Low power consumption operation for active RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) system
An operating method and low-power technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve the problems of increasing cost, increasing circuit complexity, increasing the cost of active tags, etc., to achieve the effect of extending service life and reducing average power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
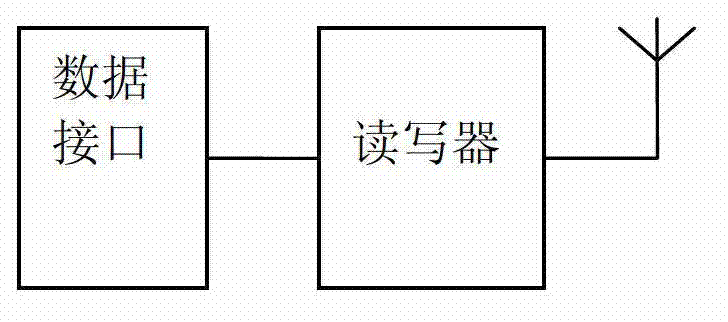
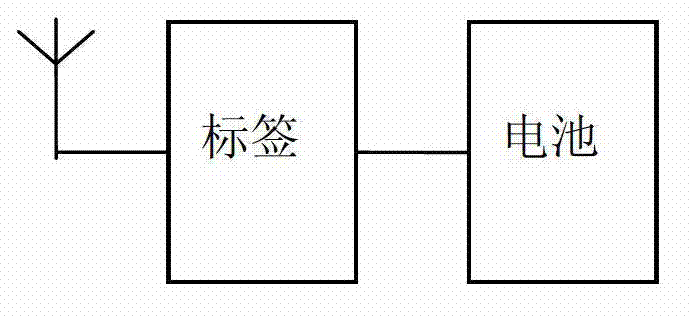
[0019] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, a typical active RFID system on which the method of the present invention relies is mainly composed of two parts: a reader-writer unit and an active tag unit. The reader starts the operation of the active tag by the command sent by the upper computer (such as PC) through the data interface. The active tag is powered by the battery, and the two units communicate wirelessly through the antenna.
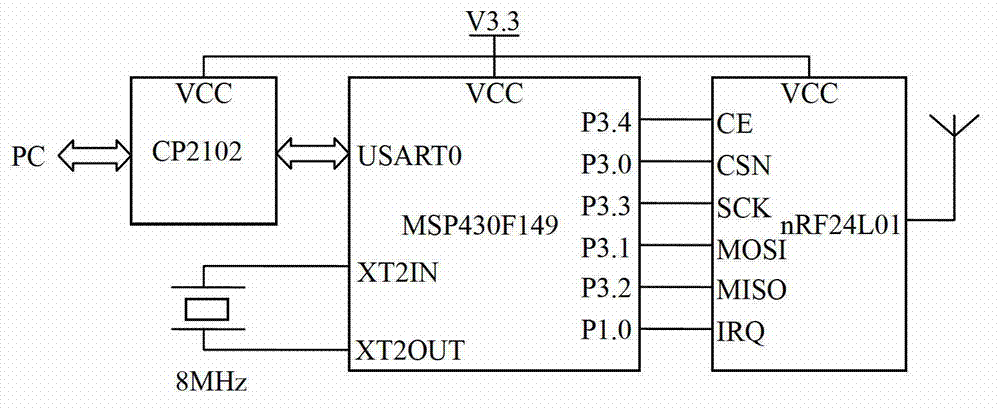
[0020] Such as Figure 1a , Figure 2a shown in figure 1 with figure 2 A specific embodiment of an active RFID system based on the principle, in this specific embodiment, the active RFID system mainly includes two parts: a reader unit and an active tag unit. The structural block diagram of the reader unit is as follows Figure 1a , mainly consists of controller MSP430F149 and 2.4GHz wireless transceiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com