Network life time prolonging method for underwater wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and survival time technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, transmission system, etc., can solve the problem of long network survival time, and achieve the effect of dispersing energy consumption hotspot areas, prolonging survival time, and reducing solution space.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The invention can be divided into two parts: base station mobility analysis and base station mobility strategy (MOSS).
[0021] (1) Base station movement analysis
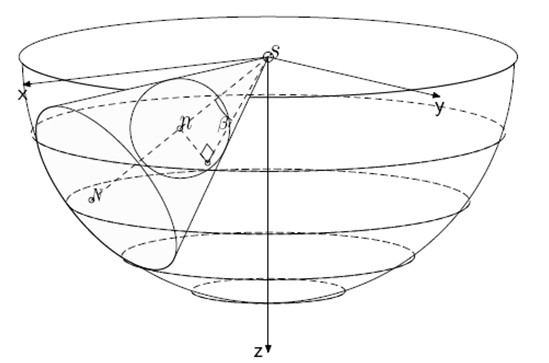
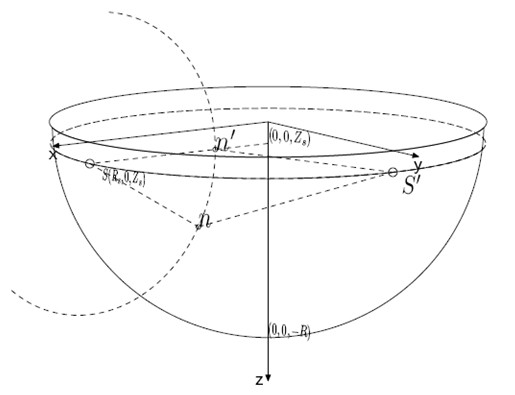
[0022] Underwater wireless sensor networks can generally be divided into two categories: two-dimensional underwater sensor networks and three-dimensional underwater sensor networks. Here we focus on 3D underwater sensor networks that can be deployed to monitor the marine environment. The characteristics of underwater sensor networks include long communication distances, slow transmission rates, and their motion with water currents. Therefore, the arrangement of sensor nodes is not very dense, and at the same time, we can use the movement of sensor nodes with the water flow to monitor the situation of an area. We assume that the entire network consists of n sensor nodes and a mobile base station. The task of the mobile base station is to collect the data collected by the sensor nodes. We denote the entire...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com