Imaging velocity analysis method of seismic scattering P-S converted wave
A technology of seismic scattering and imaging velocity, applied in seismic signal processing and other directions, can solve problems such as errors, inaccurate velocity parameters, and inability to obtain shear wave velocity values.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] Take a three-component actual seismic survey data containing 146 shots, 86 traces per shot, and 2000 sampling points per trace as an example to illustrate the implementation steps of this example:
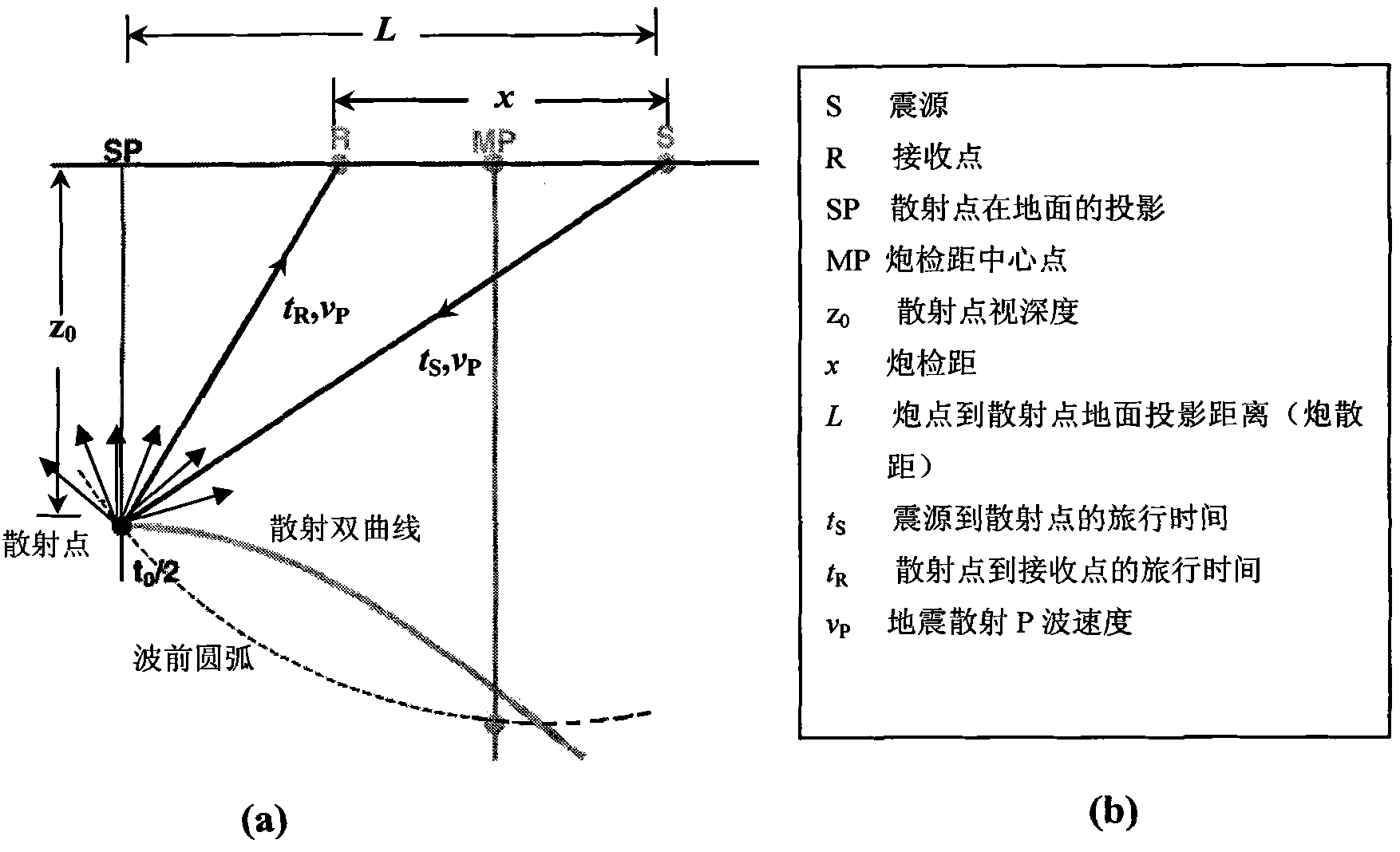
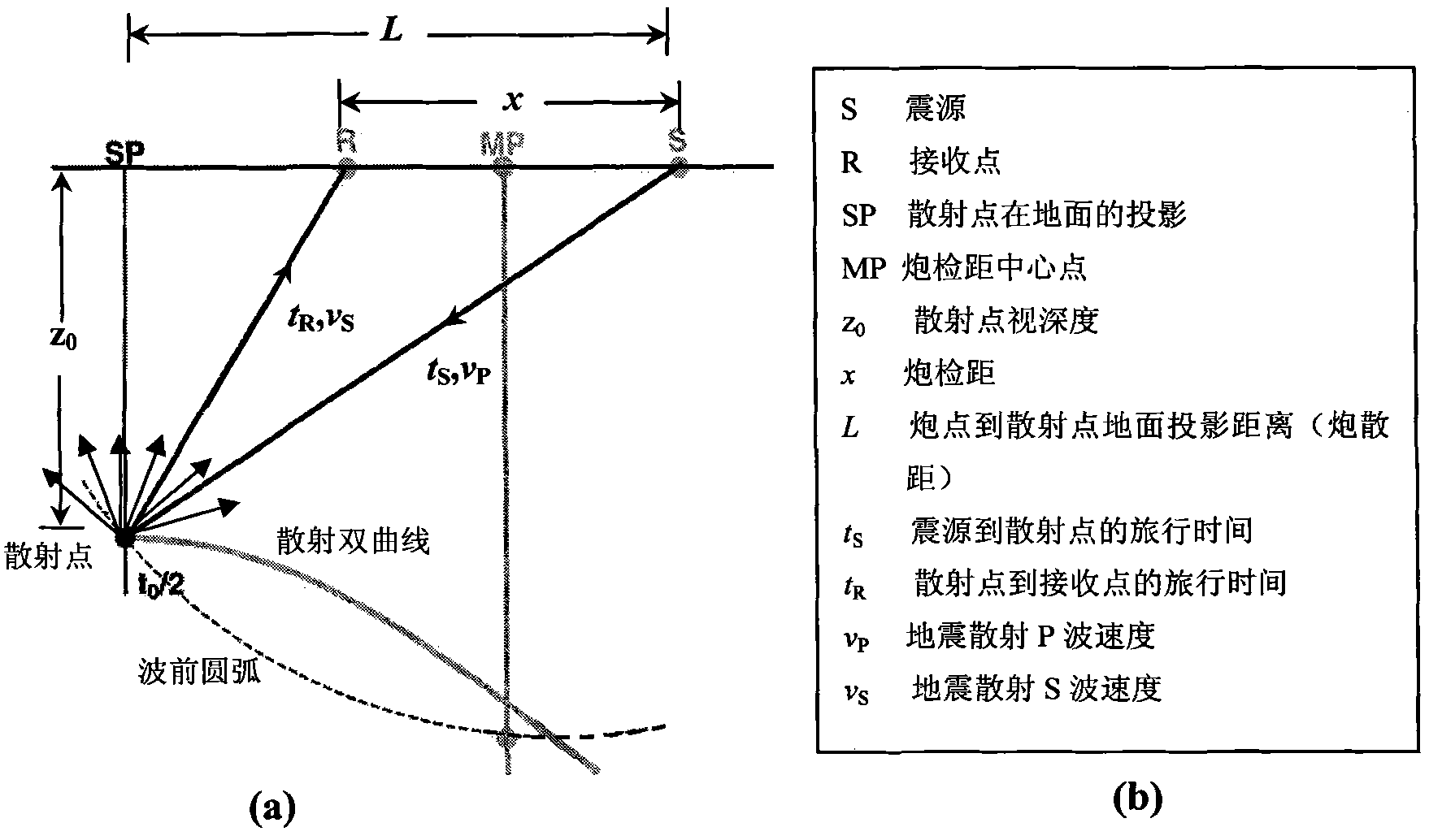
[0112] Step 1: read the P-P wave seismic data containing 146 shots, 86 traces per shot, and 2000 sampling points per