Patents
Literature
448 results about "Dithiol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
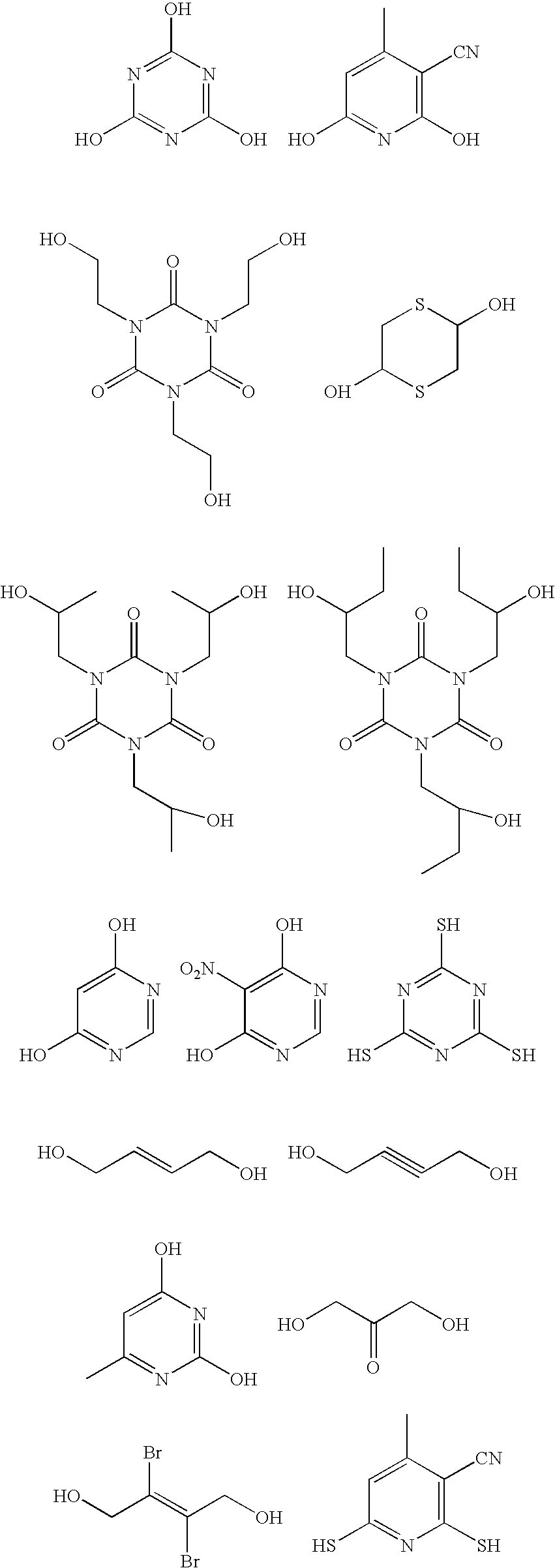
A dithiol is a type of organosulfur compound with two thiol functional groups. Their properties are generally similar to those of monothiols in terms of solubility, odor, and volatility. They can be classified according to the relative location of the two thiol group on the organic compound.
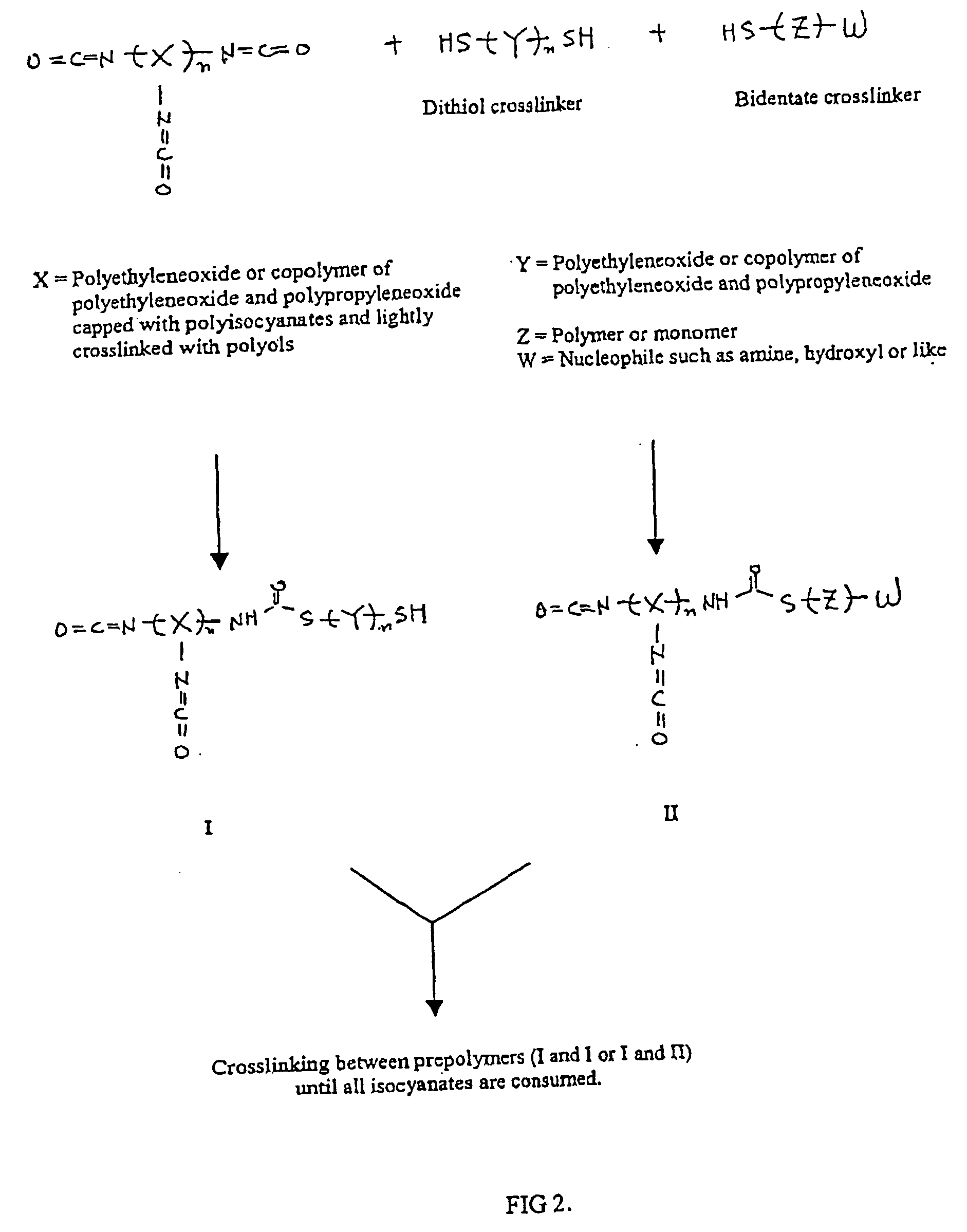
Methods and gel compositions for encapsulating living cells and organic molecules
InactiveUS7172866B2Reduce crosslinkingSimplifying and easing process developmentMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical compositionAqueous solution
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Methods and gel compositions for encapsulating living cells and organic molecules
InactiveUS20040029241A1Simplifying and easing process developmentPotential employment of such materialsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical compositionAqueous solution
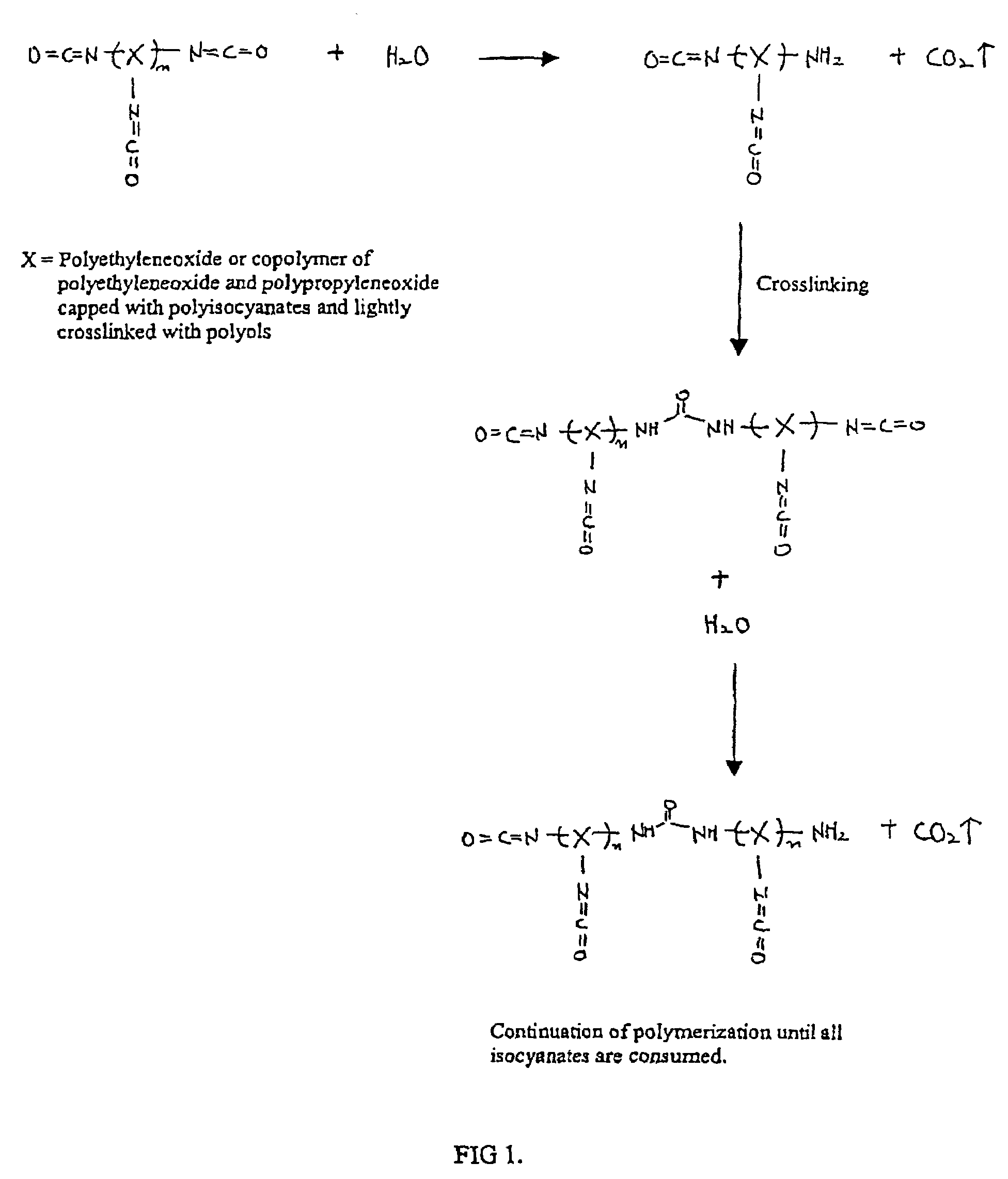
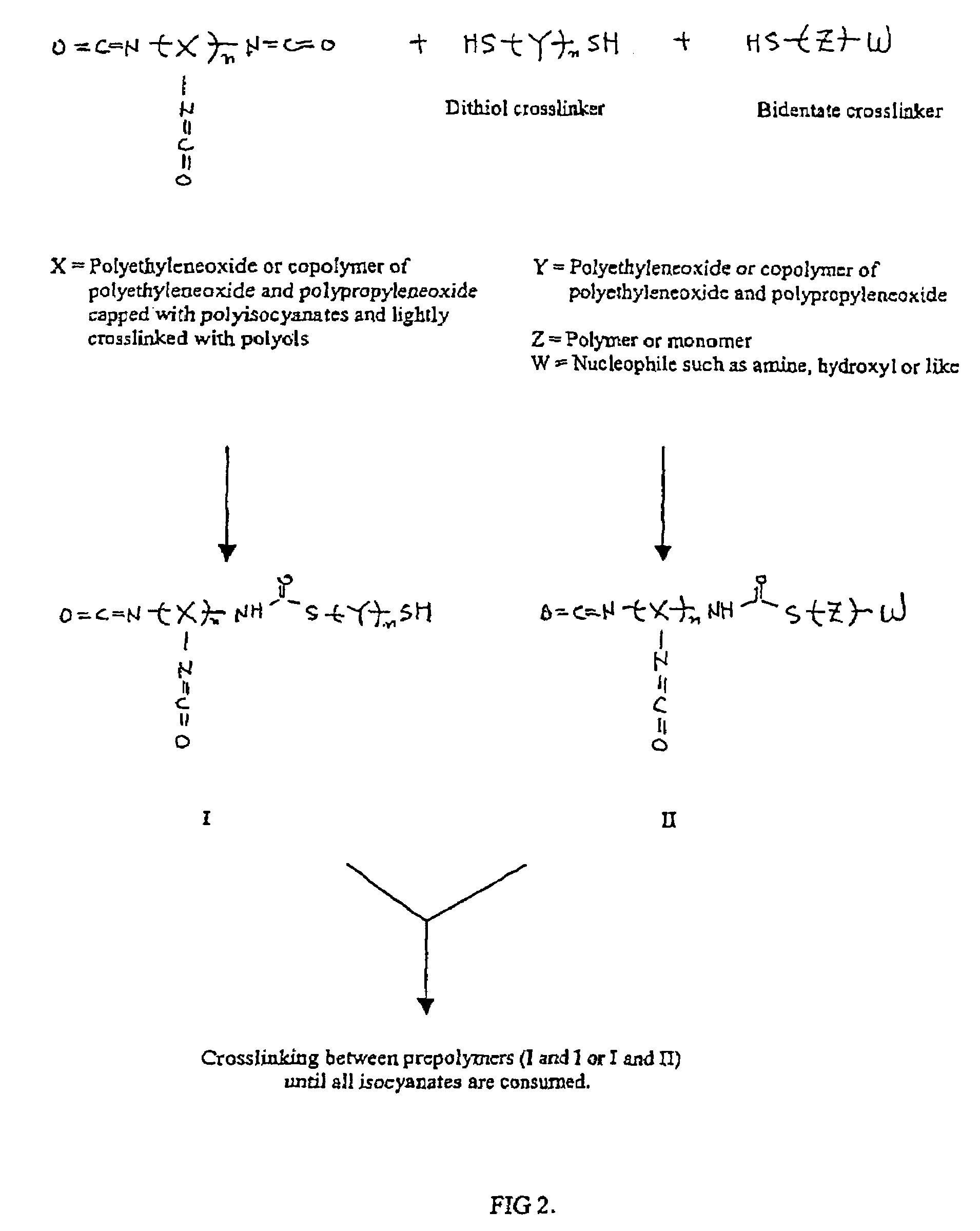
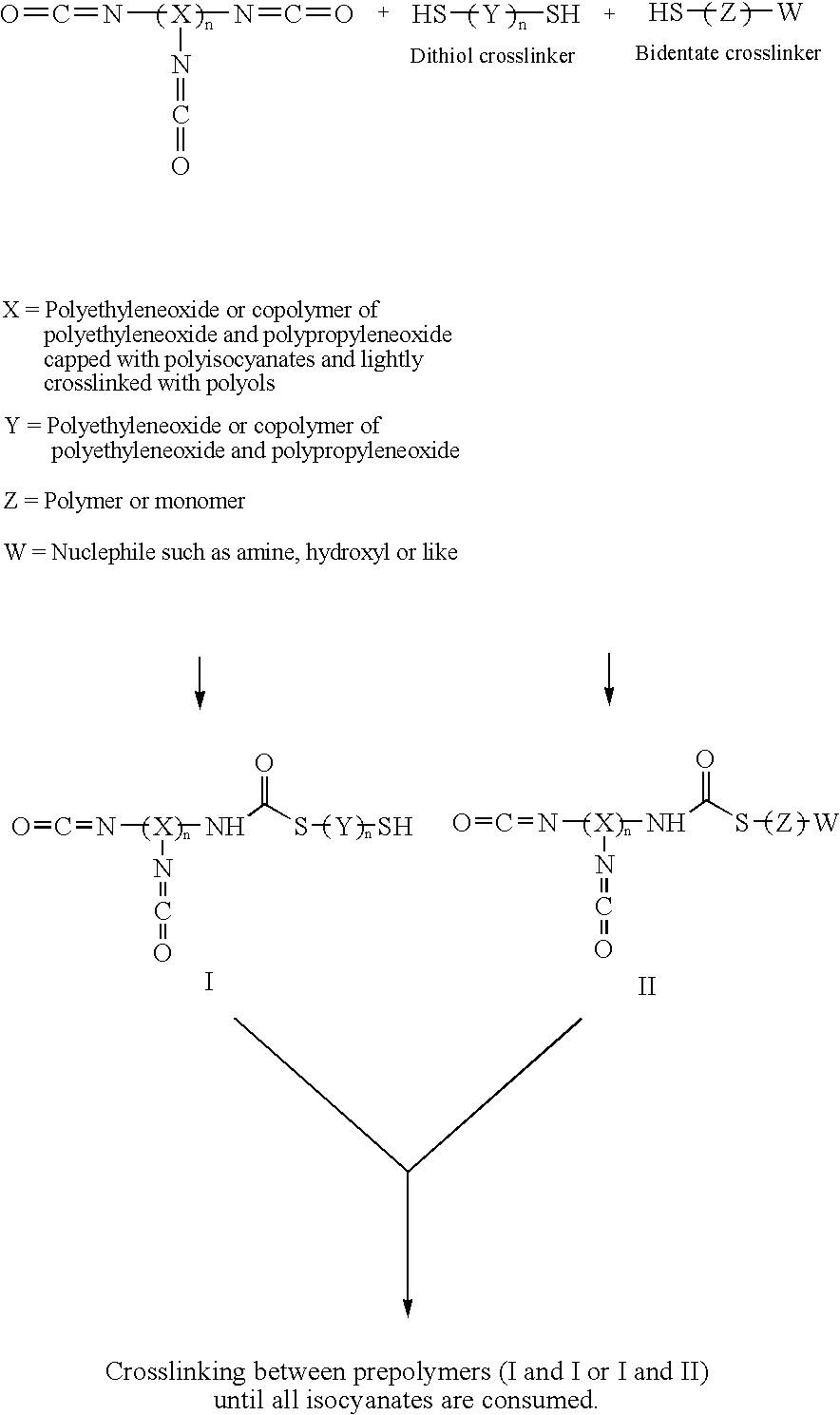
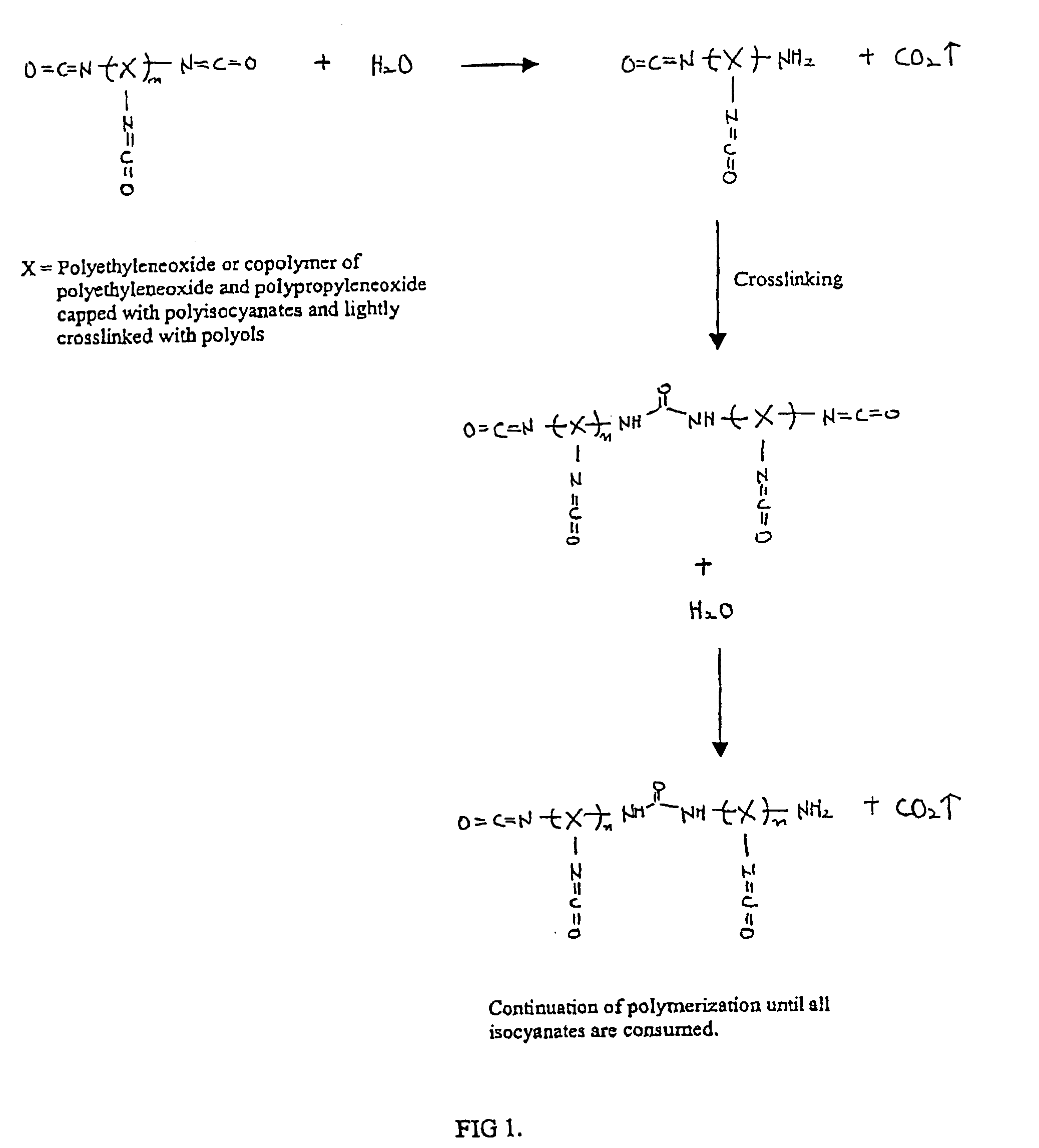
A method for encapsulating biologics within a hydrogel by using an aqueous solution of an isocyanate-functional hydrogel prepolymer which is mixed with an amount of biologics and an aqueous solution containing a dithiol crosslinking agent under physiological pH conditions. An additional bidentate crosslinking agent may be included. The product of such method may be a bioreactor or an assay device having a plurality or different biologics encapsulated at predetermined locations in a substrate.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
