A control plane bandwidth adjustment processing method
A bandwidth adjustment and control plane technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of adjustment failure, no control plane processing mechanism, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The method in this embodiment is applicable to the process when a node on an LSP (Label Switched Path, Label Switched Path) performs a bandwidth adjustment operation:
[0028] The head node of the LSP carries the bandwidth and the number of time slots to be adjusted in the signaling message, as well as the re-signaling identifier; Notify the first node of the number of timeslot information when the bandwidth does not match the adjusted timeslot;
[0029] After receiving the signaling message carrying the heavy signaling identifier, the nodes on the LSP other than the head node judge that if the adjusted bandwidth does not match the adjusted time slot, then send a bandwidth adjustment failure message to the head node of the LSP , and carrying time slot number information in the bandwidth adjustment failure message;
[0030] After receiving the bandwidth adjustment failure message, the head node performs bandwidth adjustment again according to the time slot number inform...
Embodiment 2
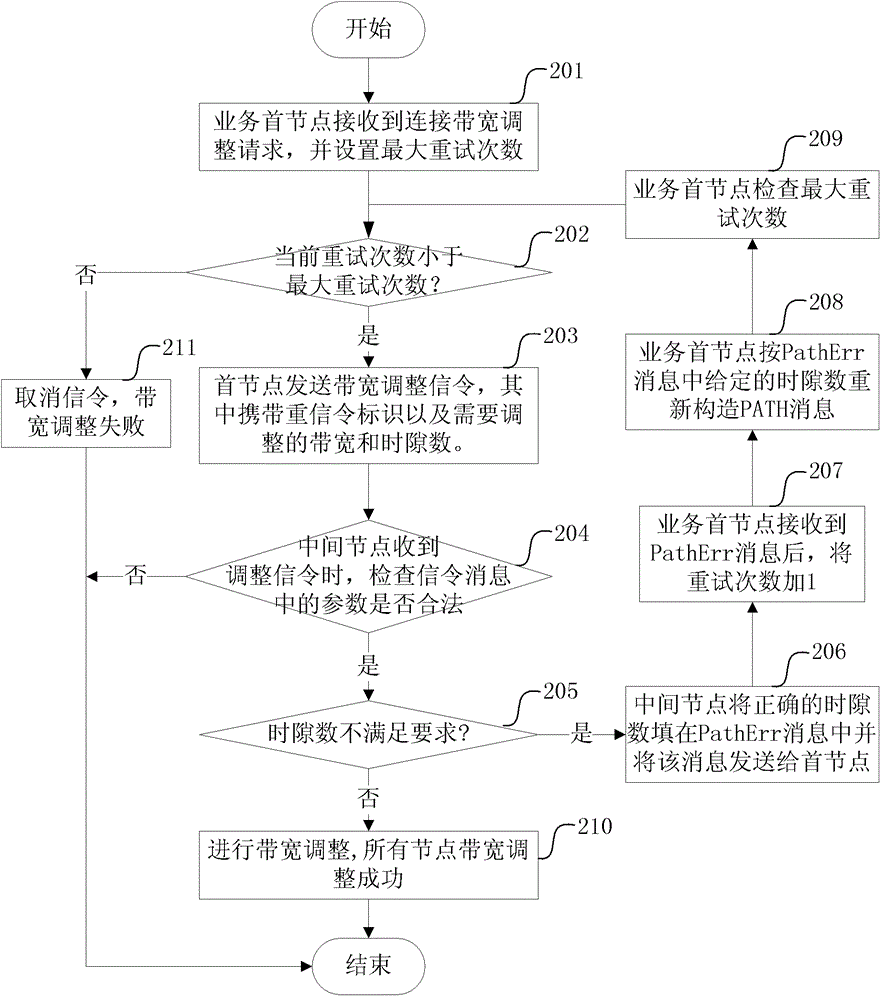
[0051] In this embodiment, the retry limiting condition is the number of retries as an example for illustration. Such as figure 1 As shown, the operation of the service head node on the LSP is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0052] Step 201, the first service node receives the connection bandwidth adjustment request, and sets the maximum number of retries;
[0053] This request is triggered by the management plane.
[0054] Step 202, judging whether the current number of retries is less than the maximum number of retries, if yes, execute step 203, otherwise execute step 212;
[0055] Step 203, the head node sends the bandwidth adjustment signaling, for example, through the Path (path) message, which carries the heavy signaling identifier and the bandwidth and the number of time slots to be adjusted;
[0056] The number of time slots here may be the number of time slots that need to be adjusted initially by the first node, or may be the number of...
Embodiment 3
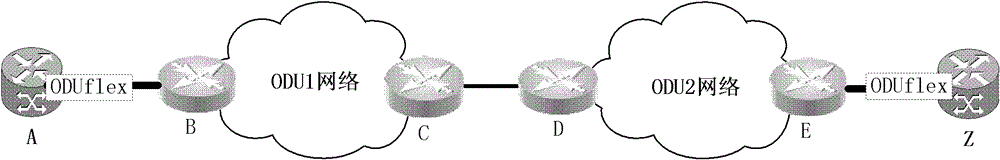
[0067] to combine figure 1 , figure 2 Describe the processing when a failure occurs in the process of increasing the bandwidth between node A and node Z. Such as figure 2 As shown, it is assumed that there is an ODUflex one-way connection with a bandwidth of 35G between A and Z, which is denoted as Con1, and this connection occupies 27 time slots in both the ODU1 network and the ODU2 network. Now due to business needs, it is necessary to increase the bandwidth of 2.5G (that is, the increased bandwidth is 37.5G); and assuming that 2 time slots are added to the ODU1 network and 3 time slots are added to the ODU2 network, the G.HAO protocol can be satisfied requirements. The processing of the control plane includes the following steps:
[0068] Step 301, node A receives a request to increase the bandwidth of 2.5G for the Con1 connection;
[0069] In this embodiment, it is assumed that the number of adjustment retries preset by node A is 3 times.
[0070] Step 302, the con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com