Partitioning method of equal-area global discrete grids based on warp and weft
A technology of longitude and latitude and equal area, which is applied in the field of global discrete grid subdivision, can solve the problems of grid non-uniformity, inconsistency, and short distance between grid points, and achieve uniform point distribution, convenient statistical calculation, grid net tightening effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
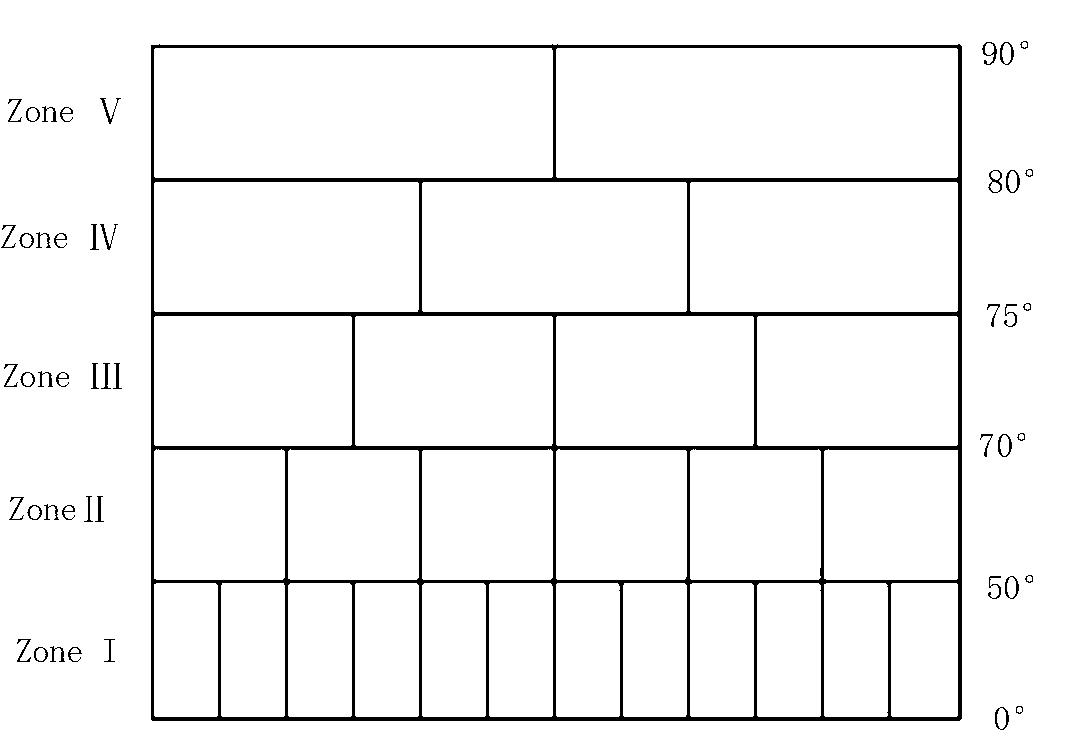
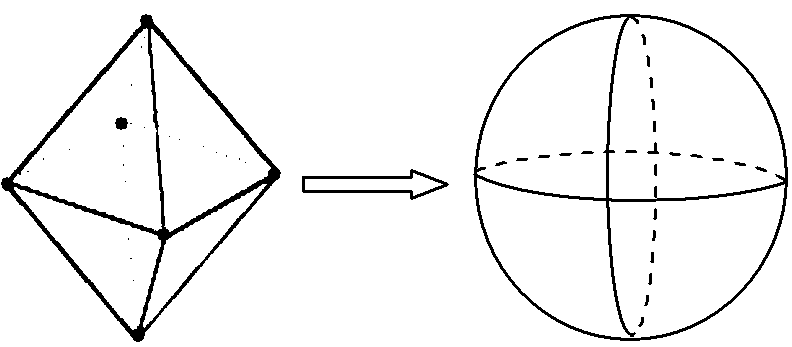
[0050] Embodiment one: see image 3 , Figure 4 , the present invention is based on the equal-area global discrete grid subdivision method of longitude and latitude lines, and adopts the hierarchical subdivision principle to carry out discrete grid subdivision on the spherical surface, including:
[0051] 1) Taking the octahedron inscribed in the sphere as the basis for global discrete grid subdivision, the initial subdivision of the sphere is carried out: first, the six vertices of the octahedron inscribed in the sphere are respectively connected to the two poles of the sphere, the equator and the main meridian, 90 The intersections of the ° meridian, the 180° meridian and the 270° meridian coincide;
[0052] Then, do the spherical center projection of the regular octahedron on the spherical surface to obtain 8 spherical triangles R 1 , R 2 ,...,R 8 , to complete the initial division of the sphere, such as image 3 shown.
