Method and device for realizing multicast load sharing
A load sharing and multicast technology, applied in the communication field, can solve problems such as DR or querier pressure, and achieve the effect of avoiding heavy load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
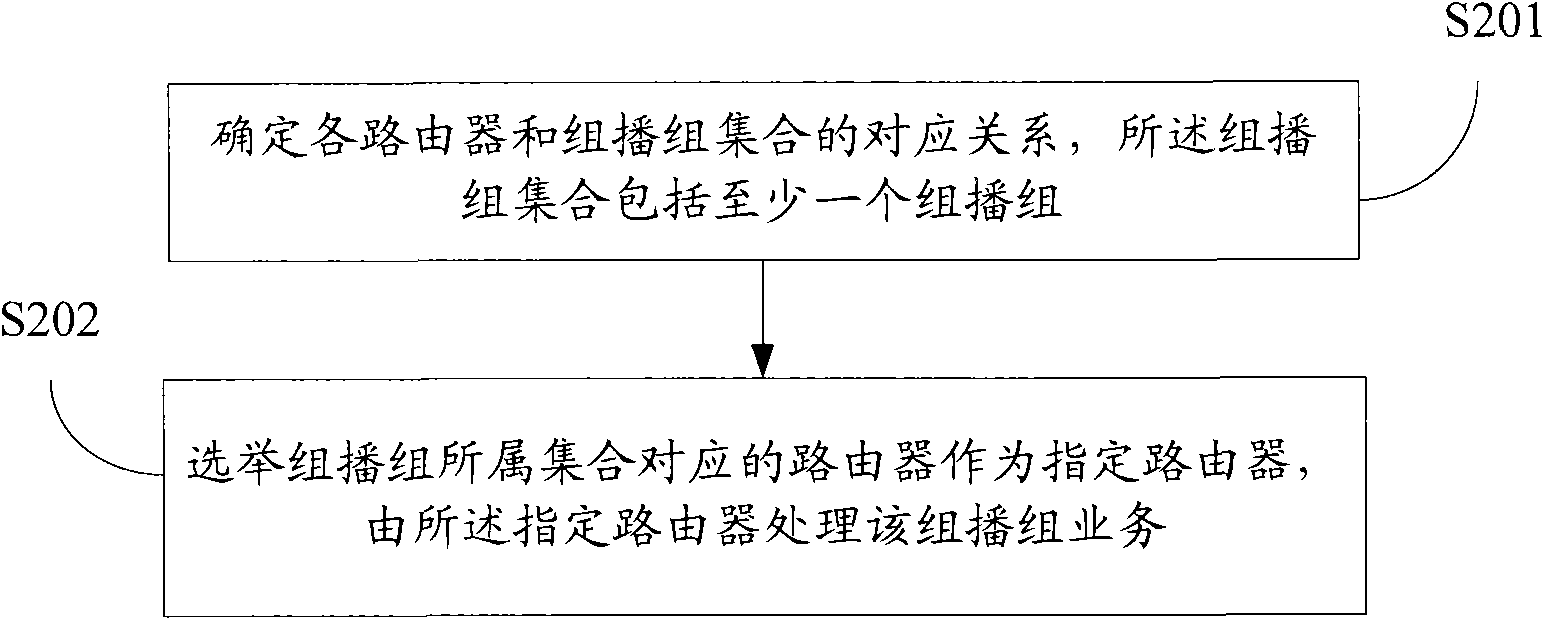
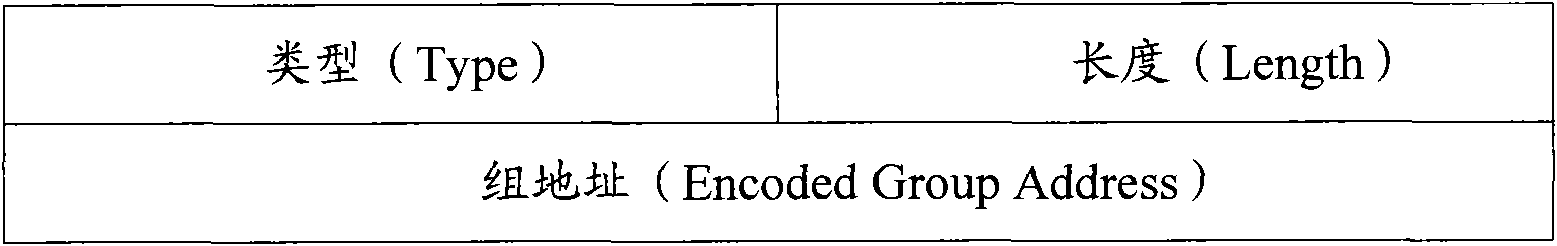
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] The following describes Embodiment 1: PIM-SM DR load sharing
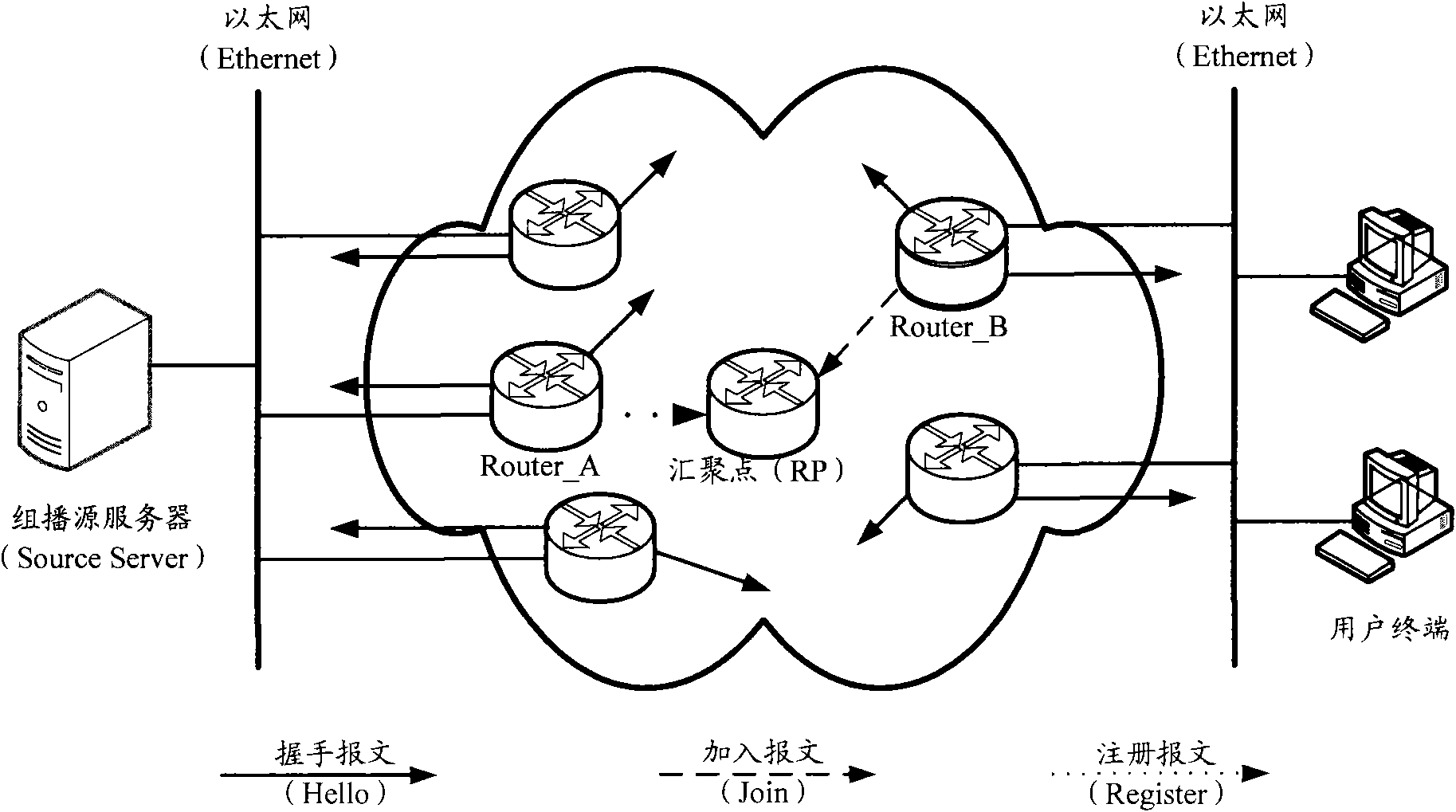
[0055] Assuming that in Example 1 Figure 5 In the configuration, PIM SM is configured on all interfaces, IGMP is configured on the interface connecting RTD / RTE to the receiver, and RTB and RTD are respectively interface-level DRs of the network segment where they are located.
[0056] Scenario 1: Source DR load balancing 1
[0057] 1. The multicast server sends 3 multicast data sources, configure RTA to serve G1, and RTB to serve G2 and G3.
[0058] 2. After RTA receives the data of these groups, on intf4, according to the longest matching principle introduced above, elect G1 among them as DR, so G1 sends a registration message to its corresponding RP.
[0059] 3. Similarly, RTB sends registration messages to their corresponding RPs for G2 and G3.
[0060] Here is a more specific example of the scenario:
[0061] 1) Configure RTD's intf2 (IP address 10.1.1.2) as 225.1.0.0 / 16 service, RTE's intf1 (IP add...
Embodiment 2
[0084] The following describes the second embodiment: PIM-SSM DR load sharing
[0085] Assuming that in the second embodiment Figure 5In this configuration, PIM SSM is configured on all interfaces, IGMP is configured on the interface connecting RTD / RTE to the receiver, and RTD is the interface-level DR of the network segment where it is located.
