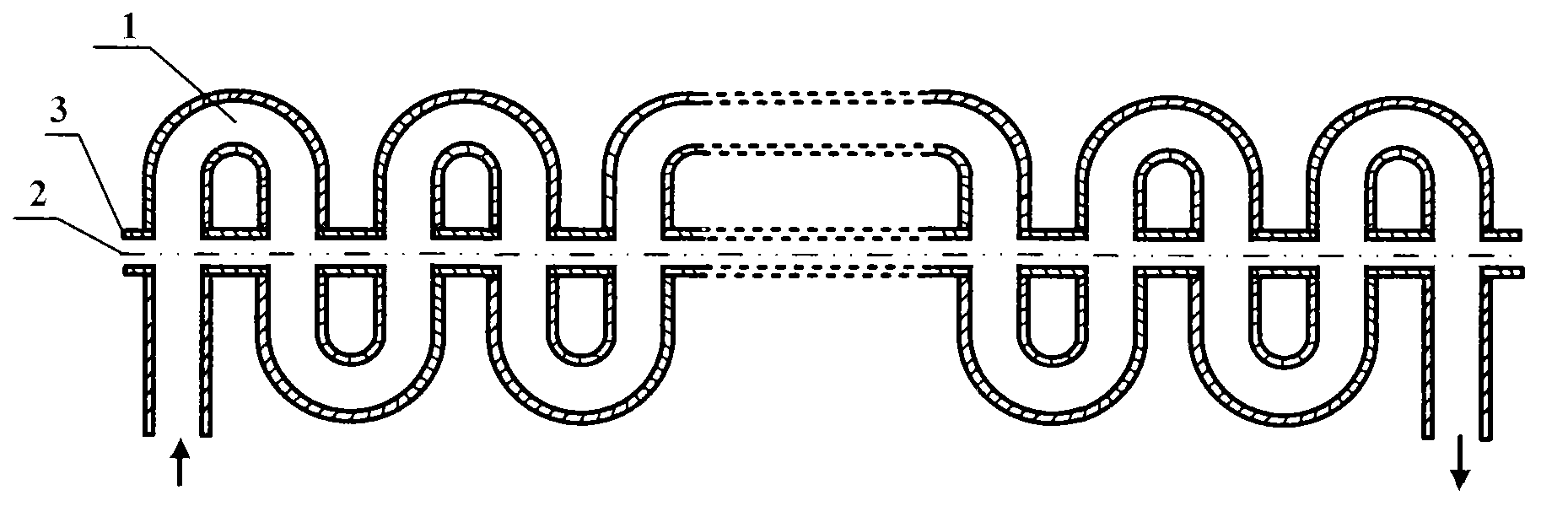
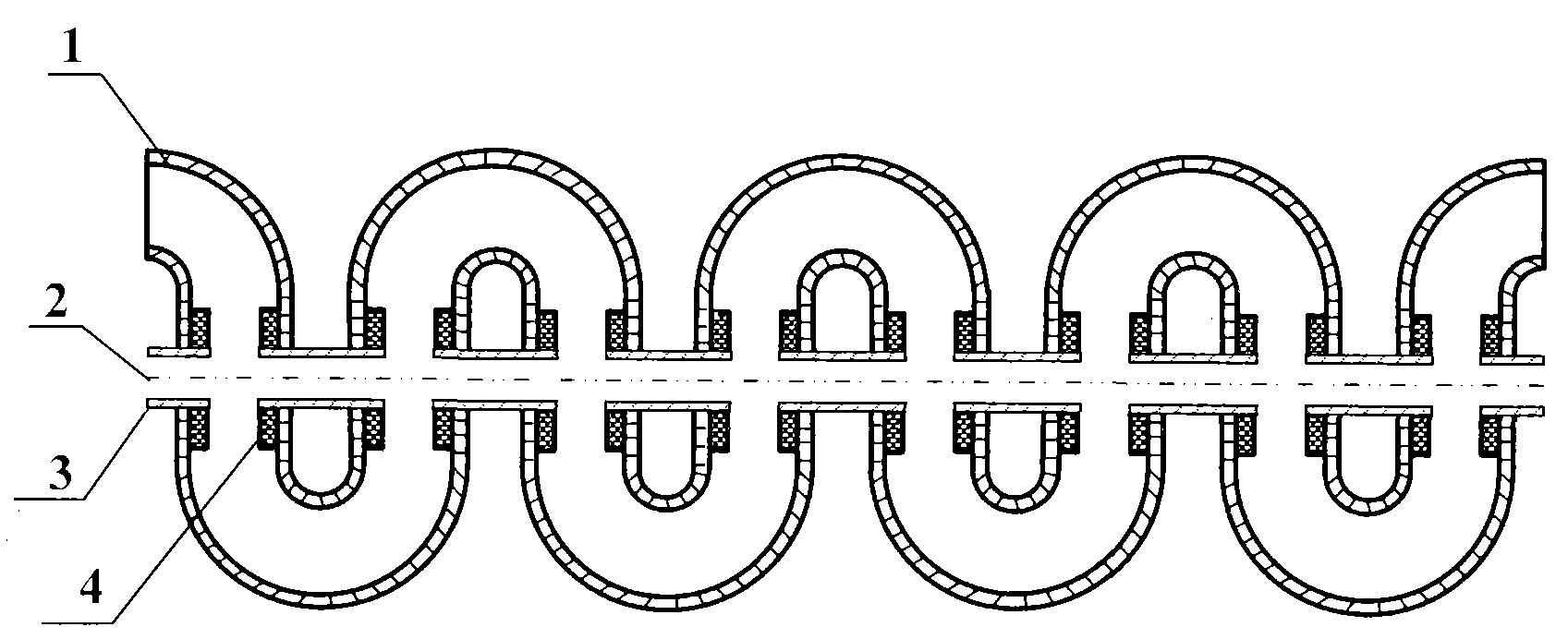
Ridge loading zigzag waveguide slow wave line
A technology of zigzag waveguide and slow wave line, applied in the field of traveling wave tube amplifier devices, can solve the problems of low coupling impedance of zigzag waveguide slow wave structure, limitation of traveling wave tube gain and efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] specific implementation plan
[0021] Such as Figure 4 and Figure 5 , in the 8mm millimeter wave band, the structural dimensions of the specific scheme of the meandering double-ridge waveguide slow wave line are as follows (unit: mm): a=5, b=0.8, L=4.56, H=2.2, r 0 =0.5, w=5, d=0.25, h=2.2. Use three-dimensional electromagnetic simulation software to simulate the ridge-loaded meander waveguide slow-wave line provided by the present invention, obtain its dispersion characteristics and coupling impedance, and compare it with the meandering double-ridge slow-wave structure and ordinary meander waveguide slow-wave line. The simulation results are as follows Figure 6 and Figure 7 shown. Curve 5 and Curve 8 are the dispersion characteristic curve and coupling impedance curve of the ordinary meandering waveguide slow-wave structure respectively, Curve 6 and Curve 9 are the dispersion characteristic curve and coupling impedance curve of the meandering double-ridge waveg...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com