Blade load reduction for wind turbine
A technology of wind turbines and turbines, applied in the field of load systems, which can solve the problems of preventing corrective pitch action, hindering immediate identification, delay, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
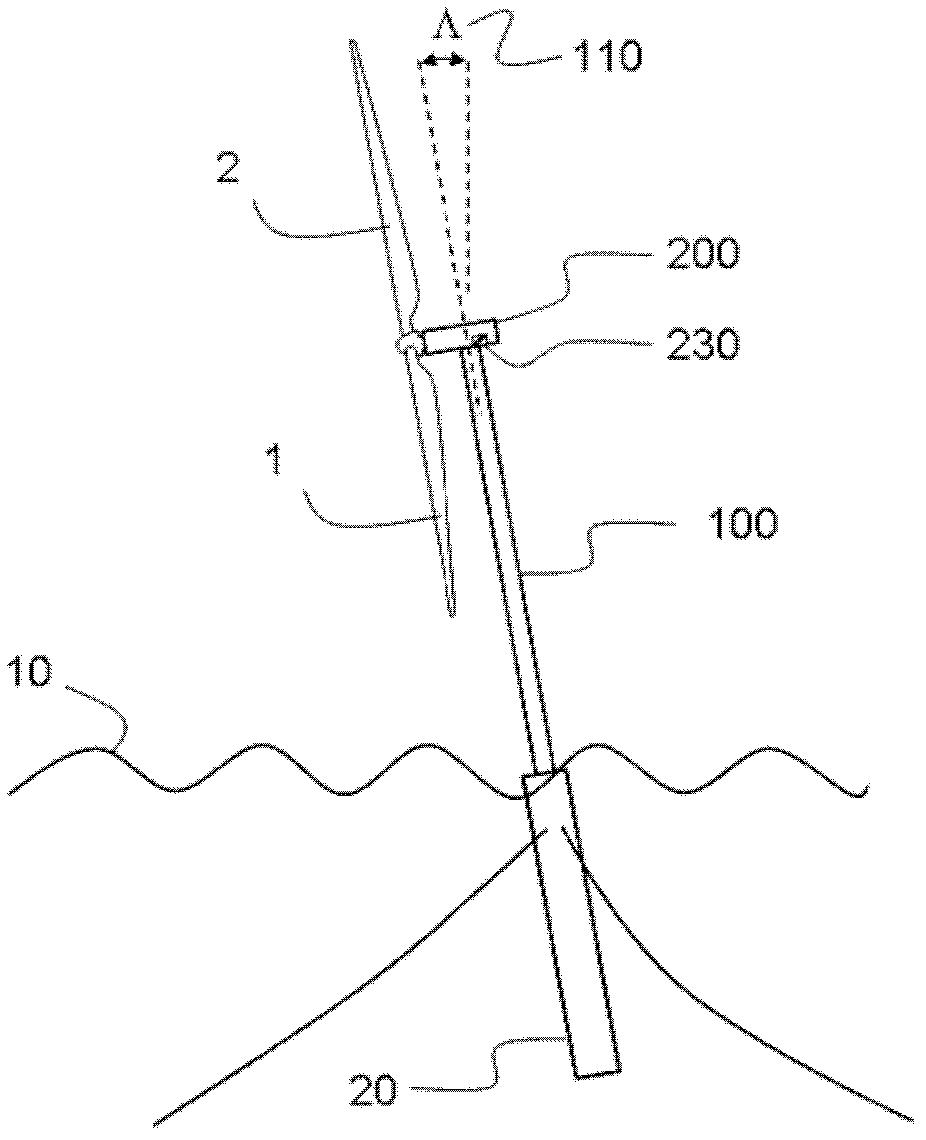
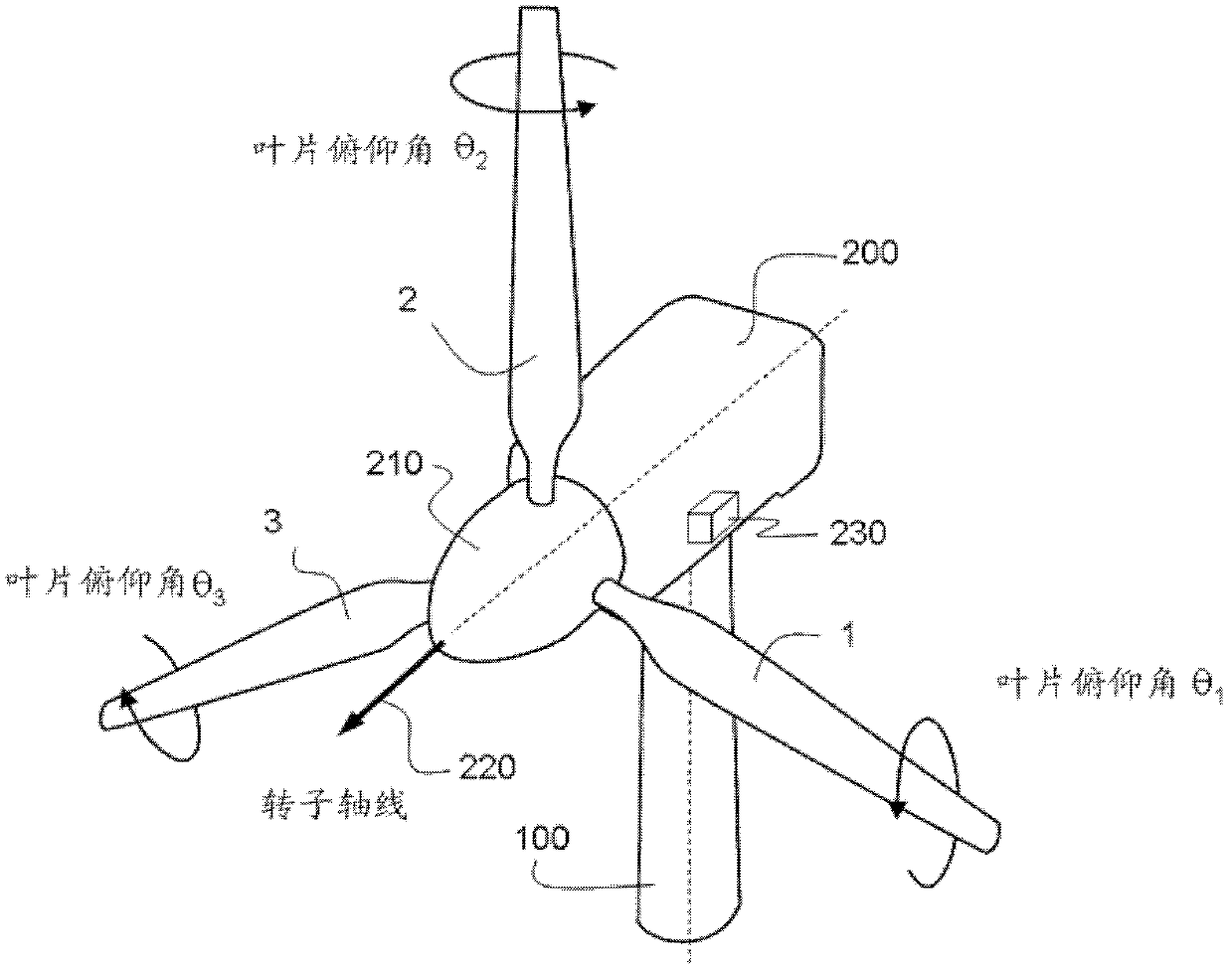
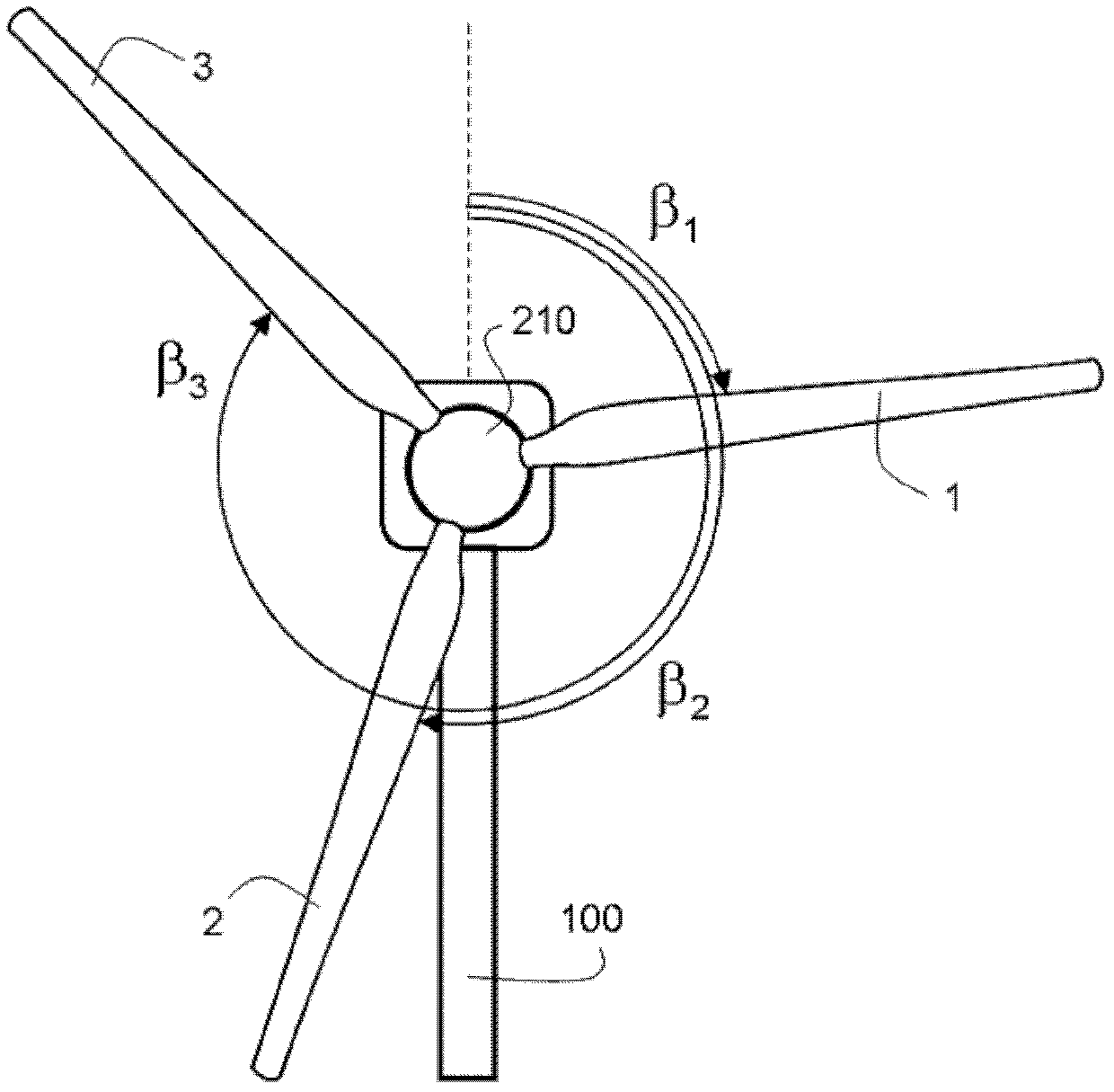
[0028] wind turbines include figure 1 and 2 Two or more blades 1 , 2 and 3 are attached to a hub 210 that rotates about an axis of rotation 220 relative to the nacelle 200 . Here, the rotational speed of the hub 210 is indicated by the letter Ω. Apart from this rotational degree of freedom, the hub is fixedly attached to the nacelle. Within the hub, each blade has a pitch change mechanism to change the angle of attack of the blade. Blade pitch mechanisms are well known in the art and are not shown in the drawings. In addition to the blade pitch degree of freedom, each blade is fixedly attached to the hub by a bearing unit. This type of rotor is called a "rigid rotor". The nacelle is supported by a tower 100 . The invention described here can be applied to both onshore and offshore wind turbine sites. exist figure 1 In , the wind turbine is shown supported by a floating structure 20 on the sea 10, which itself is attached to the seabed using cables.
[0029] sea pitc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com