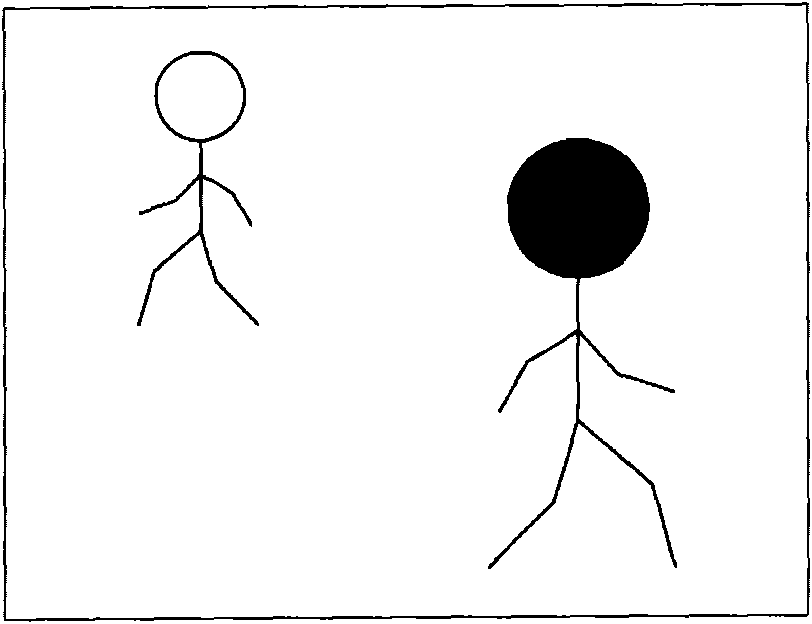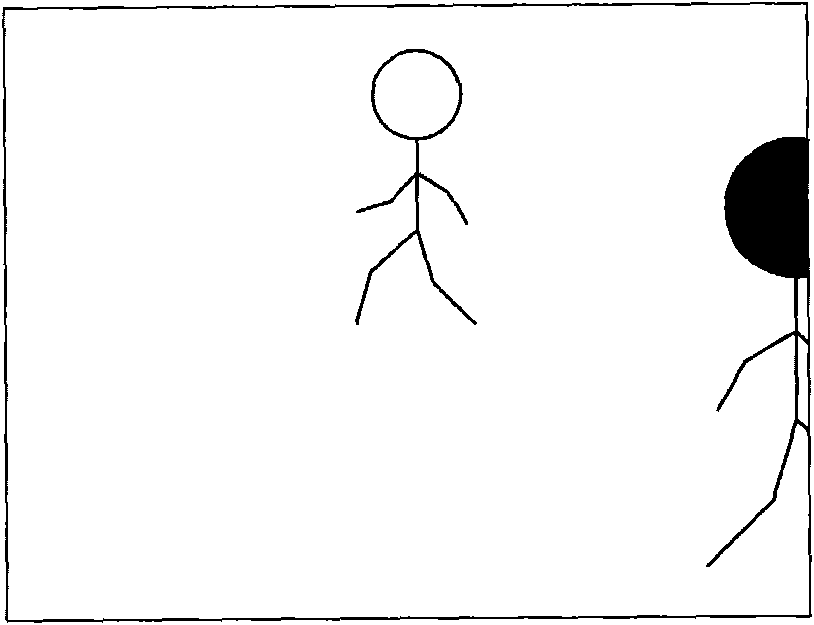Auto-focusing method and module and image pick-up device employing the method
An image capture device and auto-focus technology, applied in the field of image capture, can solve problems such as incomplete images, and achieve cost-saving and easy-to-carry effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
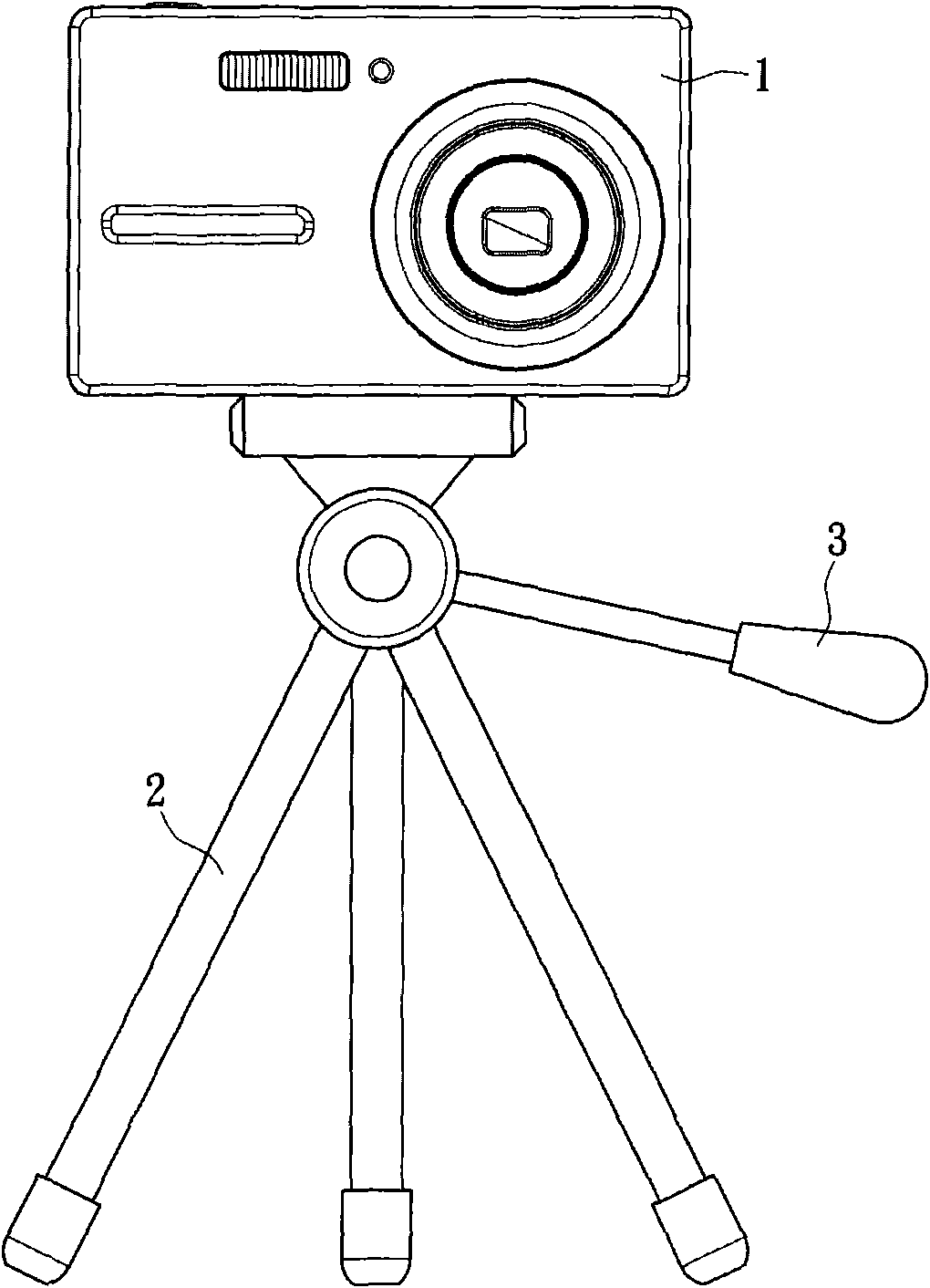
[0049] The present invention relies on the motion detection of the target in the image to keep the target within the viewing range displayed on the display without the need for the user to control the direction of the image capture device in real time.
[0050] In order to provide a more detailed illustration and description, the following will illustrate the present invention with block diagrams and schematic diagrams, so as to more clearly and clearly disclose the technical means used in the present invention, so as to highlight the advantages and capabilities of the present invention. achieved effect.
[0051] The main technical feature of the present invention lies in the image capture device with auto-focus function and its method. Therefore, the following embodiments only propose the necessary system architecture and method steps. However, those of ordinary skill in the art can clearly understand that the following In addition to the components, there are of course other...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com