Macromolecular intumescent flame resistance carbonizing agent with branching and crosslinking structure and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101643651AImprove solubilitySolve the problems caused by poor water resistanceFireproof paintsHalogenDiol
The invention relates to a macromolecular intumescent flame resistance carbonizing agent with branching and crosslinking structure which contains the repetitive structure shown as following, wherein X, Y and Z are any one of diamino, diol, diphenol and dithiol and X, Y and Z can be the same or different groups. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the intumescent flame resistance carbonizing agent and a new intumescent fire retardant system containing a new intumescent fire resistance system which comprises the intumescent flame resistance carbonizing agent and acid source, and added flame-retardant synergist and an application thereof. The intumescent flame resistance carbonizing prepared by the method of the invention has extremely good foaming and carbonizing property, low toxicity, strong water resistence and good compatibility and contains no halogen; when adding in polymer, the intumescent flame resistance carbonizing agent can not reduce the mechanical properties of the flame resistance composite material but also increase the mechanical properties; simultaneously, the synthesis technology is simple and is easy to control so that the intumescent flame resistance carbonizing agent is applicable to industrialized production.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Antireflective coating compositions
ActiveUS8329387B2Increase valuePhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolyolSulfur
The present invention relates to an antireflective coating composition comprising a novel polymer without an aromatic chromophore, where the polymer comprises a structural unit derived from an aminoplast and a structural unit derived from a diol, triol, dithiol, trithiol, other polyols, diacid, triacid, other polyacids, diimide or mixture thereof, where the diol, dithiol, triol, trithiol, diacid, triacid, diimide, diamide or imide-amide optionally contain one or more nitrogen and / or sulfur atoms or contain one or more alkene groups. The invention also relates to the novel polymer and a process for using the novel antireflective coating composition in a lithographic process.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
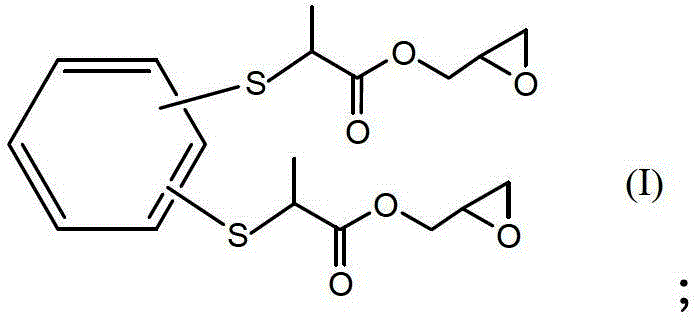
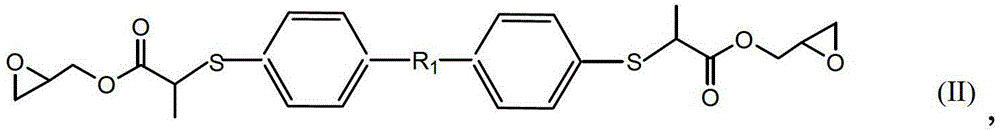
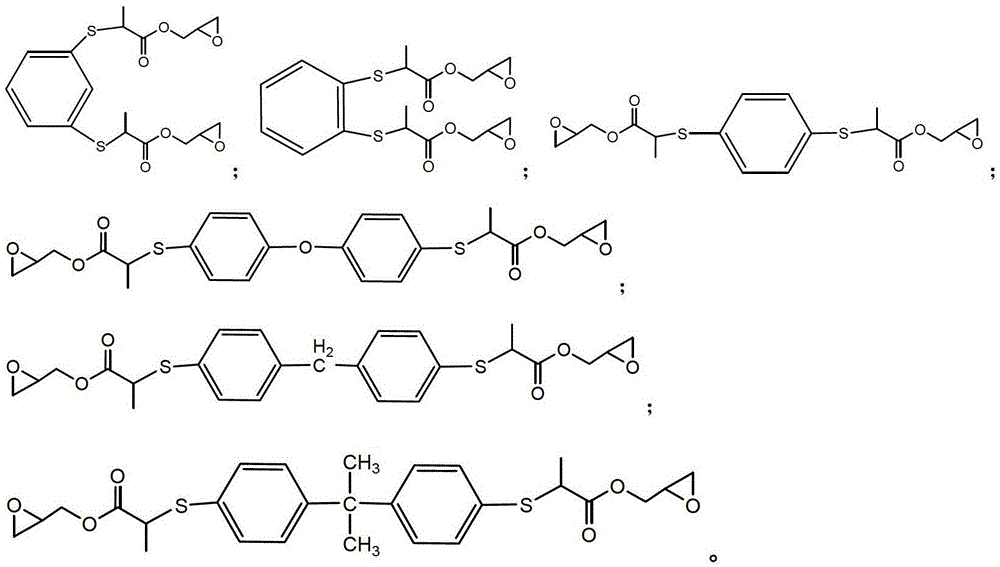
Dithiol Compounds, Derivatives, and Uses Therefor
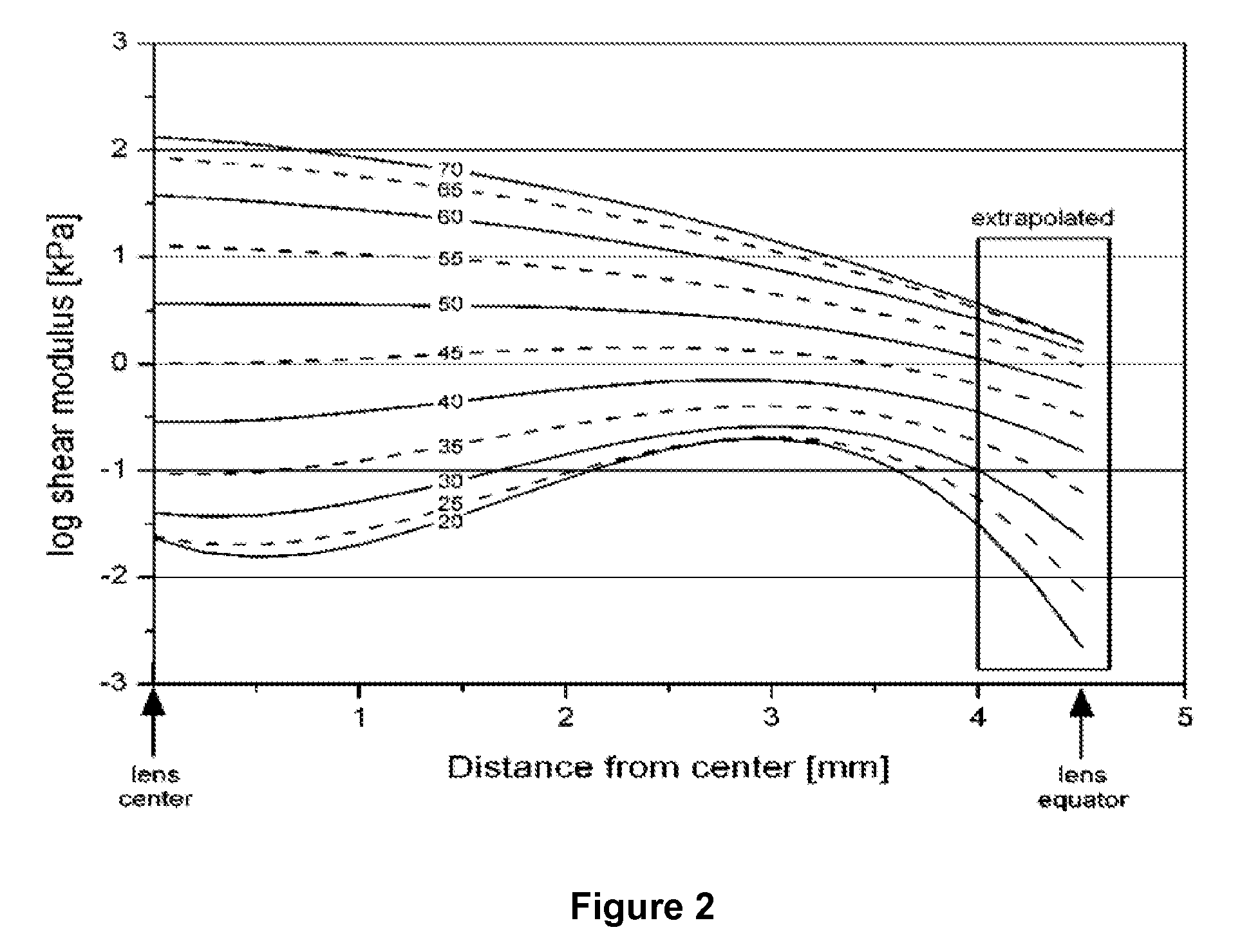
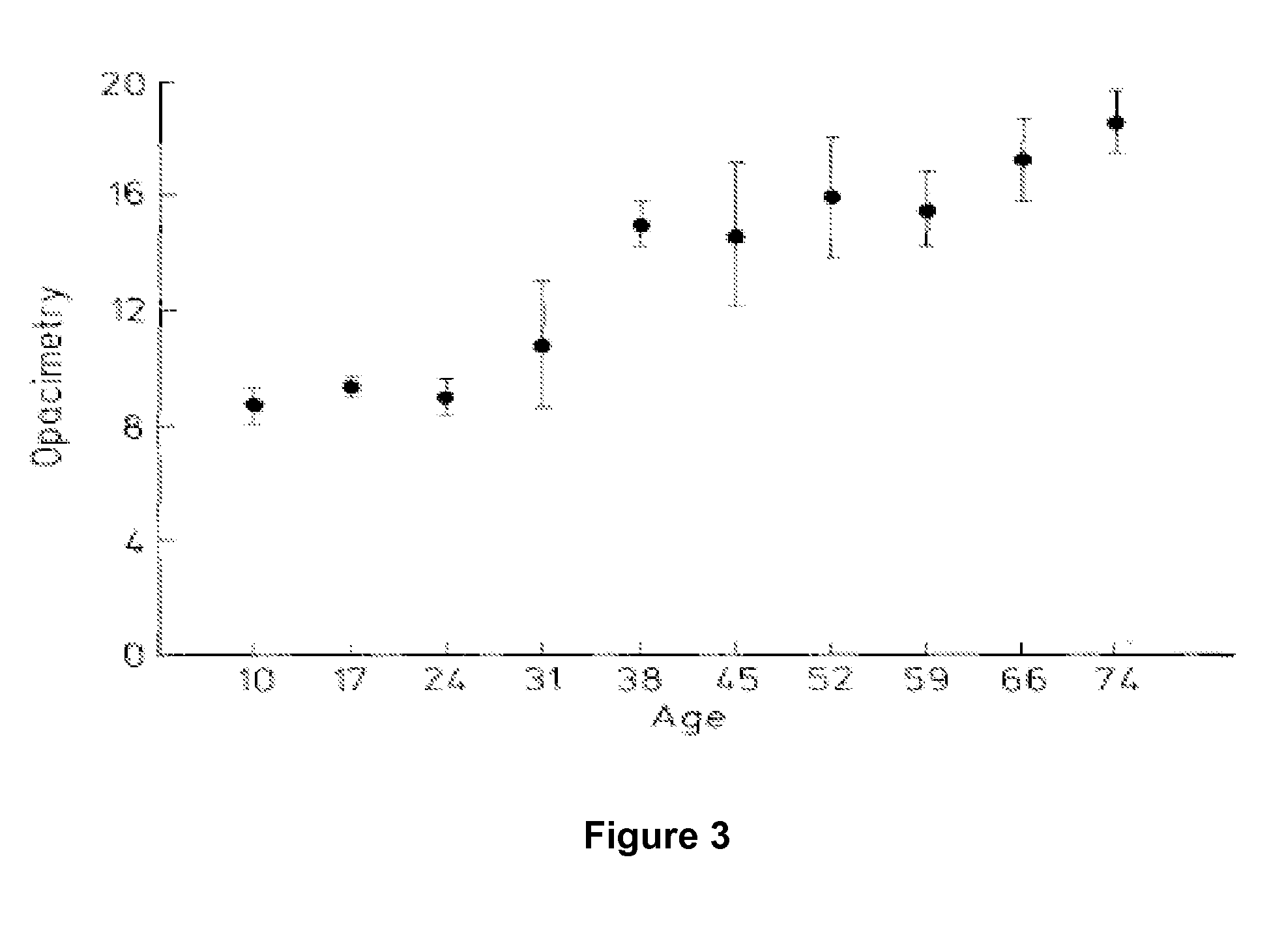
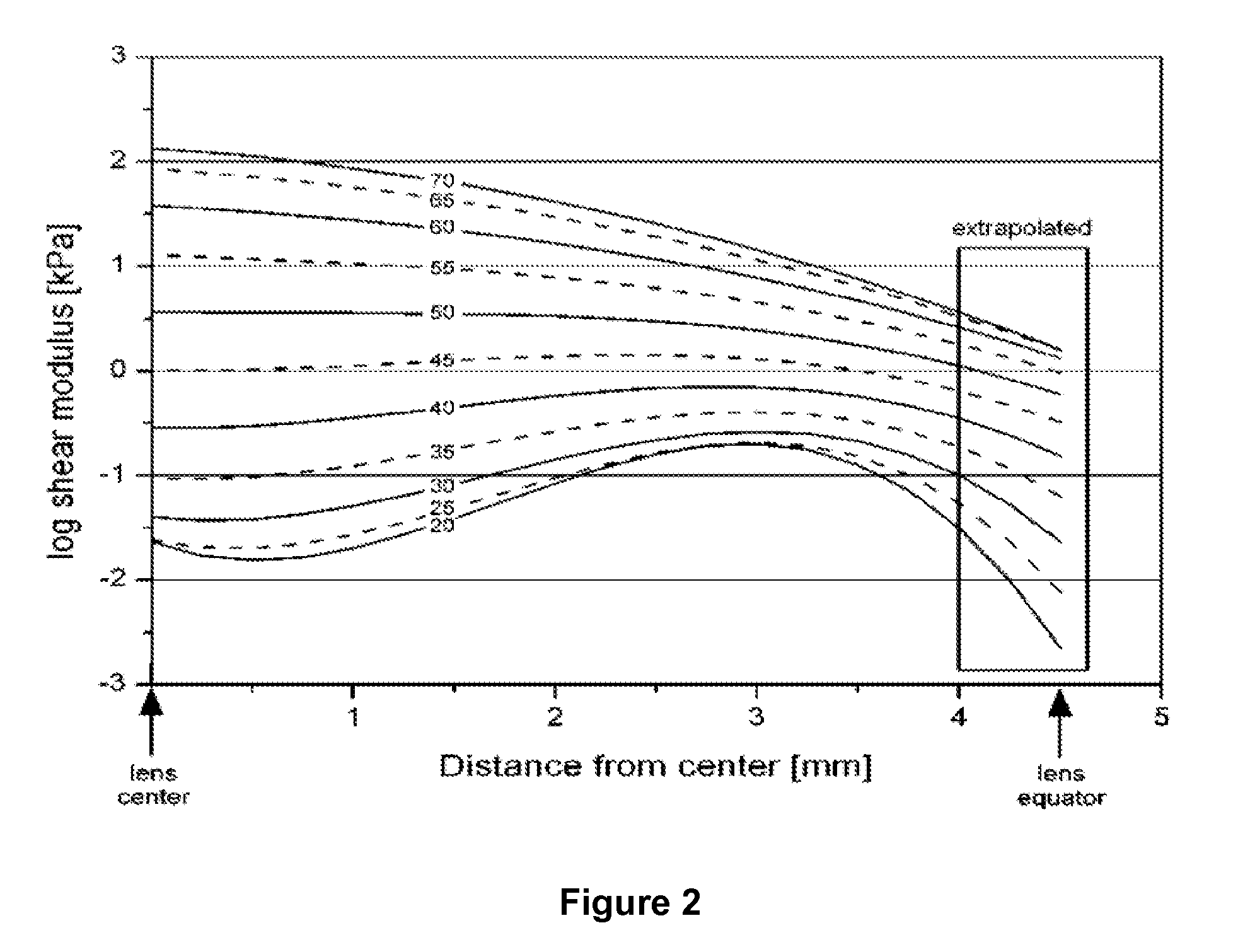
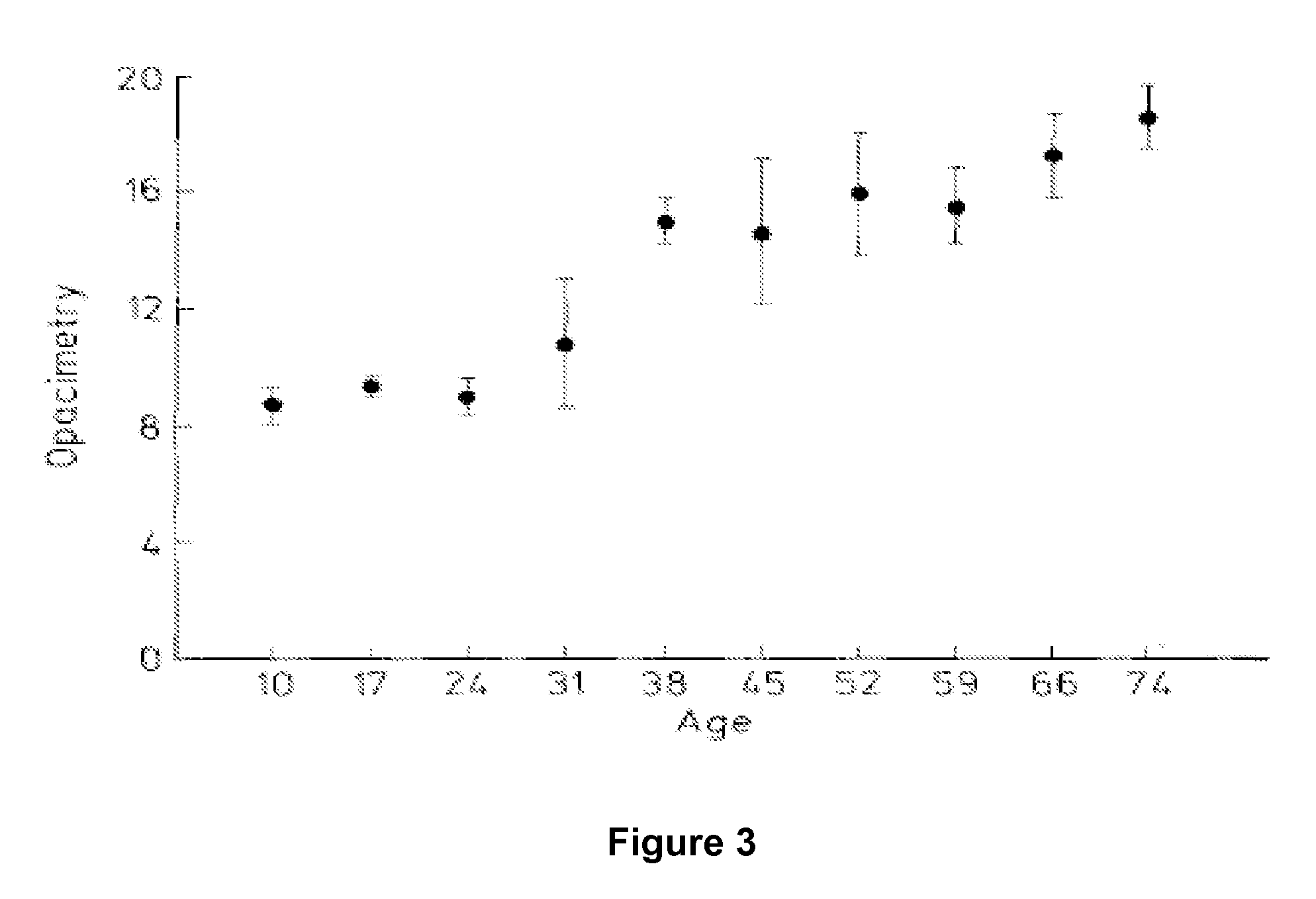
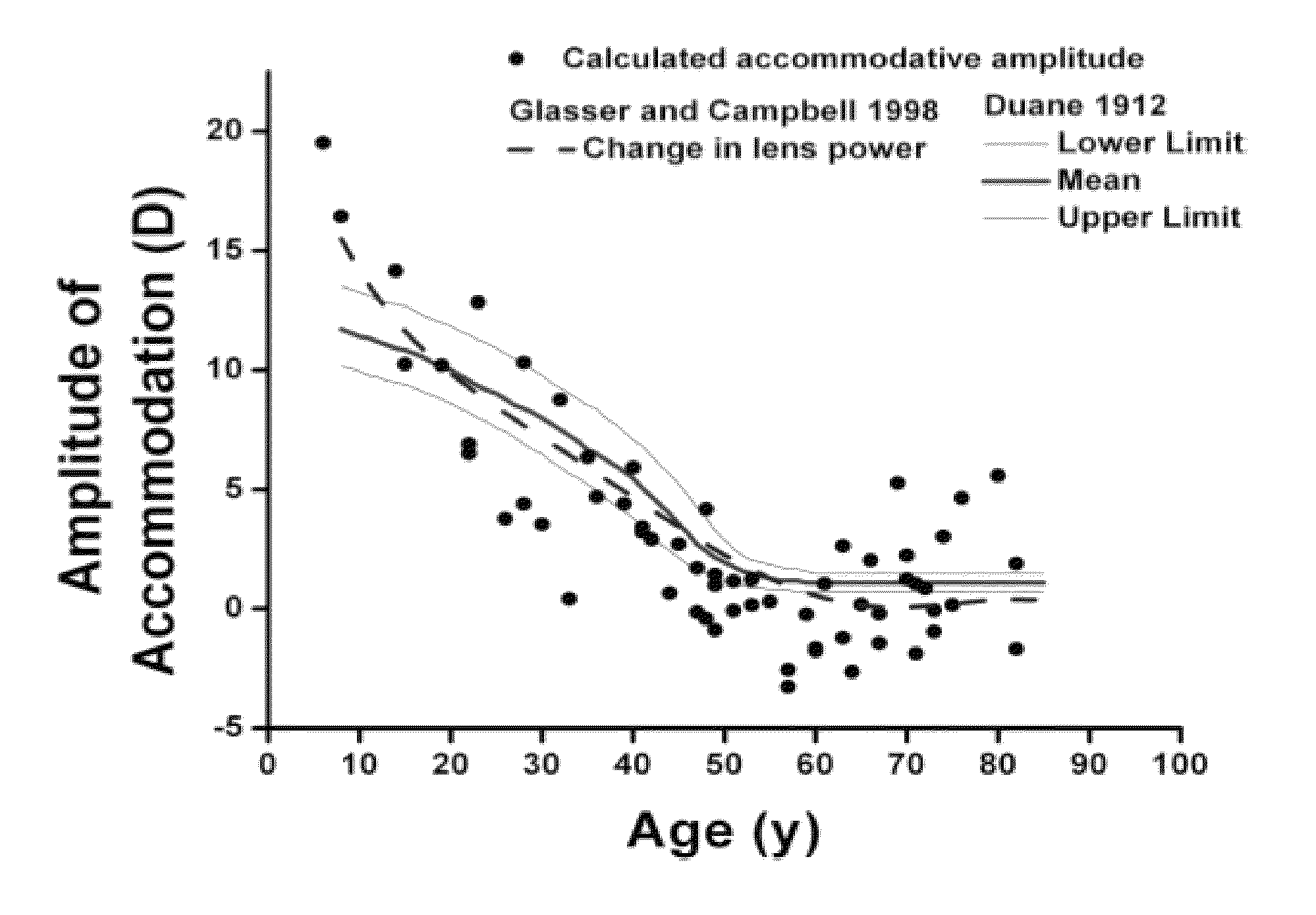
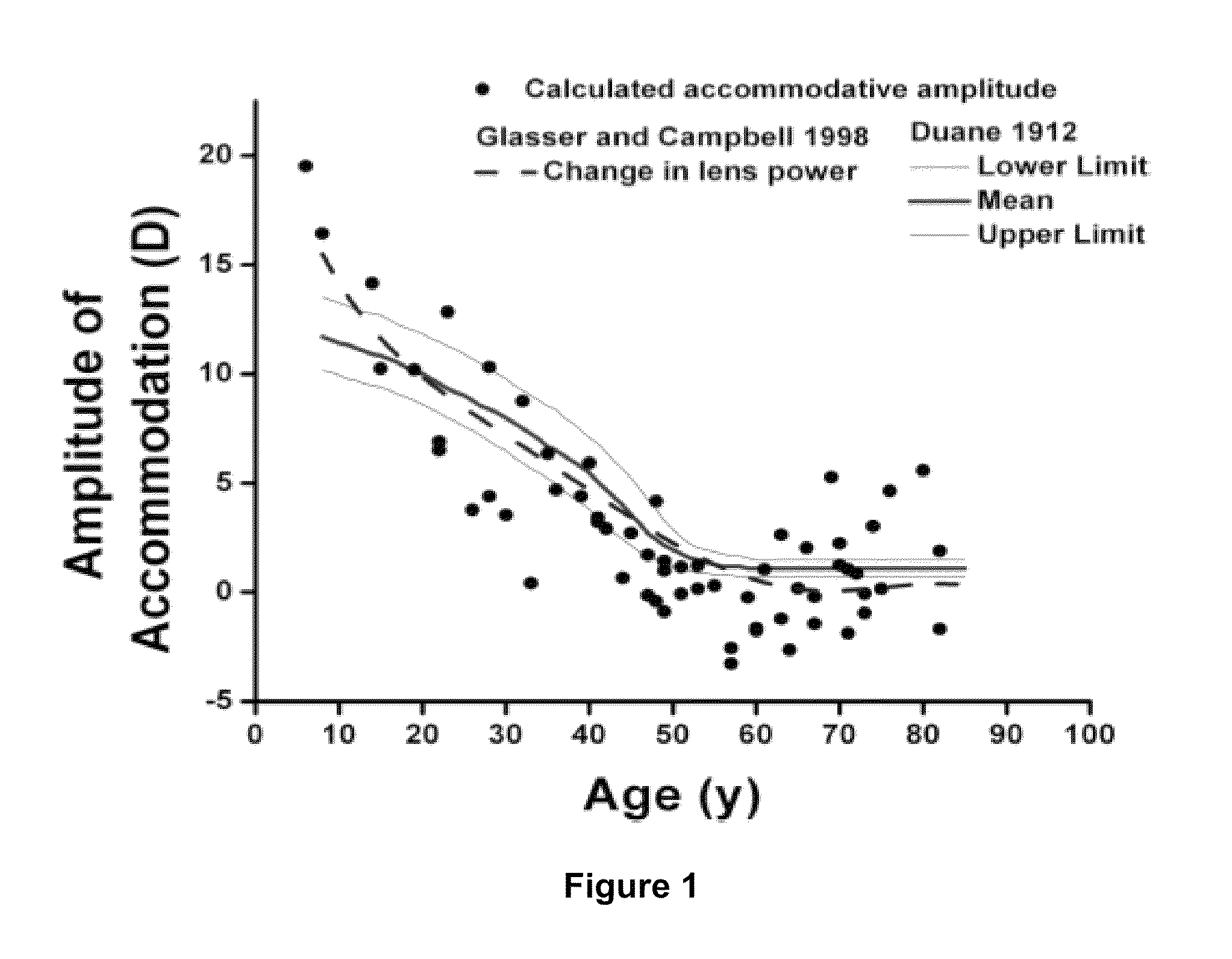
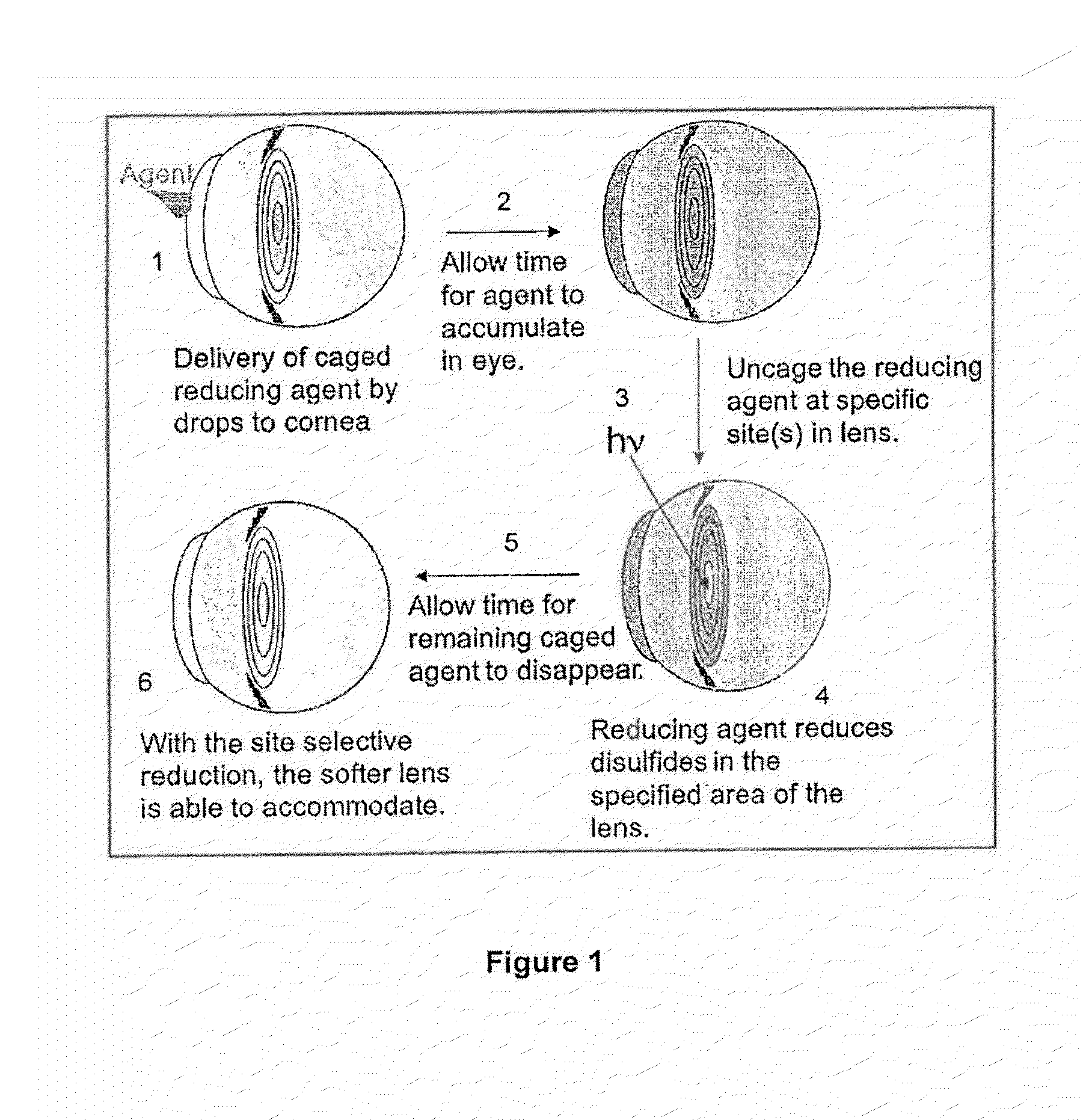
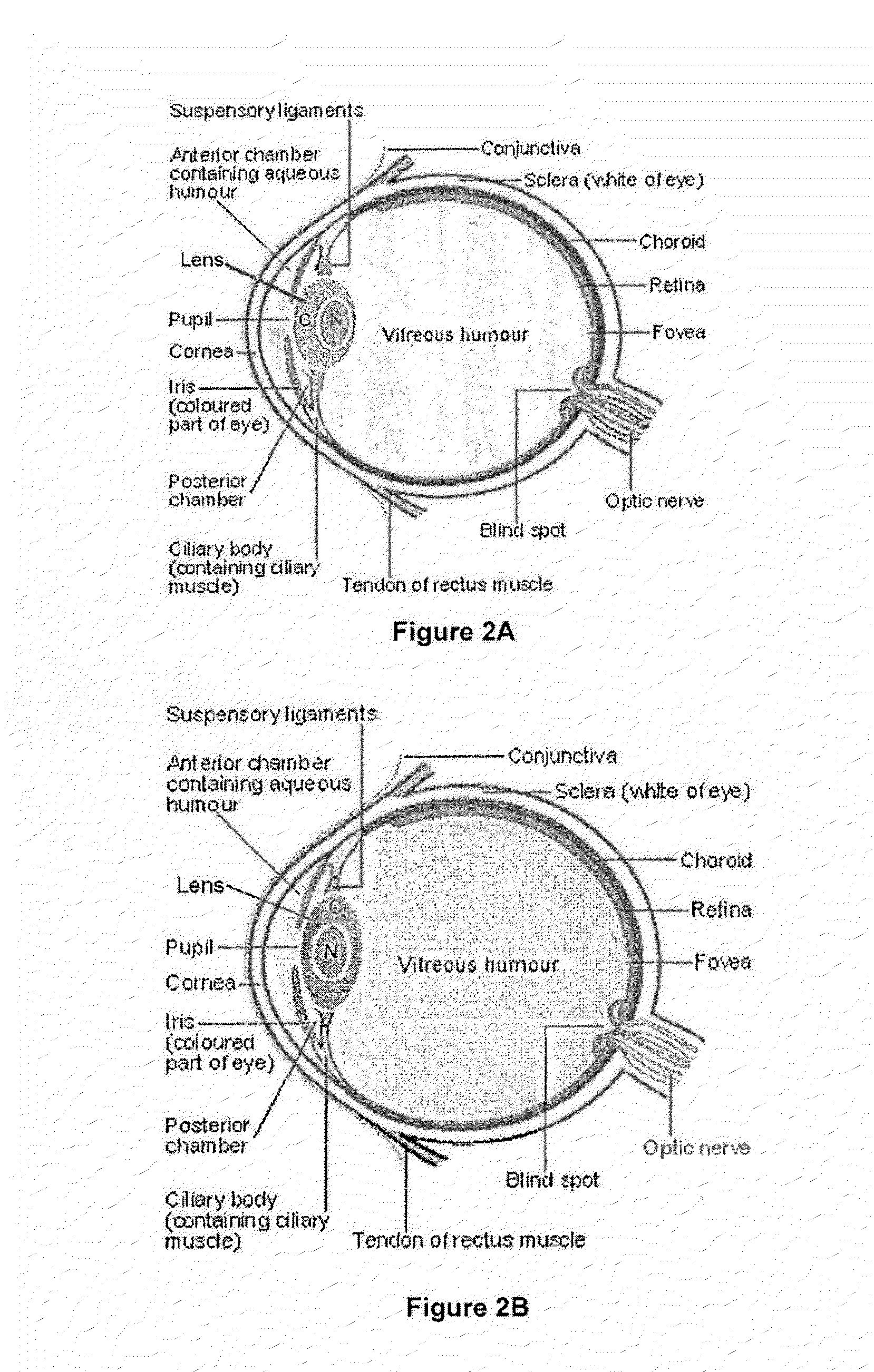
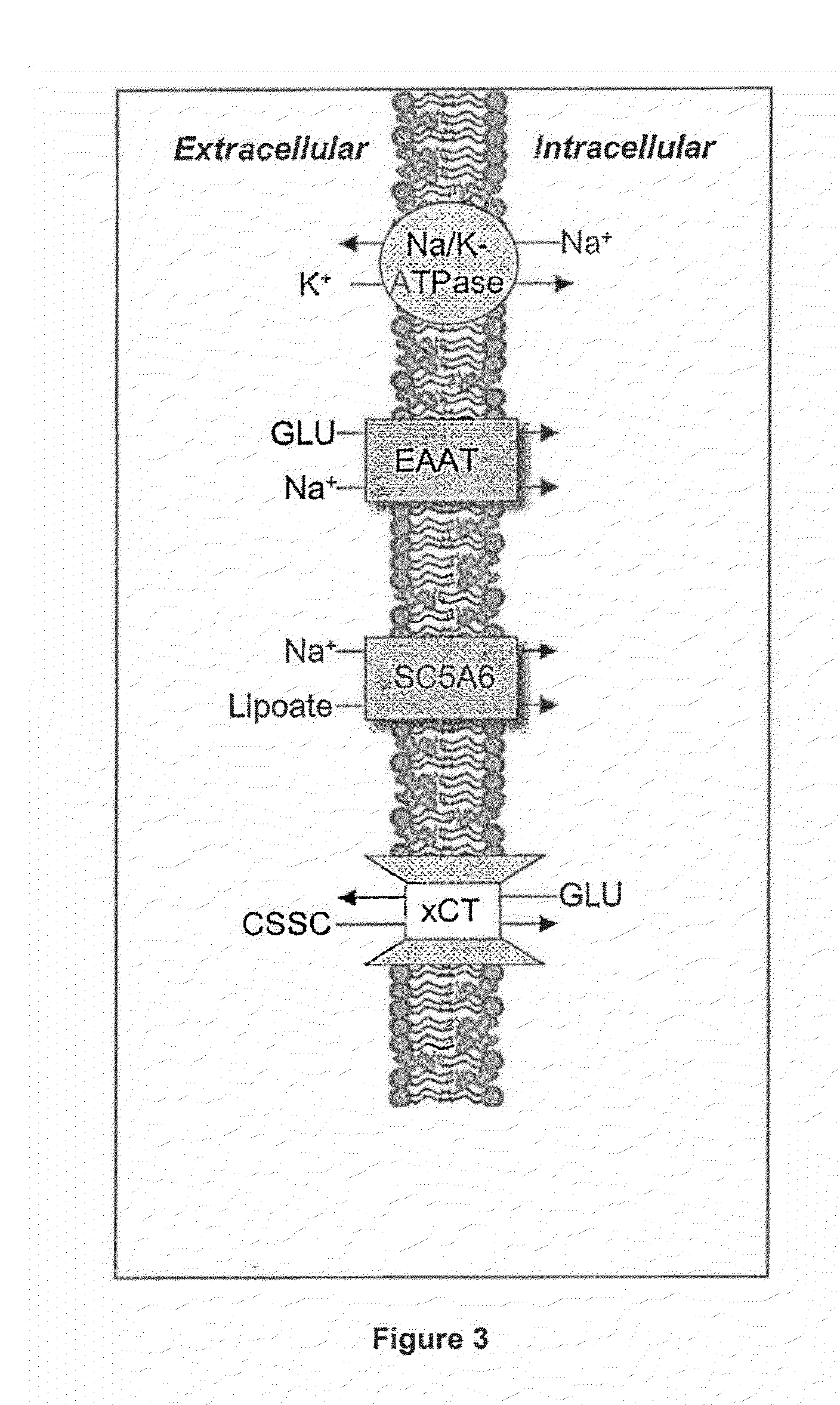
Dithiol compounds and derivatives thereof are disclosed. The agents are useful for treating ocular disease, especially presbyopia and cataract.
Owner:ENCORE HEALTH LLC
Functionalized polymers for binding to solutes in aqueous solutions
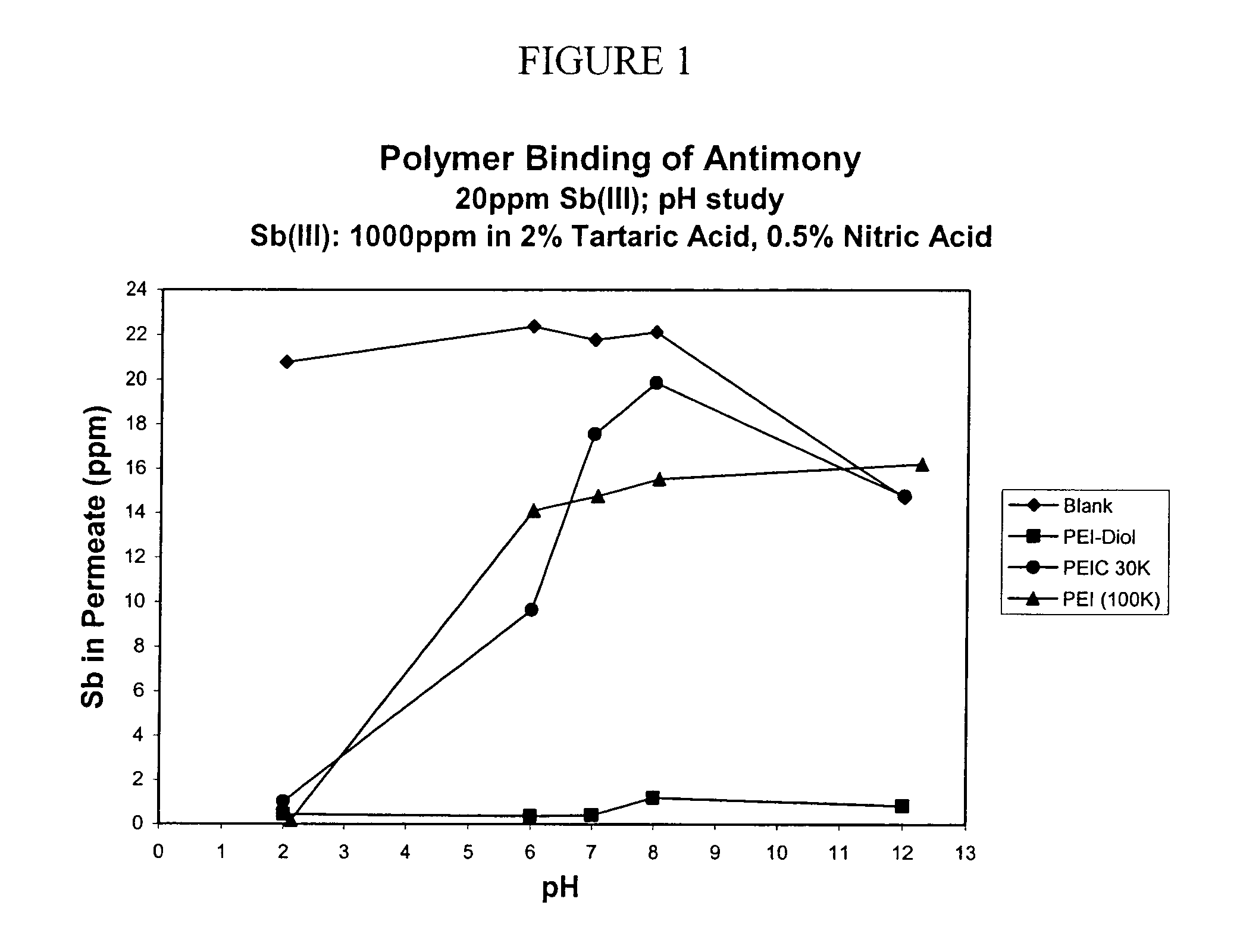
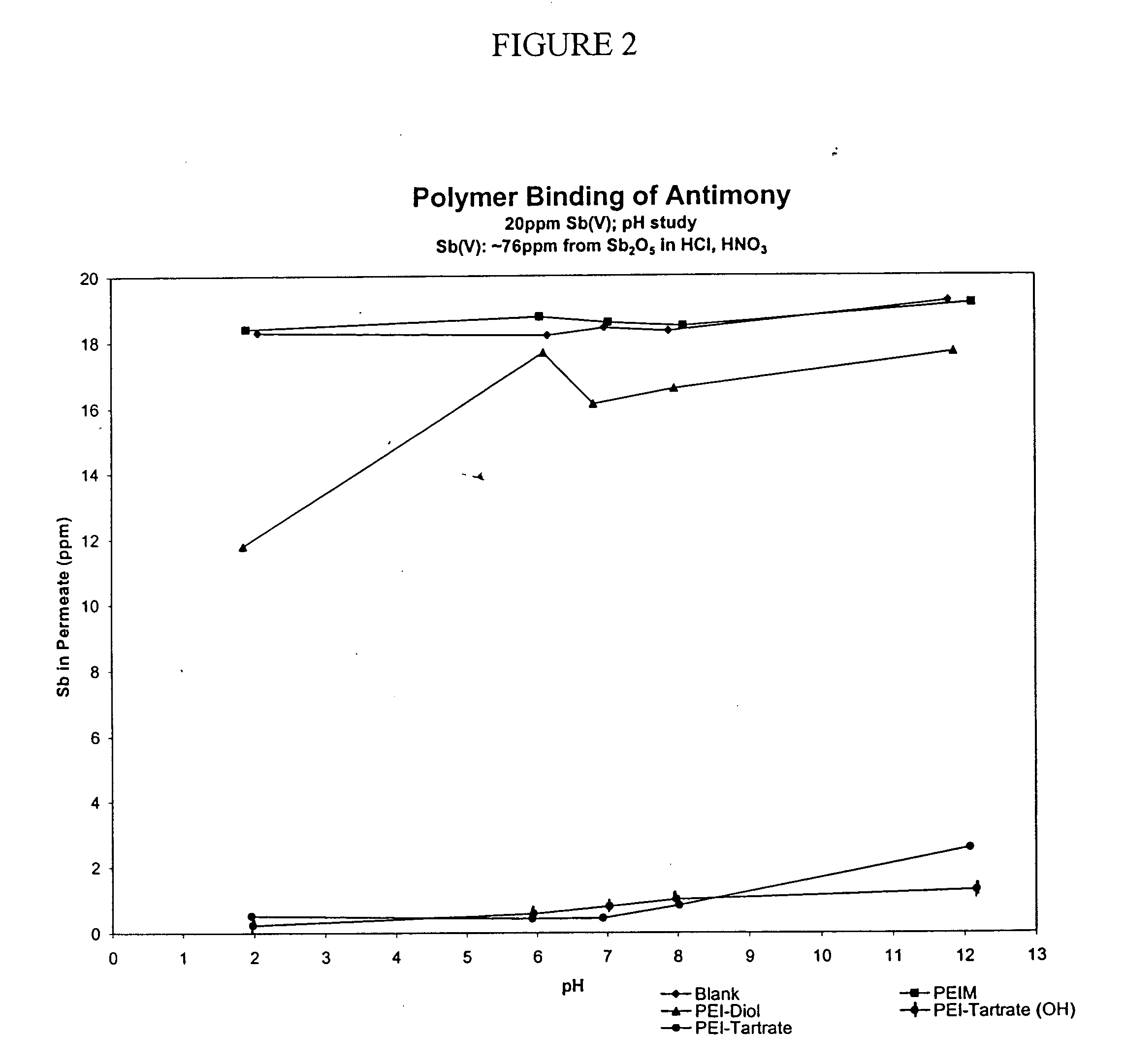
