Method and device for detection and identification of gases
A gas and molecular technology, applied in the field of gas identification, which can solve the problems of inability to immediately detect the chemical mixture to be measured, long measurement time, and complex technology.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
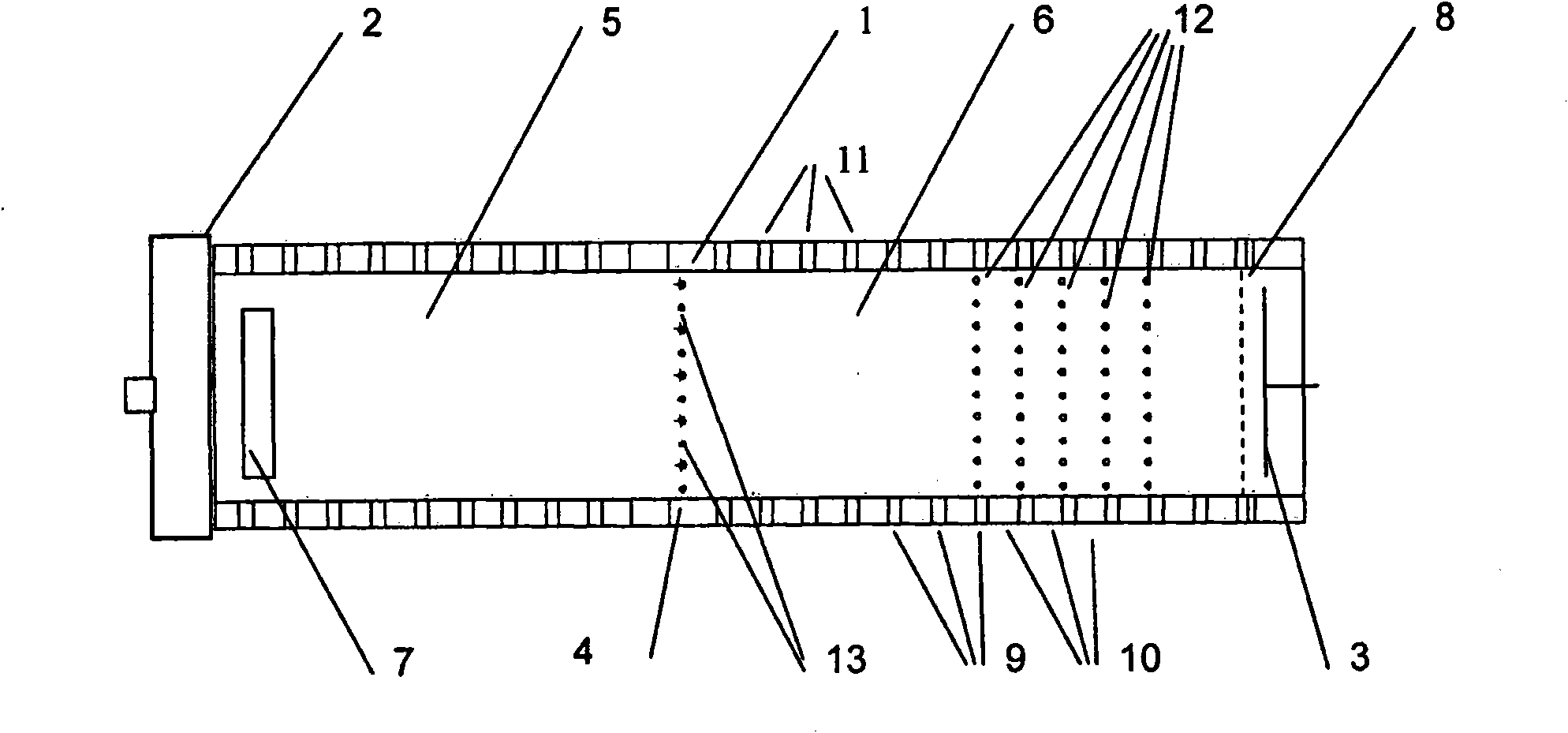
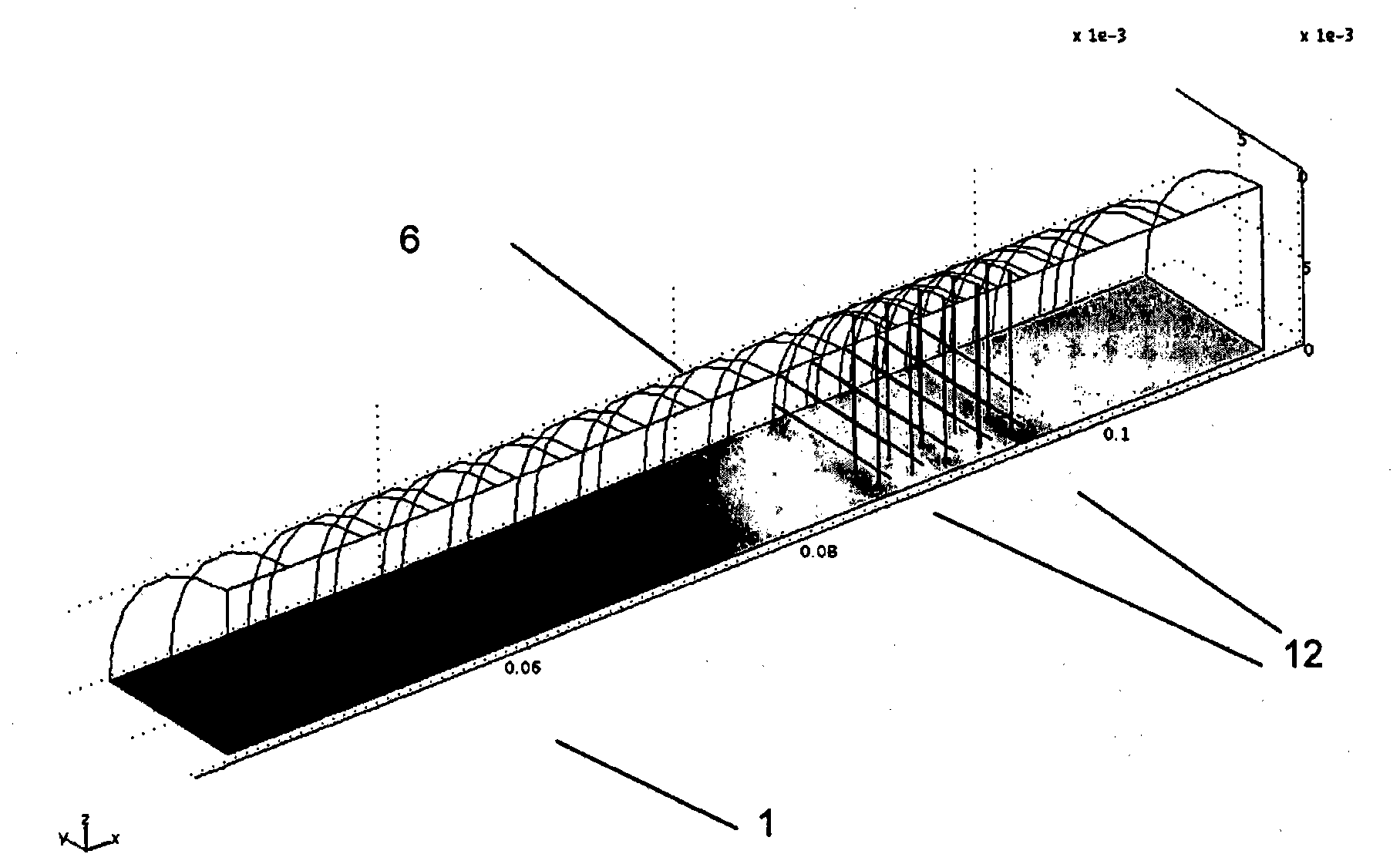
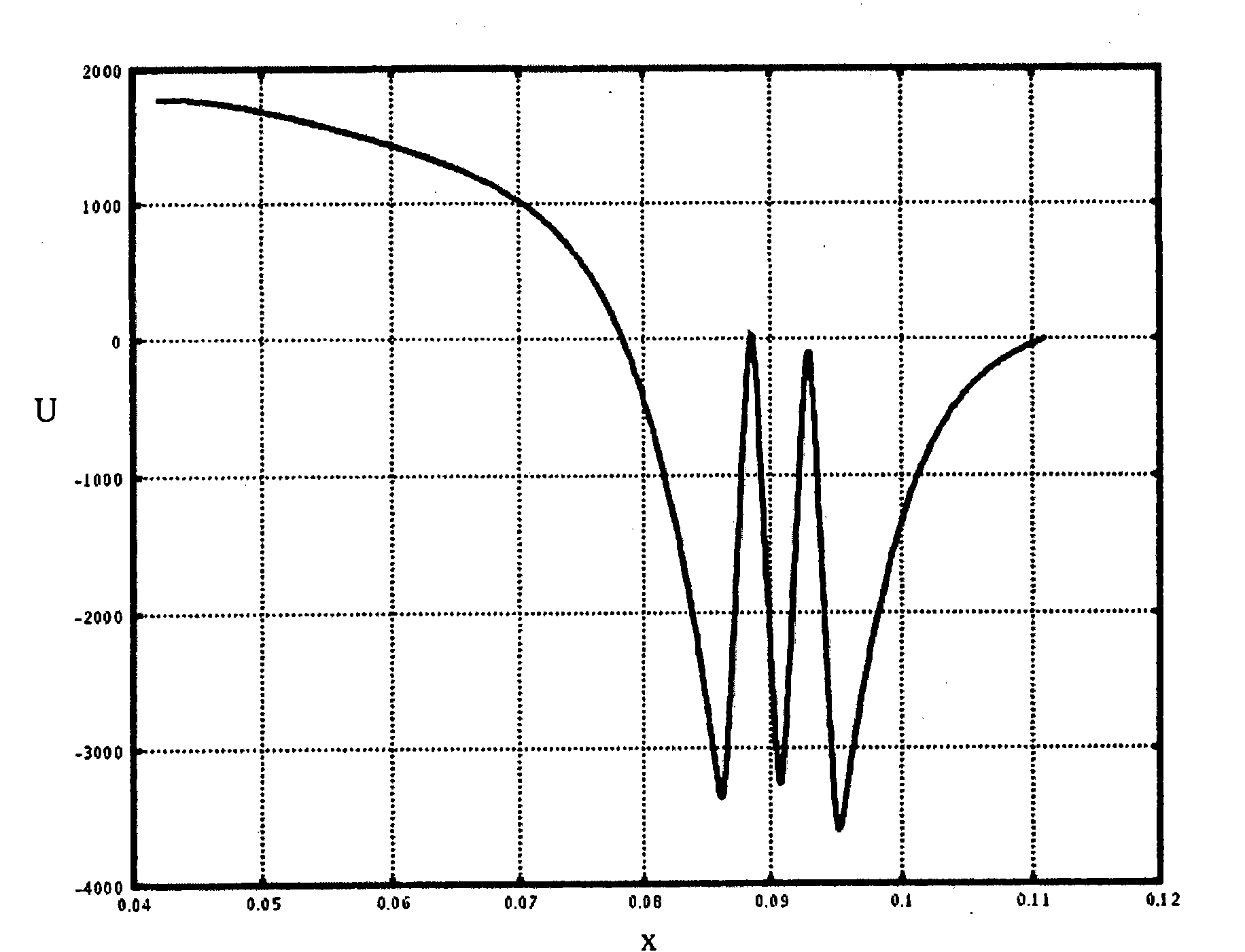
[0076] Such as figure 1 As shown, the new device for identifying gases in the embodiment includes a drift tube 1, one end of which is connected to an intake system 2, and the other end is connected to a detector 3, and its structure is a flat conductive disk.
[0077] In the drift tube 1 there is an electromotive switching network 4 , by means of which the interior space in the drift tube 1 is divided into a reaction zone 5 and a drift zone 6 . The reaction zone 5 is connected to the intake system 2 , and the drift zone 6 is connected to the detector 3 . In addition, an ion source 7 is arranged near the intake system 2 in the reaction zone 5, a shielding grid 8 is arranged in the drift zone 6, and the shielding grid 8 is located in front of the detector 3, wherein the ion source 7 is covered with a radioactive Ni63 foil, shield grid 8 is used to provide capacitive decoupling. The switching grid 4 is called Bradbury-Nielsen grid, which is composed of two conductive metal comb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com