Site-directed modification of factor IX
A factor, average molecular weight technology, applied in the field of modified factor IX polypeptides, which can solve problems such as defect coagulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0114] Embodiment 1: computer analysis (in silico analysis)
[0115] In silico analysis was performed to evaluate FIX residues at sites that are likely to be successfully used for cysteine substitution for site-specific polymer conjugation. The analysis focused on lysine, phenylalanine, and leucine residues because these charged residues are more commonly solvent exposed and because in the case of FVIII these Cystine has been the most successfully used site for polymer conjugation (see eg, US Publication No. 2006 / 0115876). Solvent exposure of lysine, phenylalanine, and leucine residues within FIX was determined using data from the crystal structure of FIX (Hopfner et al., Structure 7:989-996, 1999). Other potentially solvent exposed residues were also considered as possible sites for cysteine substitution. The computer algorithm FoldX was used to predict the effect of mutation of each residue to cysteine on the free energy of both the individual residues and the overal...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Example 2: Activating peptides
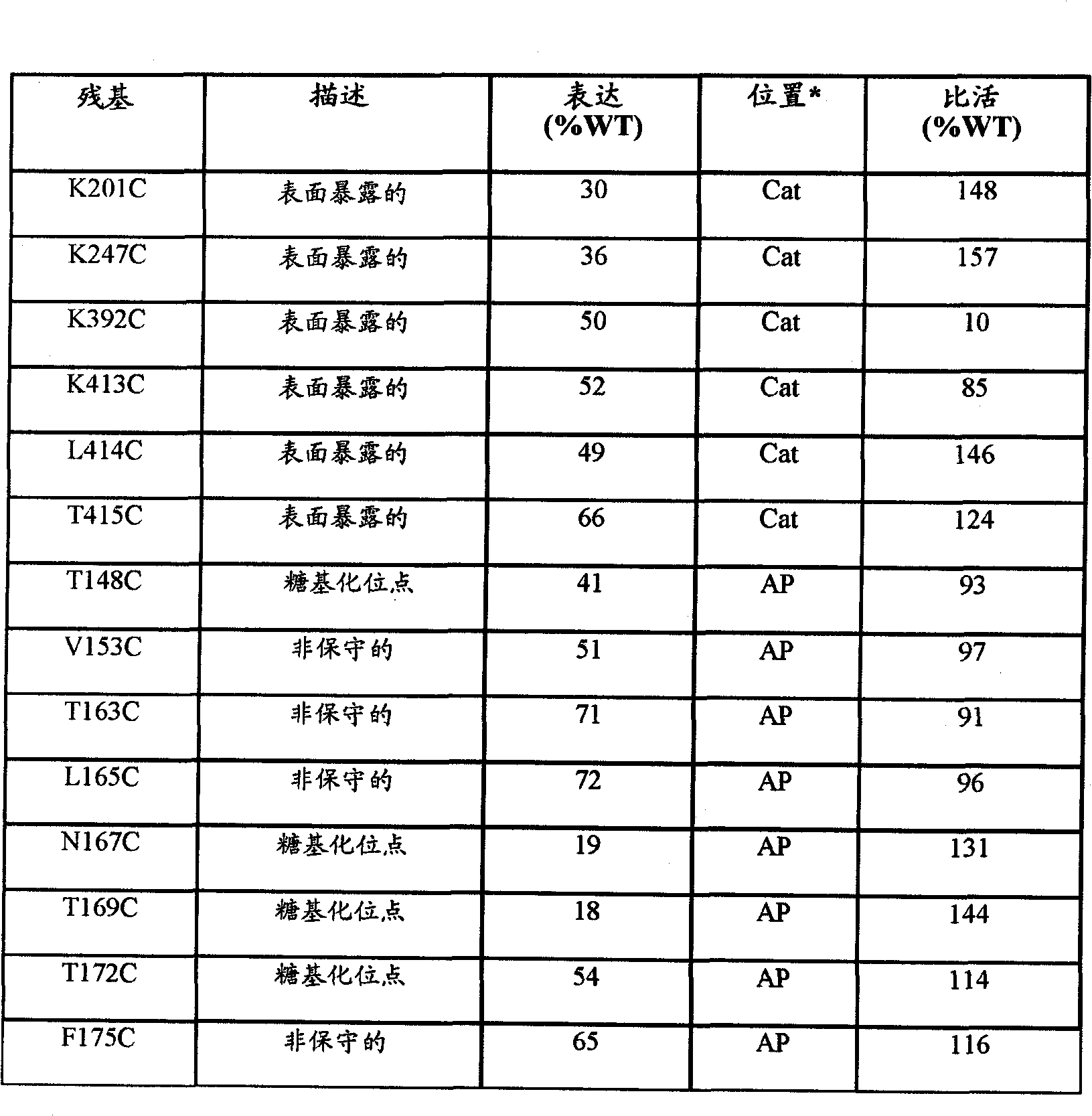
[0124] To identify potential modification sites in activating peptides that would not disrupt post-translational modifications, the amino acid sequences of activating peptides from 8 species were aligned to identify evolutionarily conserved regions ( Figure 4 ). Amino acids that are not conserved across species are unlikely to be required for FIX function (including post-translational modifications) and were therefore selected for mutation to cysteine. In addition, residues that were part of the consensus sequence of the two N-linked glycosylation sites and the site of Tyr155 tyrosine sulfation and O-linked glycosylation and phosphorylation were avoided. Based on this analysis, four amino acid residues (V153, T163, L165, F175) were selected for mutation to cysteine.
