Polysaccharide conjugate vaccine and preparation method thereof
A technology combining vaccines and polysaccharides, applied in the field of vaccines, can solve problems such as bacterial polysaccharide conjugates that have not yet been seen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
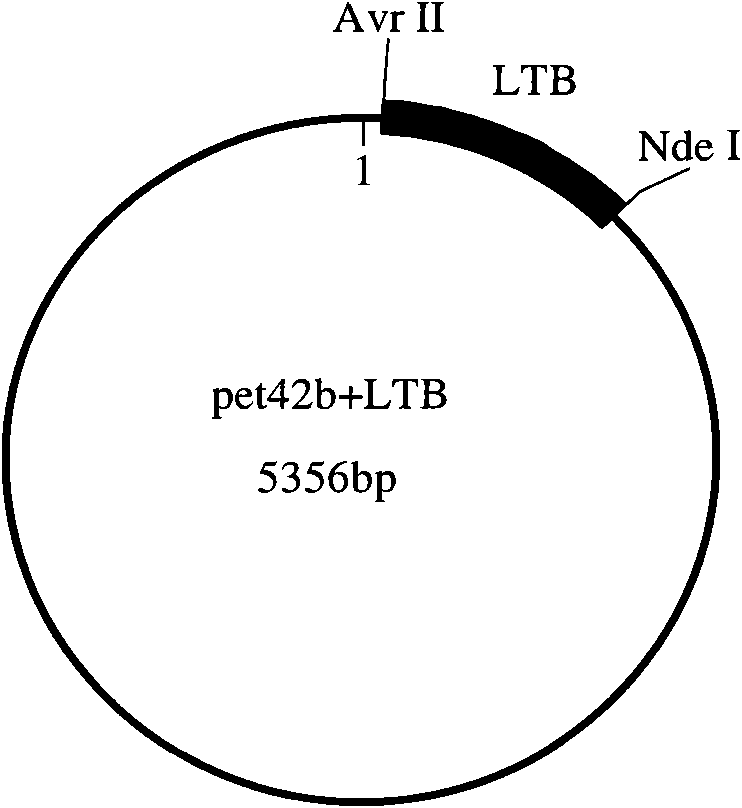
[0036] The present invention will be described in detail below by taking the combination of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB) and group C meningococcal polysaccharide (GCMP) as an example.
[0037] (1) Cloning and expression of recombinant Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit (rLTB) 1) Synthesis of LTB gene and construction of expression vector
[0038] The LTB gene sequence is selected from GENBANK, and the sequence number is GI: 157021177. According to the Escherichia coli codon usage frequency table (references: Maloy, S., V.Stewart, and R.Taylor.1996.Geneticanalysisofpathogenicbacteria.ColdSpringHarborLaboratoryPress, NY.) Optimize this sequence, add 6 histidine tags at the C-terminus of the sequence and stop codon, and then add NdeI and AvrII enzyme cutting sites at both ends of the sequence respectively.
[0039] Artificially synthesize the above-mentioned LTB gene, then use NdeI and AvrII to double-enzyme digest LTB and pET42b (purc...
Embodiment 2
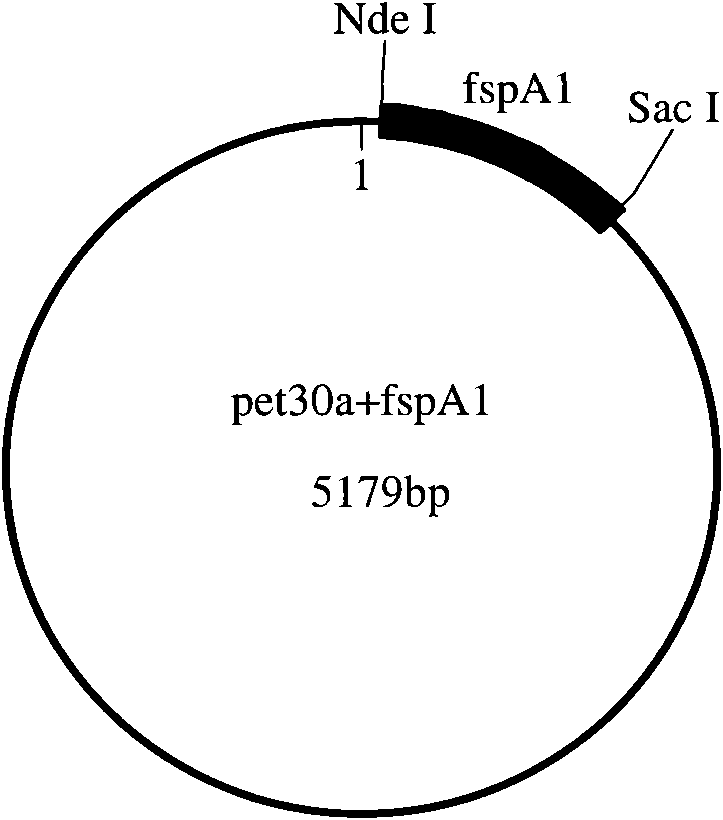
[0090] The present invention will be described in detail below by taking the combination of Campylobacter jejuni flagellar secretory protein A1 (FspA1) and group A meningococcus polysaccharide (GAMP) as an example.
