Linear compressor-driven travelling wave loop pulse tube refrigerator
A pulse tube refrigerator, linear compressor technology, applied in refrigerators, compressors, refrigeration and liquefaction and other directions, can solve the problems affecting the compactness of the pulse tube refrigerator, unfavorable applications, etc., to achieve compact structure and small pressure fluctuations. , the effect of suppressing DC flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
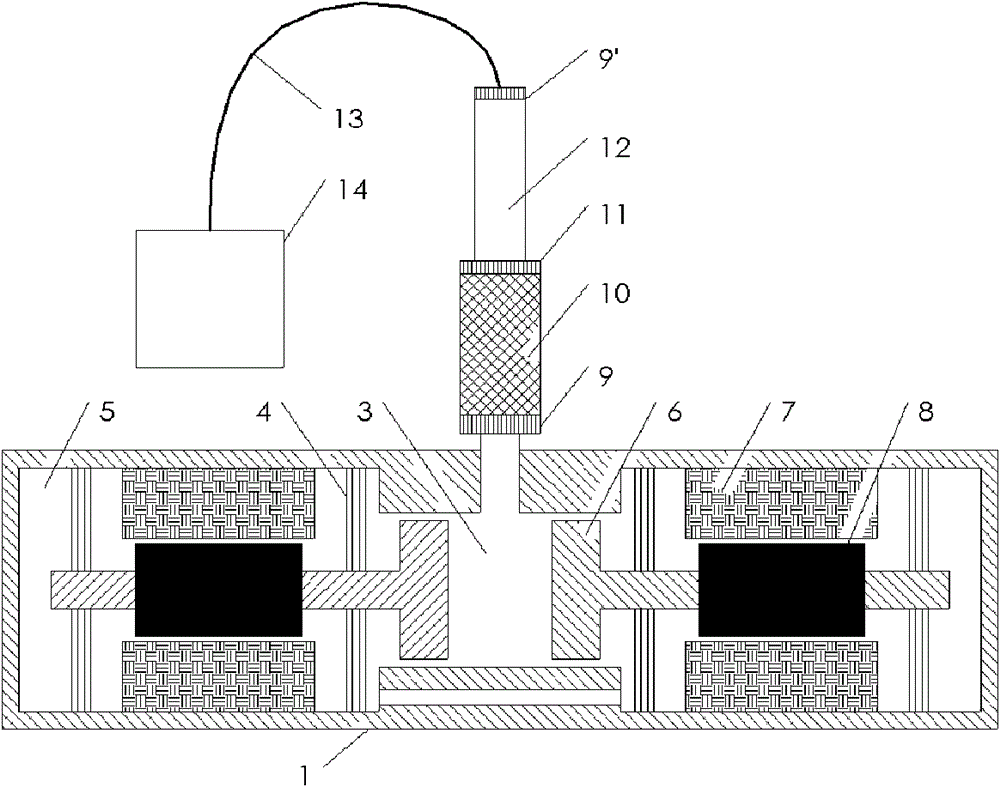
[0021] figure 2 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0022] In the traveling-wave circuit pulse tube refrigerator driven by a linear compressor in this embodiment, the linear compressor is a double linear compressor structure opposite to the left and right, and the stator 7 is fixed together with the shell of the linear compressor, which is a non-moving part. The outer circle of the spring 4 is fixed with the compressor casing, and the inner circle of the compressor supports the mover 8 and the piston 6, and the mover 8 reciprocates with the piston 6 through the electromagnetic force between the stator 7 and generates pressure waves. And the cold finger is input through the front cavity 3 of the compressor; the structure of the opposite arrangement of the compressor uses two sets of moving parts (two movers and two pistons) to move in opposite directions to offset the vibration generated, which helps to reduce the temperature of ...