[0125]As another method of site-specific modification of FIX, 4 of the 7 glycosylation sites (T148, N167, T169, T172) in the activation peptide were converted to cystein...
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3: Expression and Activity
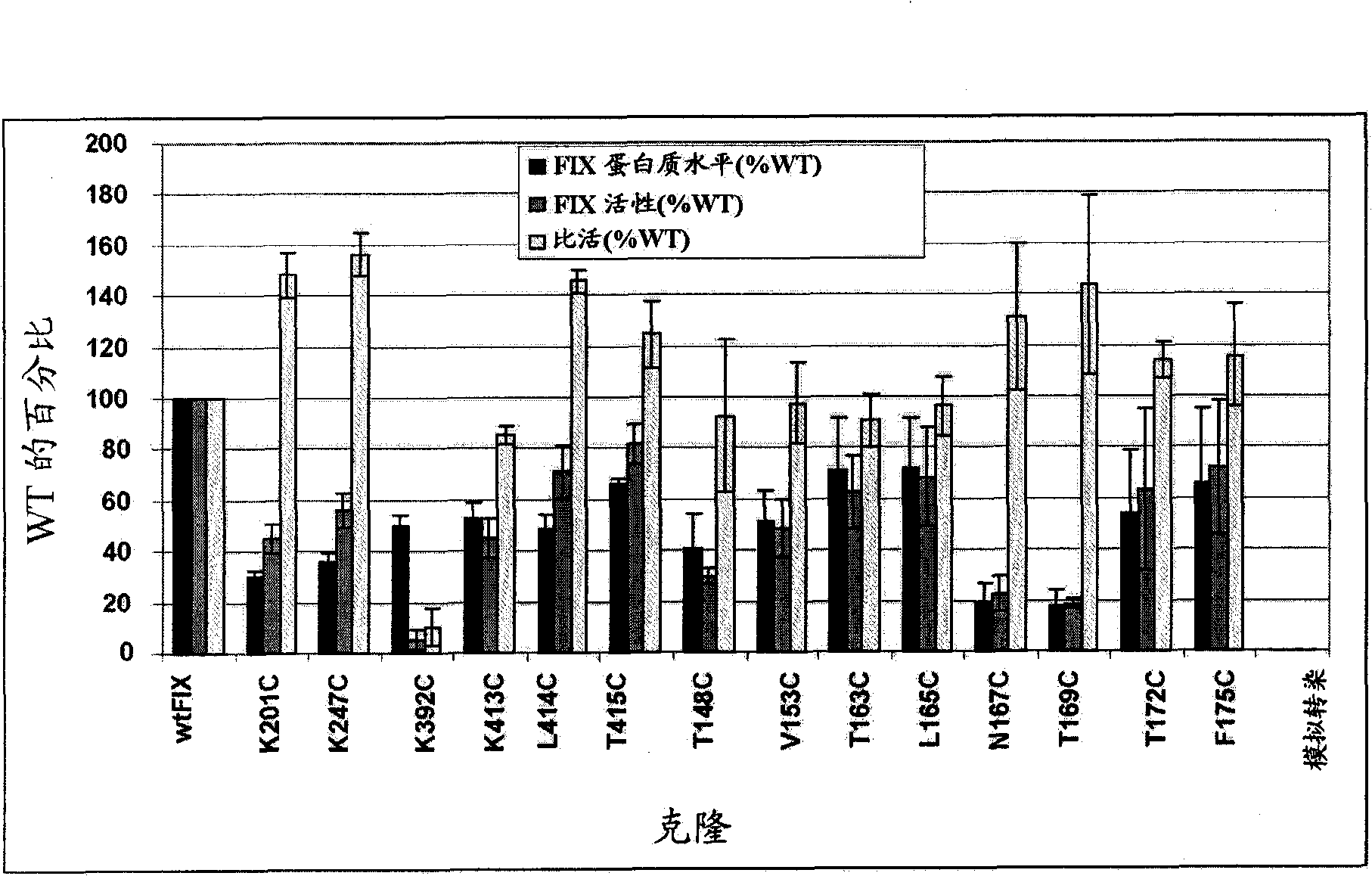
[0128] Based on the computer analysis described above, a total of 14 residues were selected as potential sites for modification, and all 14 residues were changed to cysteine by site-directed mutagenesis of the plasmid pAGE16-FIX, which -FIX contains the human FIX coding region cloned in the expression vector pAGE16 ( image 3 ). Another FIX mutein was created in which a single cysteine residue was inserted between A161 and E162 to create a 162C mutein. A consensus Kozak sequence has been added just 5' to the ATG start codon in all plasmids to ensure efficient translation initiation. The sequence of the altered FIX coding sequence was confirmed by double-stranded DNA sequencing of the entire coding region. The wild-type pAGE16-FIX plasmid and various mutant plasmids were transiently transfected into HKB11 cells, a human cell line generated by fusion of HEK293 cells with B-cell lymphoma. When various cell lines (CHO, BHK21, HKB...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap