Device and method for controlling a belt-type continuously variable transmission for a vehicle
A continuously variable transmission, control device technology, applied in the direction of elements with teeth, transmission control, belt/chain/gear, etc., can solve problems such as inability to ensure control accuracy, extraction, estimation error, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1)
[0039] First, the configuration will be described.
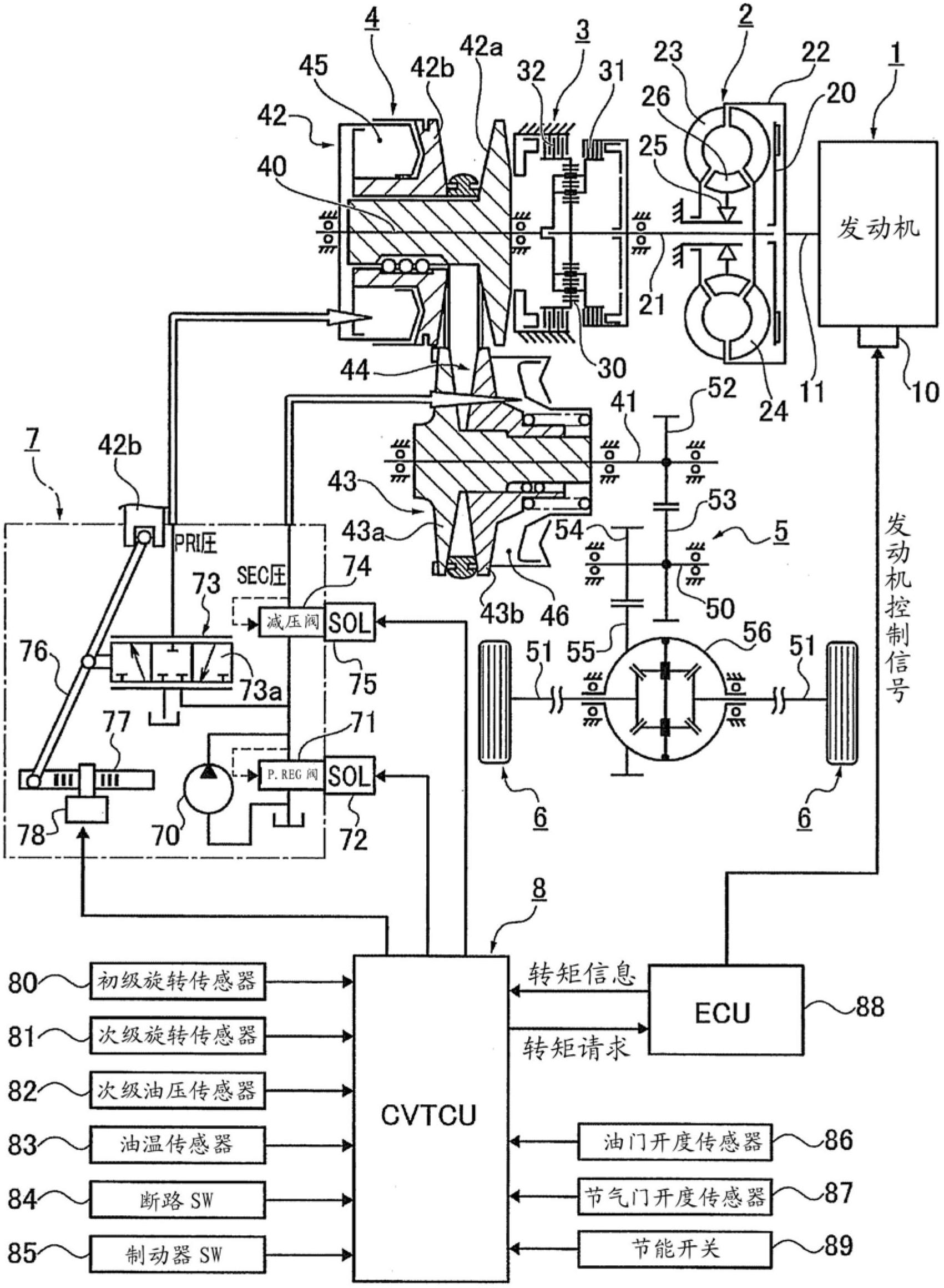
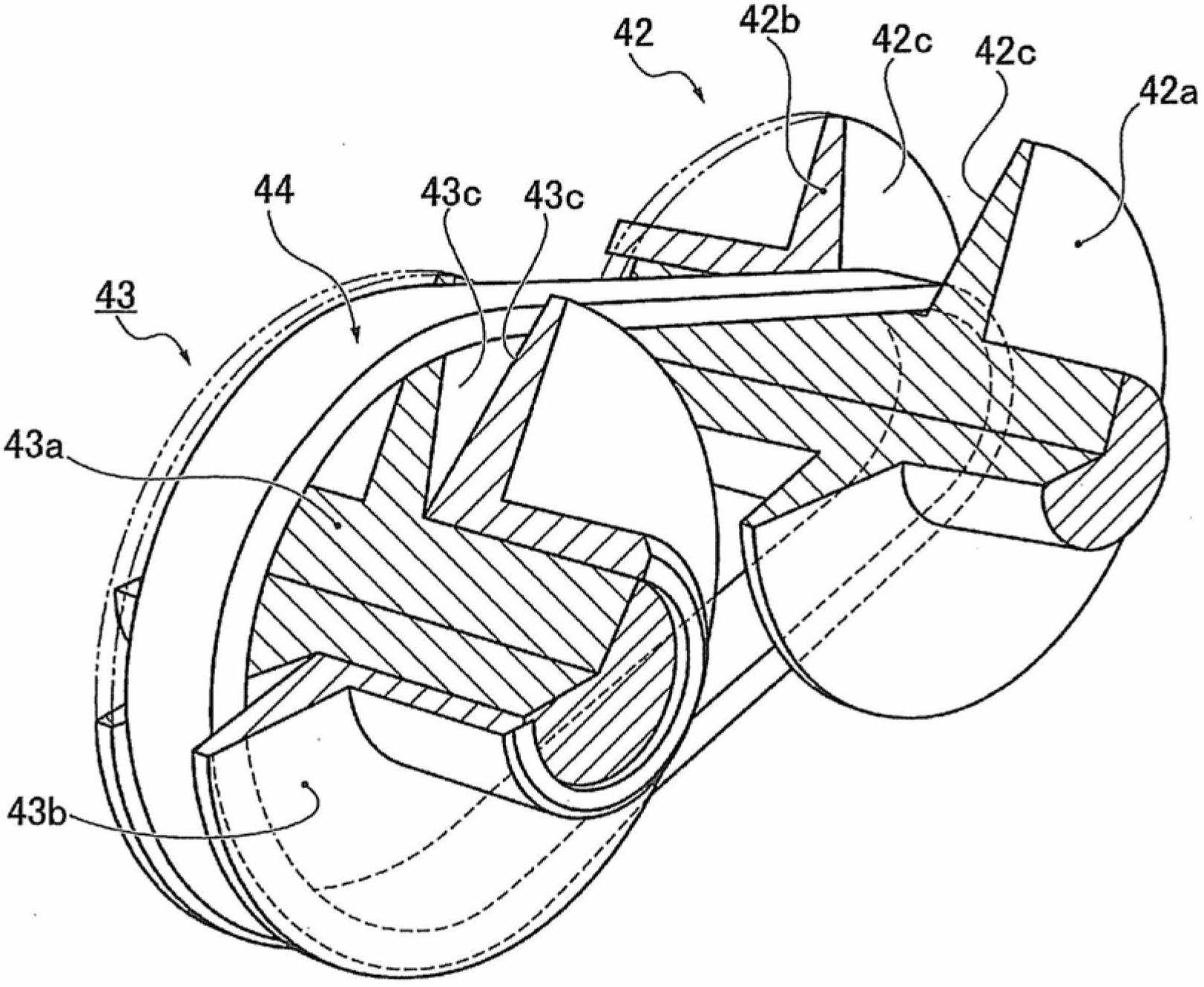