Embodiment 2
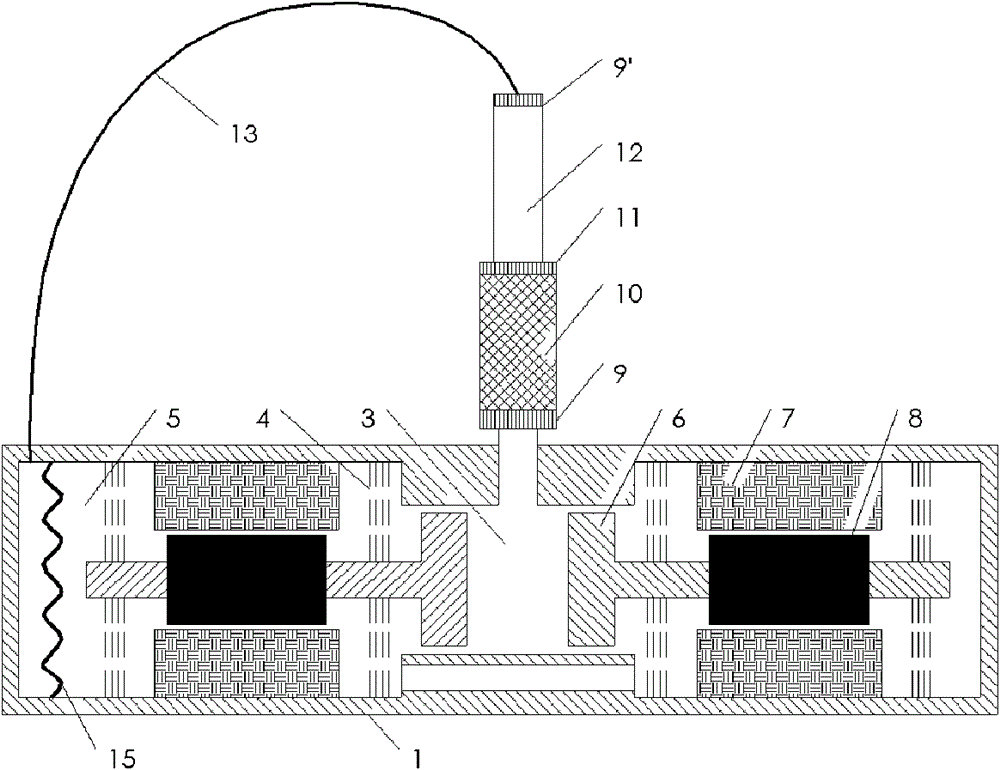
[0025] The traveling wave circuit pulse tube refrigerator driven by the linear compressor of the present embodiment, such as image 3 As shown, the compressor therein is also a double-linear compressor structure opposite to the left and right, and its structure is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that an elastic diaphragm 15 is installed in the back chamber 5. This It is mainly to suppress the DC flow in the refrigerator; if there is no elastic membrane 15, the gas flowing into the back cavity 5 from the inertial tube 13 can pass through the piston and the compressor shell (more precisely, it should be The small gap between cylinders) enters the front cavity 3, and then enters the radiator, regenerator, cold head, pulse tube, secondary radiator, inertia tube, and finally returns to the back cavity. To the cold head, it will inevitably cause a large loss of cooling capacity. Therefore, installing the elastic diaphragm in the back c...
Embodiment 3
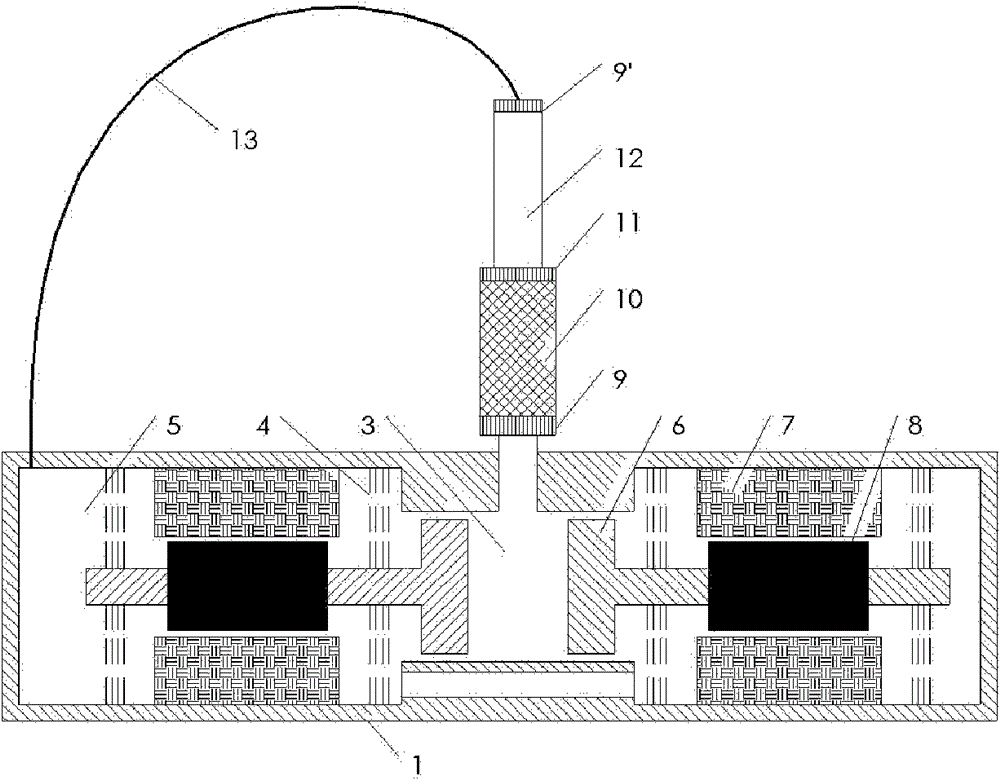
[0027] Embodiment 3: The traveling wave circuit pulse tube refrigerator driven by the linear compressor of this embodiment is composed of Figure 4 shown. In this embodiment, the regenerator 10 and the pulse tube 12 of the cold finger adopt a coaxial structure design, and the two are located on the same side of the cold head 11, so that the load to be cooled can be conveniently installed on the other end surface of the cold head . The regenerator 10 is designed as a ring structure, which just surrounds the outside of the vessel 12. The inertia tube 13 passes through the front cavity 3 of the compressor and communicates with the back cavity 5. If the inertia tube 13 is longer, it can also be directly coiled around the back cavity 5 middle.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com