Force touch sensation feedback and force intensity control method of mechanical artificial hand based on myoelectric control
A technology of myoelectric control and control method, applied in the direction of prosthesis, medical science, etc., can solve the problems that the disabled cannot take fragile daily necessities, it is difficult to adapt to normal life, and the prosthetic hand cannot control the clamping force, etc. , to achieve the effect of avoiding damage to items, returning to normal life, and taking items quickly and flexibly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment
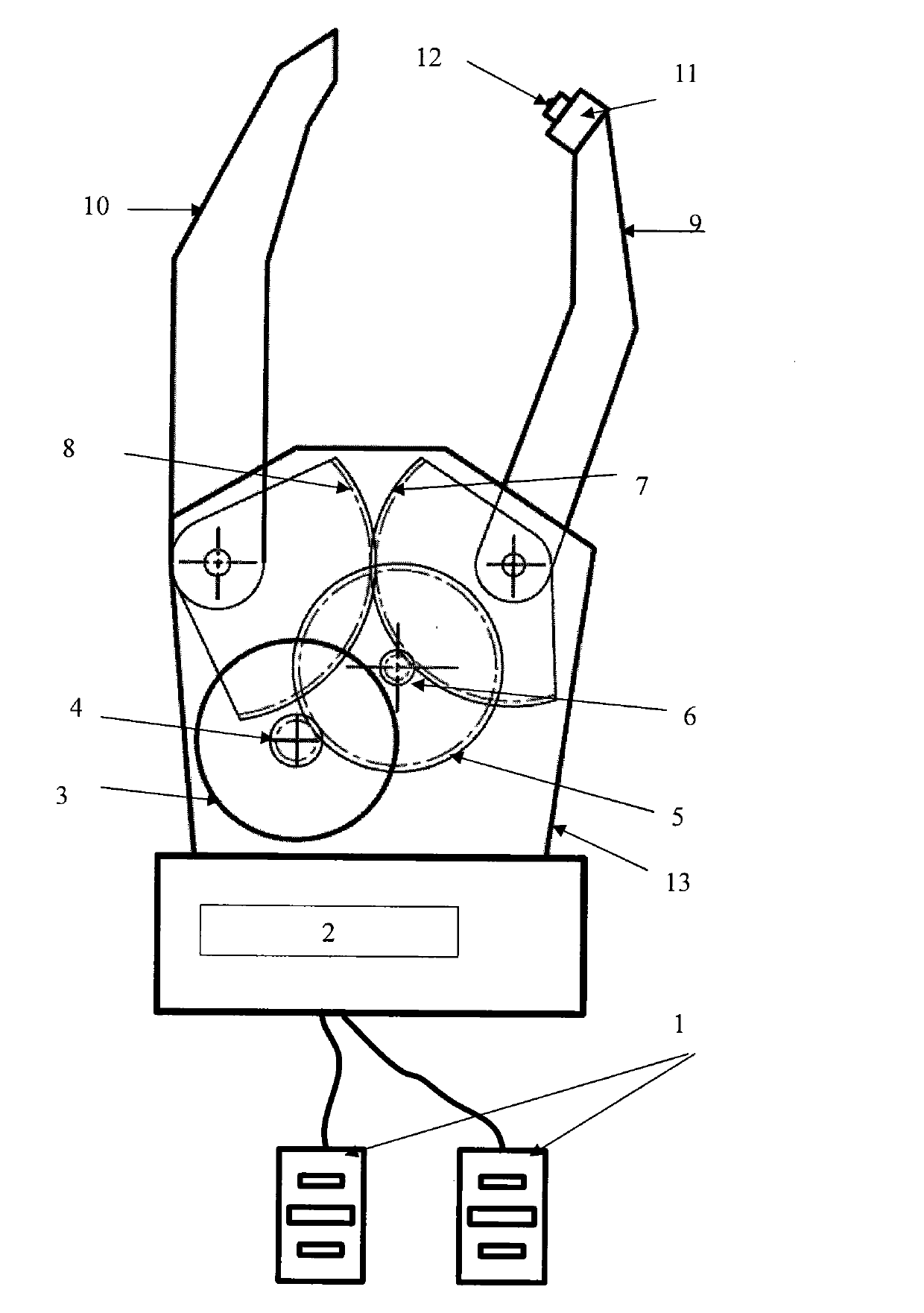
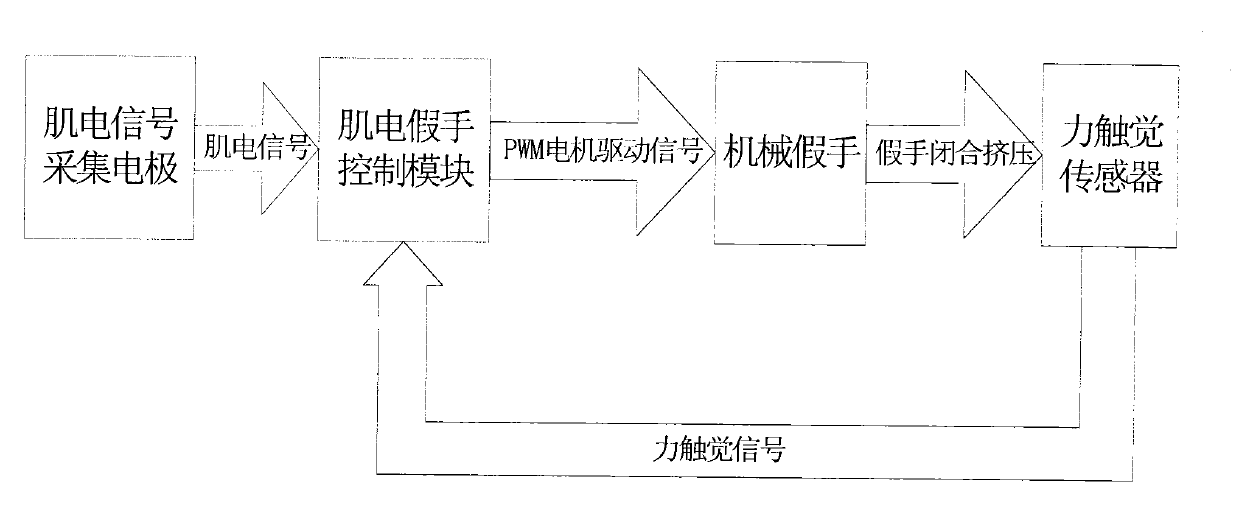
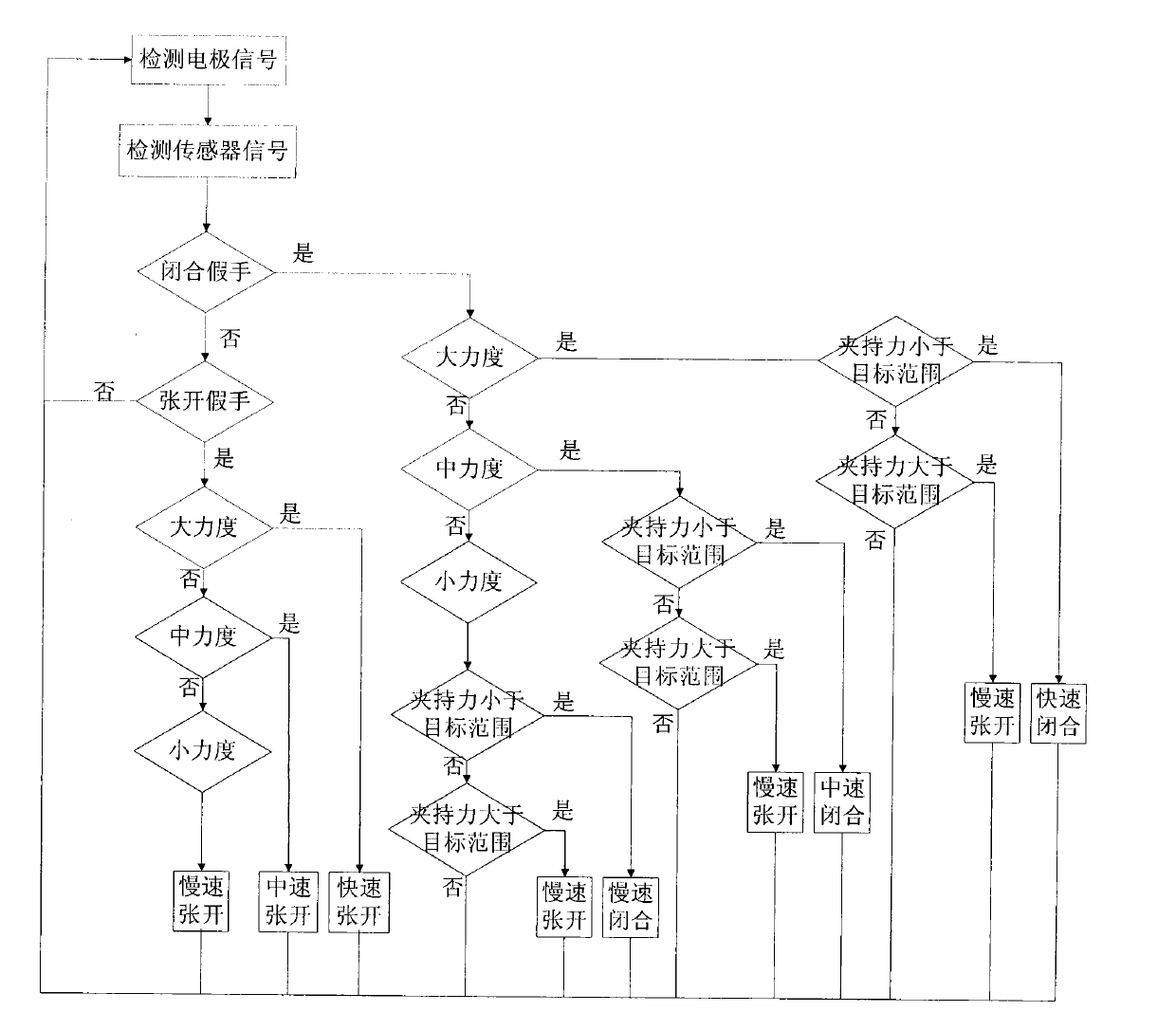
[0015] Such as figure 1 As shown (only the mechanical prosthetic hand draws two fingers for clamping in the figure), two myoelectric signal acquisition electrodes 1 are connected to the myoelectric prosthetic hand control module 2 at the root of the prosthetic hand, and the motor drive of the myoelectric prosthetic hand control module 2 The signal line is connected to the micro-DC motor 3 on the mechanical prosthetic hand 13, and the motor gear 4 installed on the output shaft of the micro-DC motor 3 is meshed with the large gear 5 for transmission, and the transmission ratio is 4:1, which plays the role of deceleration and force boosting; 5. The coaxial pinion 6 meshes with the thumb 9 root gear 7. The transmission ratio is 10:1, which also plays the role of deceleration and boosting. The shaft of the thumb 9 root gear 7 is fixedly connected with the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com