Method for identifying thermal defects by means of auxiliary heat source under condition of small temperature difference
An auxiliary heat source and thermal defect technology, applied in the field of infrared detection, can solve problems such as influence, achieve the effect of convenient detection and solve the problem of thermal defect detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0027] Specific implementation mode 1: The method for identifying thermal defects with the aid of an auxiliary heat source under the condition of small temperature difference described in this implementation mode, the specific process is as follows:
[0028] Adopt auxiliary heat source to irradiate the inner surface of the building wall 6, heat the inner surface of the wall, and stop the irradiation when the temperature of the inner surface of the wall is higher than the outside temperature by x degrees; the value range of x is [3,10]°C;
[0029] Using an infrared thermal imager to detect the temperature field distribution of the inner surface of the wall, and obtain an infrared thermogram representing the temperature field distribution of the inner surface of the wall;
[0030] Analyzing the temperature difference shown in the infrared thermogram, and then obtaining the thermal defects of the building.
[0031] The auxiliary heat source can be realized by using any existing ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0040] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the method of identifying thermal defects with the aid of an auxiliary heat source under the condition of small temperature difference described in specific embodiment 1 is that: the time for controlling the heating of the inner surface of the wall is used as the reason for stopping the heating conditions, the specific process is:
[0041] Using an auxiliary heat source to irradiate the inner surface of the building wall to heat the inner surface of the wall, the irradiation direction of the auxiliary heat source is the normal direction of the inner surface of the irradiated wall, that is, the vertical incidence, and ensure that the irradiation angle is stable, The irradiated surface of the light source is evenly distributed, and the unevenness of the irradiated intensity distribution is within ±5%; and the heat flux density of the auxiliary heat source irradiated to the wall surface is [760W / m 2 ,800W / m ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
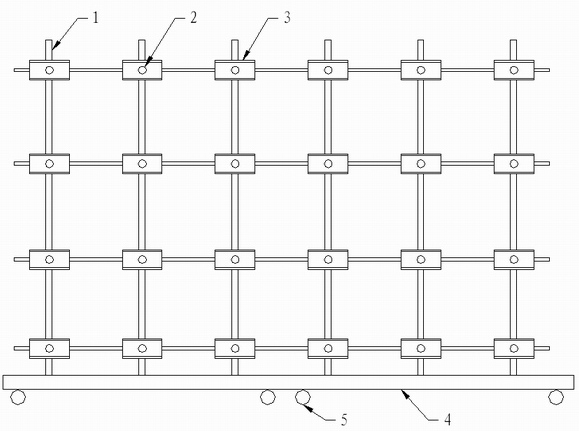
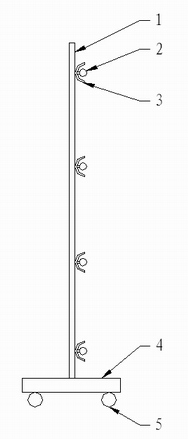
[0068] Specific implementation mode 3: This implementation mode provides a structure of an auxiliary light source, see figure 1 and figure 2 . The auxiliary light source described in this embodiment adopts an assembled structure, which is composed of a movable base 4, a bracket 1, a light source 2, and a reflector 3. The bottom of the movable base 4 is provided with wheels 5, and the bracket 1 is fixed on the movable base. On the upper surface of 4, the support 1 is a planar mesh structure, a plurality of light sources 2 are evenly distributed in a matrix and fixed on one side of the support 1, and a reflector 3 is fixed between each light source 2 and the support 1.
[0069] The auxiliary light source described in this embodiment can adjust the area of the support 1 and the distribution of the light source according to the area of the wall to be detected.
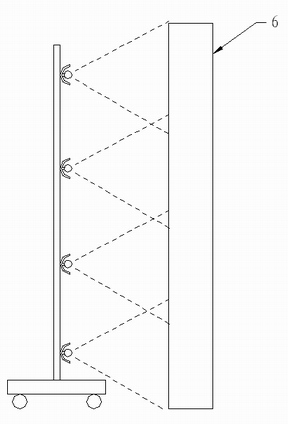
[0070] In practical application, the auxiliary light source described in this embodiment is moved to the front of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com