A functionalized polymer for binding a dissolved molecule in an aqueous solution is presented. The polymer has a backbone polymer to which one or more functional groups are covalently linked. The backbone polymer can be such polymers as polyethylenimine, polyvinylamine, polyallylamine, and polypropylamine. These polymers are generally water-soluble, but can be insoluble when cross-linked. The functional group can be for example diol derivatives, polyol derivatives, thiol and dithiol derivatives, guest-host groups, affinity groups, beta-diphosphonic acids, and beta-diamides
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Dithiol compounds, derivatives, and treatment of presbyopia
Dithiol compounds and derivatives thereof are disclosed. The agents are useful for treating ocular disease, especially presbyopia and cataract.
Owner:ENCORE HEALTH LLC
Barbecue essence and production process thereof
The invention discloses a barbecue essence, which is prepared from the following raw materials: ethyl maltol, 4-hydroxyl-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone, 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-diyhydroxyl-1,4-dithiacyclo-hexane, methyl cyclopentenotone, 2-acetylpyrazine, 2-methyl tetrahydrofuran-3-mercaptan, bis(2-methyl-3-furyl) disulfide, propyl2-methyl-3-furyl disulfide, 4-methyl-5- hydroxyethyl-thiazole, 2-methylpyrazine, 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine, 3-methylmercaptopropionaldehyde, difurfuryl disulfide, 4-methyl-4-furfurylthio-2-pentanone, 2,4,5-trimethylthiazole, 2,4,6-triisobutyl-1,3,5-dithiazine, beta-phenylethylmercaptan, 1,6-ethanthiol, 2-pentylthiophene, furfuryl mercaptan, 4,5-dimethyl-2-isobutyl-3-thiazoline, guaiacol, delta-dodecalactone, 2,4-decadienealdehyde, trans,trans-2,4- nonadienal, anisic aldehyde, butanoic acid, acetic acid, black pepper essential oil ginger essential oil, clove oil, cassia oil and an oil-soluble solvent. The invention also discloses a barbecue essence production process.
