Command decoding device and method for disordered coded commands
A technology for encoding instructions and instruction decoding, applied in the field of instruction decoding, can solve the problems of infeasibility, inflexibility, and high cost, and achieve the effect of providing flexibility and improving security.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0086] The following will refer to Figure 4 and 5 A first embodiment according to the present invention will be described.
[0087] Figure 4 An instruction decoding apparatus 4000 for out-of-order encoded instructions according to the first embodiment of the present invention is shown.
[0088] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the instruction decoding device 4000 includes a selection unit 4100 and at least one decoding unit 4200-a, 4200-b, . . . , 4200-m, where m≥1.
[0089] The selection unit 4100 has at least two inputs 1, 2, 3, . . . , N, where N≥2. The selection unit 4100 has at least one output 1, 2, . . . , m, where m≧1. Of course, the number (N) of at least two inputs may be equal to the number (m) of the at least one output, ie, m=N. Alternatively, the two may not be equal, ie, m≠N. For example, m may be larger than N, or m may be smaller than N.
[0090] The at least two inputs are used to input at least two out-of-sequence encoded instruction data. The at least...
no. 2 example
[0111] The following will refer to Figure 6 and 7 A second embodiment according to the present invention will be described. For the sake of brevity, the same parts of the second embodiment as those of the first embodiment may not be described again.
[0112] Figure 6 An instruction decoding apparatus 6000 for out-of-order encoded instructions according to the second embodiment of the present invention is shown.
