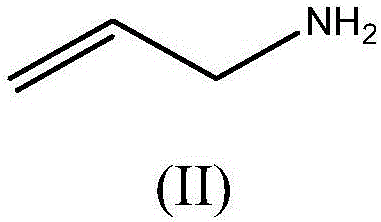
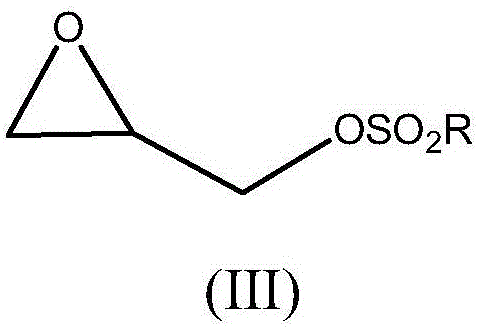
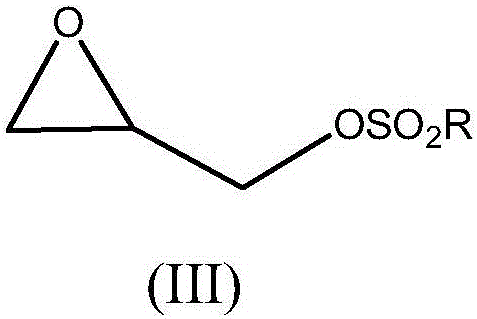
Process for preparing crosslinked polyallylamine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
A technology of polyallylamine and allylamine, applied in the field of polyallylamine or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, can solve the problems of increasing absorption and decreasing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Synthesis of Tosyl Glycidol (IIIa)
[0103]
[0104] AcOEt (800ml) and TEA (162.72g, 1.61mol) were charged into a 2-liter 3-neck flask with a magnetic stir bar, thermometer and cooler, and p-toluenesulfonyl chloride (286g, 1.5mol) was added in portions. The internal temperature was brought to 0°C and glycidol (IV) was added dropwise over a period of 1 hour. The mixture was allowed to react overnight and slowly returned to room temperature. The reaction was monitored by TLC (Hexane / AcOEt 8:2). After the reaction is complete, add 250ml of H 2 O and two clear phases were obtained. Separate the two phases and wash with 100 ml of H containing about 10 g NaCl 2 O washes the organic phase. Dehydration was carried out with sodium sulfate and AcOEt was evaporated. Pure tosylglycidol (IIIa) was obtained as a bright white, low melting waxy solid (370 g). Yield: 96%.
[0105] 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 , 200MHz): 7.791(d2H); 7.344(d2H); 4.23(dd1H); 3.937(dd1H); 3.167(m1H); 2.798(...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Synthesis of m-nitrobenzenesulfonyl glycidol (IIIb)
[0108]
[0109] AcOEt (20ml) and TEA (2.53g, 0.025mol) were charged into a 50ml 3-neck flask with magnetic stirring bar, thermometer and cooler, and m-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride (5g, 0.0226mol) was added in portions. The internal temperature was brought to 0°C and glycidol (IV) (1.84 g, 0.025 mol) was added dropwise over a period of 1 hour. The mixture was allowed to react overnight and slowly returned to room temperature. The reaction was monitored by TLC (Hexane / AcOEt 8:2). After the reaction is complete, add 10 ml of H 2 O and two clear phases were obtained. Separate the phases and wash with 10 ml of H containing about 1 g of NaCl 2 O washes the organic phase. Dehydration was carried out with sodium sulfate and AcOEt was evaporated. Pure tosylglycidol (IIIb) was obtained as a tan, low melting waxy solid (4.6 g). Yield: 78.6%.
[0110] 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 , 300MHz): 8.75(d1H); 8.52(dd, 1H); 8.24(dd1H); ...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Preparation of Sevelamer Hydrochloride Using Tosyl Glycidol (IIIa) as Crosslinking Agent
[0113] 37% HCl (38 g, 0.385 mol) was charged into a 250 ml 4-necked flask with mechanical stirrer, cooler and thermometer and diluted with water (24 ml). The temperature was brought to 2-4°C and allylamine (20 g, 0.35 mol) was added dropwise. After the dropwise addition was complete, the temperature was brought to 72-73°C. During heating, at about 40°C, VA-044 initiator (4.8 g, 0.015 mol) was added. The mixture was reacted for 4h. The aqueous solution was clear and increased in viscosity with time. The solution was brought to pH 10 with 50% NaOH and a solution of tosylglycidol (IIIa) in AcOEt (20 g, 0.0877 mol in 50 ml) was added dropwise. Additions were made over a period of 1 hour. The mixture was allowed to react overnight and a gelled product was obtained. Additional AcOEt (80ml) was added. The mixture was brought to acidic pH with 37% HCl and filtered through cloth. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com