Owner:厦门市顶味兴业香料发展有限公司
Thia-conjugated compound taking naphthalene tetracarboxylic acid diimide as kernel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101693719ASynthetic preparation is simpleHigh purityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSilica gelField-effect transistor
The invention relates to a thia-conjugated compound taking naphthalene tetracarboxylic acid diimide as a kernel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the thia-conjugated compound is shown as the follow formula; in the formula, R is C1-C30 of n-alkyl or branch alkyl. Under the protection of inert gas, 2,3,6,7-tetrabromoaphthalene tetracarboxylic acid diimide reacts with 1,1-dicyano-2,2-dithiolate disodium salt in tetrahydrofuran respectively at room temperature and the temperature of 40-60 DEG C for 0.5-2 hours and 0.5-1 hour, a silicagel column is subjected to chromatography to obtain a target compound, and the production ratio is 50-62 percent; an organic thinner film field effect transistor prepared by a solution method and taking the compound as an organic semiconductor layer achieves highest electronic mobility up to 0.15 cm2 / Vs, switch ratio of larger than 107 and threshold voltage of lower than 15V, and the performance and environment stability thereof are superior to those of common n-shaped organic semiconductors.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Dithiol Compounds, Derivatives, and Uses Therefor
Dithiol compounds and derivatives thereof are disclosed. The agents are useful for treating ocular disease, especially presbyopia and cataract.
Owner:ENCORE HEALTH LLC
Methods of treating ocular diseases using derivatives of lipoic acid
Methods of treating ocular diseases using dithiol compounds, their derivatives, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof are disclosed. In particular, methods using dithiol compounds that comprise derivatives of lipoic acid are described. The dithiol compounds are especially useful for treating ocular diseases such as presbyopia and cataract.
Owner:ENCORE HEALTH LLC
Heterocyclic-sulfur fused naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid diimide derivatives, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101885732ASynthetic preparation is simpleHigh purityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellOrganic field-effect transistor
The invention heterocyclic-sulfur fused naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid diimide derivatives, a preparation method and application thereof. In the preparation method, 2,3,6,7-tetrabromo-naphthalene diimide reacts with 2-alkyl cyanoacetate-ethylene-1,1-dithiol sodium salt, 2-mandelonitrile-ethylene-1,1-dithiol sodium salt or 2-(4-phenylacetonitrile bromide)-ethylene-1,1-dithiol sodium salt to prepare 1,3-heterocyclic-disulfide fused naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid diimide derivatives; and the 2,3,6,7-tetrabromo-naphthalene diimide reacts with 1,2-dicyanoethylene-1,2-dithiol sodium salt to prepare 1,4-dithiin cyclohexadiene-2,3-dinitrile fused naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid diimide derivatives, which further reacts to prepare alpha,beta-dicyanothiophene fused naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid diimide derivatives. The compounds are n-type organic semiconductor materials, and have wide application prospect in the field of organic electronics (organic field effect transistors, organic solar cells and the like).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
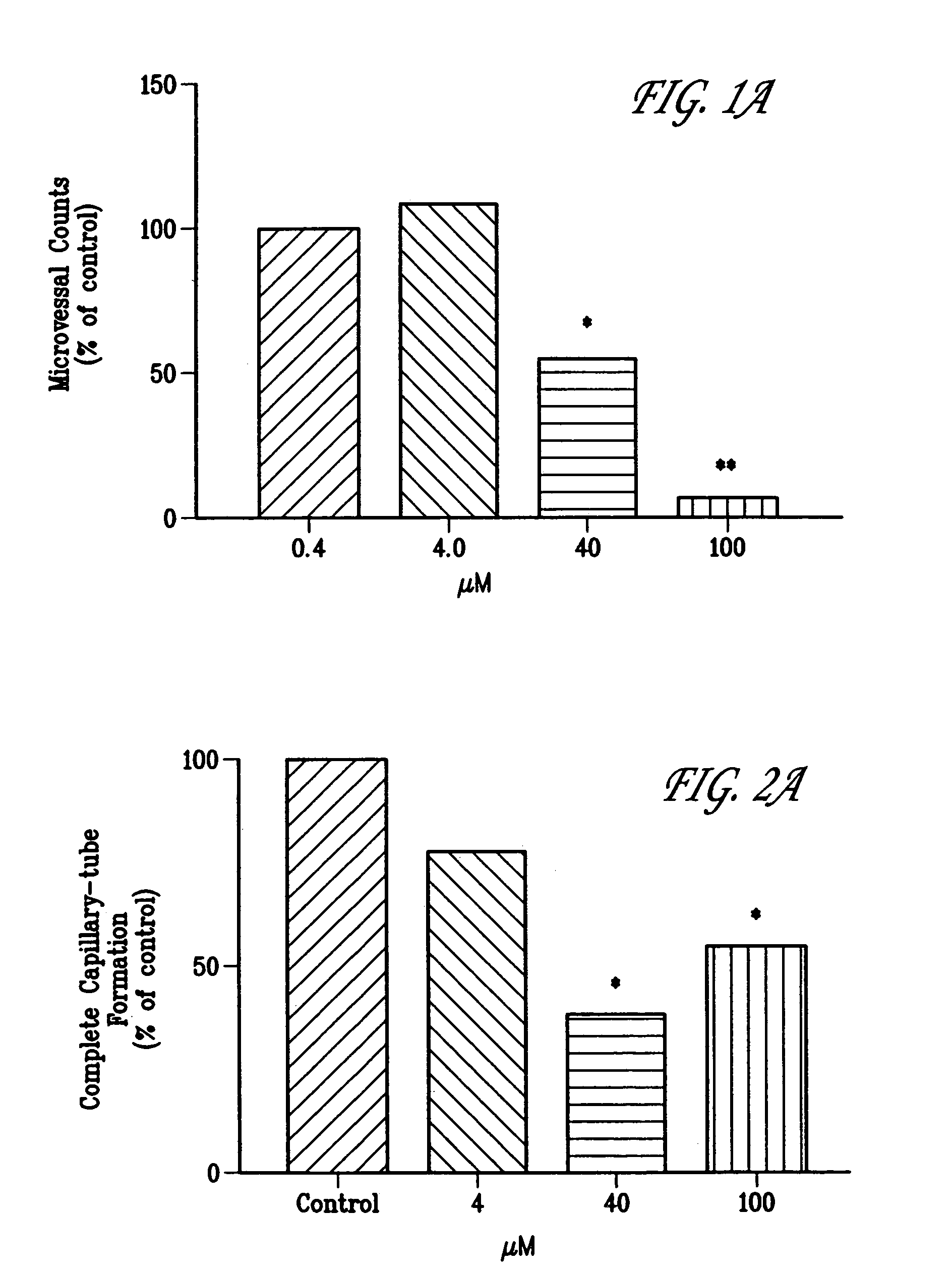
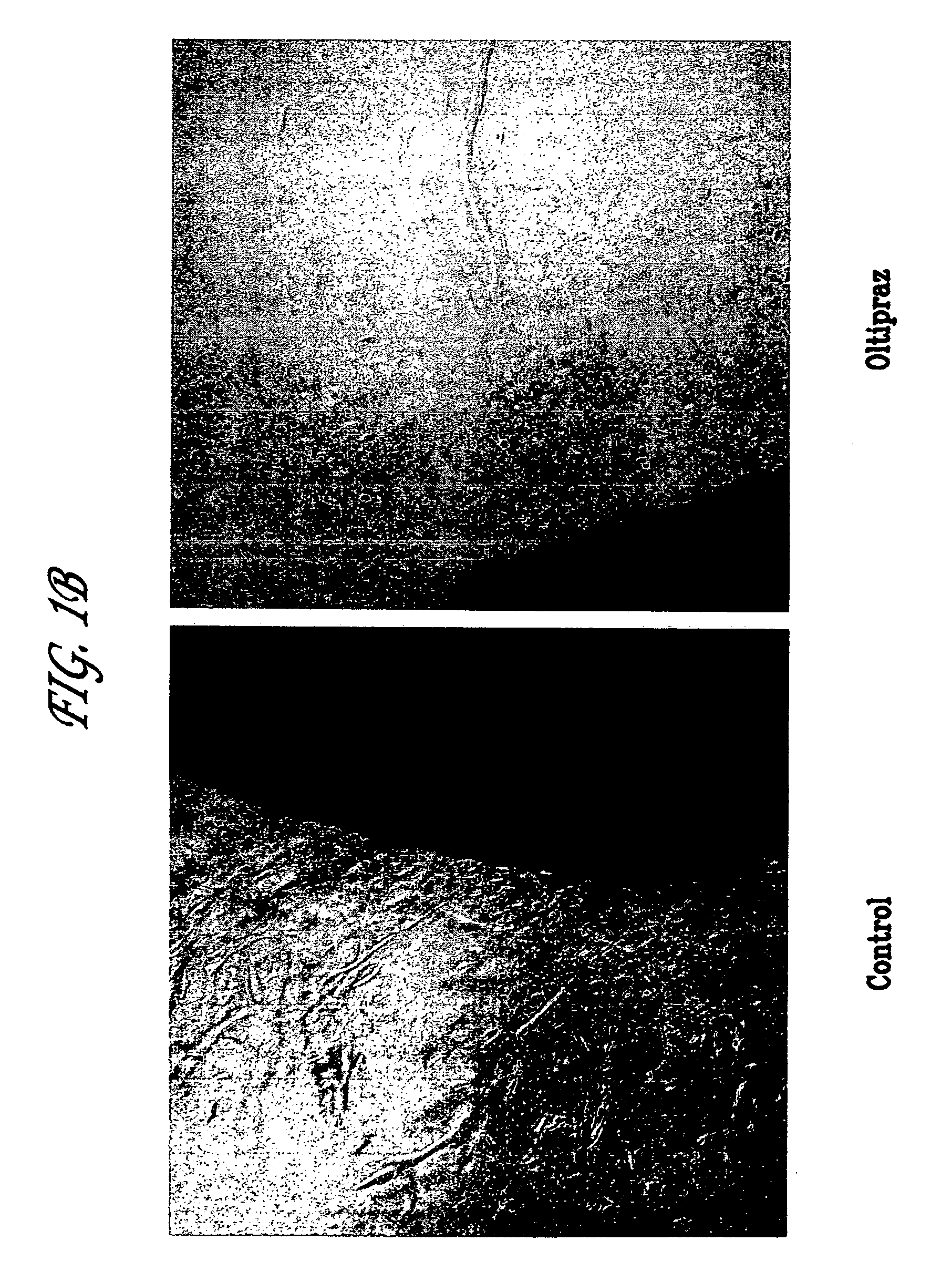
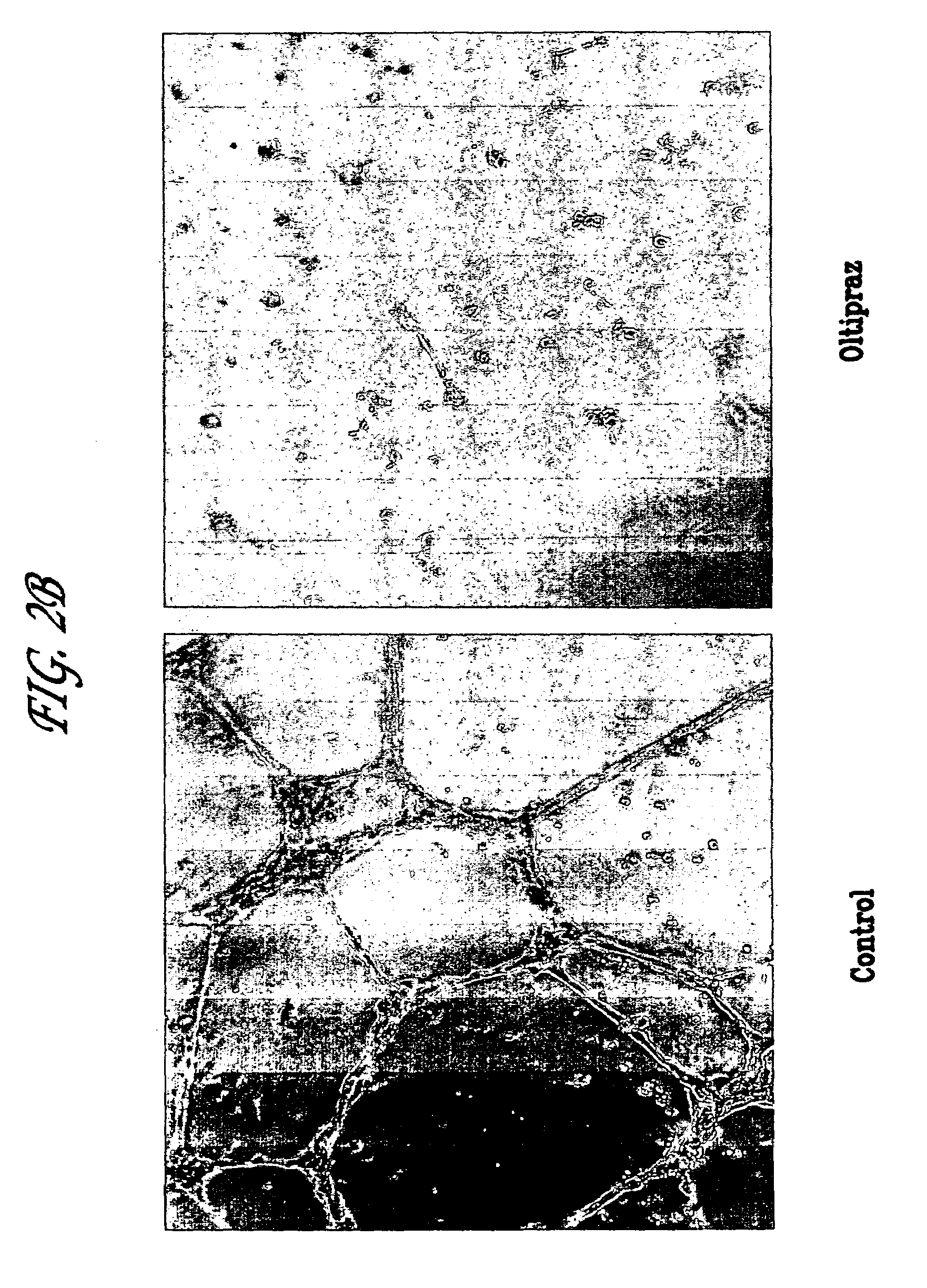
Methods for inhibiting angiogenesis
Owner:INST FOR CANCER RES
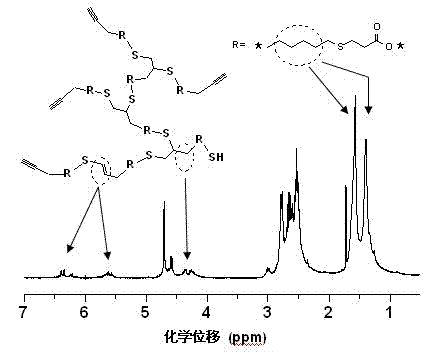
Method for preparing hyperbranched polymer through dual click chemistry
ActiveCN102181054AHigh molecular weightIncrease the degree of branchingUltraviolet lightsEvaporation
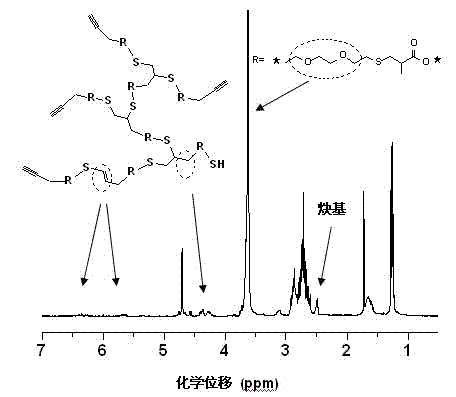
The invention discloses a method for preparing a hyperbranched polymer through dual click chemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) adding one mole of bis(thiol) compound, 0.1 to 10 moles of solvent, 0.05 to 2 moles of base catalyst, and 0.9 to 1.1 moles of compound containing alkynyl and alkenyl into a reactor sequentially under the protection of nitrogen, performing sulfydryl-alkene addition reaction at the temperature of between 10 and 40 DEG C for 0.5 to 24 hours, and performing reduced pressure evaporation to remove the solvent; and 2) dissolving the product obtained in the step 1) in 0.25 to 10 moles of solvent under the protection of nitrogen, adding 0.005 to 0.05 mole of photosensitive radical initiator or thermosensitive radical initiator, irradiating by ultraviolet light or heating at the temperature of between 40 and 90 DEG C to produce radical, performing sulfydryl-alkene addition polymerization reaction for 0.5 to 24 hours, and precipitating, separating and drying to obtain the hyperbranched polymer. The method has the advantages of no need of complex AB2 monomer synthesis and purification steps, high speed and efficiency, convenience, wide application range and the like. The obtained hyperbranched polymer containing a large amount of thioether bonds has wide application prospect in the fields of biomedical carriers, high-performance materials, additives and the like.