[0053] 2) The first layer of subdivision: for ...
Embodiment 2
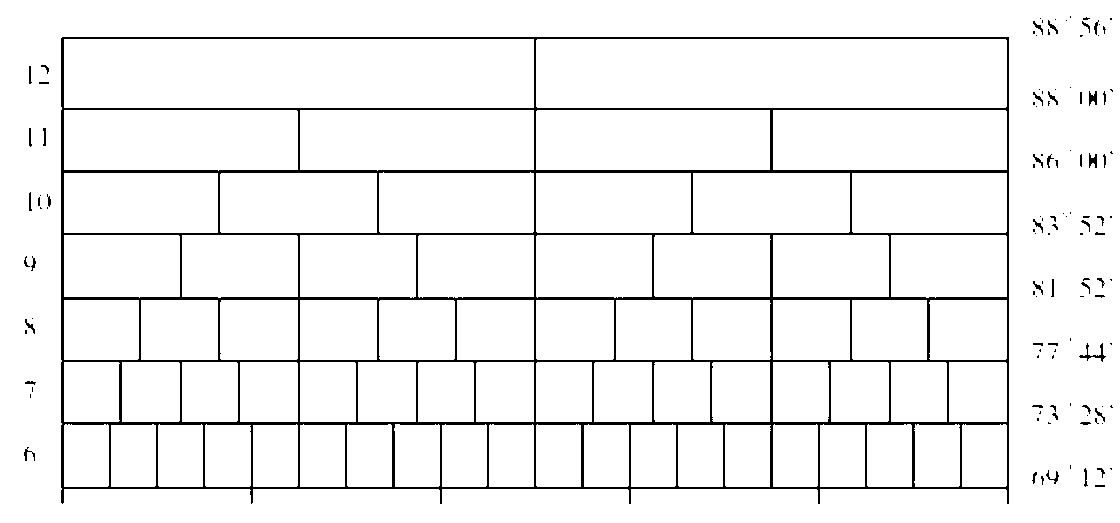
[0056] Embodiment two: see Figure 3 ~ Figure 6 , this embodiment is based on the equal-area global discrete grid subdivision method of longitude and latitude lines, and the following method is used to determine the longitude and latitude lines of each level of grid subdivision, including two cases, the first is the spherical triangular grid subdivision of longitude and latitude lines Determination, the second is the determination of the longitude and latitude of the spherical trapezoidal grid division;
[0057] (1) The method of determining the longitude and latitude of the spherical triangular grid is as follows:
[0058] like Figure 5 As shown, the longitude λ is used respectively 1 , meridian λ 2 and weft represent the 3 sides of a spherical triangle, with parallels and weft Indicates the dividing latitude line, and the longitude line λ 3 Indicates the subdivision meridian, then the meridian λ 3 The longitude of is the mean value of the longitudes of the two lo...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment three: see Figure 3 ~ Figure 6 , this embodiment is based on the equal-area global discrete grid subdivision method of longitude and latitude lines, and the calculation steps of the latitude and longitude coordinates of subdivided grid nodes are as follows:
[0067] The radius of the earth is about R=6378137.000m, then the surface area of the earth is:
[0068] S=4πR 2
[0069] =4×3.1415926×(6378137.000×6378137.000)
[0070] =511207884675544.00m 2
[0071] After the initial subdivision, 8 identical spherical triangles are obtained, and each spherical triangle is divided into 4 equal areas, then the number of units obtained after subdividing each layer of each spherical triangle is: I=4 n , n=1, 2, 3..., n is the number of layers, n=1 is the first layer, n=2 is the second layer, and so on;
[0072] According to the surface area of the earth, the cell area F obtained by subdividing each layer can be calculated. k See Table 1.
[0073] Table 1. The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com