Site specific repairing carrier system and method of blood coagulation factor genetic mutation
A technology for coagulation factors and mutation sites, which can be used in vectors, gene therapy, genetic engineering, etc., and can solve the problems of huge TALENs system, deletion mutation, repeated mutation, ectopic mutation, unsuitable gene defect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Example 1 In situ repair of some bases of the blood coagulation factor IX locus in human HEK293T cells
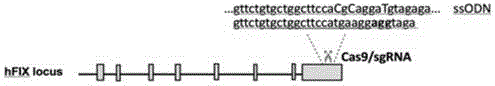
[0103] 1. Construction of vector pX458-sghF9 targeting human coagulation factor IX
[0104] Schematic diagram of gene in situ repair at FIX site in human cells by CRISPR / Cas system figure 1 shown. Obtain the DNA sequence of human coagulation factor IX from NCBI. In this example, the query sequence is the CDS region of exon 8 of the human coagulation factor IX gene. Look for 5'N in the sense or antisense strand of this CDS sequence 20 NGG3' or 5' CCNN 20 3' sequence. Among them, the first 20 bases N are the bases for complementary pairing between sgRNA and target sequence. The PAM (proto-spacer-ajacent-motif) sequence recognized by s.pyCas9 for the last three bases NGG (CCN) is not included in the sgRNA sequence. Since the promoter driving sgRNA transcription in the pX458 vector is the U6 promoter, a "G" was added to the 5' end of the sgRNA sequence to ensure t...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2, repairing the missing FIX gene fragment in the hemophilia mouse model in vivo by gene in situ repair.
[0114] 1. Information about hemophilia B mice
[0115] In this example, the hemophilia B mice carry a Y381D homozygous mutation in the FIX gene.
[0116] 2. Selection of sgRNA target
[0117] The selection method is the same as the selection of sgRNA in Example 1. The selection of sgRNA in this embodiment is:
[0118] sgmf9-forcaccggAACTCTAAGGTCCTGAAGAA,
[0119] sgmf9-RevaaacTTCTTCAGGACCTTAGAGTTcc,
[0120] 3. Construction of pX458-sgFIX gene in situ repair vector
[0121] In step 2, sgFIX-For and sgFIX-RevDNA were annealed and respectively ligated into pX458 to construct pX458-sgmf9, as Figure 5 shown.
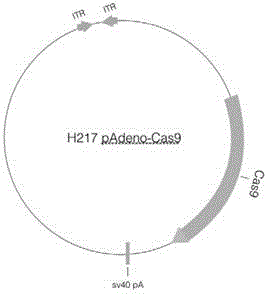
[0122] 4. Construction of adenovirus gene in situ repair vector
[0123] In Step 2, sgmf9-For and sgmf9-Rev were annealed and connected to the H271pAdeno vector. The homologous recombination repair sequence was designed according to the FIX fact...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com