Owner:杭州德烯科技集团有限公司
Function polyamide monomer, function polyamide and preparation methods
ActiveCN107501116AUnique chemical structureUnique Aggregate StructureOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationEnvironmental resistanceVegetable oil
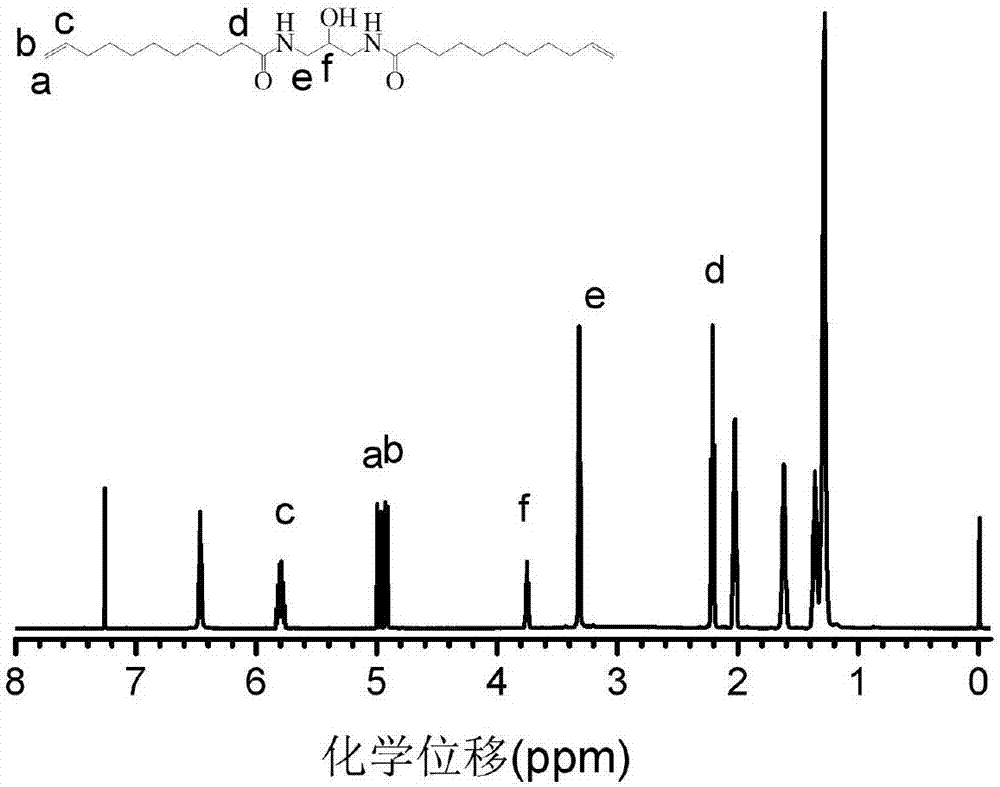
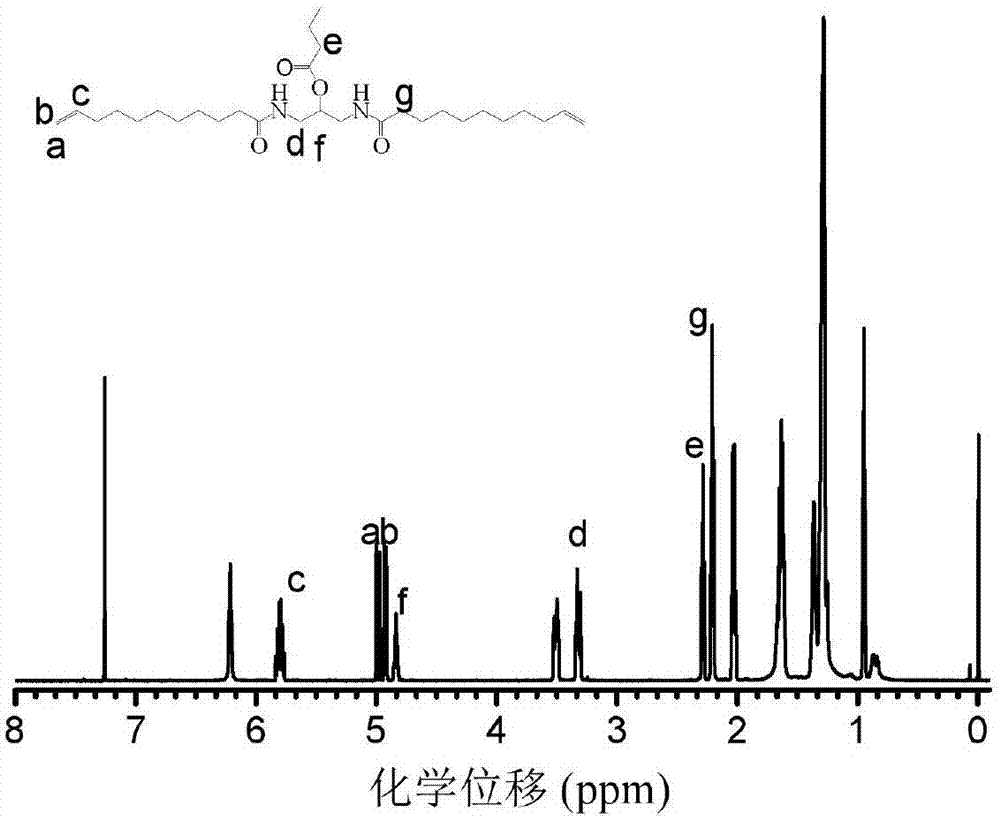
The invention relates to a function polyamide monomer, polyamide and preparation methods. A structural formula of the function polyamide monomer is shown in the description, and a structural formula of a side group R1 is -OCOR1' or -OH. A structural formula of the function polyamide is shown in the description, the n is larger than or equal to 5 and smaller than or equal to 5000, and the R2 of a main chain is disulfide. The preparation method of the function polyamide comprises the steps: dissolving the function polyamide monomer, dithiol and a catalyst into a solvent; then introducing protection gas of argon and putting into an oil bath pan to react; finally, obtaining a function polyamide product through methyl alcohol precipitation. According to the invention, a synthetic vegetable oil derivative namely the function polyamide monomer is converted into function polyamide in high efficiency, the final yield of the function polyamide is 50% to 100%, and the purity of the function polyamide is 90% to 100%. The function polyamide disclosed by the invention is synthesized from natural raw materials, has no free formaldehyde, benzene and heavy metal and can meet a national environment-friendly material standard. The function polyamide disclosed by the invention has excellent mechanical capacity and mechanical property.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
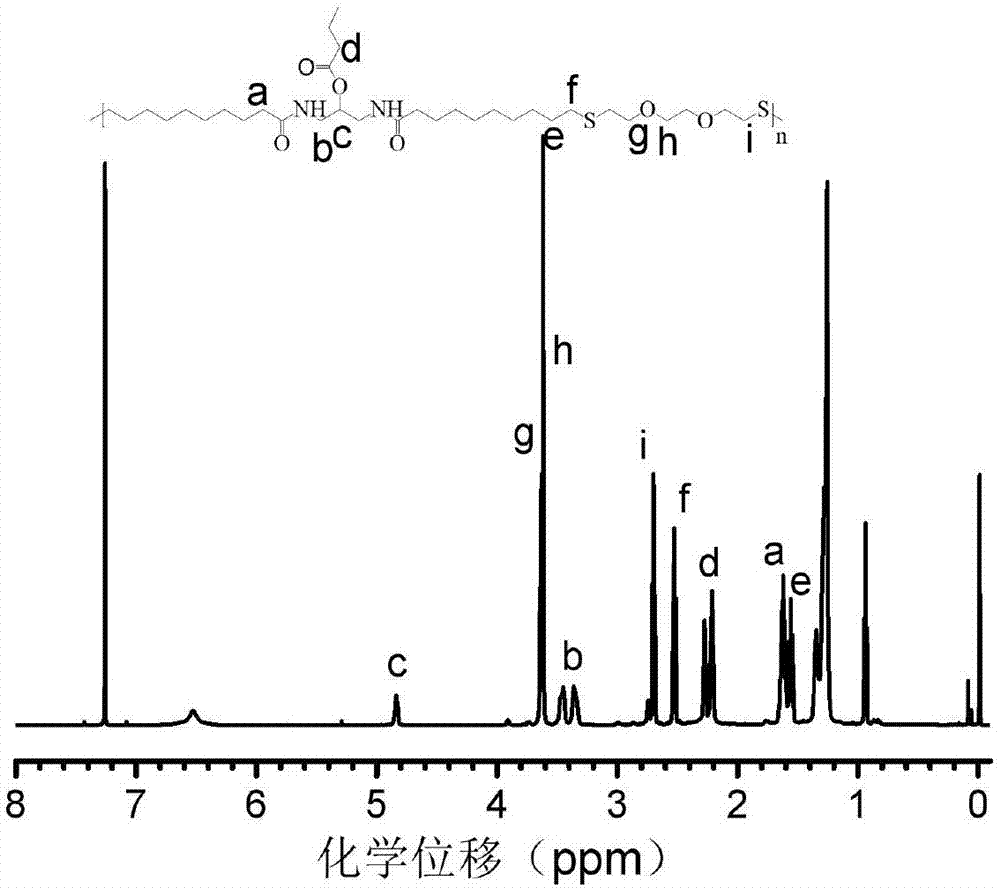
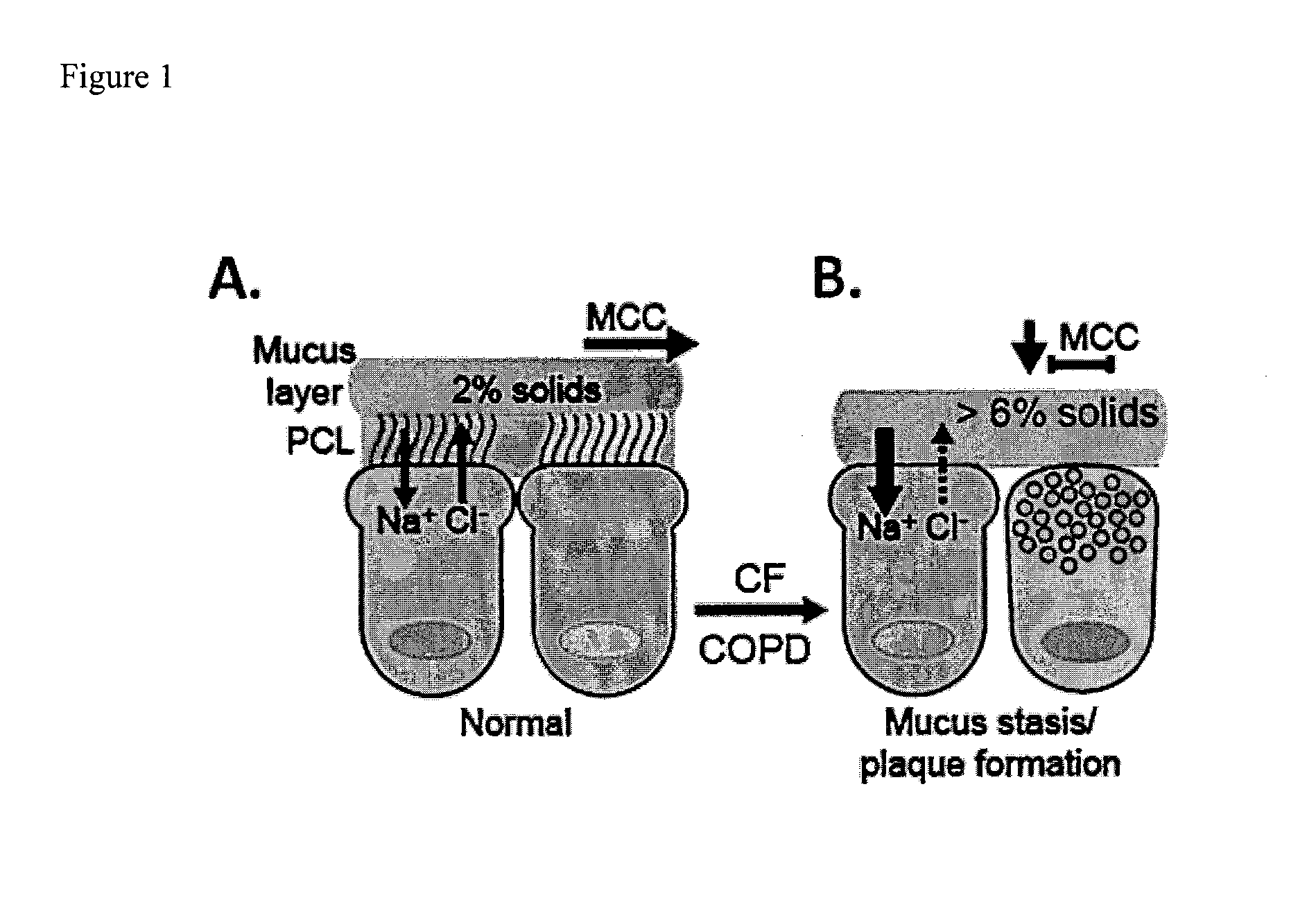
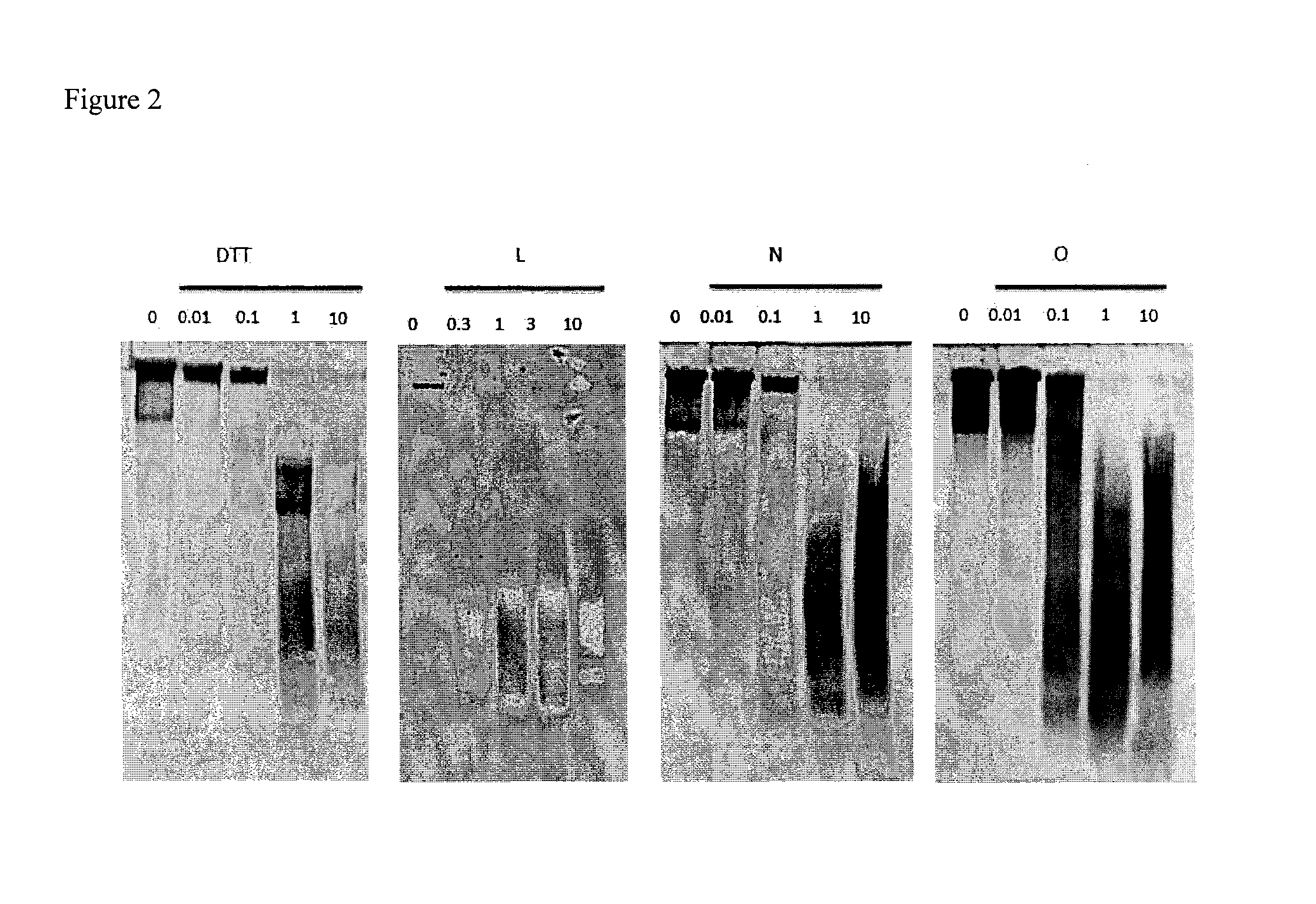
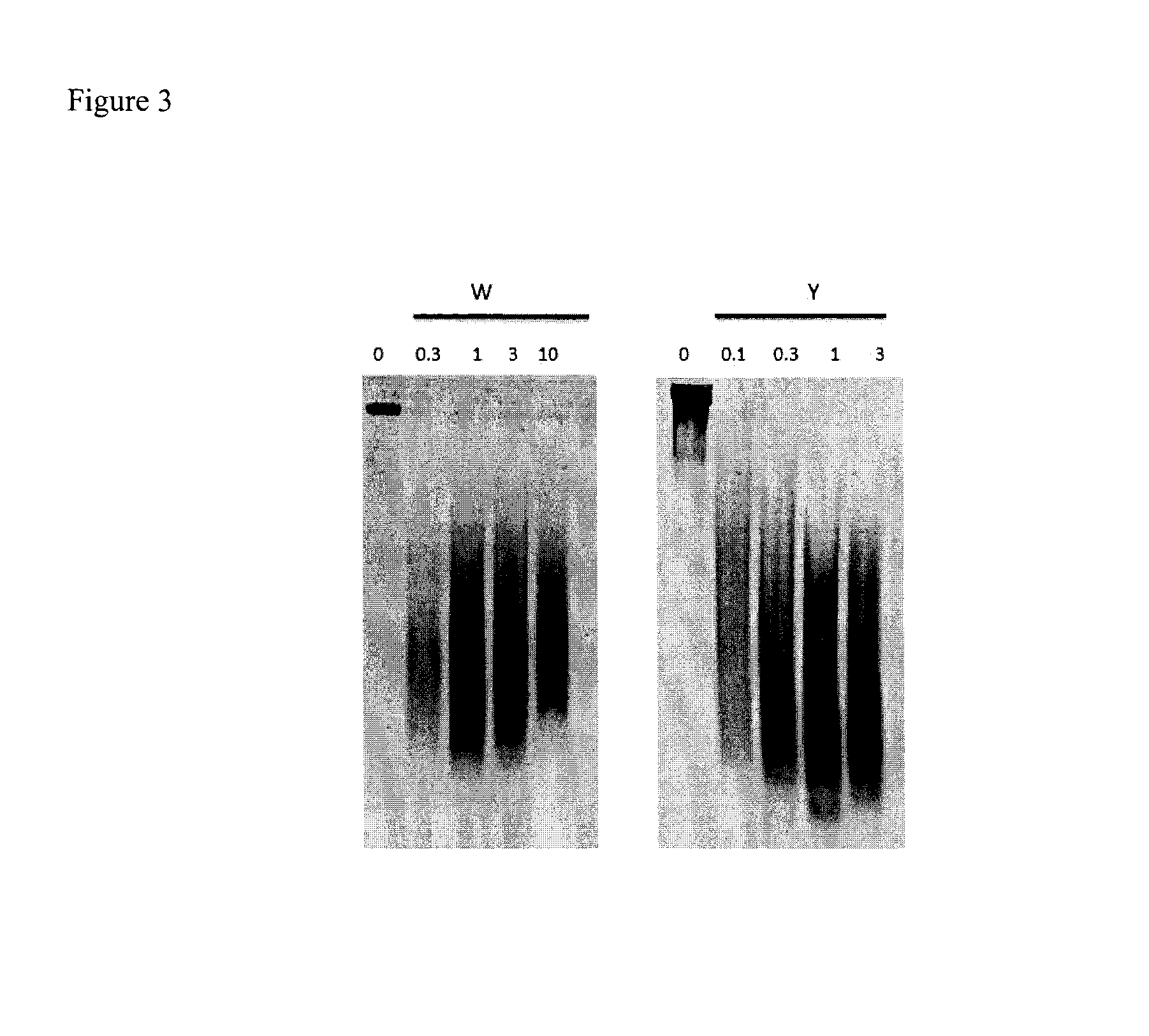
Dithiol mucolytic agents
ActiveUS20150056305A1Improve toleranceEffectiveAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryTreatment useDithiol
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Sulfur-containing epoxide resin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103145646ALow viscosityGood storage stabilityOrganic chemistryEpoxy resin coatingsGlycidyl methacrylateFlexural strength
The invention relates to a sulfur-containing epoxide resin and a preparation method thereof. The sulfur-containing epoxide resin is obtained by reacting a dithiol compound and glycidyl methacrylate in a stirring way at -5-20 DEG C for 4-10 hours. Compared with the traditional sulfur-containing epoxide resin, the sulfur-containing epoxide resin prepared through the method disclosed by the invention is lower in viscosity and higher in storage stability, can be applied to the fields of environment-friendly low-volatilization paint, low-volatilization resin, solvent-free epoxide resin insulating paint, and the like and can be directly applied without being added with an organic solvent or an active diluent; and compared with bisphenol A epoxide resin, the sulfur-containing epoxide resin disclosed by the invention is much lower in viscosity, shortened in gelation time by about 20% during solidification, enhanced in tensile strength and bend strength by about 10% and obviously increased in glass transition temperature and hardly influences the toughness. Besides, the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simpleness, low pollution and low cost.
Owner:SUZHOU TAIHU ELECTRIC ADVANCED MATERIAL CO LTD +1
Dithiol Compounds, Derivatives, and Uses Therefor
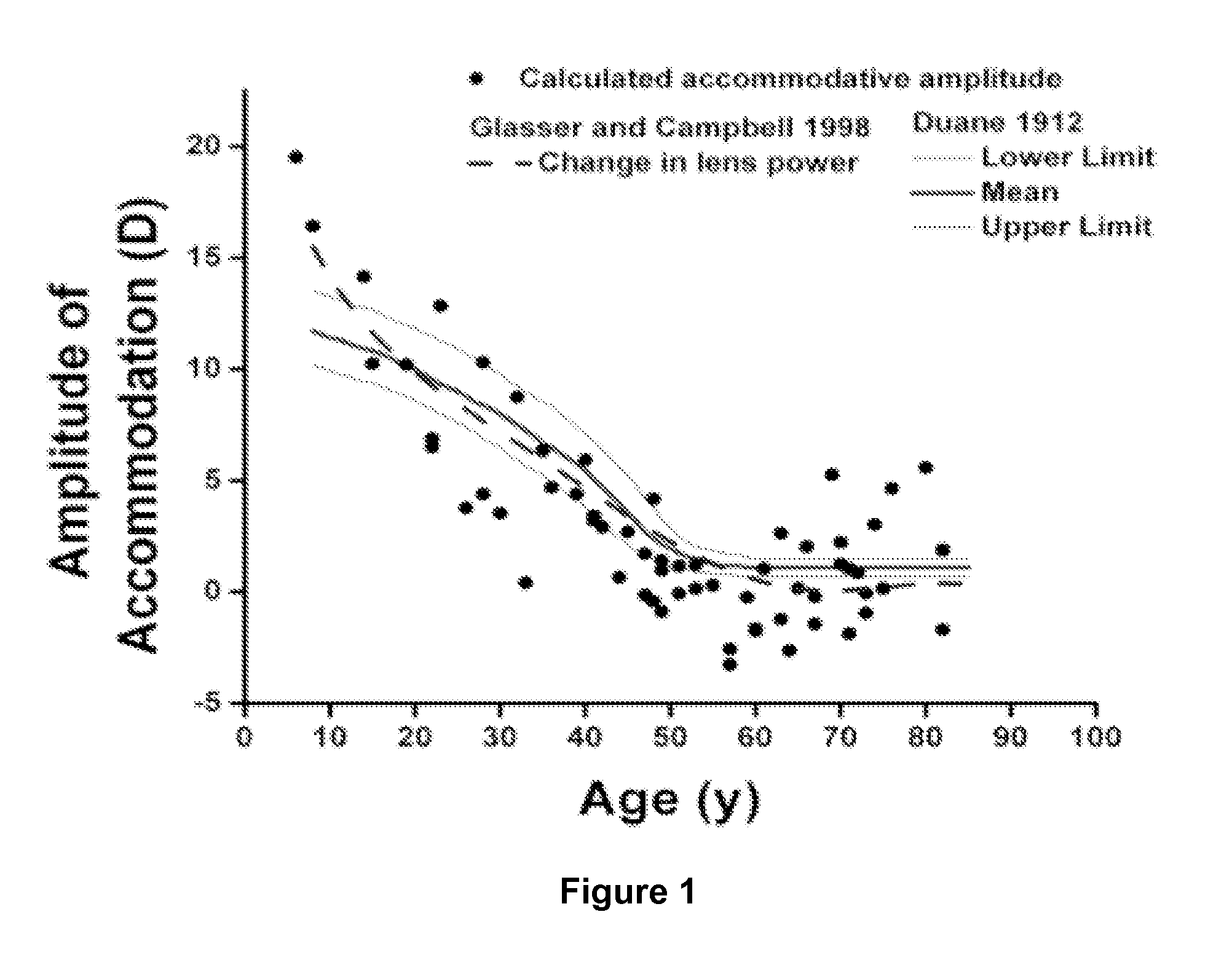
ActiveUS20140243385A1Increase and maintain amplitudeIncrease the adjustment rangeBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsDiseaseThiol
Dithiol compounds and derivatives thereof are disclosed. The agents are useful for treating ocular disease, especially presbyopia and cataract. Also disclosed are novel mercaptan compounds, particularly those including a photolabile protecting group, as well as methods of using the compounds for the prevention and treatment of ocular damage and disease.
Owner:ENCORE HEALTH LLC
Non-aqueous electrochemical device
InactiveUS6630272B1Inhibit deteriorationLower resistanceHybrid capacitor electrolytesOrganic electrolyte cellsLithium1,3,5-Triazine
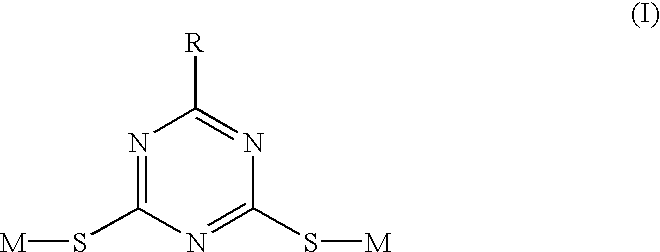
The present invention relates to an electrolyte for non-aqueous electrochemical device containing at least one of 6-substituted-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-dithiol and derivatives thereof as an additive and a non-aqueous electrochemical device, particularly a lithium secondary battery by the use thereof. The additive of the present invention forms a stable and low resistance film on the positive electrode, inhibiting characteristics of the electrochemical device from deteriorating on account of gas generated due to the decomposition of electrolyte.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Thiol functionalization method and application of nano hole metal-organic framework material
InactiveCN102949980AOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationReactive siteMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to a thiol functionalization method and application of a nano hole metal-organic framework material. Through the coordination of the nano hole metal-organic framework material containing a coordination unsaturated active site and a dithiol compound, a certain proportion of thiol in a dithiol compound molecule is connected with the coordination unsaturated active site of the nano hole metal-organic framework material through a coordination bond, and a thiol functional group is grafted to a metal-organic framework, so that the thiol-functionalized nano hole metal-organic framework material is generated. The thiol-functionalized nano hole metal-organic framework material can be used as an adsorption and separation material of heavy metal ions, and is applied to removal of heavy metal ions in a water body.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
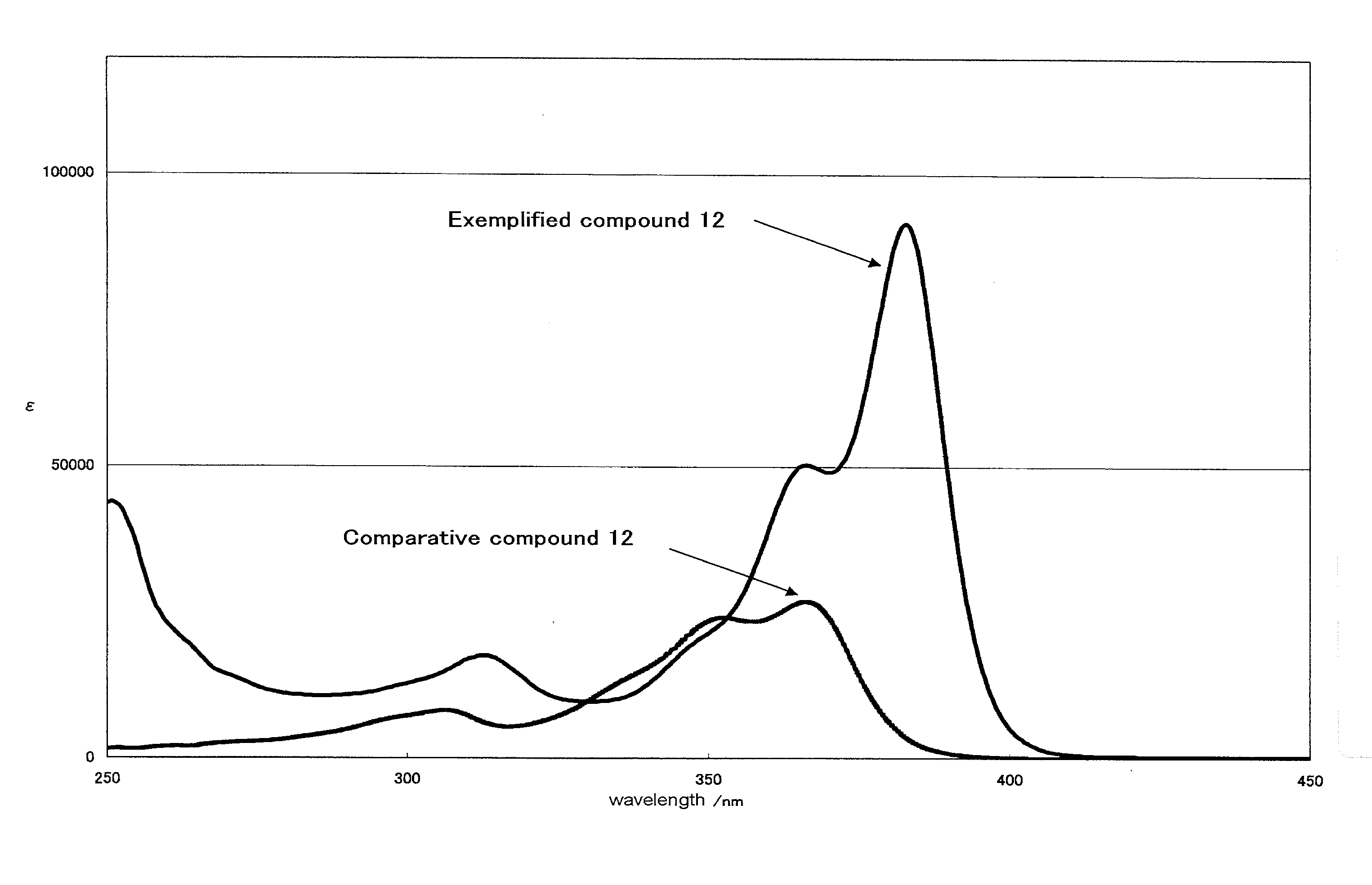
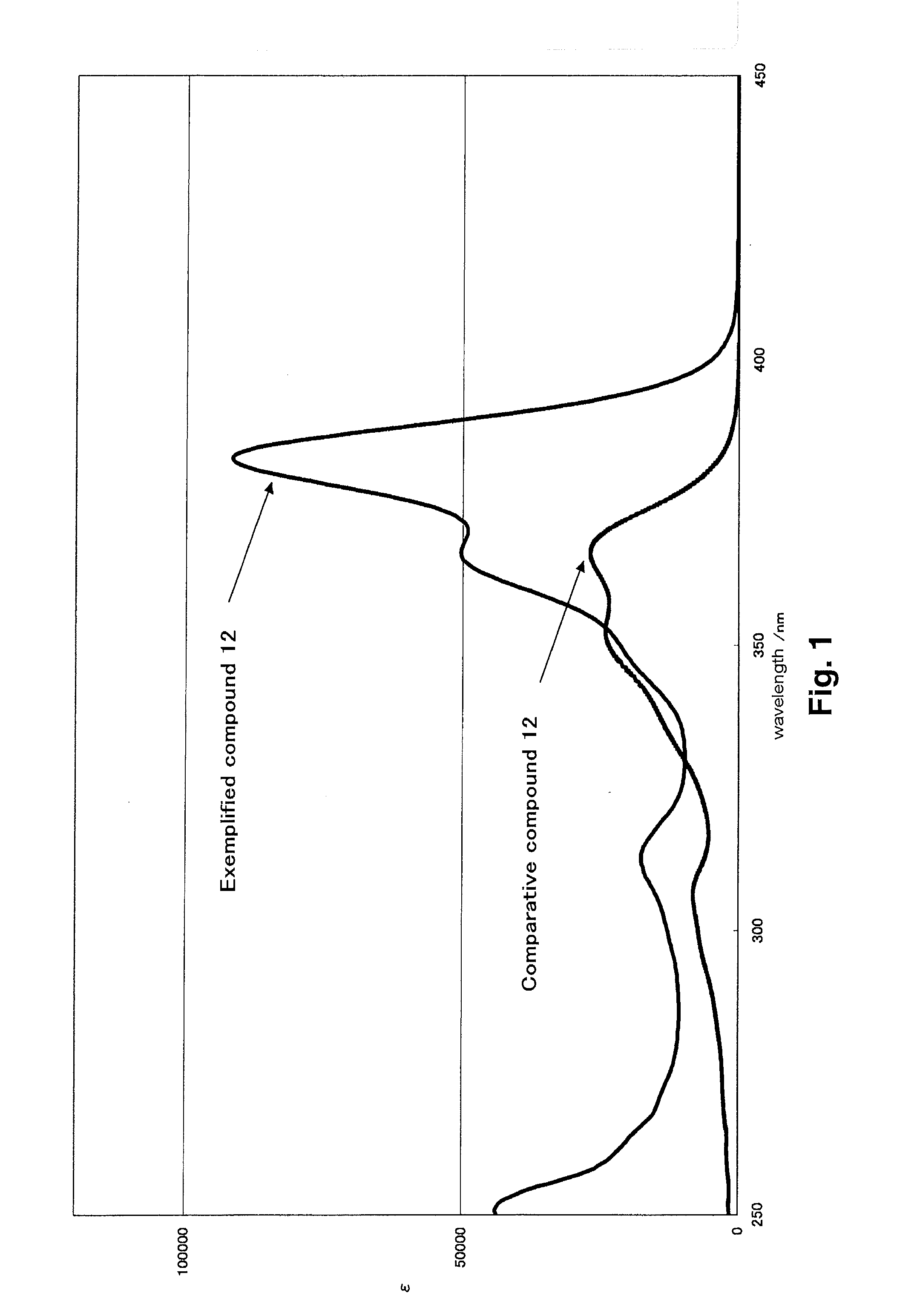
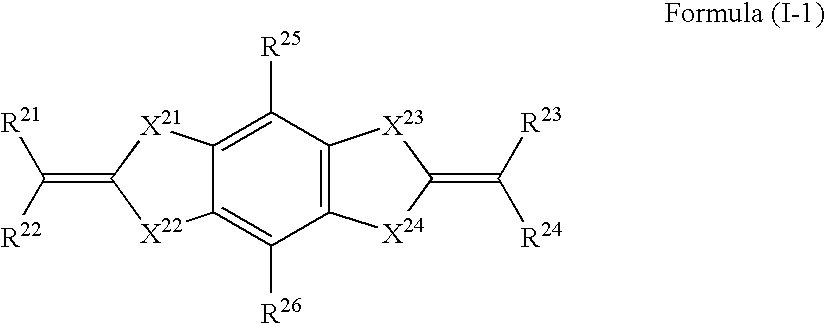
Heterocyclic compound, ultraviolet absorbent and composition containing the same
ActiveUS20100210762A1Improves UV resistancePrevent unstable compoundCosmetic preparationsGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSulfurylPolymer chemistry
A compound represented by formula (I-1):wherein R21, R22, R23 and R24 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a monovalent substituent, with the proviso that compounds, in which R21, R22, R23 and R24 each are an alkylthio group, are excluded; R21 and R22 and / or R23 and R24 each may bond to each other to form a ring, with the proviso that compounds, in which the formed ring is a dithiol ring or a dithiolane ring, are excluded;R25 and R26 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a monovalent substituent;X21, X22, X23 and X24 each independently represent a hetero atom;compounds, wherein R21, R22, R23 and R24 each represent a cyan group; X21, X22, X23 and X24 each represent a sulfur atom; and R25 and R26 each represent a hydroxyl group or a hydrogen atom, are excluded; andcompounds, wherein R21 and R23 each represent a hydrogen atom; R22 and R24 each represent an arylcarbonyl group; X21, X22, X23 and X24 each represent a sulfur atom; and R25 and R26 each represent a hydroxyl group, are excluded; and an ultraviolet absorbent, which has molecular weight of 10,000 or less and molar extinction coefficient at the maximum absorption wavelength of the ultraviolet absorbent of 80,000 or more.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for preparing sulfur-containing high-refractive-index resin
InactiveCN102993410APolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEpoxyPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for preparing sulfur-containing high-refractive-index resin, comprising the steps of (A) preparing a sulfur-containing epoxy acrylate chain segment; (B) preparing a urethane acrylate chain segment; and (C) preparing the sulfur-containing high-refractive-index resin. According to the invention, a dithiol compound is reacted with epoxy chloropropane firstly to prepare sulfur-containing epoxy; the sulfur-containing epoxy is reacted with acrylic acid to form sulfur-containing epoxy acrylate; and then a urethane acrylate prepolymer with a NCO functional group at one end is grafted at the side chain of the sulfur-containing epoxy acrylate. The resin prepared by adopting the method disclosed by the invention has higher refractive index, is provided with an ultraviolet-polymerizable acrylate double bond and can be applied to products such as light curing adhesives, coatings and the like.
