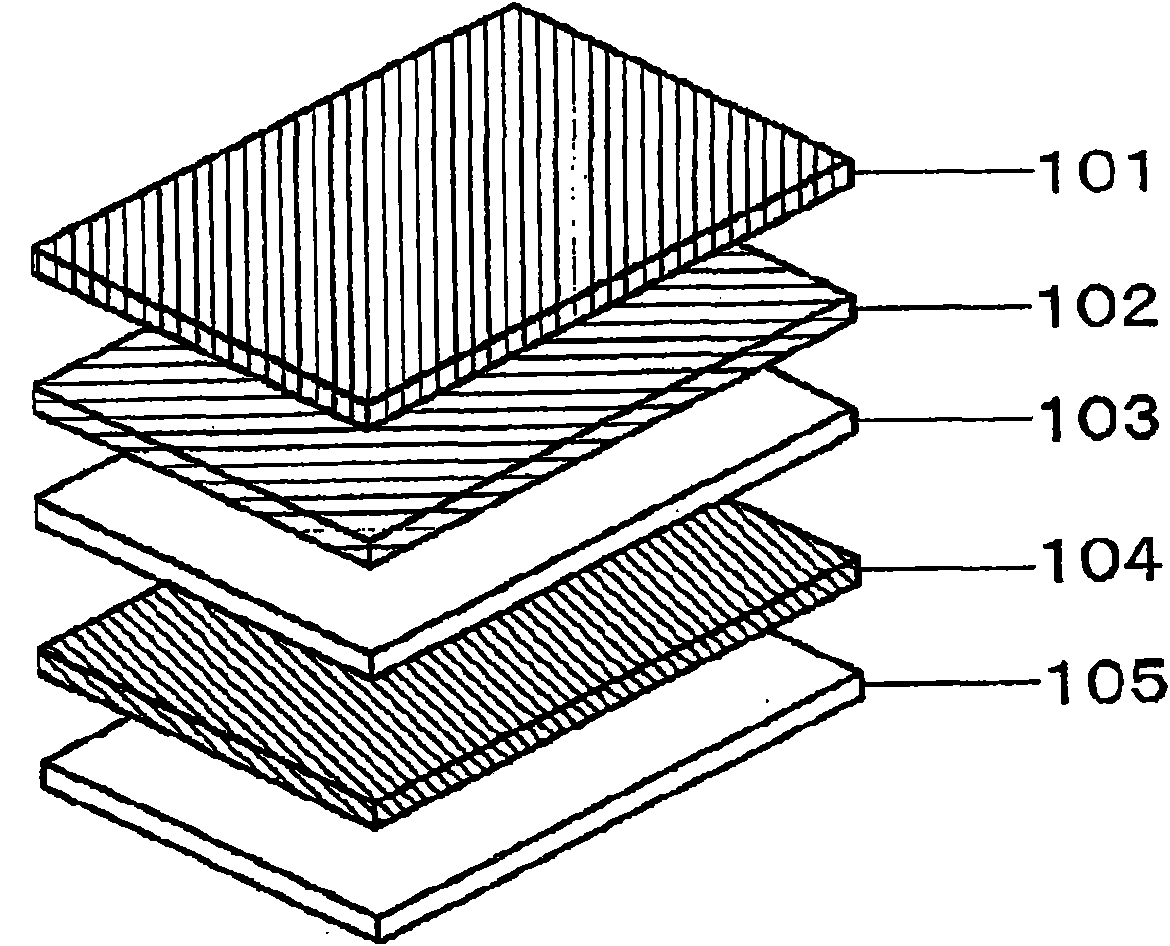
Shock absorbing material
A technology of shock absorption and impact parts, which is applied in the direction of thin material processing, flexible covering, film/flake adhesive, etc. It can solve the problem of difficulty in obtaining shock absorption, and achieve excellent flexibility and shock absorption. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0147] Polypropylene [melt flow rate (MFR) (230°C) 0.35g / 10min] 45 parts by weight, polyolefin elastomer [melt flow rate (MFR) 6g / 10min, JIS A hardness 79°] 55 Parts by weight, 10 parts by weight of magnesium hydroxide, 10 parts by weight of carbon (trade name "Asahi #35" manufactured by Asahicarbon Co., Ltd.), 1 part by weight of monoglyceride stearate, and 2 parts by weight of fatty acid amide (lauric acid bisamide) The mixture was kneaded at a temperature of 200° C. using a twin-screw kneader manufactured by JSW Co., Ltd., extruded into a strand, cooled with water, and formed into pellets. The pellets were put into a single-screw extruder manufactured by Nippon Steel Works Co., Ltd., and carbon dioxide gas was injected at a pressure of 13 (12 after injection) MPa in an atmosphere of 220°C. Carbon dioxide gas was injected at a ratio of 6 parts by weight to 100 parts by weight of the polymer. After the carbon dioxide gas is fully saturated, it is cooled to a temperature suit...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Polypropylene [melt flow rate (MFR) (230°C) 0.35g / 10min] 45 parts by weight, polyolefin elastomer [melt flow rate (MFR) 6g / 10min, JIS A hardness 79°] 55 Parts by weight, 120 parts by weight of magnesium hydroxide, 10 parts by weight of carbon (trade name "Asahi #35" manufactured by Asahicarbon Co., Ltd.), 1 part by weight of monoglyceride stearate, and a biaxial carbon fiber made by Japan Steel Works (JSW) Co., Ltd. Kneading machine, kneading at a temperature of 200°C, then extruded into strips, cooled with water, and shaped into granules. The pellets were put into a single-screw extruder manufactured by Nippon Steel Works Co., Ltd., and carbon dioxide gas was injected at a pressure of 13 (12 after injection) MPa in an atmosphere of 220°C. Carbon dioxide gas was injected at a ratio of 6 parts by weight to 100 parts by weight of the polymer. After the carbon dioxide gas is fully saturated, it is cooled to a temperature suitable for foaming, and then extruded from a mold...
Embodiment 3
[0151] Polypropylene [melt flow rate (MFR) (230°C) 0.35g / 10min] 45 parts by weight, polyolefin elastomer [melt flow rate (MFR) 6g / 10min, JIS A hardness 79°] 55 Parts by weight, 10 parts by weight of magnesium hydroxide, 10 parts by weight of carbon (trade name "Asahi #35" manufactured by Asahicarbon Co., Ltd.), 1 part by weight of monoglyceride stearate, and 2 parts by weight of fatty acid amide (lauric acid bisamide) It was kneaded at a temperature of 200° C. using a twin-screw kneader manufactured by Japan Steel Works (JSW), and then extruded into strips, cooled with water, and formed into pellets. The pellets were put into a single-screw extruder manufactured by Nippon Steel Works Co., Ltd., and carbon dioxide gas was injected at a pressure of 13 (12 after injection) MPa in an atmosphere of 220°C. Carbon dioxide gas was injected at a ratio of 6 parts by weight to 100 parts by weight of the polymer. After the carbon dioxide gas is fully saturated, it is cooled to a temperat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com