[0091] (1), Cloning and expression of FspA1
[0092] 1) Synthesis of FspA1 gene and construction of expression vector
[0093] The FspA1 gene sequence is selected from GENBANK, and the sequence number is GI: 116292639. According to the Escherichia coli codon usage frequency table (references: Maloy, S., V.Stewart, and R.Taylor.1996.Geneticanalysisofpathogenicbacteria.ColdSpringHarborLaboratoryPress, NY.) Optimize this sequence, add 6 histidine tags at the C-terminus of the sequence and stop codon, and then add NdeI and SacI restriction sites at both ends of the sequence.
[0094] The above-mentioned FspA1 gene was artificially synthesized, and then FspA1 and pET30a (purchased from Novagen) were double-digested with NdeI and SacI, and then the target fragment aft...
Embodiment 3
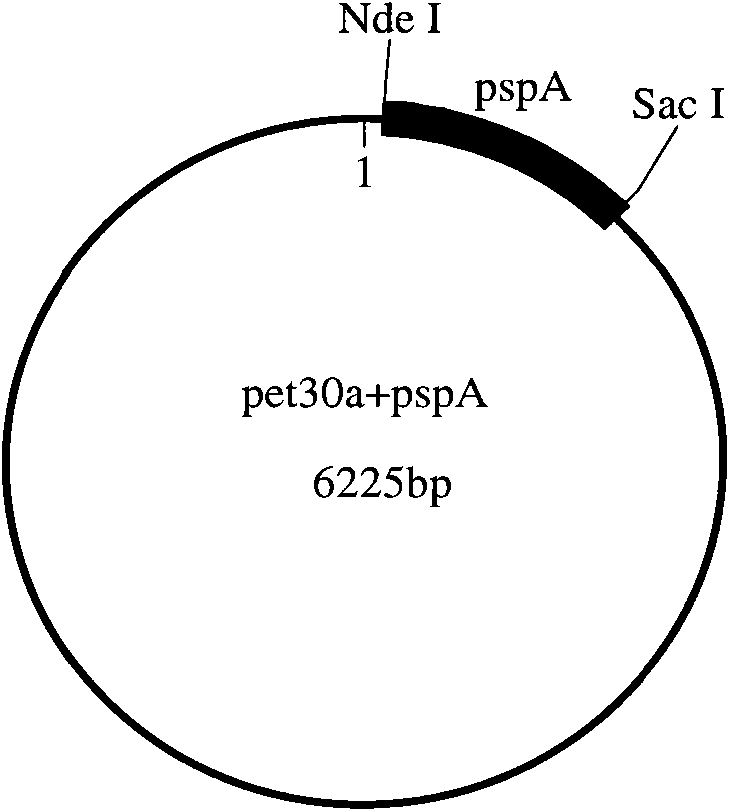
[0122] The present invention will be described in detail below by taking the combination of pneumococcal surface membrane protein A (PspA) and group A meningococcal polysaccharide (GAMP) as an example.
[0123] (1), cloning and expression of recombinant PspA
[0124] 1) Synthesis of PspA gene and construction of expression vector
[0125] The PspA gene sequence is selected from GENBANK, and the sequence number is GI:193804931. According to the Escherichia coli codon usage frequency table (references: Maloy, S., V.Stewart, and R.Taylor.1996.Geneticanalysisofpathogenicbacteria.ColdSpringHarborLaboratoryPress, NY.) Optimize this sequence, add 6 histidine tags at the C-terminus of the sequence and stop codon, and then add NdeI and SacI restriction sites at both ends of the sequence.
[0126] The above-mentioned PspA gene was artificially synthesized, and then PspA and pET30a (purchased from Novagen) were double-digested with NdeI and SacI, and then the target fragment after doub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com