Wireless input device and switching method thereof, and calculating apparatus
A technology for computing equipment and wireless input, applied in the control of wireless input devices and in the field of computing equipment, can solve the problems of cumbersome and easy misoperation, and achieve the effects of portability, simple operation, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
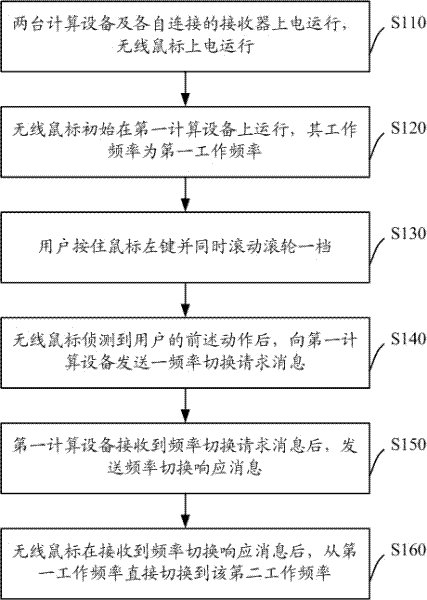
[0049] Embodiment 1. A method for switching between two computing devices controlled by a wireless mouse
[0050]In this embodiment, the two computing devices are respectively a first computing device and a second computing device. The first computing device is connected to a first receiver (Dongle), and the second computing device is connected to a second dongle. Both the first receiver and the second receiver are automatically paired with the wireless mouse when they are powered on (the process of pairing and connecting the receiving end and the transmitting end is called pairing. After the code is successfully paired, the transmitting end stores the pairing information to form a corresponding use relationship), the wireless mouse records the respective operating frequencies of the two receivers. It should be noted that, in order to effectively distinguish the two receivers, the operating frequencies of the two receivers cannot be the same.
[0051] The wireless mouse in t...
Embodiment 2
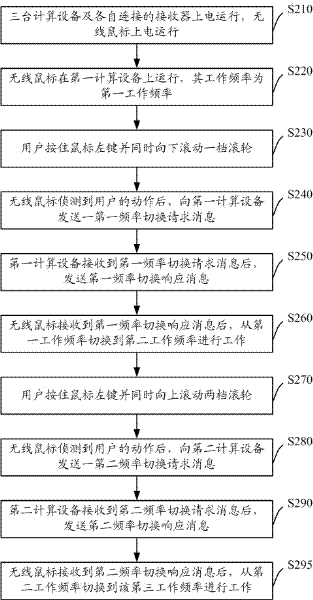
[0064] Embodiment 2. A switching method for controlling three computing devices by a wireless mouse
[0065] In this embodiment, the three computing devices are respectively a first computing device, a second computing device, and a third computing device. The first computing device is connected to the first receiver, the second computing device is connected to the second receiver, and the third computing device is connected to the third receiver. When each receiver is powered on, it will automatically pair with the wireless mouse, and the wireless mouse will record the working frequency of each receiver. It should be noted that, in order to effectively distinguish the receivers, the working frequencies of the receivers are different from each other.
[0066] The wireless mouse in this embodiment has a first working frequency, a second working frequency and a third working frequency, wherein the first working frequency is compatible with the working frequency of the receiver ...
Embodiment 3
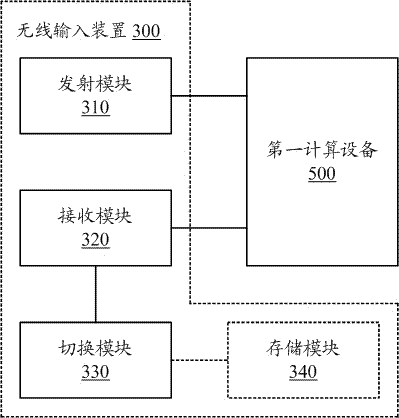
[0088] Embodiment 3, the method for switching between two computing devices controlled by a wireless mouse
[0089] In this embodiment, the two computing devices are respectively a first computing device and a second computing device. The first computing device is connected to the first receiver and the second computing device is connected to the second receiver. When the first receiver and the second receiver are powered on, they are automatically paired with the wireless mouse, and the wireless mouse records the respective working frequencies of the two receivers. It should be noted that, in order to effectively distinguish the two receivers, the operating frequencies of the two receivers cannot be the same.
[0090] The wireless mouse in this embodiment has a first working frequency and a second working frequency, wherein the first working frequency is compatible with the working frequency of the first receiver on the first computing device, and the second working frequenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com