Method of derivatising an analyte for subsequent detection through a nucleic acid based sensor
An analyte and sensor technology, applied in the field of derivative analytes, can solve the problem that the system cannot be easily implanted into small devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
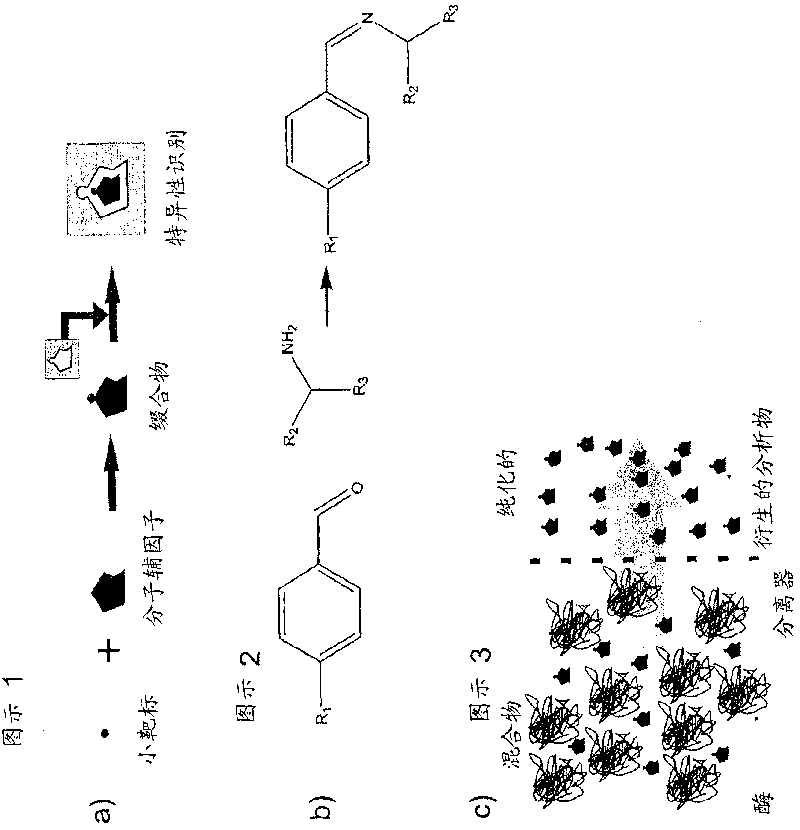
[0064] a) Analytes / small molecules according to the invention are molecules with low molecular weight (preferably in the range of 1-500 Da, more preferably in the range of 10-300 Da, most preferably in the range of 50-250 Da) and have the following classification First functional group:
[0065] Aliphatic or aromatic primary amines, secondary amines, monoamines, diamines, triamines
[0066] Aliphatic or aromatic monothiol, dithiol, trithiol
[0067] Aliphatic or aromatic monoalcohols, diols, triols
[0068] Aliphatic or aromatic monoketones, diketones, triketones
[0069] Aliphatic or aromatic monoaldehydes, dialdehydes, trialdehydes
[0070] Aliphatic or aromatic monocarboxylic acid, dicarboxylic acid, tricarboxylic acid
[0071] Aliphatic or aromatic monocarboxylates, dicarboxylates, tricarboxylates
[0072] Aliphatic or aromatic monoethers, diethers, triethers
[0073] Aliphatic or aromatic monoepoxides, diepoxides, triepoxides
[0074] Aliphatic or aromatic monohali...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com