[0086] For SSM, it is forwarded directly through SPT without RP.
[0087] Scenario 1: Receiver DR Load Balancing 1
[0088] 1. HostA, HostB, and HostC send IGMP V3 REPORT to join different source groups (S1, G1), (S1, G2), (S1, G3). Configure RTD to serve G1, and RTE to serve G2 and G3.
[0089] 2. RTD receives these IGMP V3 REPORTs, becomes the DR of group G1, sends (S, G) join to its corresponding source, obtains the data and forwards it to the receiving end.
[0090] 3. The RTE sends (S, G) join to the corresponding source for the groups G2 and G3, obtains the data and forwards it to the receiving end.
[0091] Scenario 2: D...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Embodiment 3 is introduced below: IGMP querier load sharing
[0096] Assuming that in Example 3 Figure 5 In the configuration, only IGMP is configured on the interface connecting RTD / RTE to the receiving end, and PIM-SM / SSM is configured on all other interfaces, and RTD is the IGMP querier in the network segment where it is located.
[0097] When the interface is not configured with PIM-SM / SSM, the router on the shared network segment elects an IGMP querier to be responsible for the data forwarding of this network segment.
[0098] Scenario 1: Querier Load Balancing 1
[0099] 1. HostA, HostB, and HostC send IGMP V2 / V3 REPORT to join different groups G1, G2, and G3. Configure RTD to serve G1, and RTE to serve G2 and G3.
[0100] 2. RTD receives these IGMP V2 / V3 REPORTs, becomes the IGMP querier of group G1, sends (*, G) join to its corresponding RP or sends (S, G) join to its corresponding source, obtains data and Forward to the receiving end.
[0101] 3. Similarl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com