Energy saving data metering and calculating method
A calculation method and technology of energy consumption data, applied in the direction of comprehensive factory control, comprehensive factory control, electrical program control, etc., can solve the problems of inability to compare, waste of great energy saving time, and energy consumption data no longer have reference. , to maximize energy-saving benefits and reduce labor costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
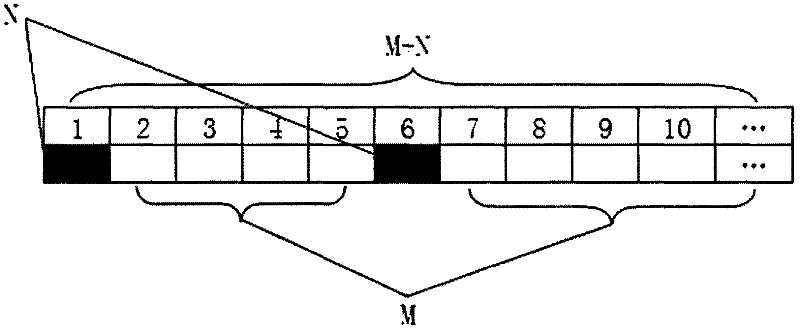
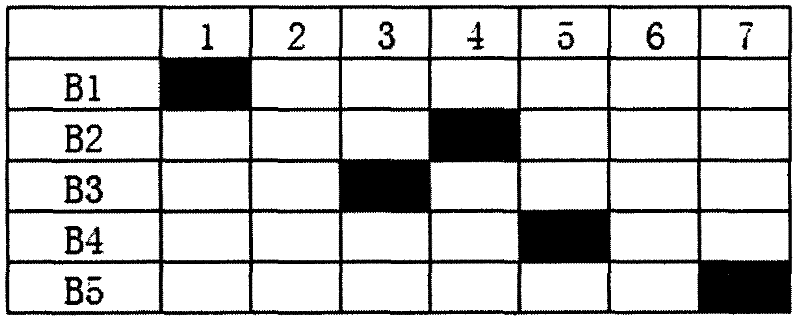
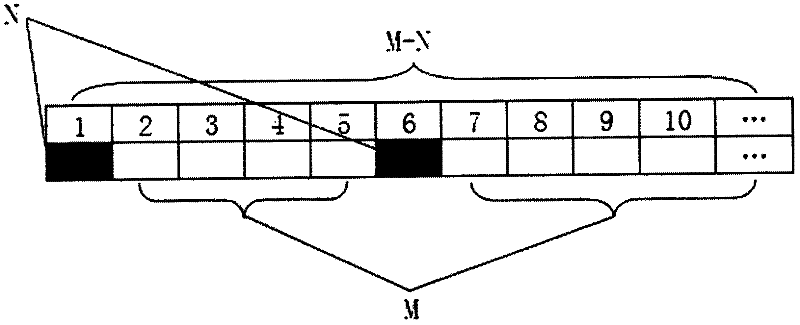
[0043] Such as figure 2 As shown, a specific energy-saving data measurement and calculation method, assuming that one day is one unit time, N=1, M=6, that is, one energy-saving cycle is 7 days, and there are 5 energy-saving nodes B1-B5 in total, the figure The shown energy saving measurement and calculation process operates in the following steps:
[0044] (1) Take 7 days as an energy-saving cycle;
[0045] (2) In an energy-saving period, the energy-saving monitoring and management system selects a day in advance, automatically, and randomly to shut down energy-saving equipment or systems, and takes the energy consumption value of this day as the daily energy-saving value in the energy-saving period. energy consumption benchmark;
[0046] (3) Turn on the energy-saving equipment or energy-saving system in the remaining 6 days, and take the average energy consumption in these 6 days as the average energy consumption per day when the energy-saving equipment or energy-saving sy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com