DVB-C2 generation and reception
A technology for receivers and generating equipment, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, modulation carrier systems, etc., to solve the problem that the baseband signal cannot shift the RF carrier frequency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
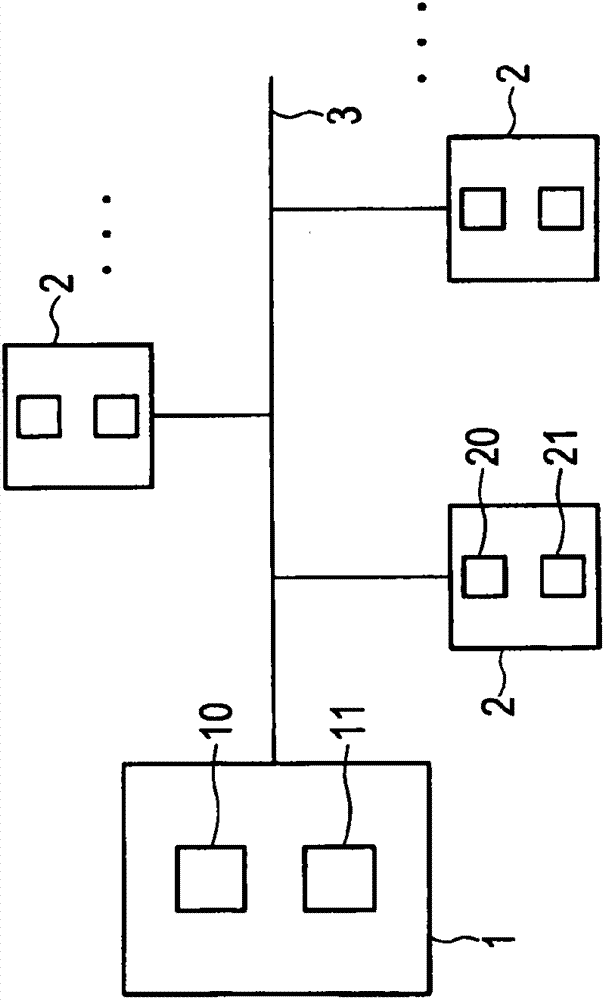
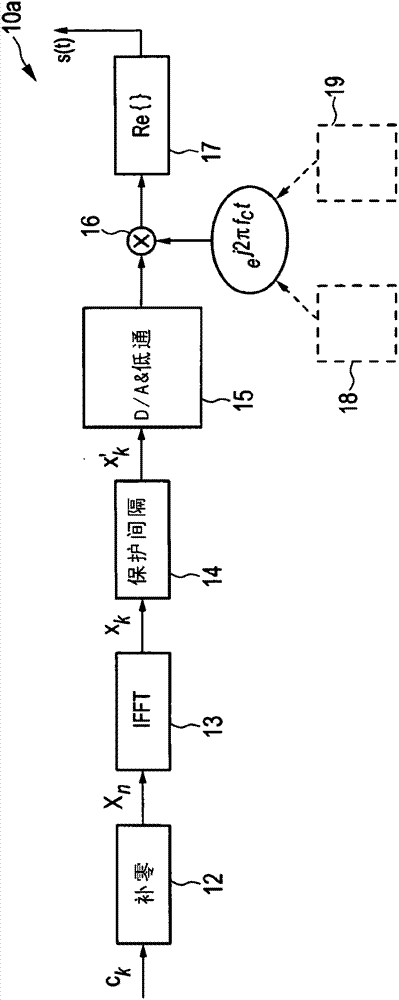
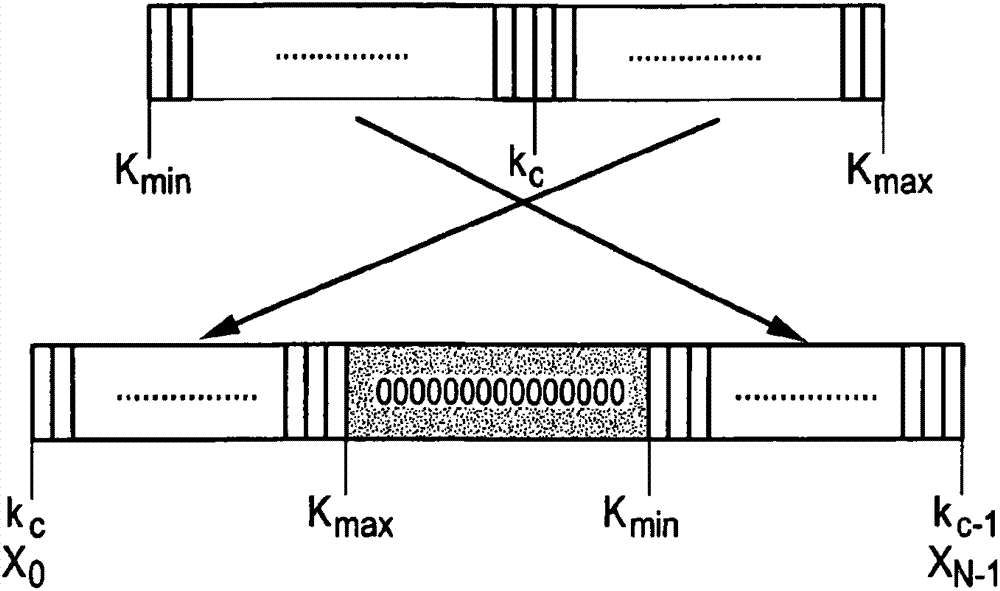
[0045] The DVB-C2 technical specification introduces a new concept of absolute OFDM, where all OFDM subcarriers are viewed with respect to the absolute frequency 0 MHz instead of the signal center frequency. In particular, the signaling block of L1 part 2 starts at an absolute frequency of 0 MHz and is divided in steps of 7.61 MHz. In contrast to other DVB standards, it is not possible to shift the C2 baseband signal to any RF mixing frequency, but is defined in a way unique to the entire cable spectrum. In particular, the pilot sequence of the OFDM signal is different for all the different frequencies. The reason for this behavior is to avoid unwanted repetitions in the frequency domain which may lead to undesirably high peaks in the time domain of the OFDM signal. Furthermore, unambiguous pilot sequences allow easy and reliable synchronization and offset compensation. While the block partitioning and associated pilot sequences for L1 part 2 are defined for the entire cable...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com