Owner:深圳市迪凯鑫科技有限公司
Meat flavor composition
The invention discloses a meat flavor composition which comprises 4-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-thiazole, 4-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-thiazole-acetate, 2-methyl-3-furanthiol-acetate, 2-methyl-butyraldehyde, 2-methyl-furanthiol, 1,6-ethanthiol, 2-acetyl-4-methyl-thiazole, 2,4-decadienal, methyl mercatopropanol, 2,6-dimethoxyphenol, clove oil, butyl lactate, 3-methyl mercatopropanol, 2-methyl-2-mercapto-undecane, 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, 2,3,5-trimethylpyrazine, 2-methyl-3-mercaptofuran, ethyl maltol and the like, with the balance being an oil-soluble solvent. The invention also provides a preparation method for the composition.
Owner:WUTONG AROMA CHEM CO LTD
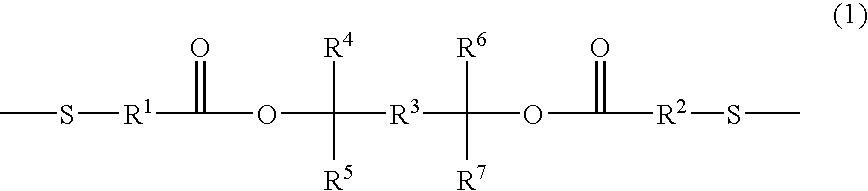
Positive photosensitive resin and novel dithiol compound
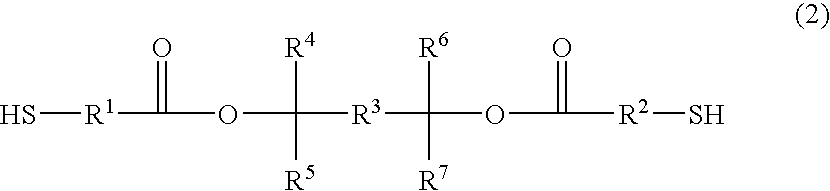
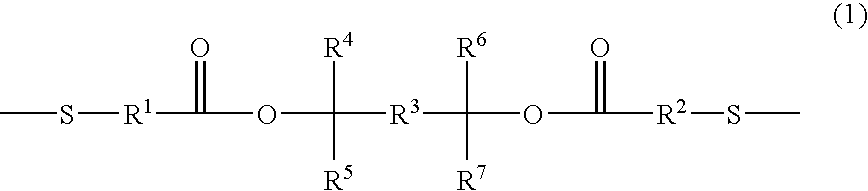
InactiveUS20060068324A1Small defectHigh sensitivityPhotomechanical apparatusPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersResistCompound a
A positive photosensitive resin having, in the high-molecular main chain, a structure represented by the following general formula (1): and a dithiol compound represented by the following general formula (2): The positive photosensitive resin can alleviate the problems of conventional technique and, when used for formation of a fine patter in semiconductor production, can show a higher resist sensitivity than conventional products and can bring about effects such as reduction in impurities after development. The dithiol compound is novel and extremely suitable for use in production of the positive photosensitive resin.
Owner:MARUZEN PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Butadiene styrene rubber composition with wear-resisting characteristic and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102432927AReduce rolling resistanceImprove wet skid resistanceSpecial tyresRolling resistance optimizationPotassium persulfatePolymer science
The invention provides a butadiene styrene rubber composition with a wear-resisting characteristic and a preparation method thereof. The butadiene styrene rubber composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of butadiene styrene rubber, 1-30 parts of modified butylbenzene powdered rubber and can also comprise 1-30 parts of hydroxyl-terminated liquid butadiene styrene rubber and the like. In the butadiene styrene rubber, the content of the bound styrene is 15-50%, and the Mooney viscosity is 30-90; the modified butylbenzene powdered rubber is obtained by modifying the surface of the butylbenzene powdered rubber prepared by a radiation crosslinking method by using ethanthiol and potassium persulfate under the existence of polyethylene glycol, wherein the content of the bound styrene is 15-60% and the average particle size is 50-300nm; and the content of gel is 70-98%. The butylbenzene vulcanized rubber can well achieve the balance among the rolling resistance, the slippery resistance and the wear resistance, and is suitably used for tread rubber.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
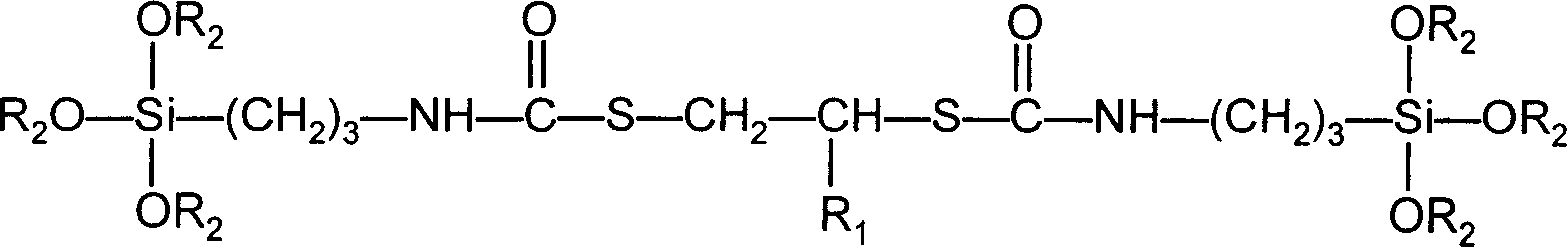
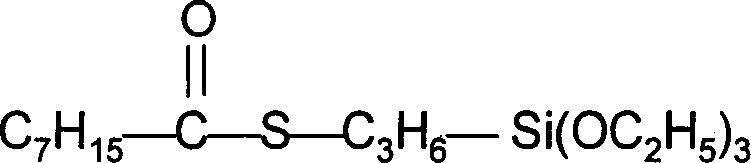
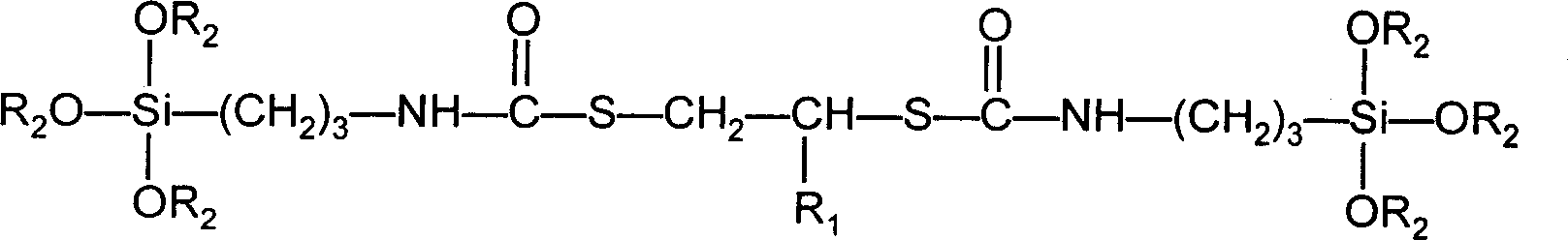
Bisilane coupler contg. sulfur and nitrogen element and prepn. thereof
InactiveCN1834100AEasy to separateSimple production processGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsThiocarbamateOrganocatalysis
This invention discloses a kind of sulphur- and nitrogen-containing silicone coupling reagent and its preparation method, that is, gamma-isocyanate propyl trialkoxyl silicane and dithiol compound react with each other at a mole ratio of 2:1 in organic solvent with the existence of organic catalyst. The mixture is then vacuum distilled to obtain a silicone coupling reagent that has two thiocarbamate units and six alkoxyls. This method has the advantages of simple technique flow, high yield and high practicability. The silicone coupling reagent based on this invention has good thermo stability and considerable coupling effect. It is a good substitution of conventional silicone coupling reagent and can be used in fumed silica-containing rubber so as to promote the comprehensive properties of vulcanized rubber.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
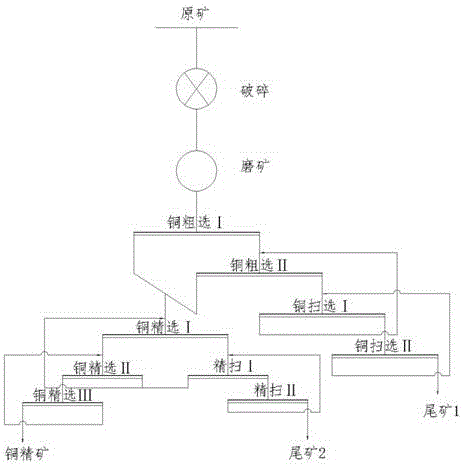
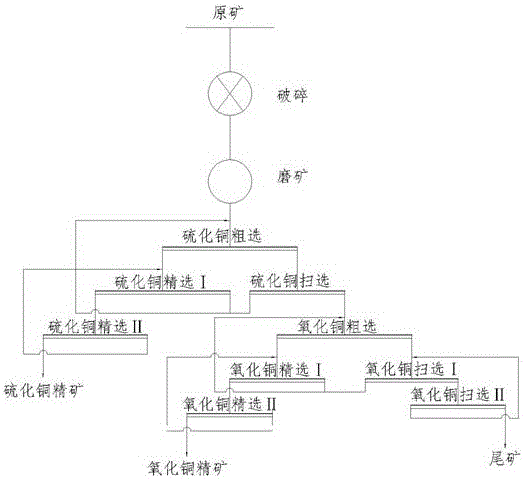
Flotation method of copper oxide ores
The invention discloses a flotation method of copper oxide ores. The method comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding ores, and performing floatation on the ores. Aiming at different distribution of the copper oxide ores, the flotation method adopts synchronous flotation and asynchronous flotation, so that the recycling rate of valent copper elements in the ores is improved, a plurality of types of flotation products can be easily produced and the value of the products is improved. Compared with traditional copper oxide flotation, the flotation method has the advantage that an efficient flotation capturing agent is formed by combining amyl-xanthate and nonyl hydroxamic acid, so that the recycling rate of whole copper and the quality of ore concentrate are improved. In order to strengthen a flotation process of the copper oxide ores, ethylenediamine phosphate and 2,5-dithiol-1,3,4-thiodiazole are used as floatation activating agents, so that the floatation efficiency can be improved, and meanwhile, the floatation recycling rate of copper oxide can be greatly improved.
Owner:CINF ENG CO LTD
Preparation method of intelligent antibacterial polypeptide coating layer
InactiveCN105288584AControllable and high grafting rateHigh grafting rateAntibacterial agentsAntifouling/underwater paintsAntioxidantAntibacterial activity
A preparation method of an intelligent antibacterial polypeptide coating layer is a method universally applicable to different substrate materials. The preparation method includes the following steps: firstly, placing the substrate materials in a low temperature plasma generator main body chamber, vacuumizing, then introducing argon, loading with voltage and current, and carrying out plasma treatment; secondly, rapidly placing the substrate materials after treatment in a methanol solution with a certain amount of dimercaptan; and then, carrying out a reaction of the obtained substrate materials having the surface containing sulfydryl and an antibacterial polypeptide containing sulfydryl under an action of an antioxidant, and forming disulfide bonds. When the antibacterial polypeptide coating layer makes contact with bacterial cells, the disulfide bonds on the surface of the substrate materials are broken and are reduced to release the antibacterial polypeptide containing sulfydryl, so as to play a role of sterilization. The antibacterial activity of the antibacterial polypeptide in a free state is higher than that of a same antibacterial polypeptide covalently immobilized on a material surface, and the usage amount of the antibacterial polypeptide can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
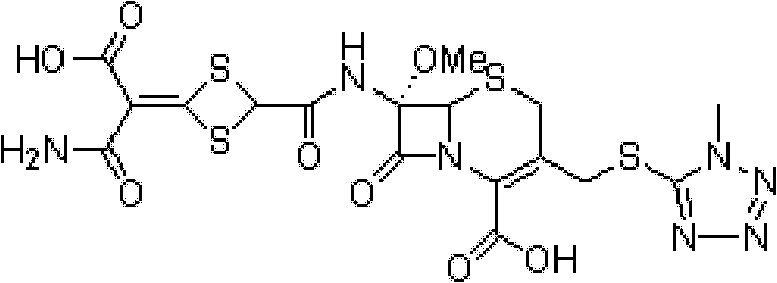
Preparation method of cefotetan
The invention relates to a preparation method of cefotetan. The method comprises the steps of: under an alkaline condition, reacting the starting raw material 7-MAC with chloroacetyl chloride in an organic solvent so as to obtain the intermediate CefoD-1; under nitrogen protection, adding aluminium trichloride into anisole, stirring for dissolving, and leaving the obtained solution for standby application; taking another organic solvent, into which the intermediate CefoD-1 is added under stirring, then adding the standby solution for reacting, thus obtaining the intermediate CefoD-2; reactingthe intermediate CefoD-2 with 3, 5-dithiol-4-isothiazole formic acid trisodium salt until that a sampled cefotetan tautomer is detected less than 4.0%, after the reaction conducting a post-treatment,thus obtaining cefotetan. With improved yield and reduced cost, the method of the invention, without final heating concentration, can generate products with a shallow color and almost invariant purity.
Owner:HAINAN HERUI PHARMA +1
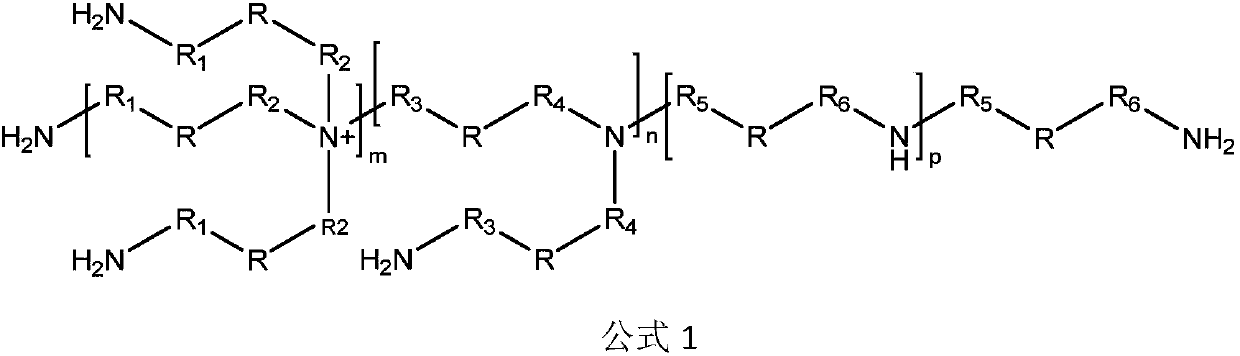
Degradable polyurethanes and composites thereof
Among others, the present invention provides isocyanate resin compositions which include an isocyanate compound containing two or more isocyanate functional groups; a chain extender comprising a degradable diamine and optionally a dihydric alcohol, a polyether diol, a polyester diol, a diamine, a dimercaptan, or a bisphenol; and a cross-linker comprising a degradable polyamine and optionally a trifunctional, tetrafunctional or polyfunctional polyhydric alcohol, polyether polyol, polyester polyol, polyamine, polymercaptan, or polyphenol.
Owner:ADESSO ADVANCED MATERIALS WUXI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com