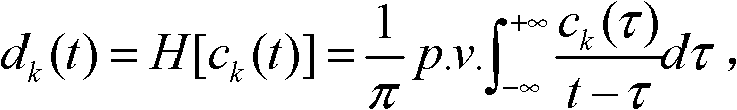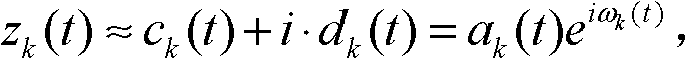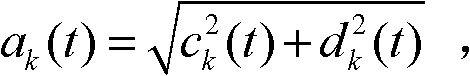Hilbert-Huang Transform end effect inhibition method based on grey theory
A technology based on gray theory and endpoint effects, applied in complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to obtain the Hilbert spectrum of the intrinsic mode function and effectively extracting the essential characteristics of the signal, and achieve high short-term prediction accuracy, fast calculation speed, The effect of reducing endpoint effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0020] Specific implementation mode 1: Combination figure 1 To explain this embodiment, the method for suppressing the end effect of the Hilbert-Huang transform based on the gray theory described in this embodiment, the specific steps are:
[0021] Step 1: Initialize p=1; q=1; r q (t)=s(t); h pq (t)=s(t); c q (t)=s(t); SD=1000; where, (t∈N + ) Is the given signal to be processed; where p represents the number of inner cycles, q represents the number of outer cycles, r q (t) represents the function of the residual error of the qth cycle, h pq (t) represents the function of the intermediate variables generated in the p-th inner loop and the q-th outer loop, c q (t) represents the qth IMF, SD represents the termination criterion;
[0022] Step 2: Judge r q (t) Whether it is monotonous, if yes, go to step 8; otherwise, go to step 3;
[0023] Step 3: Take 0.2≤ε≤0.3, judge whether SD>ε holds, if yes, go to step 7; otherwise, go to step 4; where ε represents the selected threshold;
[0024]...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0044] Specific implementation manner 2: This implementation manner is an example of a method for suppressing the Hilbert-Huang transform endpoint effect based on gray theory. Select a nonlinear non-stationary complex signal s(t) as the original signal of this embodiment, s(t)=15*sin((t / 80) 1.5 *π)+3*sin((t / 100) 0.8 *π)+(t / 500+5), t=1:1:3000.
[0045] Step 1: Initialize p=1; q=1; r q (t)=s(t); h pq (t)=s(t); c q (t)=s(t); SD=1000; among them, the original signal to be processed is (t∈[1,3000]∩N + ); where p represents the number of inner loops, q represents the number of outer loops, r q (t) represents the function of the residual error of the qth cycle, h pq (t) represents the function of the intermediate variables generated in the p-th inner loop and the q-th outer loop, c q (t) represents the qth IMF, SD represents the termination criterion;
[0046] Step 2: Judge r q (t) Whether it is monotonous, if yes, go to step 8; otherwise, go to step 3;
[0047] Step 3: Take ε=0.2, judge w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com