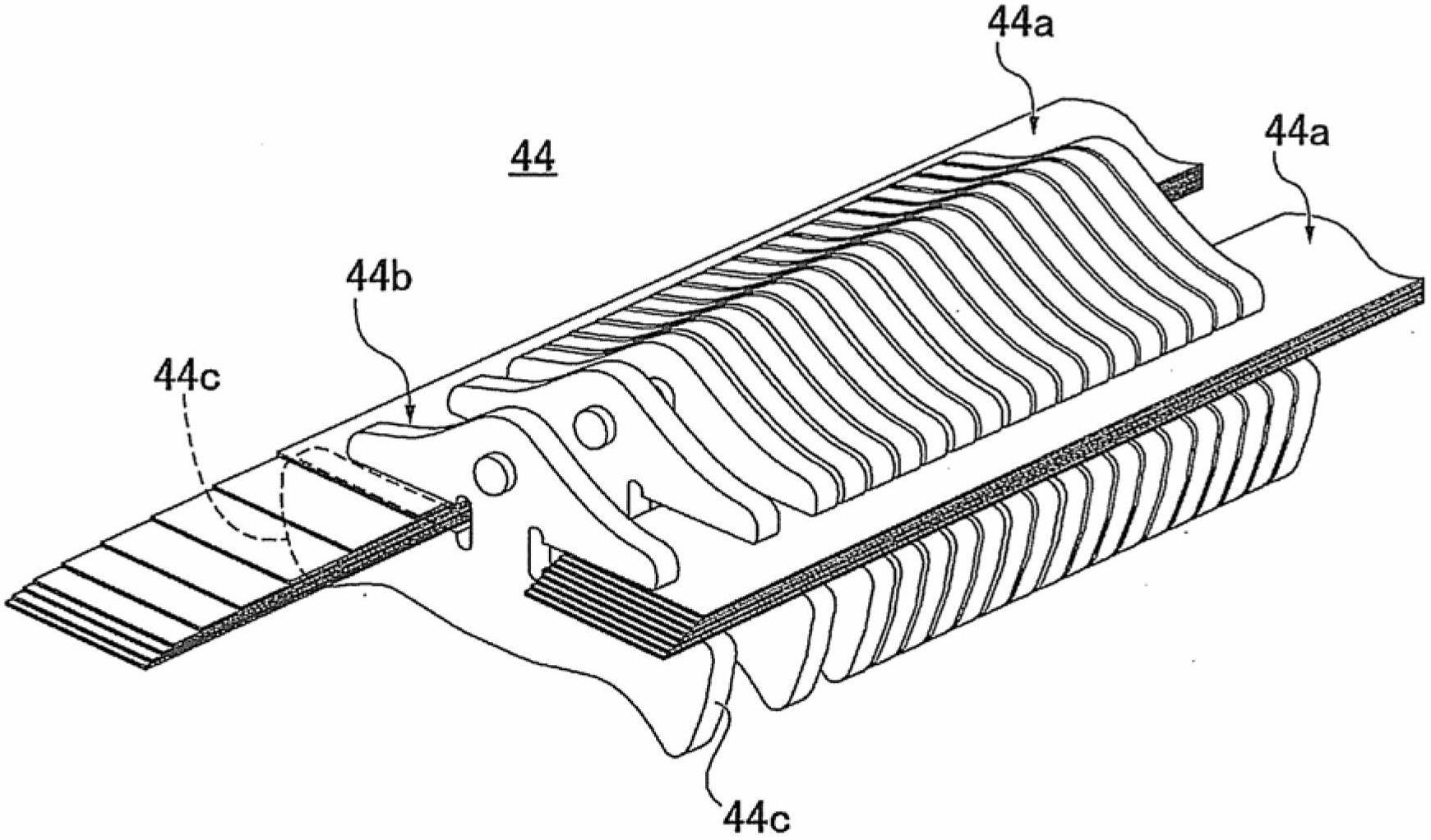
[0040] figure 1 It is an overall system diagram showing a drive system and a control system of a belt-type continuously variable transmission for a vehicle to which the control device and control method of the first embodiment are applied. figure 2 It is a perspective view showing a belt-type continuously variable transmission mechanism to which the control device and control method of the first embodiment are applied. image 3 It is a perspective view of a part of the belt of the belt-type continuously variable transmission mechanism to which the control device and control method of the first embodiment are applied. Below, based on Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 The system configuration will be described.
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, the drive system of the belt-type continuously variable transmission for vehicles includes an engine 1, a torque converter 2, a forward-reverse switching mechanism 3, a belt-type continuously...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com