[0113] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the instruction decoding device 6000 includes a selection unit 6100 and at least one decoding unit 6200-a-1, 6200-a-2, . . . , 6200-m, where m≥1.
[0114] The selection unit 6100 has at least two inputs 1, 2, 3, . . . , N, where N≥2. The selection unit 6100 has at least one output 1, 2, . . . , m, where m≧1. As mentioned above, the number (N) of at least two inputs may be equal to the number (m) of said at least one output, ie, m=N. Alternatively, the two may not be equal, ie, m≠N. For example, m may be larger than N, or m ...
no. 3 example
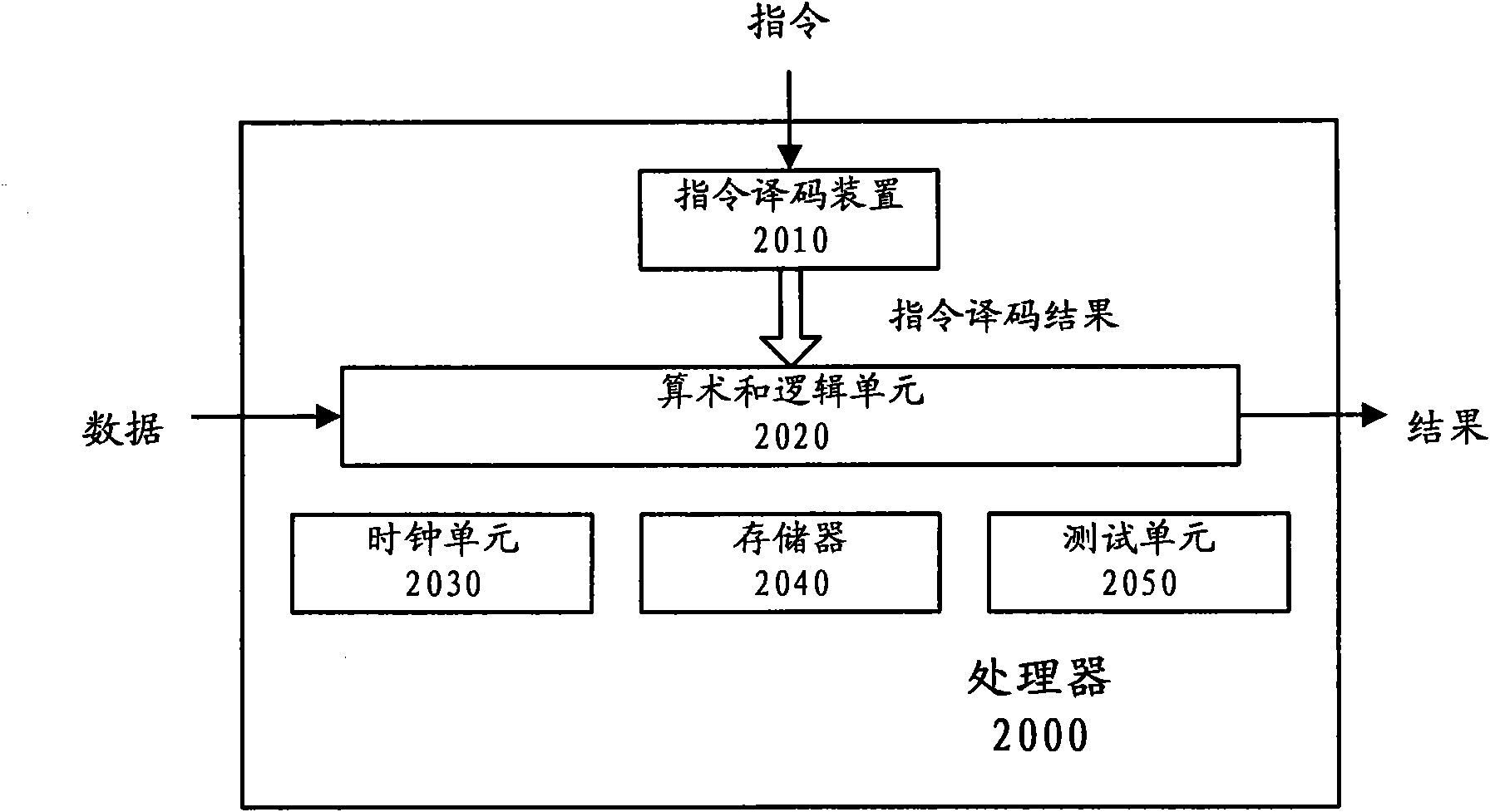
[0168] A third embodiment according to the present invention may include a processor, for example, as figure 2 shown. The processor comprises instruction decoding means for out-of-order encoded instructions and an arithmetic and logic unit according to the invention.
[0169] The arithmetic and logic unit receives instruction decoding results (control information) from the instruction decoding means. The arithmetic and logic unit performs corresponding arithmetic and logic processing on the input data according to the decoding result of the instruction, and outputs the result.
[0170]
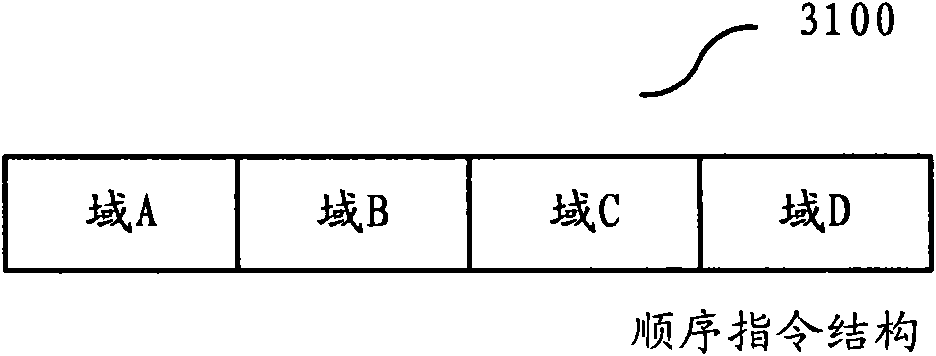
[0171] Fig. 8 shows Example 1 according to the present invention. Figure 8A An out-of-order encoded instruction structure 8100 is shown in an out-of-order permutation. Figure 8B An exemplary instruction decoding apparatus 8200 for out-of-order encoded instructions is shown.
[0172] Such as Figure 8A As shown, the out-of-order encoded instruction structure 8100 includes four fields,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com