trace into the two-dimensional array F, and load the observation system parameters into the trace header of the original seismic data, and based on Observation system and acquisition parameters calculate the location and coordinates of scattering points;
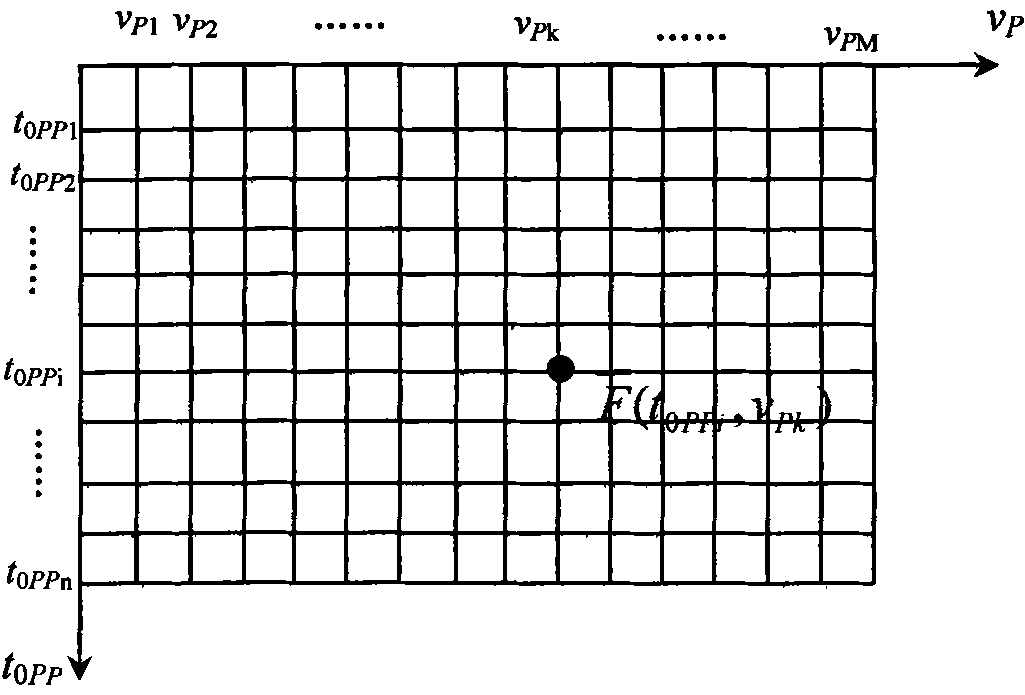
[0113] Step 2: According to the seismic scattering P-P wave time-distance hyperbolic equation, on the shot set, fix t 0PPi In the case of , choose a velocity v arbitrarily Pk , the speed can determine a hyperbolic trajectory, and superimpose or correlate the scattering amplitudes at each offset along the hyperbolic trajectory, and then weight and sum the energy of the same scattering point to obtain the cor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com