Method and device for detecting cross site scripting
A cross-site scripting attack and detection method technology, applied in computer security devices, special data processing applications, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
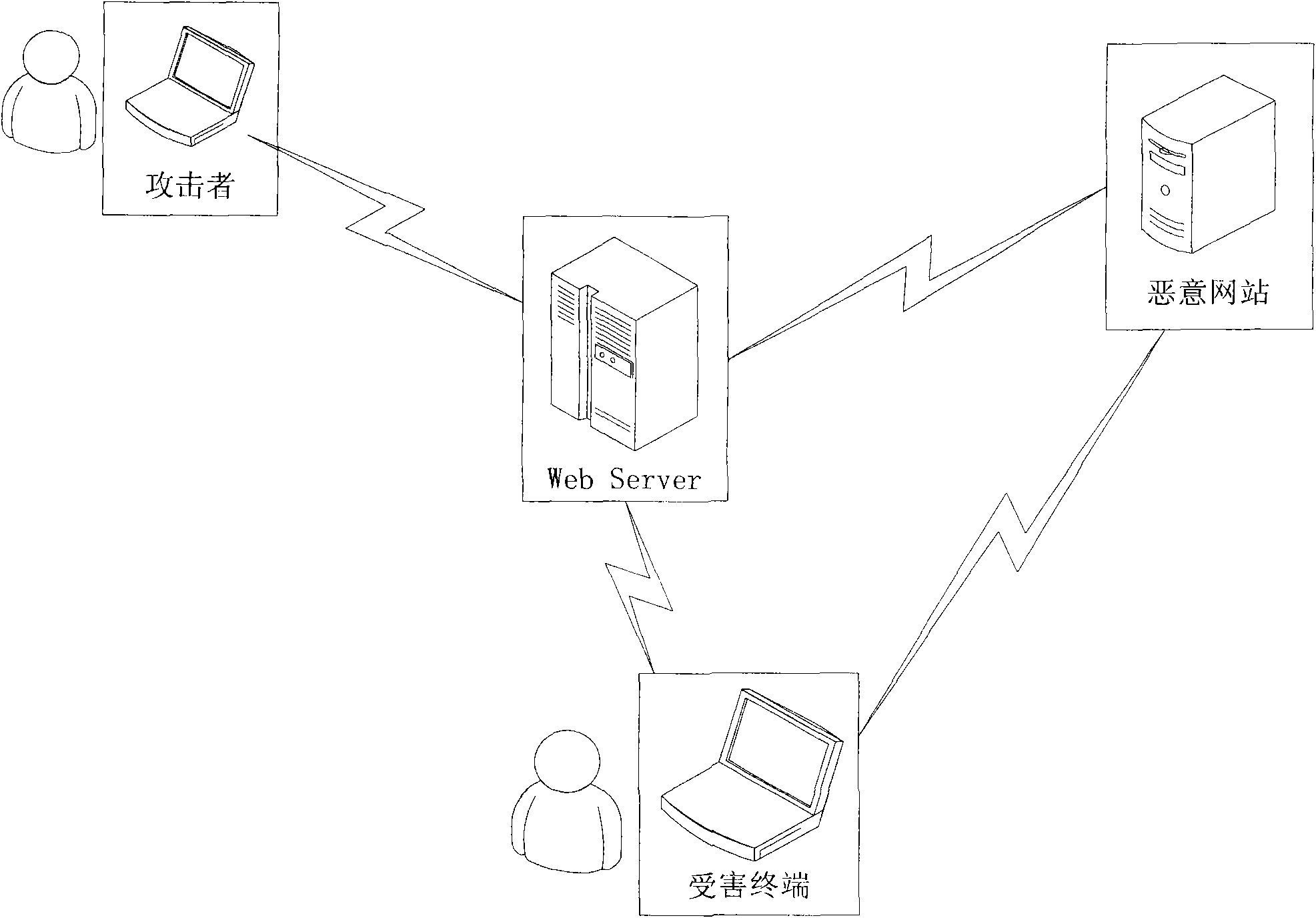
[0050] Embodiment 1, a detection method for a cross-site scripting attack, such as figure 2 shown, including:
[0051] a. For the captured HTTP return page, find the active tag (Active Tag, abbreviated as AT); add the probability P of each layer label including the active tag in the captured HTTP return page to the inverse , and find the arithmetic mean value as the embedded JavaScript reasonable index EJSRF of the active label; extract the JavaScript script in each active label;
[0052] Wherein, the active label is an HTML label that does not have other HTML labels between the JavaScript script, and the probability P of the label is the probability that the JavaScript script directly appears in the label;
[0053] B, the extracted JavaScript script is encoded and restored to obtain the coded byte quantity EBN (Encoding Bytes Number) of the JavaScript script; semantic restoration is carried out to obtain the number of times the string is spliced by using semantic deformat...
Embodiment 2
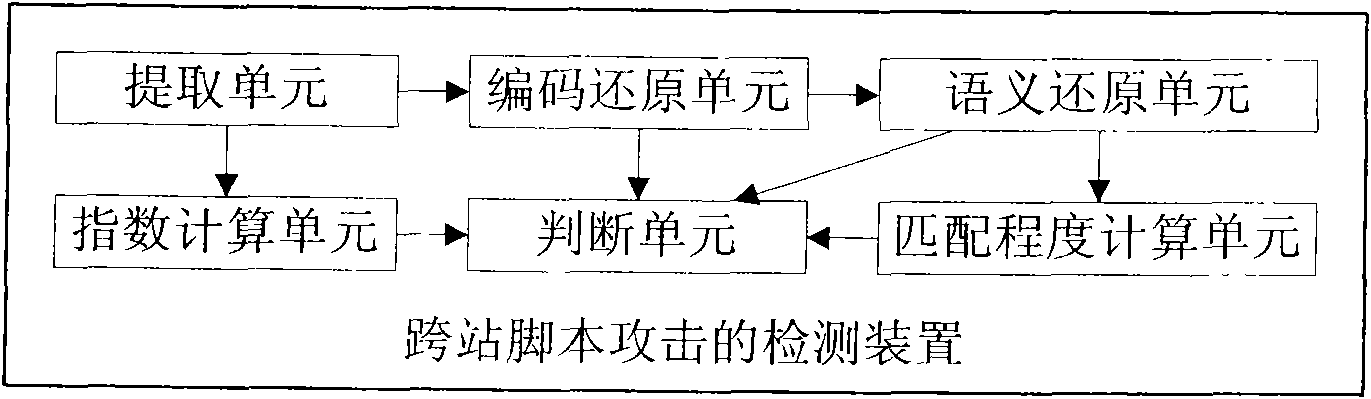
[0141] Embodiment 2, a detection device for a cross-site scripting attack, such as image 3 shown, including:
[0142] The index calculation unit is used to add the inverses of the probabilities P of the tags of each layer including the active tag in the captured HTTP return page, and calculate the arithmetic mean value as the reasonable value of the embedded JavaScript of the active tag. Index EJSRF; The active tag is an HTML tag that does not have other HTML tags between the JavaScript script; the probability P of the tag is the probability that the JavaScript script directly appears in the tag;
[0143] The extracting unit is used to find the active tags in the captured HTTP return page and notify the index calculation unit; extract the JavaScript script in each active tag;
[0144] An encoding restoration unit is used for encoding and restoring the extracted JavaScript script to obtain the encoded byte quantity EBN of the JavaScript script;
[0145] The semant...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com